bio 1114 final
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
mircroevol
changes within
a population over generation
(single species)
marcoevol
evolutionary
changes that result
in different species
(speciation
interference
More closely related species will share
more similar characteristics than less closely
related species
homology
similarity resulting from
common ancestry
plesiomorphy
character state found
in the ancestor of the group (the
outgroup will have plesiomorphic
characteristics)
apomorphy
derived character states
found in descendants of the group;
evolutionary novelties acquired AFTER
divergence from the ancestral group
synapomorphy
shared, derived
character states that indicate
homology
• More closely related groups will
share more synapomorphies
monophyletic grp
a common ancestor and all of its descendants
paraphyletic grp
a group
containing a common ancestor
but NOT all of its descendants
homoplasy
character states appear the same in 2
taxa but NOT evolved from common
ancestor → Polyphyletic groups: a group
characterized by 1 or more
homoplasies
parsimony
simple is best
morphological species concept
organisms of the same species share more similar
characteristics with each other than those of different species because of a longer
shared evolutionary history
genetic species concept
organisms of the same species share more similar DNA
than those of different species because of a longer shared evolutionary history
biological species concept
species are groups of organisms that can interbreed
and produce fertile offspring and are reproductively isolated from other species
limitations to species concepts
Biological species concept: hybrids (offspring of produced by 2 species mating),
extinct organisms, asexually reproducing species
• Morphological species concept: variation within species is tremendous, what
variation is relevant?
• Genetic species concepts: variation within species is tremendous, what variation is
relevant?
speciation
the process by which populations attain reproductive isolation
mechanical isolation
Morphological differences, often in
genitals, result in mating
incompatibility
bahaviourl isolation
Mating behavioral differences prevent mating:
• Incorrect courtship displays
• Can’t recognize mating signals
reduced viability
hybrids either fail to develop or are very frail and unlikely to
survive
temporal isolation
species breed during different time of
day, season, or year
allopatric
reproduction prevented by geographic isolation of a
previously continuous population
vicariance
population split by the formation of a geographic barrier
parapatric
Geographically continuous
populations over extremely vast
distances (para = through, patra =
homeland) experience divergence
sympatric
peciation occurs in populations that live in the same geographic
area
niche
the specific biotic and abiotic resources
used by a species
competive exclusion
2 species will never be
perfectly equally successful at utilizing a
resource so more successful competitor will
exclude the other from its nich
resource partition
similar species can
coexist in an area if they use different sets of
similar resources or the same resource at
different times
population
a group of individuals of the same species living in the same area
est pop w/ mark recapture

carrying capacity
max pop siz enviorn can have
survivorship
% of the
population that survives to a
given age
• = # of individuals surviving to a
given age/total individuals
type 1 survivorship
High survival rates until
later age
• Traits of species with this
survivorship pattern?
• Relatively few offspring with
high parental care → lower
death in early age
• Example: Elephants
type 2 survivorship
Roughly equal
proportions die in each age
class
• Example: ground squirrels
type 3 survivorship
Very high mortality in
early life but low mortality for
older age groups
• Traits of species with this
survivorship pattern?
• Production of large #s of
offspring without parental
care
• Example: Oaks trees, 1000s
of acorns
interspecific interact
interactions
between individuals of different specie
intraspecies interact
interactions
between members of the same species
parasitisim
+/- relationship in which the
parasite derives nutrition from its host
which is harmed in the process
• Parasite typically lives in/on host
• Ectoparasites: parasites that feed
externally on their host
• e.g. ticks feed on blood from host’s skin
• Endoparasites: parasites that feed
internally
• e.g. heart worm
commensalism
+/0 relationship between two species in which one benefits
while the other is unaffected
mutualism
+/+ relationships in which individuals from both species benefit
eco engineer
species that directly and dramatically
alter their physical environment such that habitat is
maintained or created
interspecific competition
a -/- interaction between individuals of different
species competing for shared resources
fundamental/ realized niche
Fundamental niche: the full suite of resources potentially used by a species in
absence of competition
• Realized niche: the portion of a species’ fundamental niche actually used in the
presence of competition
greenhouse gas
gases in the atmosphere that
absorb long-wave radiation
reflected off Earth’s surface
and then re-radiate that heat
back toward Eart
what happens when co2 levels increase
Amount of heat
escaping to outer space
decreases
• Amount of heat re-
radiated back to Earth’s
surface increases
More GHGs in atmosphere
= more heat trapped =
warmer Earth
turnover rate of c
how quickly C moves from one pool to another
residence time c
how long
C remains in a pool before
moving to another
biospheric pool
C stored in
living tissue (mostly
photosynthetic organisms)
- fast turnover and short
residence time (respiration,
death/ decomposition)
fossil fuel
C stored in geologic
deposits formed from organic
matter
• Coal = C in rock form
• Oil: C stored in tiny gaps
between rock
carbon fixation
process of
converting inorganic C into
organic C compounds in living
tissues
carbon sinks
reservoirs that
accumulate C
3 types of orbital cycles
1. Obliquity: changes in how tilted
Earth’s axis is → cycles last ~41,000
years
2. Eccentricity: changes in how circular
our orbit around the sun is → cycles
last ~100,000 years
3. Precession: changes in the direction
of Earth’s tilt → cycles last 19,000-
23,000 years
urban heat island
Urban
areas are hotter than
surrounding, less urbanized
areas
• Why?
