human body orientation
1/181
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
182 Terms
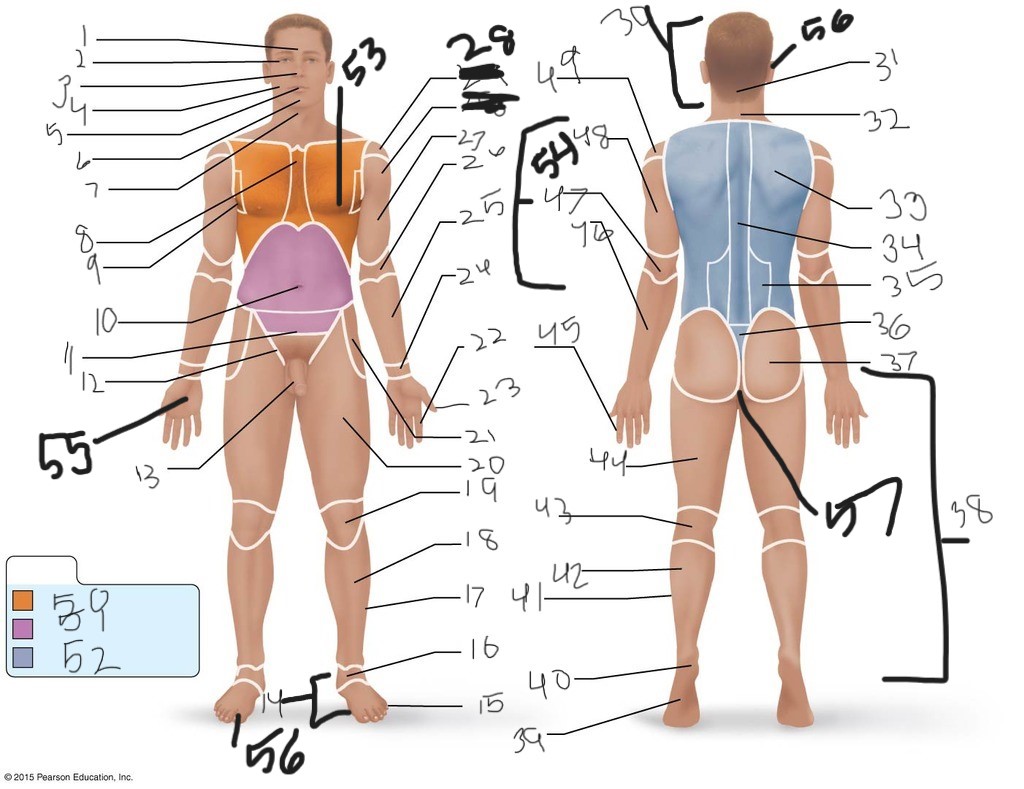
