AWS Cloud Foundations0- Module 5: Networking and Content Delivery
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
AWS Academy: Cloud Foundations
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
Two or more machines that are connected together in order to communicate
Computer Network
T/F A network can be logically partitioned into subnets
True
A unique number assigned to a machine in order to be identified uniquely
IP Address
32-bit address
IPv4 Address
128- bit address
IPv6 address
A way to express a group of IP address that are consecutive to each other
Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR)
In the OSI model, this layer’s function is Means for an application to access a computer network. Ex. HTTP(S), FTP, DHCP, LDAP
Layer 7 - Application
This layer’s function is to Ensure application layer can read the data and Encryption. Ex. ASCI, ICA
Layer 6 - Presentation
This layer in the OSI model enables order exchange of data
Layer 5 - Session
This layer in the OSI Model provides protocols to support host-to-host communication. Ex. TCP, UDP
Layer 4- Transport
This layer of the OSI Model is in charge of routing and packet forwarding (hubs and switches)
Layer 2 - Data Link
This layer of the OSI Model handles transmission and reception of raw bitstreams over a physical medium
Layer 1 - Physical
Enables you to provision a logically isolated sections of the AWS cloud where you can launch AWS resources in a virtual network that you define
Amazon VPC
Amazon VPC give you control over your virtual networking resources, including:
Selection of IP address range, Creation of subnets, and Configuration of route tables and network gateways
a range of IP addresses in a VPC
Subnet
The resource used to move data to and from a VPS to the public internet
Internet gateway
The rules that dictate how traffic is going to flow into and out of our subnets
Route
directs traffic destined for elsewhere in the VPC, so that anything that is moving within the VPC can communicate with each other. This traffic never leaves the VPC.
Local Route
An optional layer of security for your VPC that acts as a firewall for controlling traffic in and out of subnets.
Network ACLs (Network Access Control List )
An ______ gateway serves two purposes: Provides a target in your VPC route tables for internet traffic and to perform network instances that were assigned public IPv4 addresses.
Internet gateway
How do you have a subnet public?
You attach an internet gateway to your VPC and add a route entry to the route table associated with the subnet
A Network Address Translation
NAT gateway
What enables instances in a private subnet to connect to the internet or other AWS services but prevents the public internet from initiating a connection with those instances?
NAT gateway
When creating a _____ gateway, you must specify the public subnet in which this gateway should live and an elastic IP address to associate with this gateway. after creation, you must update the route table that is associated with one or more of your private subnets to point internet-bound traffic to the gateway.
NAT gateway
Enables customers to share subnets with others AWS accounts in the same organization in AWS Organizations
VPC Sharing
Separation of Duties, Ownership, security groups, efficiencies, no hard limits, and optimized costs are all benefits of ______.
VPC Sharing
A networking connection between two VPCs that enables you to route traffic between them privately. Instances in either VPC can communicate with each other as if they are within them privately.
VPC Peering
T/F: When setting up a peer connection, AWS creates rules in your route table to allow the VPCs to communicate with each other through the peering resource.
False: You create the rules
T/F: VPC peering has come restrictions, including: IP address range cannot overlap, Transitive peering is not supported, and you can only have one peering resource between the same two VPCs.
True
Suppose that you have three VPCs: A, B, and C. VPC A is connected to VPC B, and VPC A is connected to VPC C. However, VPC B is not connected to VPC C implicitly. To connect VPC B to VPC C, you must explicitly establish that connectivity. what is this an example of?
Transitive peering not being supported
1.
Create a new virtual gateway device (called a
virtual private network (VPN) gateway
) and
attach it to your VPC.
2.
Define the configuration of the VPN device or the
customer gateway
. The customer gateway
is not a device but an AWS resource that provides information to AWS about your VPN device.
3.
Create a custom route table to point corporate data center
-
bound traffic to the VPN gateway.
You also must update security group rules. (You will learn about security groups in the next
section.)
4.
Establish an
AWS Site
-
to
-
Site VPN (Site
-
to
-
Site VPN) connection
to link the two systems
together.
5.
Configure routing to pass traffic through the connection.
1.Create a new virtual gateway device (called a virtual private network (VPN) gateway) and attach it to your VPC.
2. Define the configuration of the VPN device or the customer gateway. The customer gateway is not a device but an AWS resource that provides information to AWS about your VPN device.
3.Create a custom route table to point corporate data center-bound traffic to the VPN gateway. You also must update security group rules.
4.Establish an AWS Site-to-Site VPN (Site-to-Site VPN) connection to link the two systems together.
5.Configure routing to pass traffic through the connection.
What are these steps for?
Connecting your VPC to your remote network
Enables you to establish a dedicated, private network connection between your network and one of the DX locations.
AWS Direct Connect
This private connection can reduce your network costs, increase bandwidth throughput, and provide a more consistent network experience than internet-based connections
AWS Direct Connect
A virtual devices that enables you to privately connect your VPC to supported AWS services and VPS endpoint services that are powered by AWS PrivateLink.
VPC endpoint
This gateway simplifies network architecture and enables efficient traffic routing between different environments. Uses the hub and spoke topology.
