Chapter 10--Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition Reactions
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
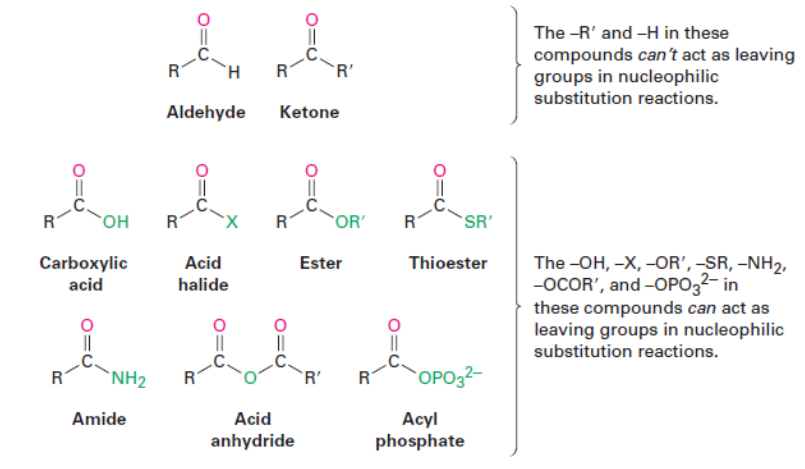
Nature of Carbonyl Compounds
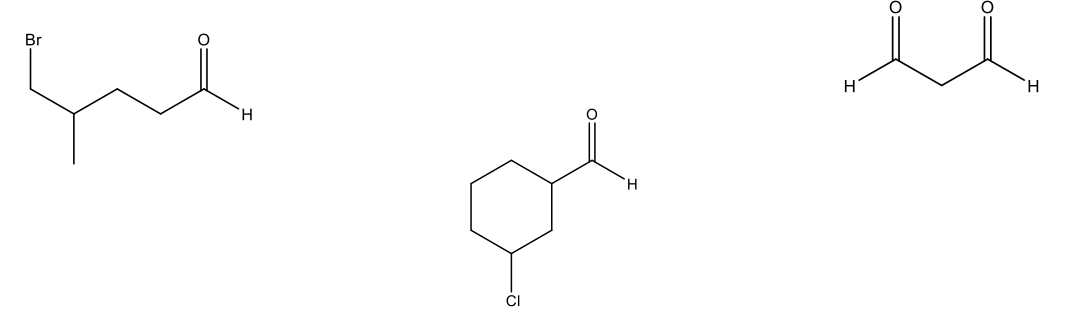
Naming Aldehydes
Aldehydes (-CHO) = drop “-e” from alkane and add “al” ending
“carbaldehyde” ending if aldehyde is coming off of a cycloalkane
Benzaldehyde if aromatic parent group
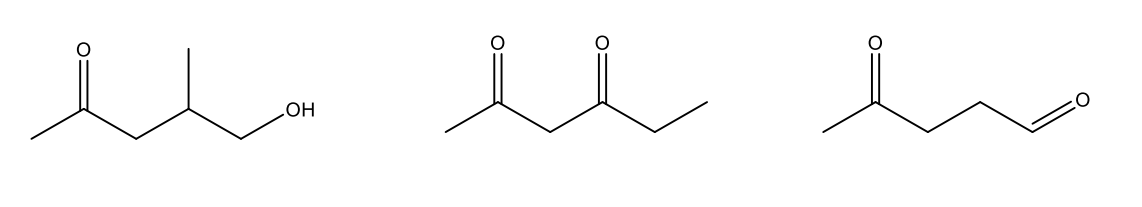
Naming Ketones
Ketone = drop “-e” from alkane and add “-one” ending
Both aldehydes and ketones are higher priority than alkanes, alkenes, halides, and alcohols.
Aldehydes are a higher priority than ketones.
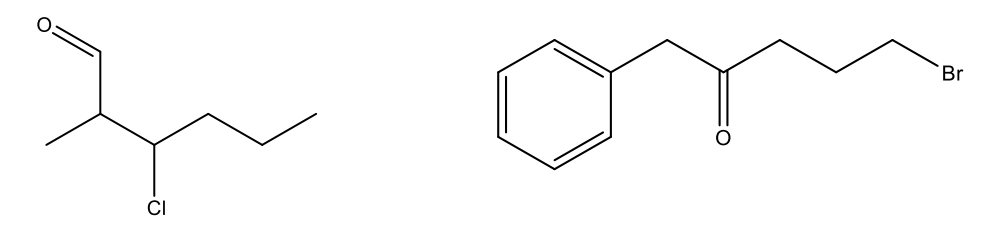
Name the following molecules using IUPAC naming.