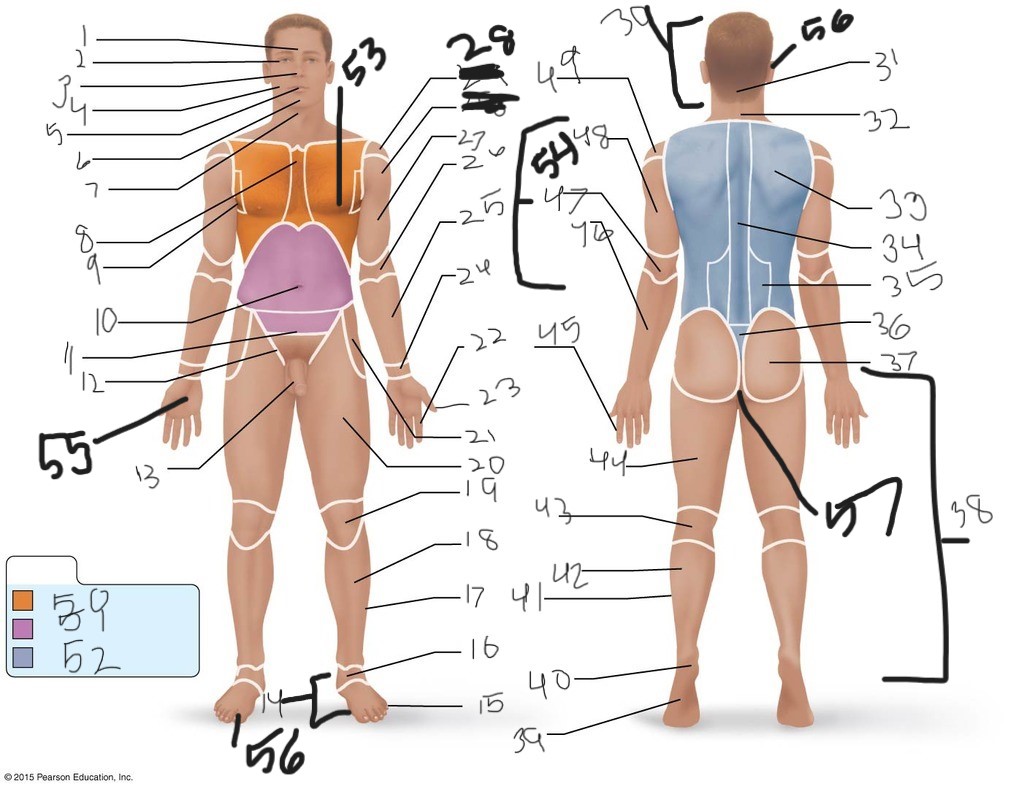
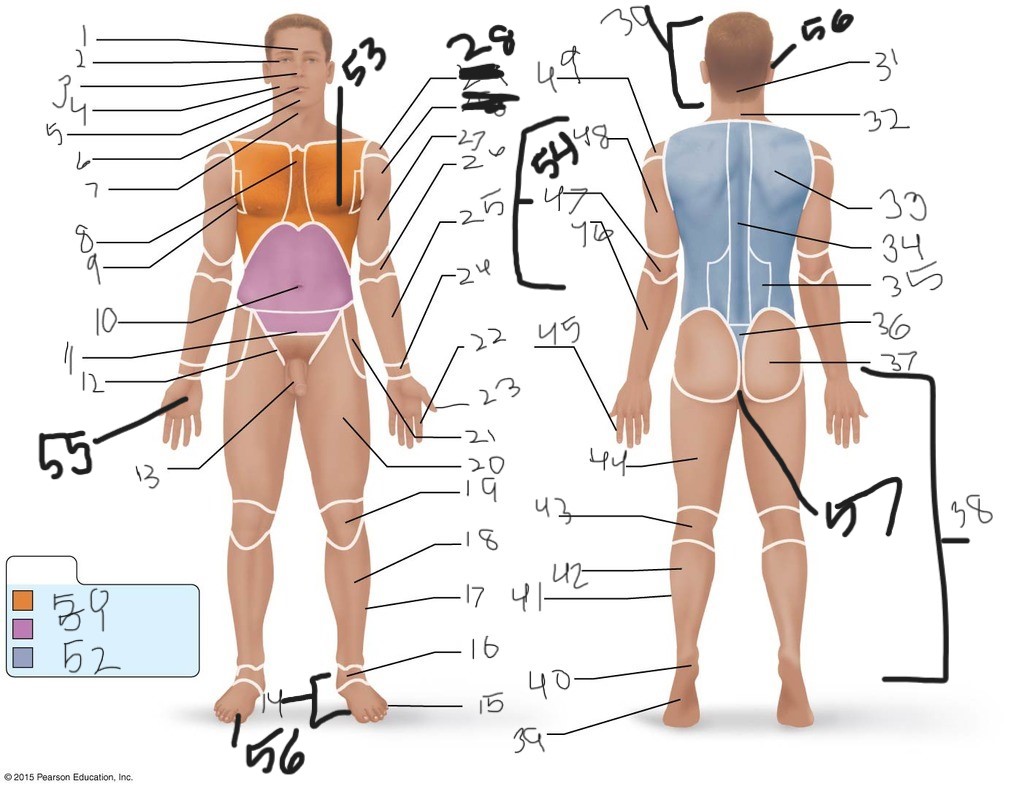
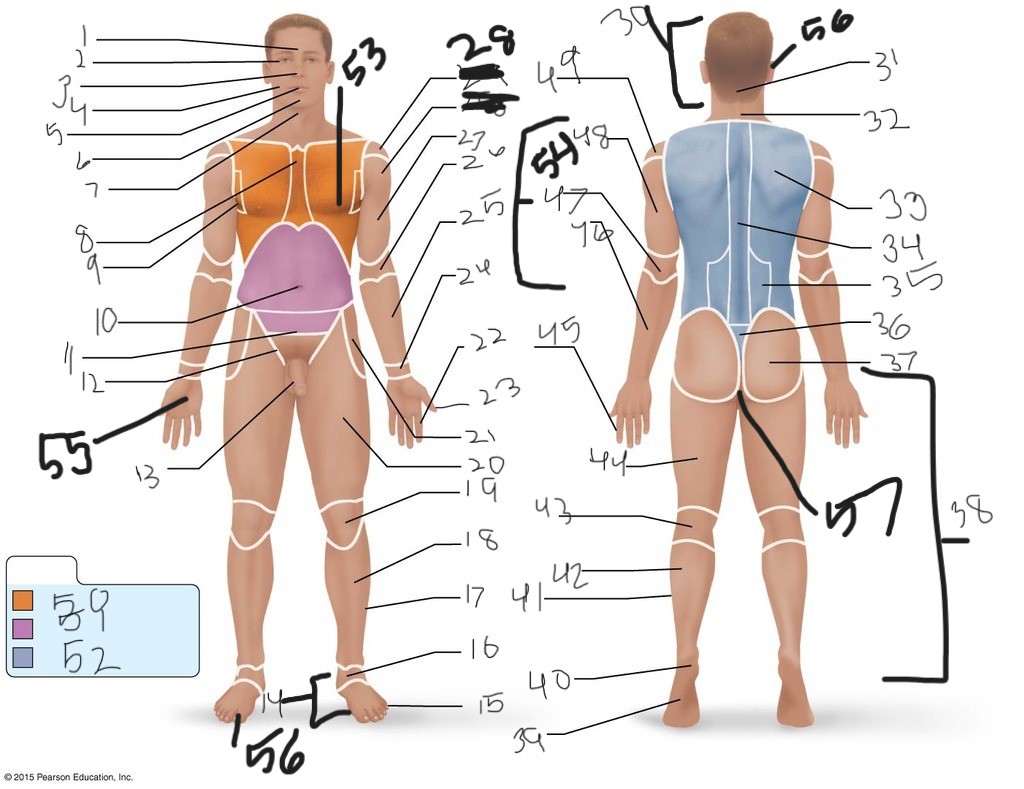