• Dark surfaces heat up a LOT
• Vegetation actively cools
power dissipation index
aggregate measure of storm
intensity, frequency, and
duration
• measure of total
hurricane power over a
year’s hurricane season
extinction
loss of all indiv of species
backgroud extinction rate - constant extinction
mass extinction - rapid decline in large # of species, higher than bg extict rate
adaptive radiations:
pds of evol change when orgs form many new species w/ adaptations to diff niches
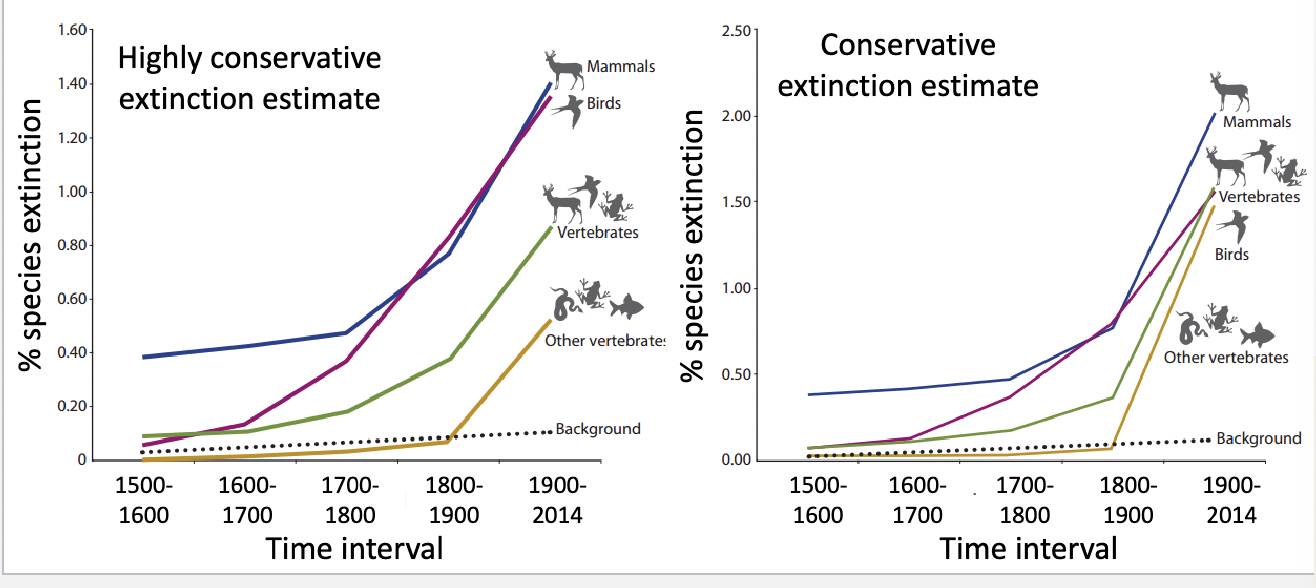
modern extinction rates
classified as: extinct, extinct in wild, presu,es extinct
2 types:
highly conservative estimate: includes on;y species classified extinct
conservative estimate: includes species classified as extinct in
the wild or presumed extinct.
