Christmas SBA
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
Patients with a banana allergy, may react to what other fruits? What other allergy may present as an issue?
- kiwi, passionfruit, avocados, chestnut
- latex
How might you deal with a patient presenting with a cold sore?
delay tx
- prodromal cold sore (early HSV-1), advised to post-pone urgent
What are the symptoms of a prodromal cold sore?
- itching, tingling, burning
- can use aciclovir
- dental procedures can excacerbate, increase discomfort, expose others
How could you assess the patient with a cold sore, if treatment is possible at the appointment/ or reschedule?
- ask if in active stage
- how long have they had it
- do they regularly get it
- if active & tx non-urgent > reschedule (7-14d)
- explain why - risk to you & pt, risk of contagion, could delay healing
- if urgent: follow strict infection control, PPE, consider antiviral prohpy, reduce aerosol & contact
- documentation
What is clinical governance?
- systemic framework through which HC organisations: dental practices, ensures continuous improvement in quality & safety of pt care
- set of principles & standards: aim in achieving high quality HC
- commitment to accountability, transparency, responsibly in clinical practice
What are the 7 key components in clinical governance?
- pt safety
- clinical effectiveness
- risk mx
- audit & QI
- staff training & edu
- pt involvement & feedback
- accountability & leadership
Pigmented BCC vs. Melanoma: Origin and cell type
BCC: basal cells, located in lowest layer epidermis, caused by sun exp, most common & typically least aggressive type of cancer
melanoma: melanocytes, cells prod melanin, more aggressive, can metastasise to other parts
Pigmented BCC vs. Melanoma: Appearance and clinical features
BCC: smooth, shiny, slightly translucent, dark brown/blue/black, pearly/waxy border, telangiectasias may be visible, grow slowly, rarely spead, can be locally invasive & damage surrounding tissue if untreated, usually painless, occ bleed/ulcerate
Melanoma: dark, irregularly pigmented, irregular shape, uneven border
Pigmented BCC vs. Melanoma: Behaviour and aggressiveness
BCC: slow grow, unlikely to metastasise, if left untx can grow deep into skin & underlying structures (local damage)
Melanoma: high pot to metastasise, often req prompt aggressive tx
Pigmented BCC vs. Melanoma: Diagnosis
- both confirmed by biopsy
- dermatoscopy used for both, can help distinguish
Pigmented BCC vs. Melanoma: Treatment
BCC: surgical excison, MOHs mirographic surgery, sometimes: cryotherapy, topical meds, photodynamic therapy, dep on case
Melanoma: dep on stage, surgical excision w/ wider margins to ensure complete, adv may req: immunotherapy, targeted therapy, radiation, chemo
Metronidazole affects with warfarin:
- m can increase INR
- inhibits w metabolism, particularly S-enantiomer, more potent anticoag
> inhibits cytochrome p450 enzymes: particularly CYP2C9, responsible for breaking down warfarin in liver
- therefore w levels in blood risk, increased anticoag effect
- therefore increased bleeding risk
- close monitoring req
- 2-4, checked 24-72hrs b4
How is aspirin contraindicated in children?
- reyes syndrome: lead to vomiting, confusion, seizures
- esp <16
- rare, life-threatening can be
- can cause swelling of liver & brain
- cause not understood fully
- ass w/ asp use during viral infection: influenza & chicken pox
- alt to asp: paracetamol, ibuprofen
- exceptions: aspiring presc for Kawasaki dx/certain paeds heart conditions
What is the eruption date for the upper canine? Permanent and Primary
prim: 16-22 months
perm: 11-12y
Relationship between bulimia and erosion of incisors:
upper
- freq exposure to stomach acid
- primarily HCl, corrosive to enamel
- direct acid contact, chemical erosion, progression of damage, perimylolysis pattern
- sensitivity, pain, aesthetic changes, risk damage
- support, edu, F, OHI adv
Perimylolysis
acidic gastric contents that are expelled during vomiting come into contact w/ tooth tissue, leading to dental erosion
Pregnancy gingivitis:
- What is it?
- Causes & Contributing factors:
- Complications:
- Management
- due to hormonal changes (caused by an increase in estrogen & progesterone levels), make gums more sensitive to plaque build up
- esp 2nd/3rd trimester 60-70% women
- causes: progesterone can enhance bf, more prone to inflammation, immune response changes, increased plaque (vomiting, nausea), acid exposure (acid reflux, vomit)
- compl: ass periodontal dx
- mx: OH, regular dental visits, diet, hydration, antibacterial rinses
What are the guidelines associated with GA and eating?
- imp to minimise risk of aspiration, can lead to pneumonia etc.
- stop eating solid at least 6hrs before
- clear liquids up to 2hrs before
- breast milk up to 4hrs before
- formula milk restricted to 6hrs before
What are the options for management of intraradicular pathology?
RCT or apical surgery
(apicoectomy, root resection, repair of root perforation or resorption defects, removal of broken fragments of the tooth or a filling material, & exploratory surgery to look for root fractures)
- extraction
What are the main contraindications related to intraradicular pathology?