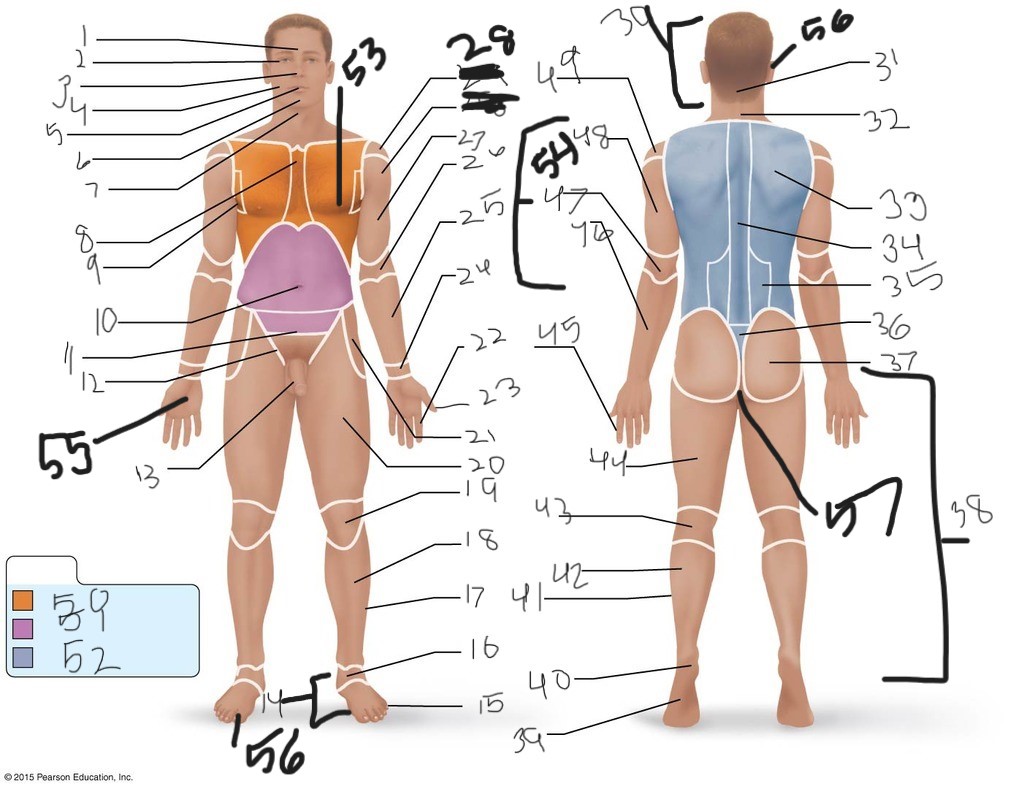
1. \
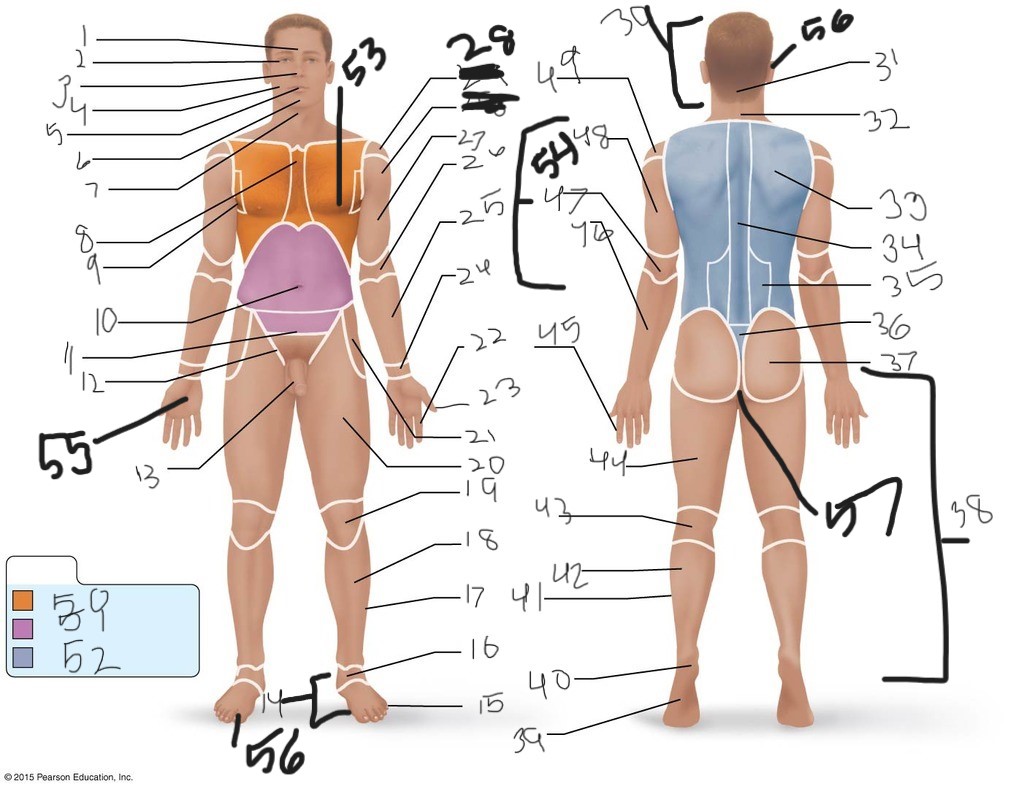
2. \