3 chloro-2-methylhexanal
5-bromo-1-phenylpentan-2-one
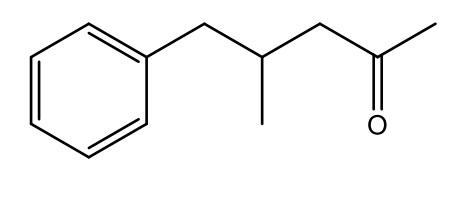
What is the IUPAC name of the following structure?
4-methyl-5-phenylpentan-2-one
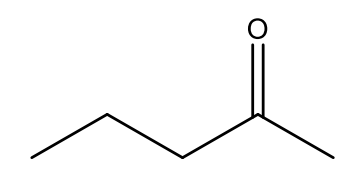
Which option below will result in the following molecule as the major organic product?
Reacting pentan-2-ol with sodium dichromate and acid
Nucleophilic Addition Reactions
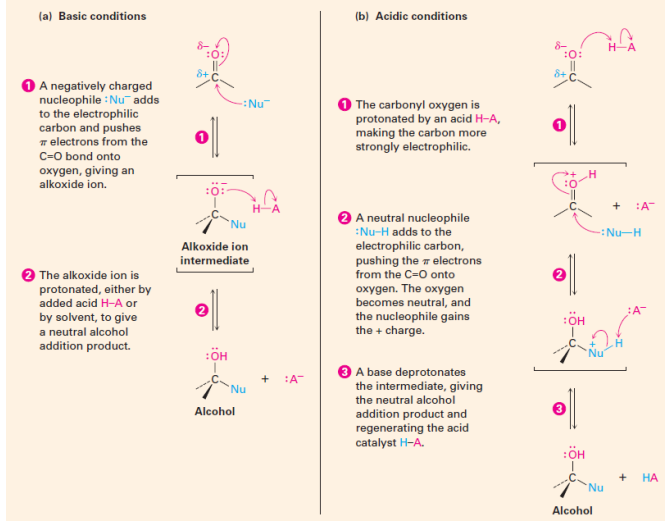
Nucleophilic Addition Reactions