- severe PA abscess/acute infection
- chronic or untreated PA pathology
- anatomical complications: severe root resorption, curved, fractured roots
- uncontrolled systemic conditions: DM, CVD, other systemic issues
- failure to achieve adequate disinf
- non-vital tooth
Indications for a PMC:
- Asymptomatic (no pain, no swelling or sinus)
- No radiographic evidence of pulpal involvement or interradicular pathology
- Small carious lesions only - loss of no more than ⅓ of the marginal ridge. Any more indicates likely pulpal involvement due to large pulp horns of primary teeth e.g. > 1/2 dentine
Signs indicating pulpal involvement:
- Sinus (nb. interradicular abscesses may drain through the gingival margin rather than through a sinus in the mucosa)
- Swelling
- Radiographic pathology: the anatomy of primary teeth (notably the thin pulp chamber floor) means this often presents as interradicular radiolucency at the bifurcation.
- Pain which is spontaneous, severe or requires analgesia use.
- Radiographically visible deep caries.
- Extensive cavitation and loss of more than 1/3 of the marginal ridge. In these cases, it is very likely that there is pulpal inflammation.
When is a sickle cell test done?
newborn screening
- early detection > prompt tx
- vaccination, penicillin prophy, early intervention for prev further infection/complications
Symptoms of SCD:
Shortness of breath
Chest pain
Palpations (irregular heart beat)
Syncope (fainting)
- pain episodes (SC crisis)
- anaemia
- swelling of hands & feet
- fatigue
- delayed growth
- freq infections
FH of SCD:
- genetic testing can be performed: preconception - assessed if both partners carry SCT, if both there is a risk > genetic counselling to consider?
- more prev: african, mediterranean, middle eastern, indian ancestry
Diagnosis of haemoglobinopathies:
- Hb electrophoresis - identify types Hb in blood
- CBC - indicate anaemia etc...
- DNA testing - confirms presence of gene
Herpetic gingivostomatitis:
- HSV-1 (can be 2)
- young children, & ppl w/ weakened immune system
- initial fever, irritability, malaise, gingivitis, stomatitis
- oral lesions: blisters around gums, lips, tongue, ROM, diff eating etc...
- lymphadenopathy, pain
- highly contagious (autoinoculation)
- diag: clinical eval, lab (PCR, DFA)
- tx: aciclovir, analgesics, OTC, OHI, fluids
- complications: secondary bacterial infection, herpes keratitis (eye), dehydration
Autoinoculation
the process of transferring a virus from one part of the body to another through scratching or rubbing a lesion & then touching other areas of the body, resulting in infection
Docosanol
aciclovir
Syphilis
Treponema pallidum
- primary: chancre appears 2-3w after exposure to bacterium, heals on own, tongue, lips, mouth, often painless, oval, firm edges, raised
- secondary: snail track ulcers
- tertiary: gumma, serious complications
other > rash, mucous patches, lymphadenopathy, fever, sore throat, headaches
- diagnosis: DFM, serologic tests
- tx: penicillin (IM)
- prev: safe sexual practice
Leukaemia
- characterised uncontrolled growth of abnormal wbc's, can interfere w/ normal bc prod & func
- bleeding gums: thrombocytopenia (low platelet), disruption normal bc prod in bm > easy bruising, nosebleeds, bleeding gums esp spontaneous
- tiredness, anaemia, frq infections, unexplained bruising, paleness, lymphadenopathy, night sweats, weight loss