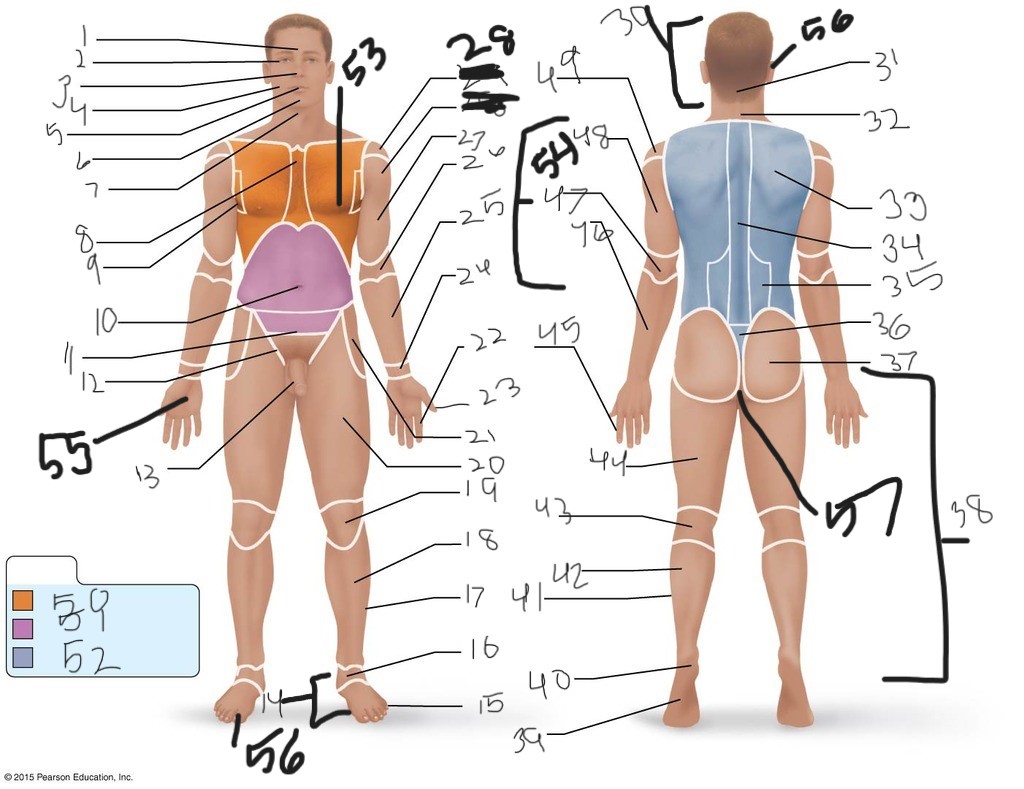
3. \
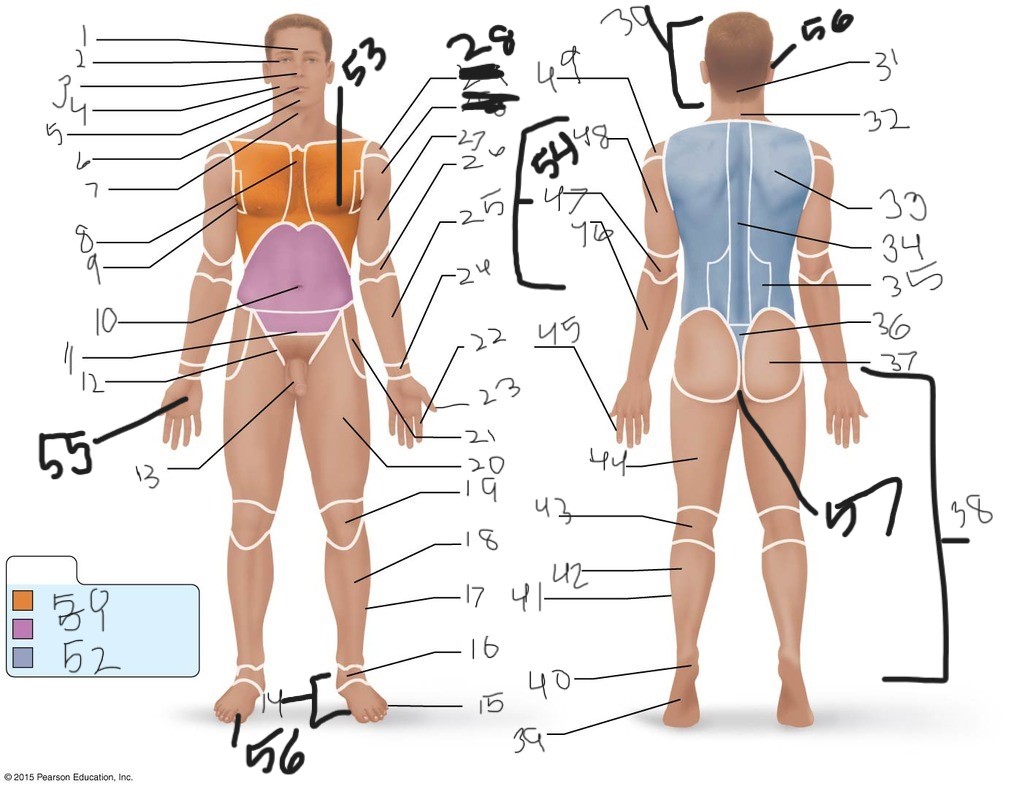
4. \
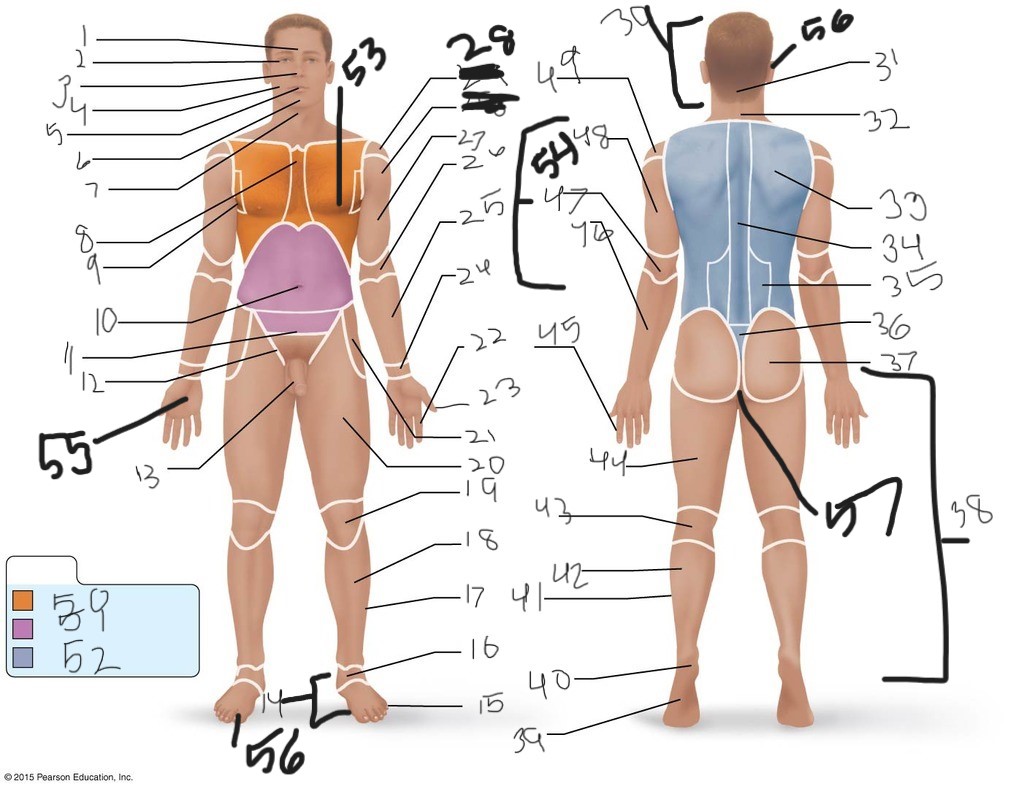
