Lecture 6 | Chemical Causes of Cancer IV Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor (cont) Pesticides
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Mechanism of action of Dioxin
Not genotoxic: does not interact directly with DNA, does not cause mutations (directly)
acts epigenetically via a protein receptor
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR)
can bind dioxin and other aromatic hydrocarbons
Once bound to a ART, it dimerizes into AhR:ARNT heterodimer
This dimer binds DNA at xenobiotic response elements (XRE)
Regulates transcription of genes involved in xenobiotic metabolism cell proliferation and differentiation
Highly expressed in the liver
Transcriptional activators and repressors
ex: Ah receptor
Binds specific DNA elements upstream of the start site of transcription nd regulate transcription
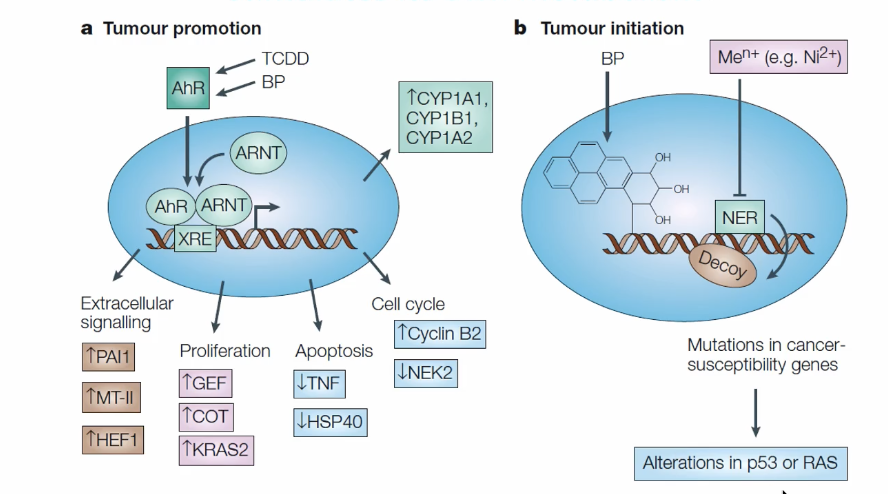
Dioxin mechanism
Regulates expression of drug/xenobiotic metabolism genes by binding ti AhR
cannot go into cell by itself
so it binds to AhR
comes into contact with nucleus transporter and is directed to Arnt
Found upstream of transcription start site
Bind to the XRE of the Cyp1a1 gene
This will increase transcription of Cyp1a1 → allows more phase 1
Bad outcome
Transcriptional targets of Ah Receptor
Activated genes involved in both phase 1 and phase ii
phase 1:

dioxin acts indirectly as an initiation
phase 2:

cell proliferation and differentiation:

dioxin acts as a tumor promoter
Therefore Dioxin is a complete carcinogen
Exogenous ligands for AhR
Flavonoids, carotenoids, indole-3-carbinol, resveratrol
all AhR agonists/antagonists
Impact of AhR depends on what binds to it
Endogenous AhR ligands
AhR is best known for binding exogenous, carcinogenic compounds like BaP and dioxin but:
Products derived from Trp
Virulence factors
Possible part of a defense system to bacterial infections
Receptor-mediated effects of dioxin are pleiotropic and synergistic with other carcinogens
If dioxin exposure occurs at the same time as Aflatoxin B1 then:
dioxin activates AhR which increases Cyp1A2
In combo with aflatoxin B1 they produce harmful AFB1-8,9oxide which is a DNA adduct which causes cell proliferation genes
So impacting phase 1 enzymes and cell proliferation genes
causes increased mutagenic carcinogenic
what is u are also eating phytochemicals
can also activate AhR which will decrease impact of AFB1-8,9
B[a]P interactions with dioxin
Ligand for AhR
exhibits both genotoxic and non genotoxic effects
Stimulates its own metabolism
Genetic variation in Phase 1 and 2
Pesticides
Non genotoxic carcinogens and are classified as tumor promoters
Usage: insecticides, fungicides, herbicides, rodenticides
Bad: increasing worldwide
due to increased demand for food
Good news: decreasing US
Usage in the US
Peaked 1981
Pesticides adverse health effects
General population: exposure in food
Bystander exposure: home, serial drift
Occupational
Poisionings
3 milllion agricultural workers left with health effects
Problem with testing
Inadequate testing: most testing done by the companies that produce the pesticides
long term effects on general population are not known
tolerance levels are often set too high
raw and processes food are not treated the same
not having an accurate measurement of total human exposure