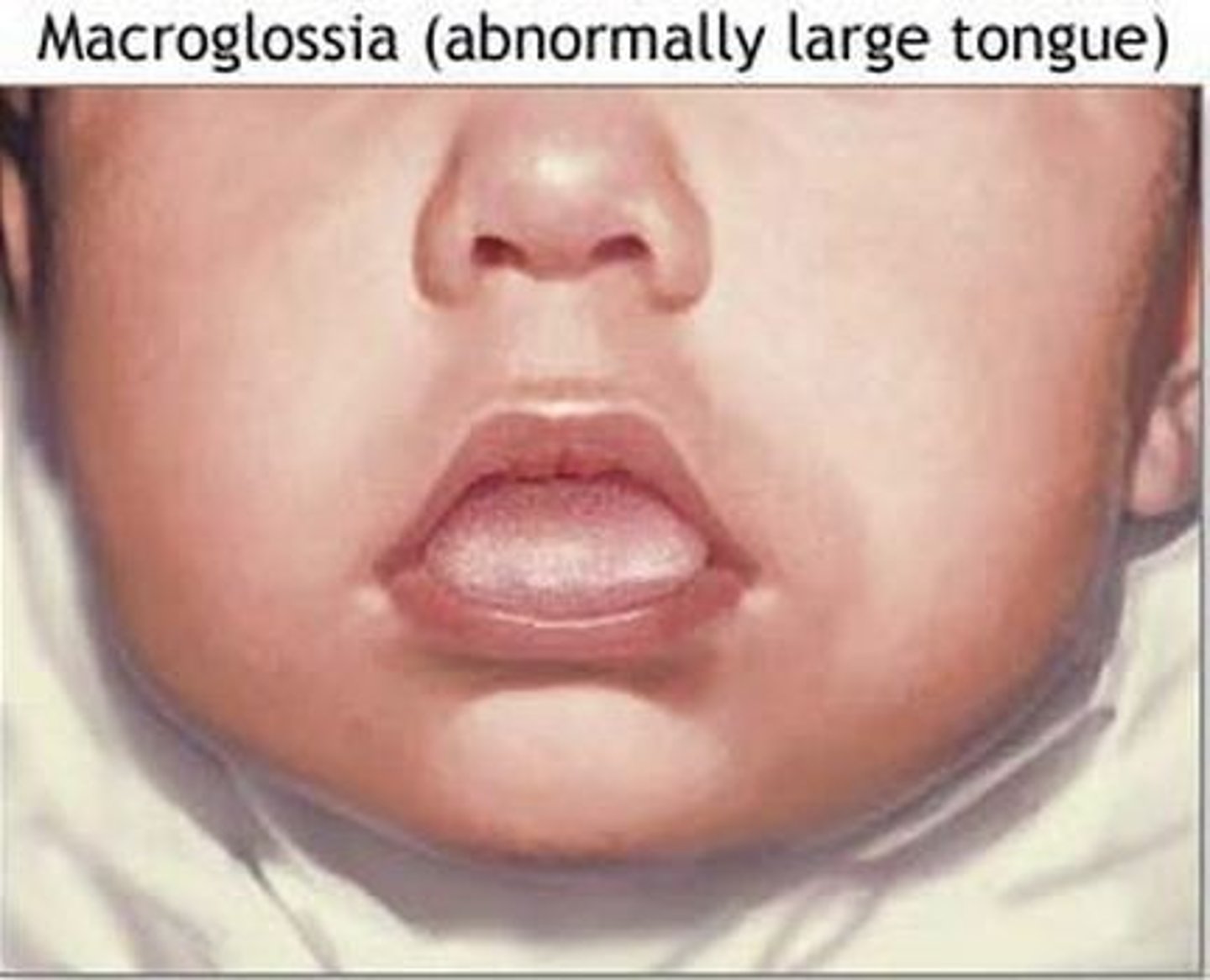
Down syndrome and Macroglossia:
- large tongue, common feature tris 21 in some cases
- may be larger due to hypotonia (low muscle tone) of oral & facial muscle, cause tongue to protrude/ appear larger
- can cause issues w/ teeth alignment > malocclusion, diff closing mouth
- other causes: congenital hypothyroidism, Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome, acromegaly, mucopolysaccharidoses
If a periodontitis patient has BPE codes of 0s, presenting as stable, and is experiencing excessive recession, what could you do?
refer to perio specialist for gingival graft
- no signs infl, bleeding or pocketing
- recession: brushing trauma, perio, poor OH
- may have increased pocket depths >5mm, may still be stable!
- compliance needed
- indications: aestehtic, sensitivity, increased root caries, progressive recession
What is the maximum amount of lidocaine you could give to a 20kg child?
20 x 4.4/44 = 2 cartridges
20kg child max dose w/out eph = 3mg per kg weight, 3mg/kg x20 = 140mg
20kg child max dose w/ eph = 7mg/kg, x20 = 140mg
Painkillers for emergency pain and omeprazole:
- NSAIDS, paracetamol, opioids
- omeprazole may be presc if concern about stomach irritation (esp NSAIDs) - protect against gastric ulcers & acid issues particularly in pts at risk of GIT complications
What material would you use to treat root caries?
GIC
- arrest decay, restore, prev further damage
- F- release, adhesion to dentine, moisture tolerance, biocompatibility, ease of use
- dx: typically brown, soft, discoloured near gumline
- remove, could condition, fill, post-op OHI for prev
Restoring MIH teeth:
- GIC = reduced sensitivity, more cost-effective
- bond to tooth
- CHECK
What is saucering in implantology?
- marginal BL around implants
- bone at top starts to resorb, creating concave/saucer-shaped app
- tends to be more noticable in ant region as aesthetics & thinner bone structure
Causes and management of saucering:
- biomechanical stress, micro-gap & bacterial infiltration, surgical technique, biological width
- mx: proper implant positioning, immediate placement techniques, regular maintenance (OHI, monitoring, ABs?, antibactierals etc...)
Biological width
the distance that is established by the JE & CT attachment to the root surface of a tooth. This can also be described as the height between the deepest point of the gingival sulcus & the crest of the alveolar bone.
Management of a pregnant patient who suffers with a gag reflex, BPE code 3's and a high periodontal disease risk:
- MW
- don't brush after
- prevention, then FPA
- consider anxiety mx
How would you manage a large amalgam filling presenting with pulpal pain?
- assess size of filling, condition of tooth, properties of A
- thermal conductivity of A: transmission of hot & cold sensations to pulp more effectively
- large filling esp close to pulp, temp changes can irritate
- can lead to pulpitis
- when remaining dentine layer is thin, prov less protection to pulp for external stimuli, increasing risk irritation
- no chemical bone - microscopic gaps can form b/t filling & tooth
- cusp flexure & stress - large filling can place stress, flex during chewing, lead to microfractures/cracks, cause pain. Delayed H2 expansion
- post-op sensitivity
- remove amalgam, temp fill if not sure IP/RP, radiograph & then see.