5. \
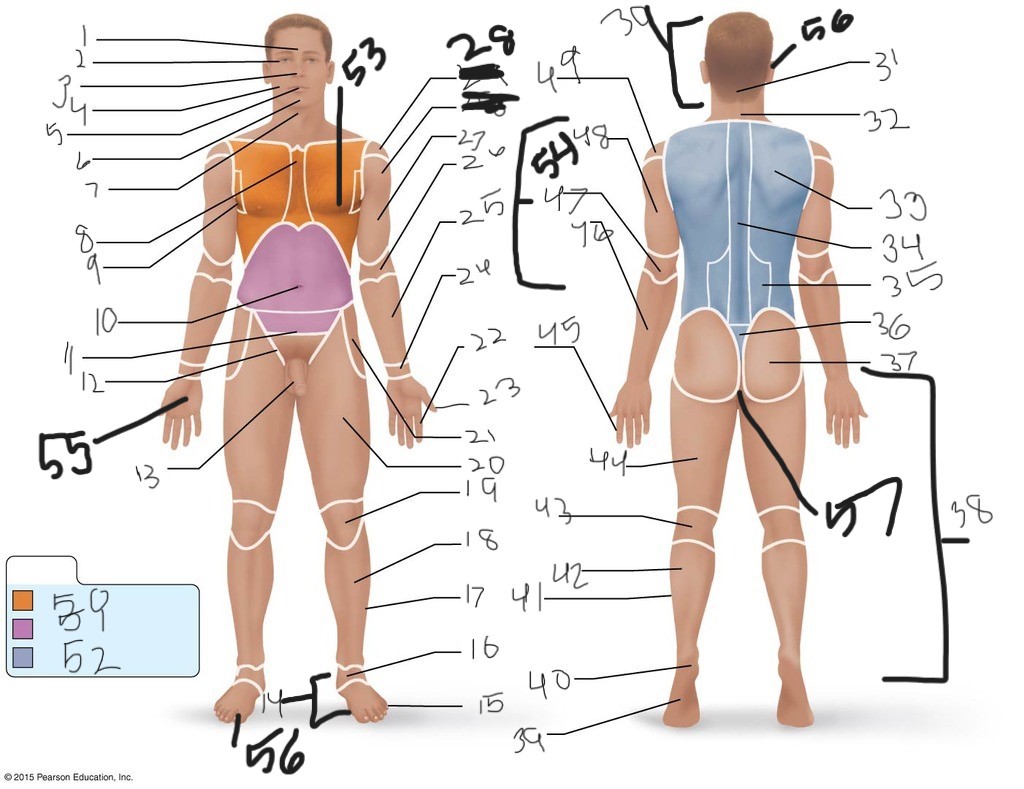
6. \
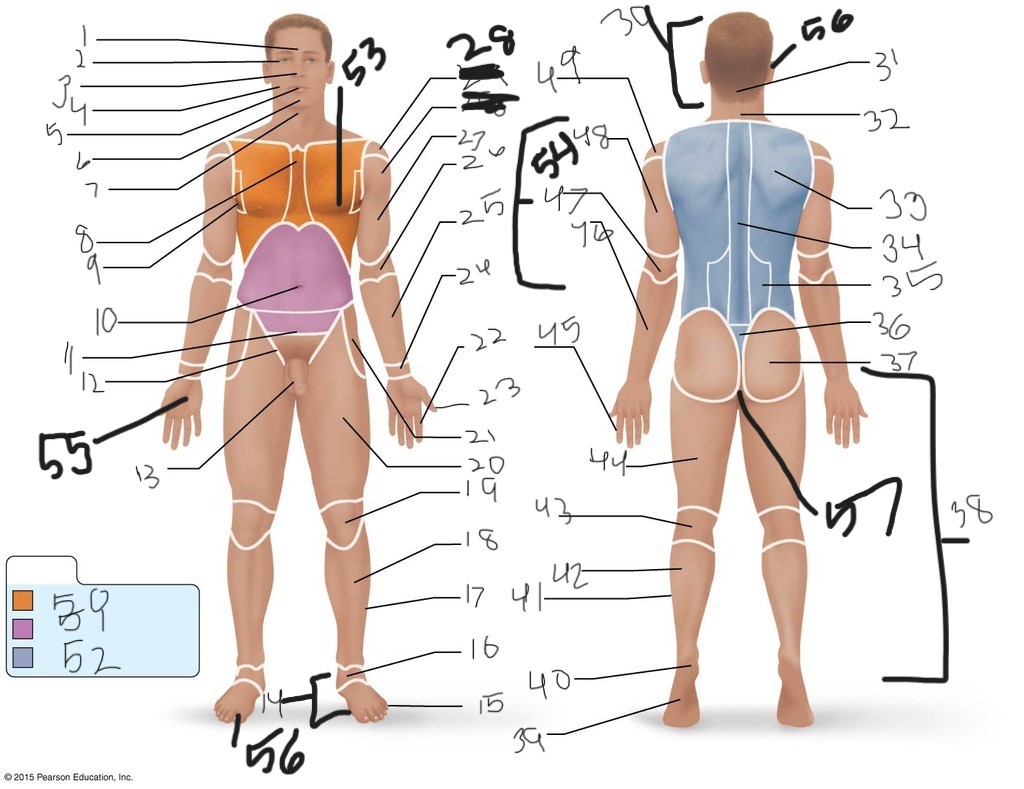
cervical (neck)