AWS Transit Gateway
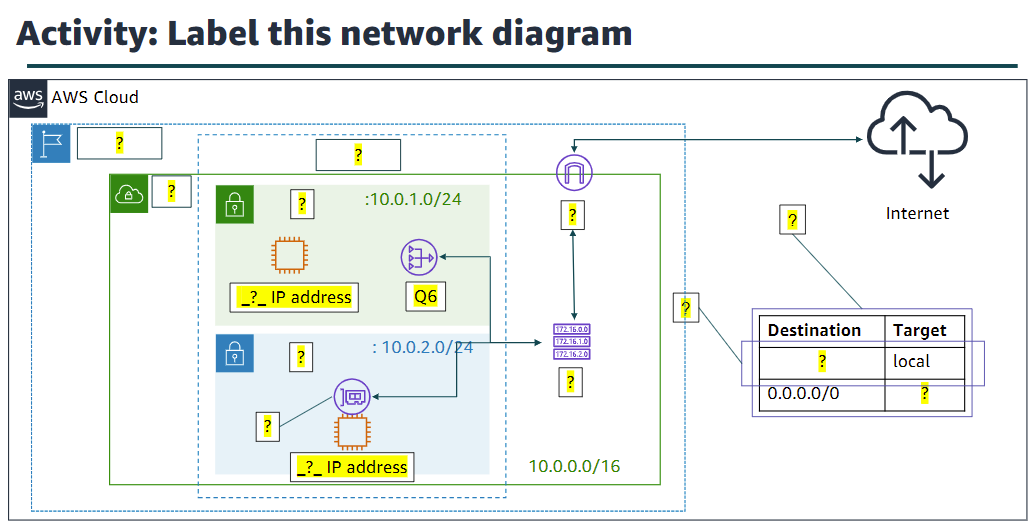
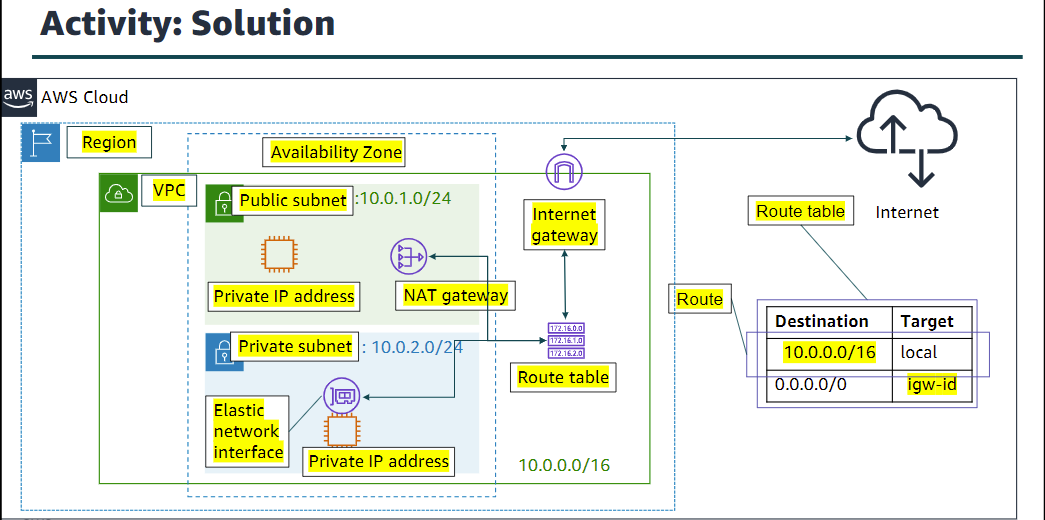
Label Diagram
Acts as a virtual firewall for your instance, and it controls inbound and outbound traffic.
Security Groups
_____ act at instance level, not the subnet level. Therefore, each instance in a subnet in your VPC can be assigned to a different set of _____.
Security groups
T/F: Default Security groups deny all inbound traffic and allow all outbound traffic.
True
_____ are stateful, which means that state information is kept even after a request is processed.
Security groups
To add another layer of security to your VPC, you can set up ______ with rules that are similar to your security groups.
Network ACLs
T/F: Each subnet in your VPS doesn’t need to be associated with a network ACL
False: Each subnet in your VPS must be associated with a network ACL. If you don’t explicitly associate a subnet with a network ACL, the subnet is automatically associated with the default network ACL
T/F: Network ACLs are stateless, which means that no information about a request is maintained after a request is processed
Se in single-server environments
Simple routing
Assign weights to resource record sets to specify the frequency
Weight routing
Helps improve your global applications
Latency routing
Routes traffic based on location of users
Geolocation routing
Routes traffic based on location of your resources
Geoproximity routing
il over to a backup site if your primary site becomes unreachable.
Failover routing
Responds to DNS queries with up to eight healthy record selected at random
Multivalue answer routing
Designed to give developers and businesses a reliable and cost-effective way to route users to internet applications by translating domain names ( like www.example.com) into the numeric IP addresses (like 192.0.2.1) that computers use to connect to each other.
Amazon Route 53
T/F: The DNS resolver checks with your domain in Route 53, gets the IP address, and returns it to the user.
True
T/F: Multi-Region deployment improves your application’s performance for a local audience
False : Multi-Region deployment improves your application’s performance for a global audience
A fast CDN (content delivery network) service that securely deliveries data, videos, applications, and application programming interfaces (APIs) to customers globally with low latency and high transfer speeds
Amazon CloudFront
____ is different from traditional content delivery solutions because it enables you to quickly obtain the benefits of high-performance content delivery without negotiated contracts, high prices, or minimum fees
Amazon CloudFront
This services benefits include: Fast and global, security at the edge, highly programmable, deeply integrated with AWS, and cost effective
Amazon CloudFront benefits
Charged for the volume of data transferred out from Amazon CloudFront edge location to the internet or to your origin
Data transfer out
T/F: You are charged for the number of HTTP(S) requests
True
T/F: No additional charge for the first 1,000 paths that are requested for invalidation each month. Thereafter, $0.005 per path that is required for invalidation
True
T/F: $200 per month for each custom SSL certificate that is associated with one or more CloudFront distributions that use the Dedicated IP version of custom SSL certificate support
False: $600 per month