What conditions result in the manifestation of a bulls-eye rash?
> erythema multiforme - multi-ring-like
- can be caused by prev infection, herpes
- itching, burning
tx - corticosteroids, antivirals, antiseptics
> urticaria is diff - raised welts, allergic response, tx w/ antihistamines, corticosteroids
> lyme dx: bulls-eye rash, tick-bourne, expanding rash, fever, fatigue, tx - ABs
What is the cause of a patient only being able to open their mouth 20mm?
- indicates restricted opening, usually 45mm
- trismus? can result from various issues involving MOM, TMJ, systemic conditions
- muscles involed: lat pt (dep), suprahyoid (mylohyoid, geniohyoid, dig - dep)
- causes: muscle spasms, tightness, TMD, infection, trauma, systemic conditions
A patient is experiencing exam stress from MOM, what are the steps to take?
- often indicates conditions related to myofacial pain/TMD
- take comprehensive assessment, initate initial conservative mx, pharmacological therapy, occlusal appliances, refer to specialist, follow-up monitoring
> analgesics, muscle relaxants, topical analgesics
Where does the secondary palate develop from?
maxillary process
- sep oral & nasal cavities
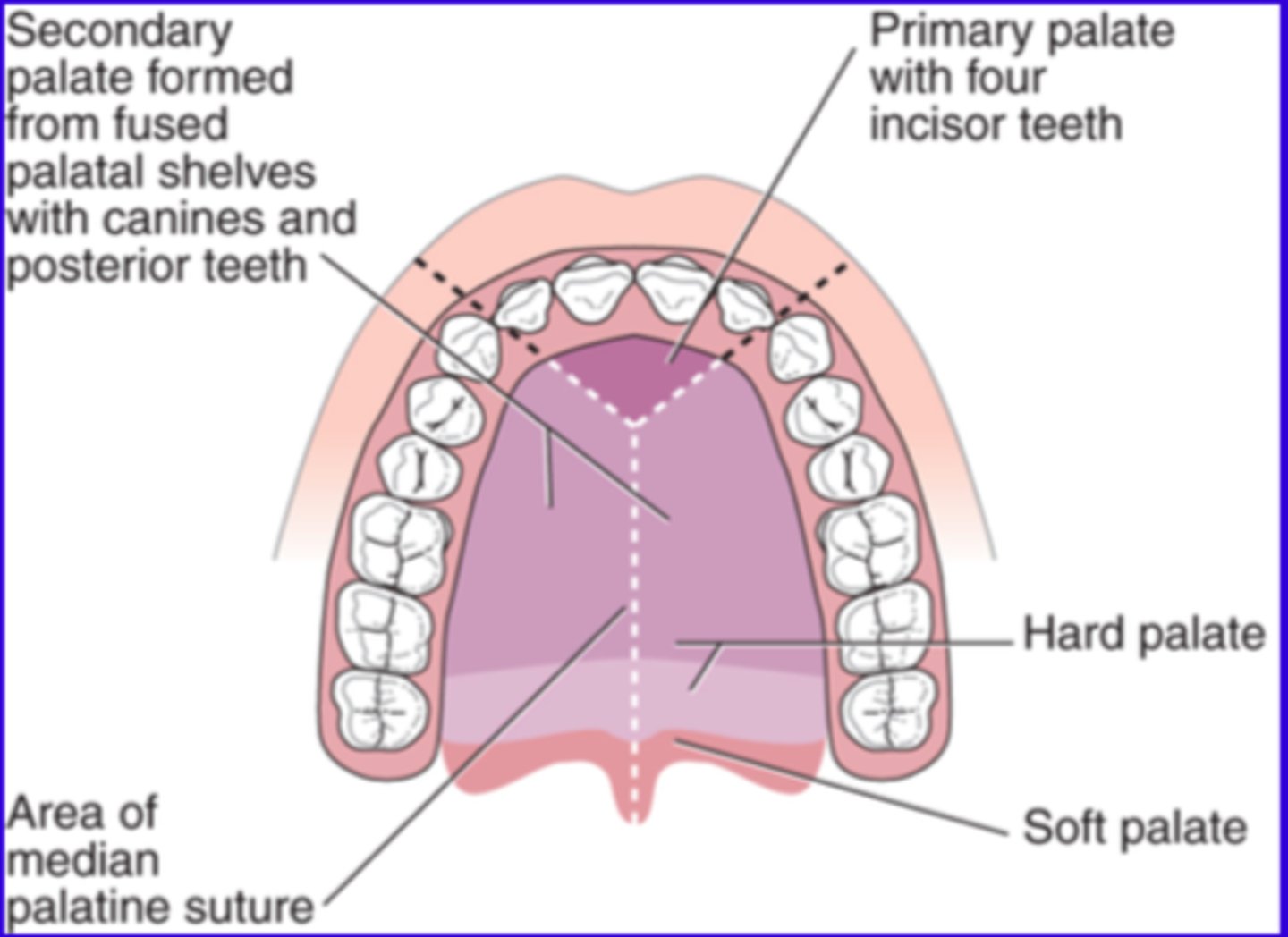
Steps of palatine development:
- formation palatal shelves w6-7
- elevation & fusion of palatal shelves w7-8
- fusion w/ primary palate & nasal sepia w8-12
- dev of hard & soft palate
Formation of palatal shelves:
- 2 issue outgrowths - palatal shelves form on either side of maxillary prominences
- shelves: extension of maxillary prominences, growth vertically on either side of developing tongue within OC
Elevation and fusion of palatal shelves:
- as fetus growth, tongue descends, allows palatal shelves to elevate & move towards each other horizontally above the tongue
- once the palatal shelves are horizontally aligned begin to grow towards each other & eventually meet in midline
- medial edge epithelium - at point of contact dissolves, allowing underlying mesenchyme to fuse (creates continuous structure)
Fusion with primary palate and nasal sepia:
- secondary plate fuse w primary palate at incisive foramen
- forms U lip & ant most part of hard palate
- developing secondary palate also fuses w/ nasal septum superiorly, which completes the separation b/t oral & NC's
Development of hard and soft palate:
- ant portion of secondary plate ossifies to form hard palate
- posterior portion remains unossified, forming soft palate & uvula
What condition can result during secondary palate formation?