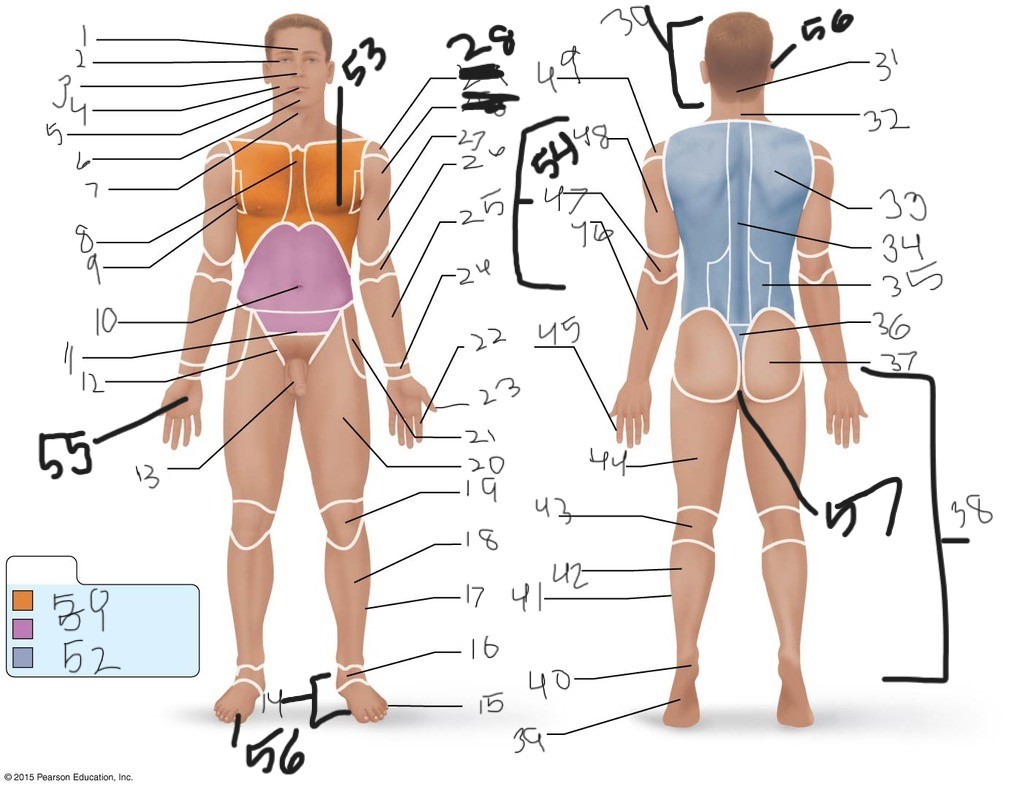
8. \
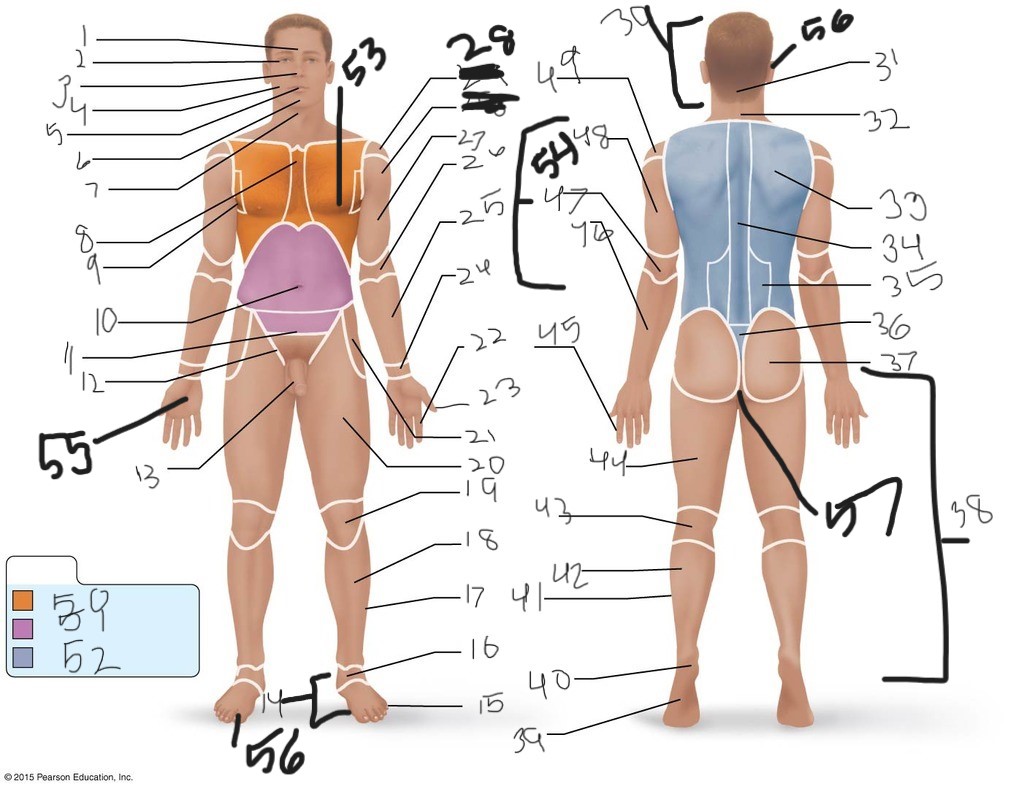
9. \
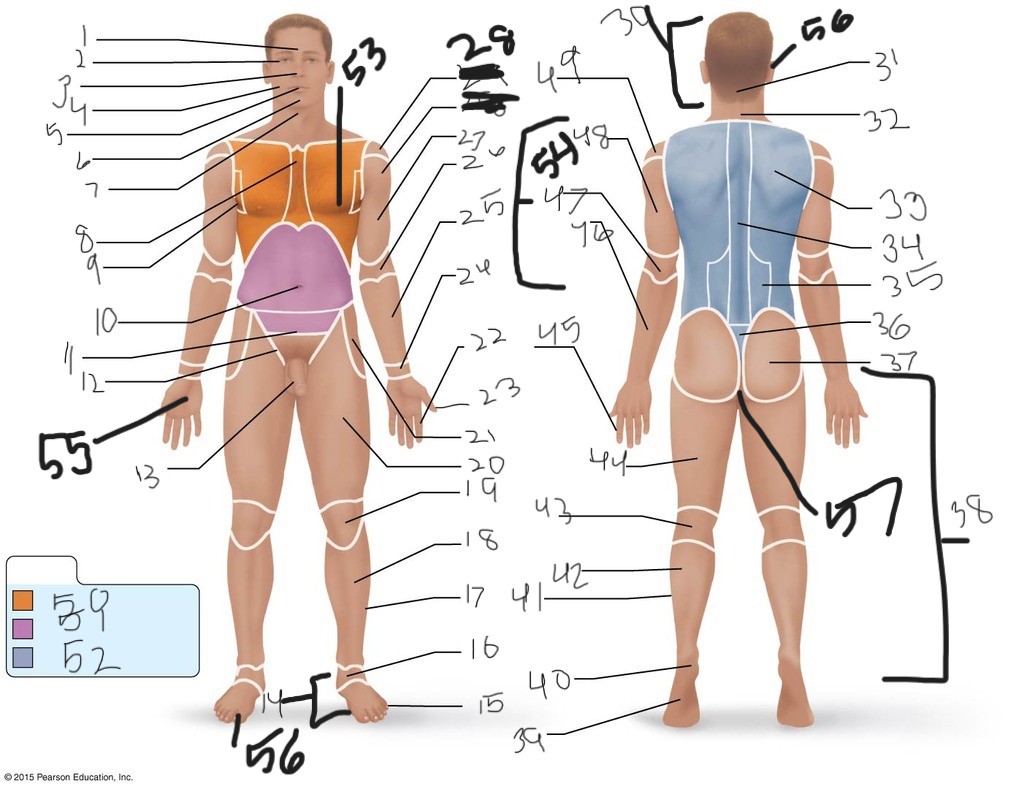