prokaryotes
orgs w/ cells that lack membrane-bound organelles + nuc
include bacteria, archea
smaller genomes + ribo
plasmids: small indep replicaing circular dna mol
binary fission: one cell splits in two
eukaryotes
org w/ cels that have membrane-bound organelles + nuc
include protists, plants, fungi, and animals
archea
singl;e cel prok
usually extremophiles → live in extreme conditions
extreme thermophile: live in extreme heat
extreme halophiles: live in extemely salty enviorns
connection w/ mitro and chloro
lipid bilayers
circular dna + indep replication
own ribo that r smaller than cell ribo
both reproduce by splitting (close to fission)
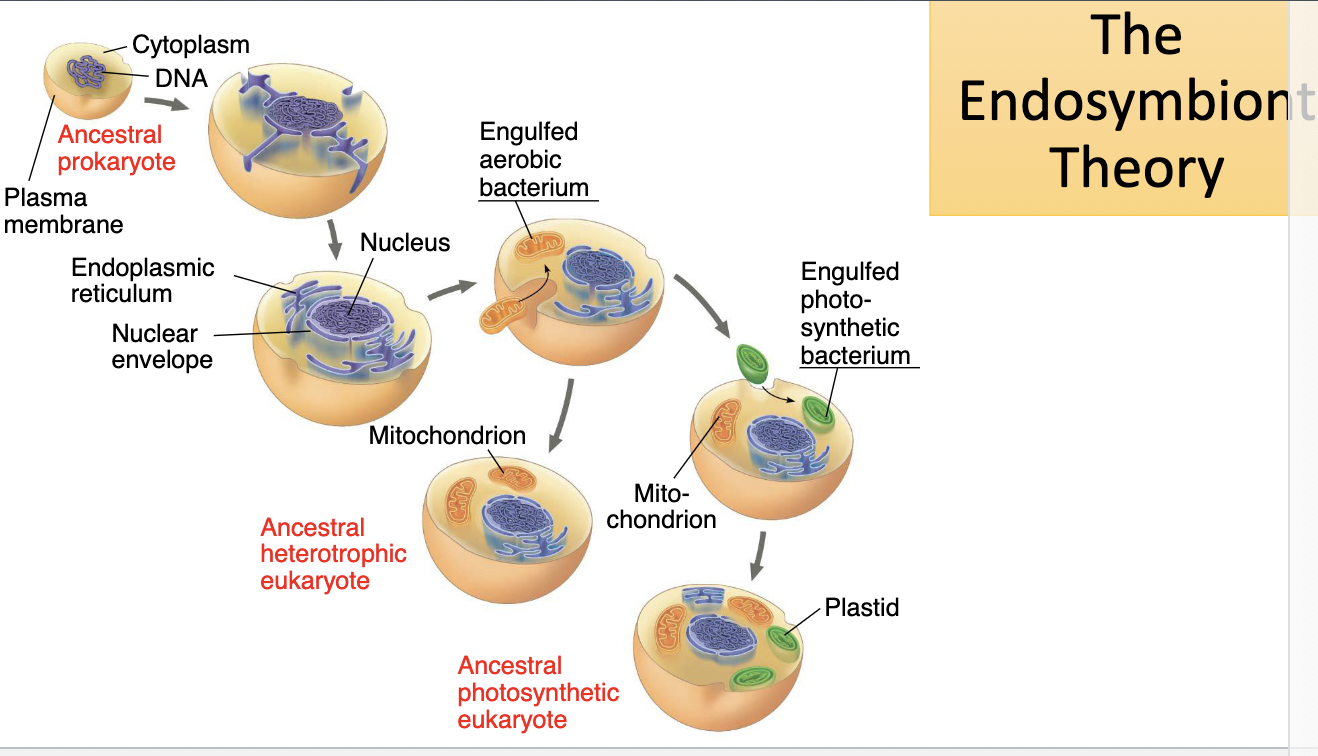
endosymbiont theory
mito and cloro derived from ancestral pro that r engulfed by another cel
relationship became symbiotic
protists
grp of unicell euk orgs that aren’t fungi, plants, and animals
some r more related to plants, animals, or fungi than other protists for no one accepted phylogeny
most euk r protists
green algae
photosyn protists
gA = protists = close relatives of land plants
paraphyletic grp
features of ga relates to land enviorn pressures
enbryos not protected by parent orgs
flagellated gametes: gametes to swim in water
no internal structural support
no vascular tissue
challenges for movment to land evol
challenges
avoid desiccation
devel supportive tiss
gamestes that dont need water to fertilize
adaptation:
vascular tiss
pollen
seeds
flowers
benefits of moving to land
sunlight
higher co2 concentrations
fewer herbivores + pathogens (in early life)
nutrient rich soils
bryophytes
non vascular plants
usually small
live in moist places

vascular tissues
tissues wn/ cells that form tubes to transport water, nutrients, and sugars
2 types: xylem + phloem
xylem: dead vessel elements cells form tubes to transport water (root to shoot)
contain lignin (polymer that gives structural support)
phloem: living tube cells that transport sugar (leaves to plant)
ovules and pollen
ovules - femal gamete where plant is produces
has protective covering via mem
pollen - male structures that produce sperm