cleft palate
- common congenital malformation
- can affect only the secondary palate or can also involve the primary palate depending on where the fusion process was disrupted
KV
- control x-ray peam penetration: quality/max energy of photons prod
- high energy xrays can penetrate denser tissues > lower kvp less energy xrays
- contrast: high: lower image contrast, more grey. low kvp: higher contrast
- pt dose: higher kvp lower mAs = red dose
20 stone
127kg (27 stone - 177kg)
Betamethasone
corticosteroid, glucocorticoid
- red inflammation, itching, immune response
- skin disorders
- can have spray rhinitis
Beclomethasone
corticosteroid, glucocorticoid
- asthma, allergic rhinitis
- red inflammation
- inhalers, nasal spray
MOA for -azole's:
inhibit ergosterol synthesis, key component of fungal cm's = cell death
nystatin same
How would you manage erythema migrans?
- reassurance, pt edu
- symptom mx: analgesics, OHI, dietary mx
- topical: corticosteroids, vitamin supplements
- monitoring, follow-up
- if app changes, discomfort worsens = refer
What LA to use for retained LRE?
- consider child's age: rule of 10
- IDB?
RAS
- current
- painful ulcers
- mx: topical corticosteroids, antiseptics, analgesics, dietary mods, SLS
- major & herp: systemic meds? corticosteroids, immunomodulatory, doxy for herpetiform
RAS - minor
- most common
- <1cm
- 1-5
- non-keratinised mucosa (insdie cheeks, lips, under tongue)
- heals 7-14d
- mild-mod pain
RAS - major
- >1cm
- 1-3
- either keratinised/non-k
- 2-6w
- often scars
- signif pain
RAS - herpetiform
resembles HSV
- 1-3mm
- clusters 15-30
- any mucosa
- 7-14d
- may scar: not as likely
Oral cancer management:
- MD approach
- combines: medications, surgical, supportive therapes tailored to stage & location of disease & pts overall health
- initial eval includes: clinical exam, biopsy, imaging studies, staging
- tx: surgical mx (primary tumour resection, neck dissection), radiation therapy (surgery CI, adjunct), chemo, targeted therapy (cetuximab EGFR inhibitor & immunotherapy), supportive care, palliative care
- follow-up
- site: lip better outcome than tongue/FoM
Side effects radiation therapy:
mucousitis, xerostomia, ORN
Cancer supportive care:
- speech & swallowing rehab
- nutritional support
- pain mx
- mx side effect
Instrument flow for decontamination:
1. dirty zone: used, seg of sharps, single use, reusable
2. cleaning: manual (scrubbed under water), US (bath), w-d (automates & standardises)
3. inspection: debris, damage
4. sterilisation: autoclave, wrapped/unwrapped, ensure process validated & logged
wrapped - B, unwrapped - N
5. cooling & drying
6. storage
What are the contraindications to IHS?
- young children: uncoop, anxiety, behavioural issues (may req IV, oral instead)
- diabetes if unstable/unmonitored
- MS if also have resp muscle weakness, or stress/fatigue exacerbate
- conditions causing partial/complete obstruction of U airway: deviated septum, allergies, adenoids, sleep apnea
- severe resp disorder
- preg not rec in 1st trimester - teratogenic risk (caution in 2/3, avoid)
- psychiatric conditions
- vitamin B12 def (sensitive to neurological deteroriation)
- substance abuse history
- middle ear problems
When could you refer a mucocele?