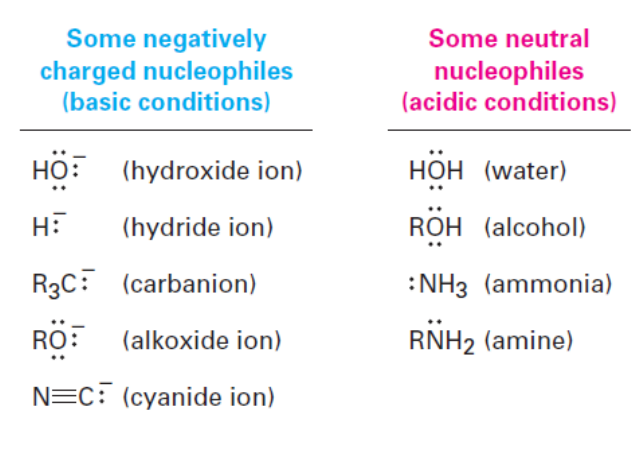
Nucleophilic Addition Reactions Summary
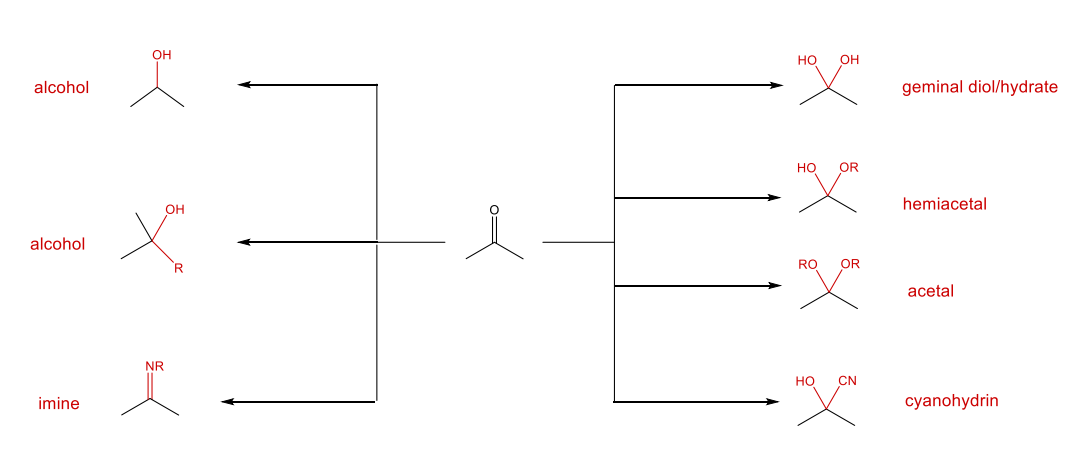
Nucleophilic addition: nucleophile adds to the carbon of the carbonyl group
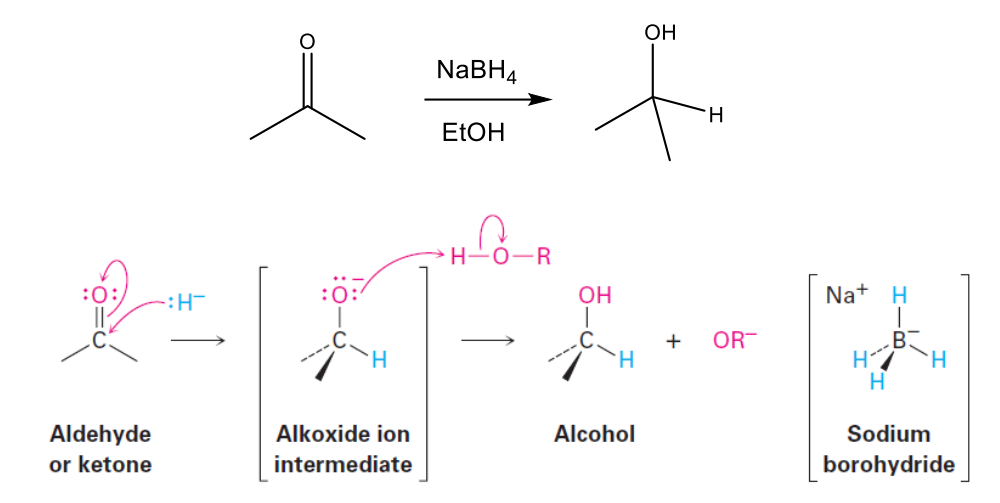
Alcohol Formation: Reduction
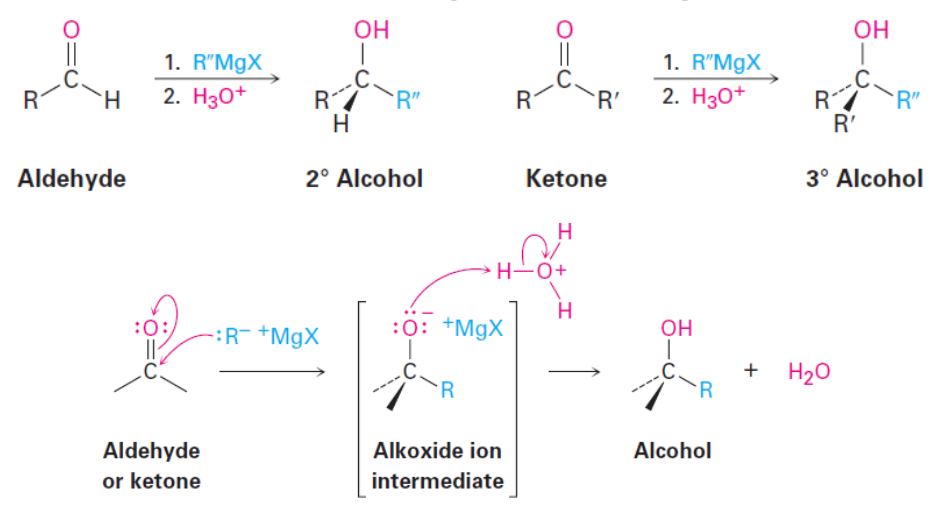
Alcohol Formation: Grignard Reagents
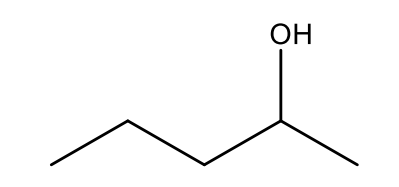
Which option below will result in the following molecule as the major organic product?