10. \
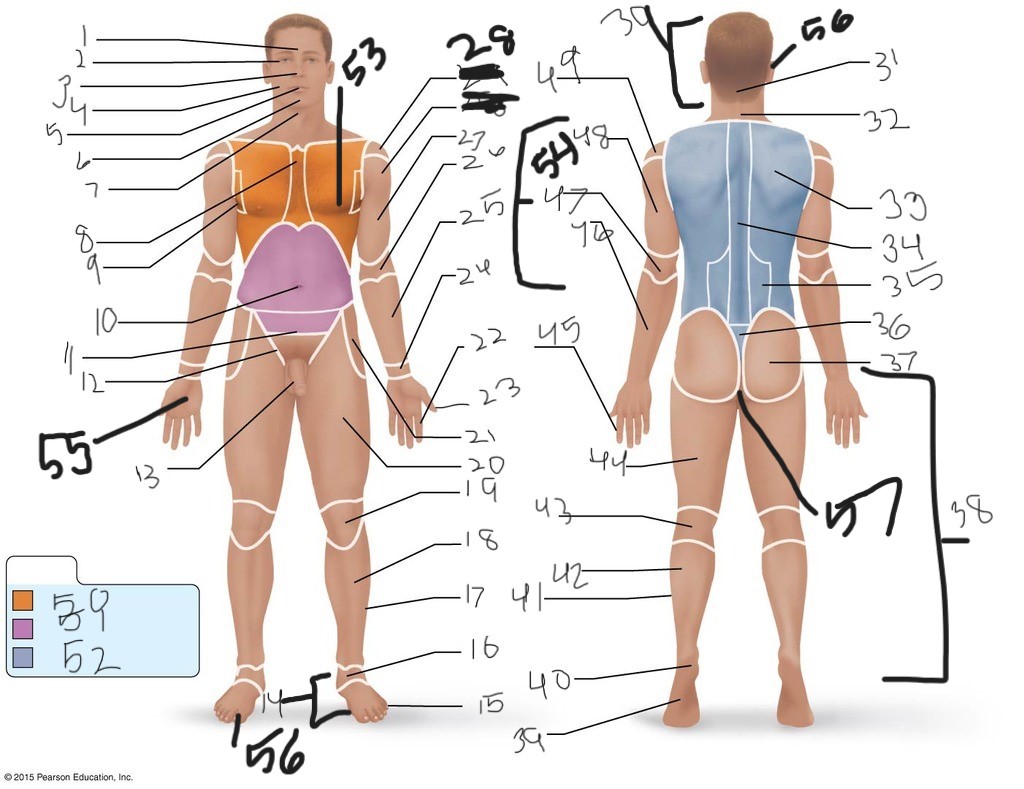
11. \
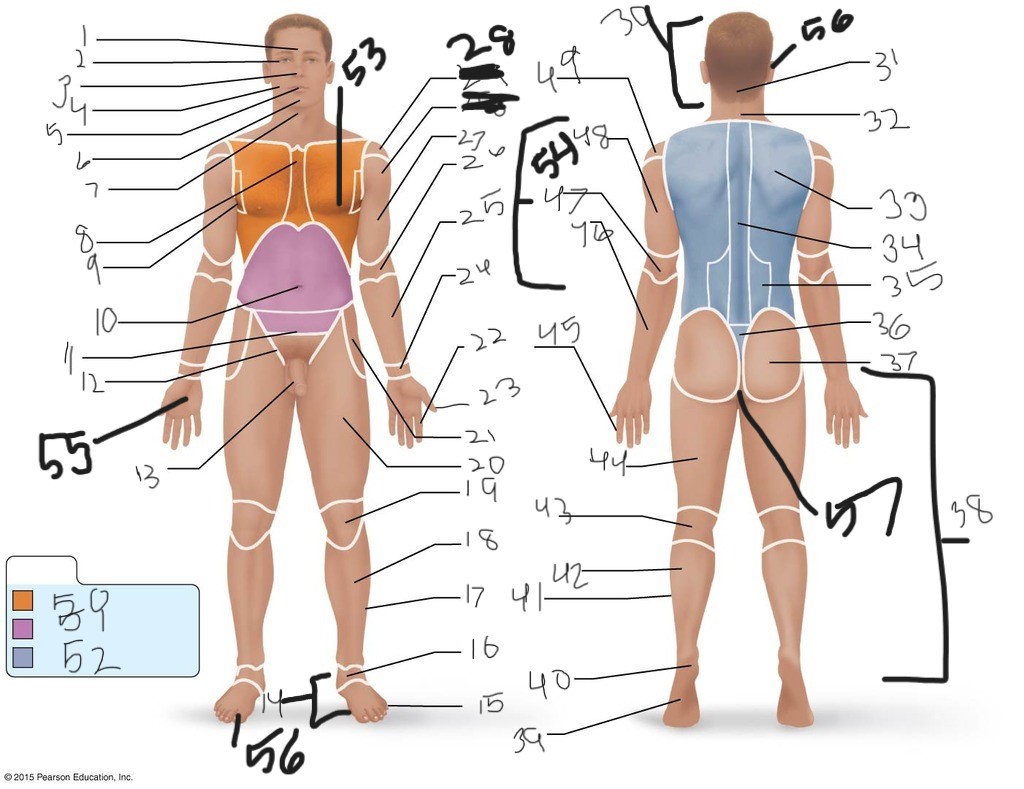
12. \
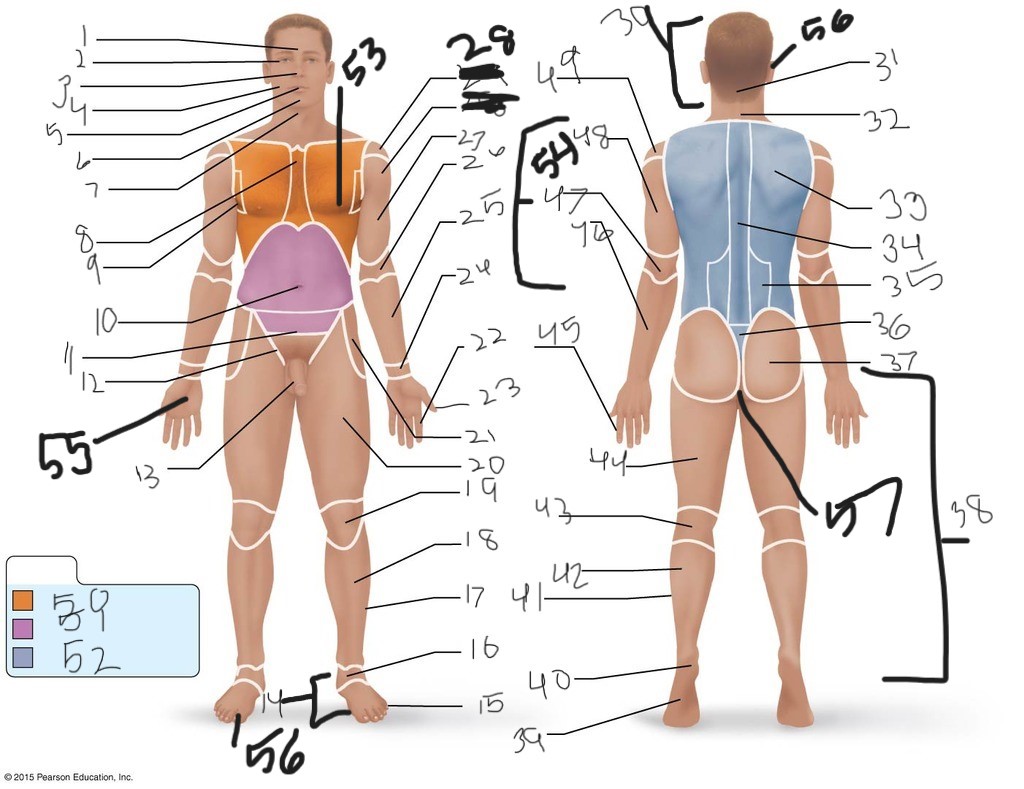