- ref nec if persistent, recurrent, large, symptomatic, if diag uncertain
- small uncomplicated: may resolve spontaneously, should be monitored for changes/persistence
Size of composite: Fillers
Properties:
- shrinkage of MMA reduced by incorporating large amounts glass fillers
- methyacrylate monomers have high coefficient of thermal expansion - ceramic fillers reduce
- improve mechanical properties
- use of heavy metals provides radiopacity
- means of controlling various aesthetic features (colour, transluency, fluorescence)
- increasing filler particle size range > improves packing density
- modification of filler particle shape such that particles have tendency to interlock, making it more diff to flow past
Types:
- composition: variety of silica-based glass fillers
- particle size: smaller, smoother - softer glasses allow a reduction in the size
- traditional: glass filler particles 10-20um, largest 40um, dull surface app
- microfilled resins: colloidal silica 0.01-0.05um (0.02um av), v large SA in contact w/ resin, diff to obtain high filler loading > 2 stage procedure developed
- hybrid/blended compsites: large filler particles 15-20um, small amount colloidal silica 0.01-0.05um
- small-particle hybrid composites: filler particles 0.1-6.0um, usually combined w/ colloidal silica, smoother surface finish
- 'nanocomposites': incl components w/ at least 1 dimension of the order of <100nm
Who disposes of the LA needle after using?
- clinician - as soon as double locked
- key considerations w/ safety & training to ensure compliance of staff w/ ICP & safety protocols, ensuring safe envs for pt & staff
Technique for an IDB:
hit bone after 2-3cm, asp, 1.7, widthdraw a bit, 0.5ml
- semi-reclined
- identify landmarks - pterygomandibular raphe, coronoid notch, contra-lateral PMs
- TA, insert 2.5cm, bone, withdraw, asp, 1.7ml.
- withdraw 1-2mm, asp, 0.5ml
- long buccal if needed
Post: check anaesthetised, monitor for adverse reaction, document
Processes diagram - maxillary
- aranatomical structures
- arise from 1st pharyngeal arch
- contribute to formation U face
What is the GDC made up of?
6 registrants, 6 lay
- registrants: dentists, nurses, hyg, therapists, ortho the, CDT
- lay: lay council members who are involved but don't have a background in dentistry
- other staff:
> executive: manage operations, policy development, investigations, experts in regulation, law, HC mx etc...
> advisors & committees: law, PH, ethics, prov advice & contribute to decision making
What is the GDC registration fee, and what might happen if you pay past the deadline?
- risk of being removed > prev practicing in UK
- may incur late fees
- if removed, can seek reinstatement by paying outstanding fees, may take time
What is its purpose?
- enter name, covers you for year, dates & fees diff for DPF, not requntil application checked & meets requirements for registration.
- if specialist, have to pay fee & annual retention fee
Why does sertraline provide high caries risk?
SSRI
- xerostomia
- changes in oral pH
- diff cleaning teeth?
- increased risk ging/perio dx
- pot for increased sugar consumption
- red SF allows food particles & bacteria to accumulate on tooth surfaces.
- saliva contains bicarbonate ions, which neutralise acids produced by cariogenic bacteria. Without sufficient saliva, the oral env becomes more acidic, favouring demin of enamel.
- saliva is rich in Ca & PO4 ions, which are essential for remin enamel & maintaining its integrity. Xerostomia reduces the availability of these ions.
- dry conditions promote the adherence and growth of bacterial biofilms: harboring acidogenic bacteria that metabolise dietary sugars into acids.
- saliva contains antimicrobial proteins like lysozyme, lactoferrin, & immunoglobulins, which help control oral microbial populations. With red saliva, oral microbiome becomes more pathogenic, increasing caries risk.
- prev: sipping water, sugar-free gum, OTC
MOA:
> inhibiting the reuptake of serotonin into presynaptic neurons, increasing serotonin levels in the synaptic cleft. SSRIs also affect the autonomic nervous system, which plays a key role in regulating saliva production.
> can indirectly reduce parasympathetic stimulation of salivary glands. Saliva production is largely mediated by ACh acting on muscarinic receptors in salivary glands. By modulating neurotransmitter balance, SSRIs can interfere with this pathway, leading to reduced saliva secretion.
> may also affect the balance of sympathetic and parasympathetic innervation to salivary glands.
CPD hours for radiology?
5hrs per 10y cycle
How many chest compressions should be done per minute of CPR?
100-120bpm
How would you administer glucagon IM?
- inject into skin of lower abdomen, thigh, U arm
- hold 5s
- release
When should you give medication for a seizure which has reached status epilepticus?
