L21 Bioinformatics III - Identification of proteins
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
what is genomics used to find out
what could the cell do
what is transcriptomics used to find out
what intends the cell to do something
what is proteomics used to find out
what the cell is actually doing
what is metabolomics used to find out
what did the cell do
how many genes are spliced in genomics
20000 (10000 genes/cell)
how many transcripts are given post-translational modifications in transcriptomics
100,000
how many proteic forms form metabolomics from proteomics
10^5 - 10^6
give examples of some mass spectrometres
LTQ orbitrap XL
Q exactive
MALDI TOF
orbitrap fusion
triple TOF
what will spectral lines never have
the exact same value
how is tolerance defined to solve the problem of spectral lines never having the exact same value
when a value is within the tolerance window of another value, algorithms consider them equal
since in MSMS there are 2 spectra, what 2 tolerances are needed
precursor ion
fragments
what is the tolerance of the precursor ion
limits the database to the peptides having the same mass
what is the tolerance of the fragments
determines which lines in the spectrum are used
either for technical or biological reasons, many peptides have…
post-translational modifications which affect their mass
what are fixed modifications
those affecting all the amino acids of the same type
give an example of fixed modifications
the carbamidomethylation of cysteine (57.02 Da)
give an example of variable modifications
the oxidation of methionine (15.99 Da)
what are variable modifications
those affecting part of the amino acids of the same type, but not all
what are the cells doing
they are busy taking glucose from the blood and storing it as glycogen via glycogenesis
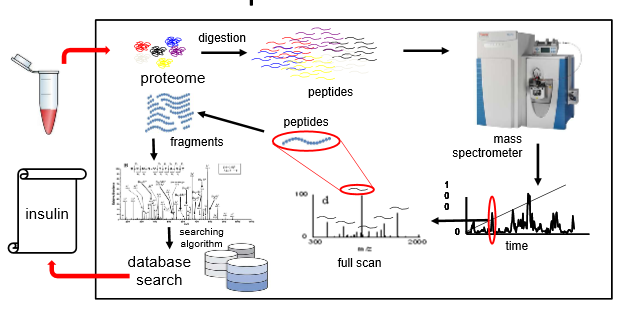
overview of protein identification