Reacting pentan-2-one with sodium borohydride
AND
Reacting butanal with CH3MgBr, followed by treatment with acid
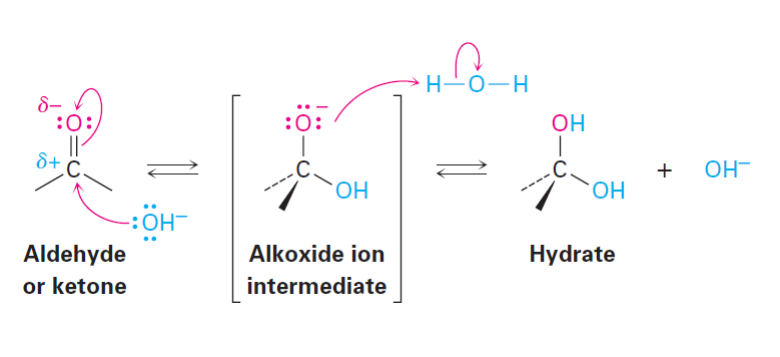
Hydrate Formation: Basic Conditions
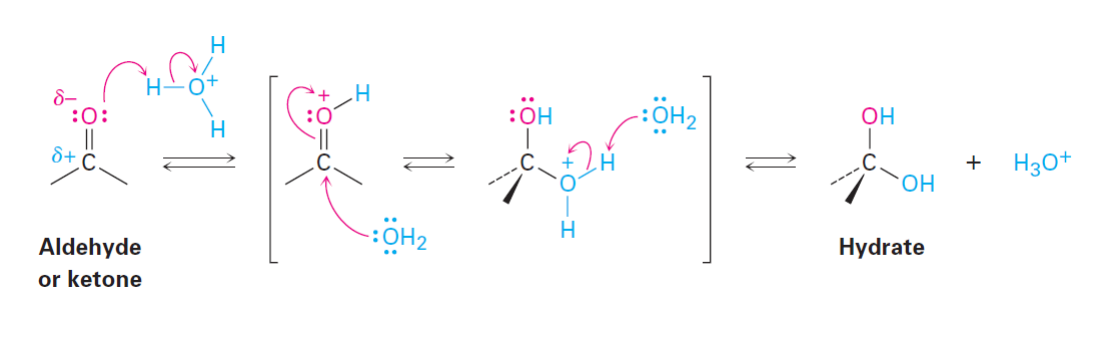
Hydrate Formation: Acidic Conditions
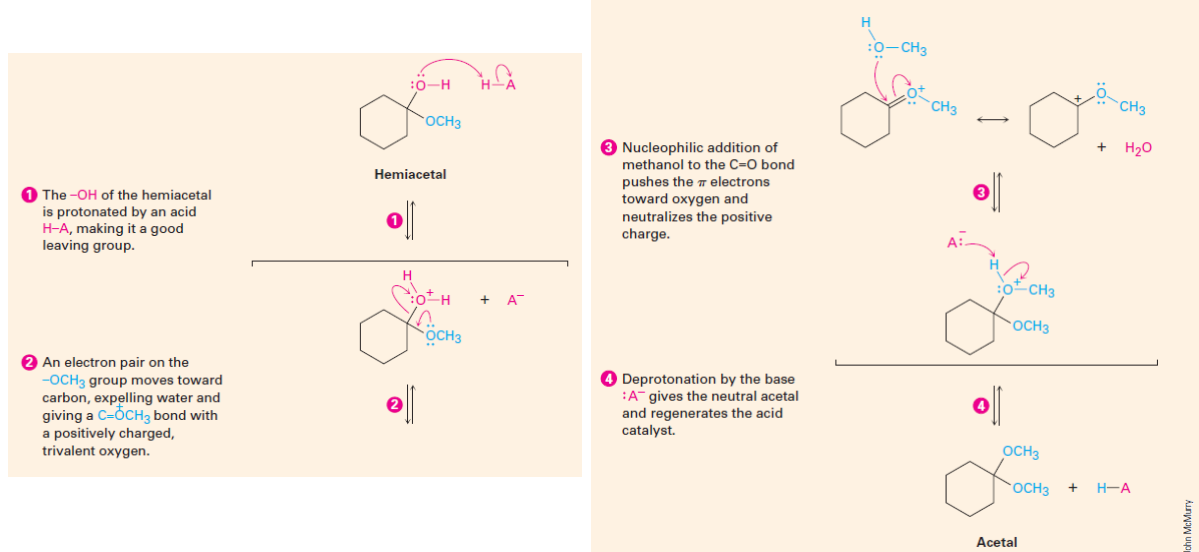
Acetal Formation Mechanism
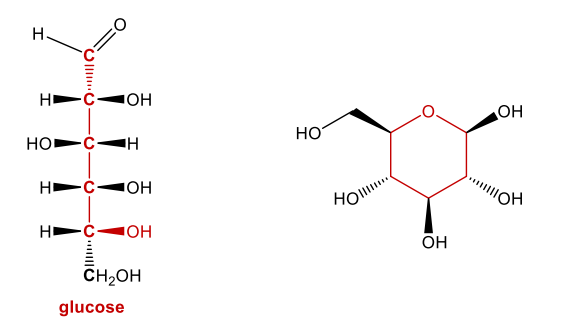
Acetal Formation: Sugars
Describes a broad class of molecules
Type of carbohydrate
Simplest is glucose
Carbs are metabolized in body to glucose (4 cal per gram)
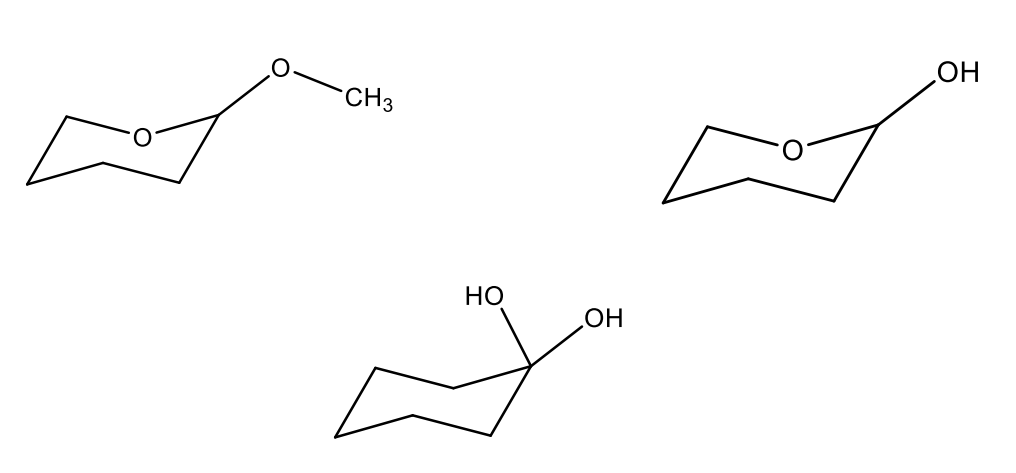
Identify each compounds as either a hydrate, hemiacetal, or acetal.
(far left) acetal because two -OR groups
(middle) hydrate because 2 -OH groups
(far right) hemiacetal because 1 -OR, 1 -OH
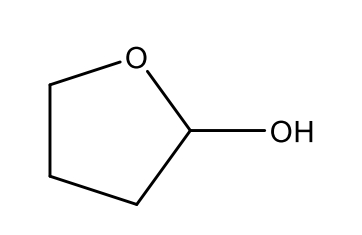