- lasts 5m>/recurrent seizures w/out recovery inb/t
- managed as ME to prev neurological inury/death
- convulsive or non-convulsive
1. secure airway, O2, monitor resp & cardiac func
2. buccal midazolam 10mg > if no response, call 999 if not done so
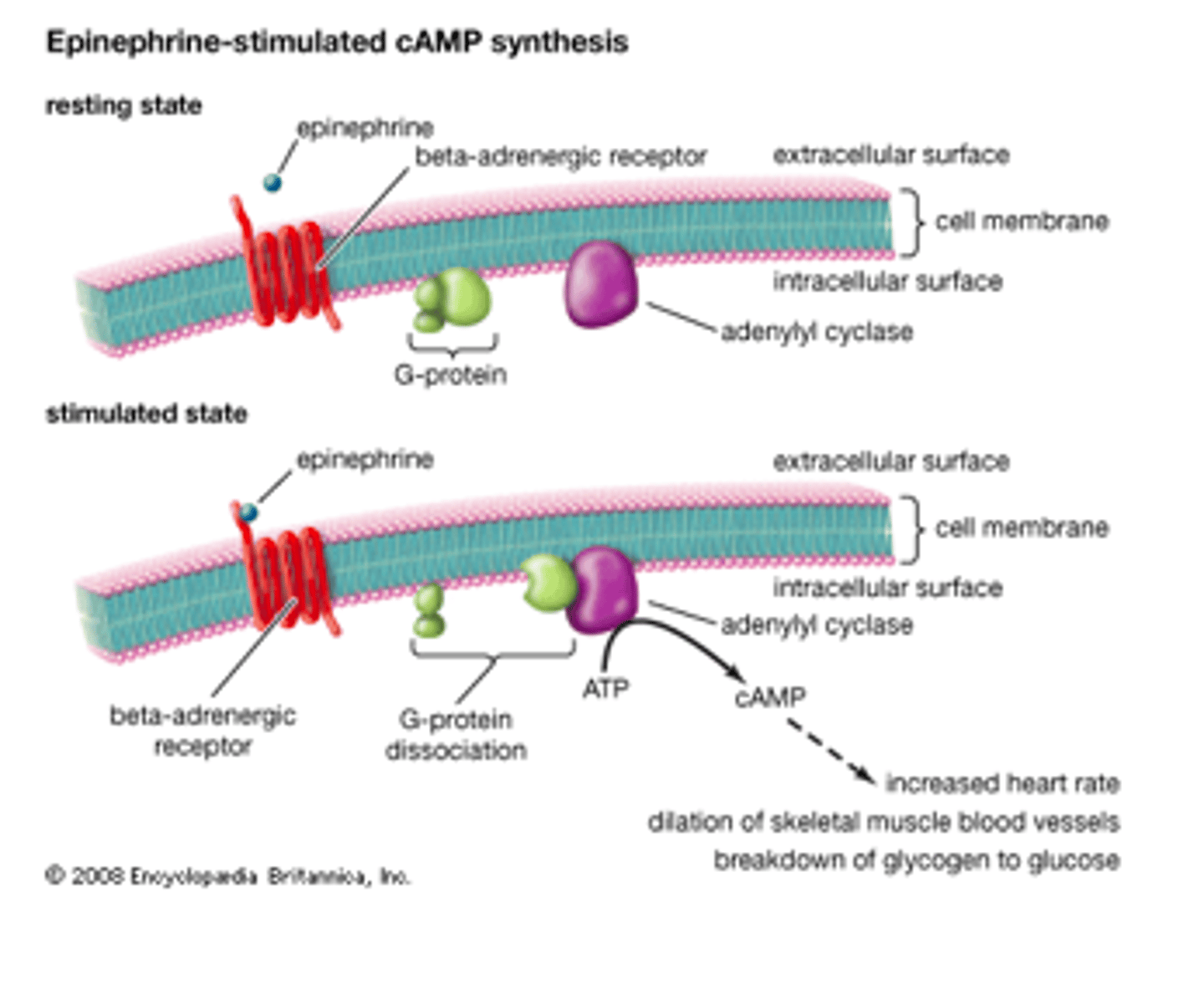
What is the MOA of epinephrine?
alpha-1, beta-1, beta-2 agonist
general: increase HR, bp, dilates airways, raises bgl, mobilses energy stores
alpha 1&2:
- 1 found in sm, esp bv
- 2 found in presynaptic nerve terminals, serve as inhibitory feedback mechanisms
> alpha 1 cause vc: increases bp
beta:
- 1 primarily heart
- 2 sm lungs, bv, other tissues
- 3 adipose tissue, involved in lipolysis
> beta 1 increase HR, contractility, conduction velocity (increase CO)
> beta 2 mediate vd, increases bf to tissues during stress
Other:
- decrease insulin release from pancreas, limits glucose uptake, ensure remains for brain & muscles
- pupil dilation through alpha 1 receptors in eye
What to do if a patient is unconscious and breathing?
Could be due to: syncope, head injury, intoxication, seizures, hypo, med conditions
ABCDE approach
- call 999 when unconscious & not waking, stops breathing, signs of ME, if unsure of cause
How does stannous fluoride/chloride work as a desensitising agent?
MOA summary:
- occlusion of tubules prev fluid mov
- prev ext stimuli reaching nerve endings
- antibacterial
- remineralisation
Effect on dentition:
- protective layer on dentine tubules: when applied, reacts w/ Ca & PO4 ions, forms insoluble stannous salts, occlude tubules, flow fluid restricted.
- antibacterial/microbial: help reduce growth plaque bacteria
- remineralisation: F component contributes, reduces porosity of enamel, more resistant to sensitivity, incorporation of Ca&PO4 to enamel structure
Clinical application:
- sensodyne
- mouth rinses
- Fv gels
- less common in commercial
How many cusps do molars have?
U6 - 4/5 dep on coc. (bigger ml cusp)
U7 - 4 (bigger ml cusp)
L6 - 5
L7 - 4
8's more irregular but most likely 4
What is the purpose of drying your hands in hand hygiene?