sperm delivered to egg via pollen
seeds
primary dispersal mech for seed plants
pollination: transfer of pollen to portion of plant that has ovule
pollen tube: releases sperm into female portion of plant
fertilization transformed ovule to seed
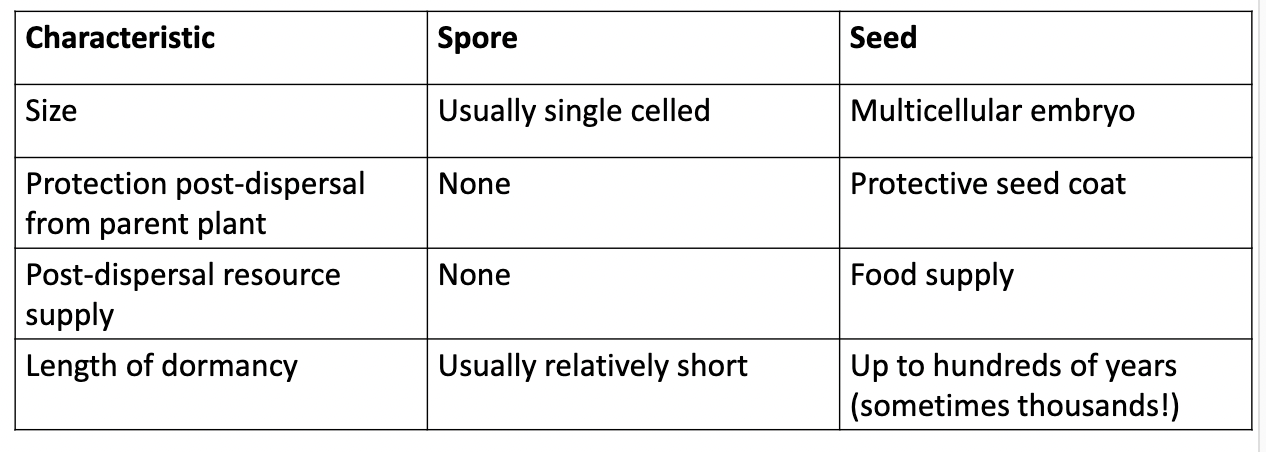
seeds vs spores
gymnosperms
naked seeds (not contained in fruits)
seeds often form on cones
conifers - cone bearing plants
reproduction
not flagellated
reproduce through ovulate/pollen cones
wind pollinated
angiosperm
seed plants w/ flower and fruit
flowers - mode of reproduce in angiosperms
sepal - sterile outermost area of flower
petal - sterile whorl used to attract pollinator
carpel - female part of flower (stigma, style, ovary)
stamen - male part of flower (anther, filament)
pollen dispersal adaptations
animal pollinated
prominent petals
coroful
tube like structures
wind pollinated
prominent stamen
no/ lower # of petals
not colorful
fungi
heterotrophs - feed by breaking down compounds outside their bodies
have hydrlytic enzymes → breakdown mol nto form udsed by fungi
chytrid
unicell parasitic fungus
chytridiomycosis: chytrid fungal infection of skin of amphibians
*IMPORTANT: chytrid case study
cooperative behaviour
in grps: indiv raise non-offspring young
many birds, mammals, and insects
breeding: indiv sacrifice reproduction to devote energy to raising relative’s young (helpers)
altruism: reduces indiv fitness while increasing the fitness of another
somehow causes fitness beenfits for helpers
types of fitness
direct fitness - fitness gained trhough allele transmission by offspring
indirect fitness - gaines through allele transmission by helping relatives rear offspring
inclusive fitnes - fitness gained through direct + indiret fitness
relatedness
probability that 2 indiv shared a given allele
must quantify relatedness to predict if cooperation/altriusm will occur
hamilton’s rule
indiv should behave altrusitically if fitness gain es » fitness lost from no reproduction

reciprocal altruism
indiv interact many times + change indiv interactions base on past behaviours