How would you classify the following structure?
hemiacetal
Acetal Formation Synthesis Example
Can be used as protecting groups
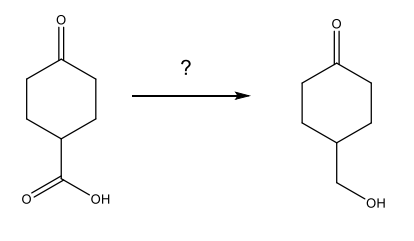
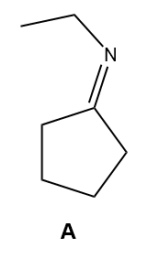
Nucleophilic Addition of Amines: Imine Formation
NH3 and RNH2 add to aldehydes and ketones to yield imines.
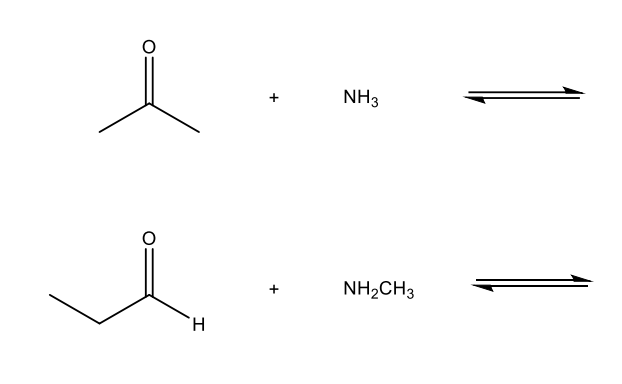
Which option below will result in the following molecule as the major organic product?
Some negatively charged nucleophiles (basic conditions)
HO - (hydroxide ion)
H - (hydride ion)
R3C - (carbanion)
RO - (alkoxide ion)
N (triple bond) C (cyanide ion)
Some neutral nucleophiles (acidic conditions)
HOH (water)
ROH (alcohol)
NH3 (ammonia)
RNH2 (amine)
Nucleophilic Addition of Amines: Cyanohydrin Formation
-CN adds to aldehydes and ketones to yield cyanohydrins.