- prevent recontamination: optimise the removal of potentially pathogenic MO's
- effectiveness hand sanitisers
- skin integrity
- reduction of transmission > transmission of bacteria is more likely to occur from wet skin than from dry skin, airborne particles
- compliance to hygiene protocol
- reduce friction & clinginess
- effectiveness in bacteria removal
Alpha 1 receptor: Epinephrine
- Location
- Main actions
- Effects of epinephrine
- sm, bvs, eyes, bladder
- vc, mydriasis (dilation), uterine contraction
- increase bp, dilation pupils, bladder relaxation
Alpha 2 receptor: Epinephrine
- Location
- Main actions
- Effects of epinephrine
- presynaptic nerve terminals, CNS, peripheral nerves
- inhibit NTM release, reduce sympathetic tone
- red further synaptic activity, decrease insulin secretion in pancreas (more glucose avail)
Beta 1 receptor: Epinephrine
- Location
- Main actions
- Effects of epinephrine
- heart, cardiac muscle
- increase HR, increase force contraction, conduction velocity
- boost CO, enhances electric conduction in the heart
Beta 2 receptor: Epinephrine
- Location
- Main actions
- Effects of epinephrine
- sm, lungs, bv, uterus
- bronchodilation, vd, uterine contraction
- improve airflow, increase bf to muscles during stress, reduce uterine tone
Beta 3 receptor: Epinephrine
- Location
- Main actions
- Effects of epinephrine
- adipose tissue, bladder, heart
- lipolysis, bladder relaxation
- mobilise energy reserve by breaking down fat stores
How long should you store sterilised instruments which are wrapped?
1y
What is the dose of adrenaline for a 7-year-old?
300mg (6-12)
0.3mls 1:1000 IM
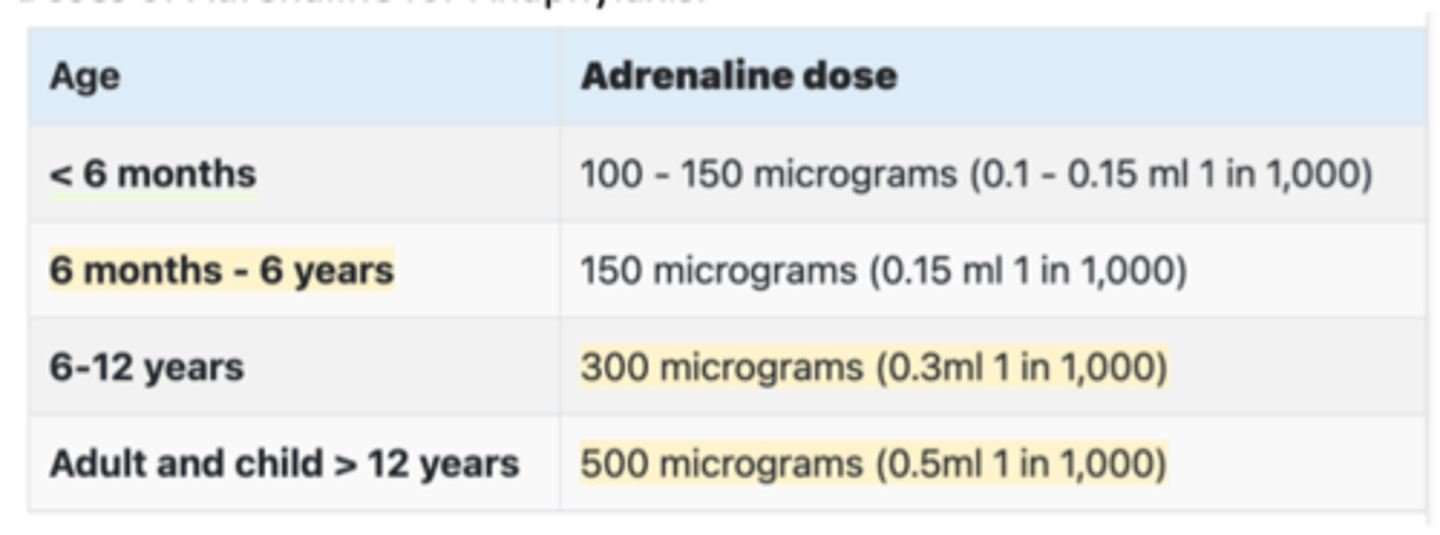
Dose of glucagon:
<6 (<25kg) 0.5mg IM
>6 (>25kg) 1mg IM
Dose of midazolam:
1>5: 5mg
5>10: 7.5mg
10<18: 10mg
What is systematic desensitisation?
- behavioural therapy designed to reduce phobic anxiety through the principle of Classical conditioning. Suffers are cured if they learn to relax in presence of phobic stimulus.
- guidance of therapist
- key principles: gradual exposure, relaxed response, classical conditioning
What method of fluoride delivery has been the most effective in reducing caries in the UK?
water fluoridation 1984
ACVPU
Alert, confusion, voice, pain, unresponsive
What is a very common drug allergy?
penicillin
sBPE teeth
6 1 | 6
6 | 1 6
What is a predictor of spontaneous space closure?
suggest bifurcation development of the second molar as a predictive factor? NOT SURE ON THIS ONE