13. \
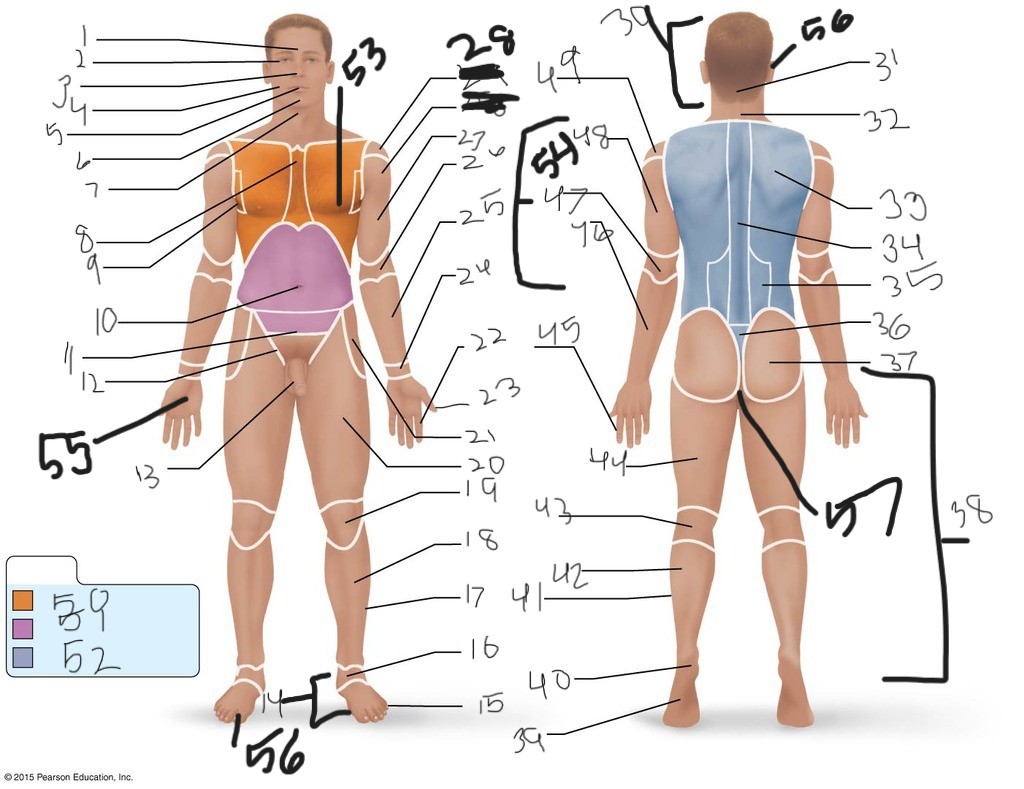
14. \
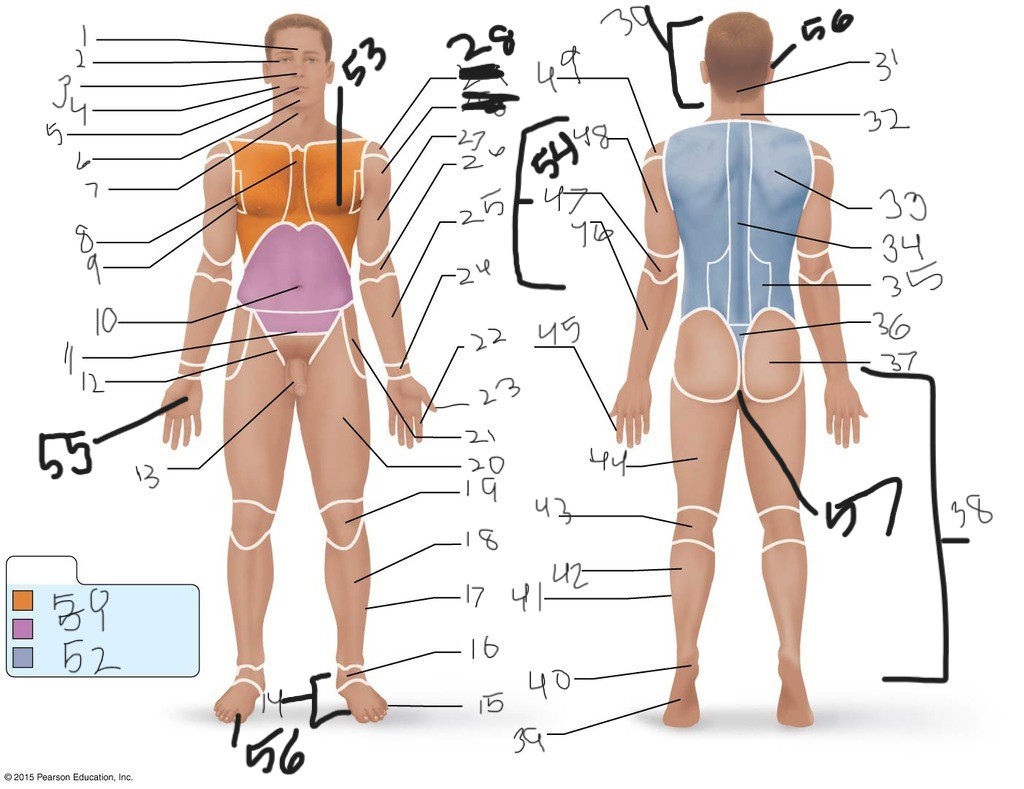
15. \
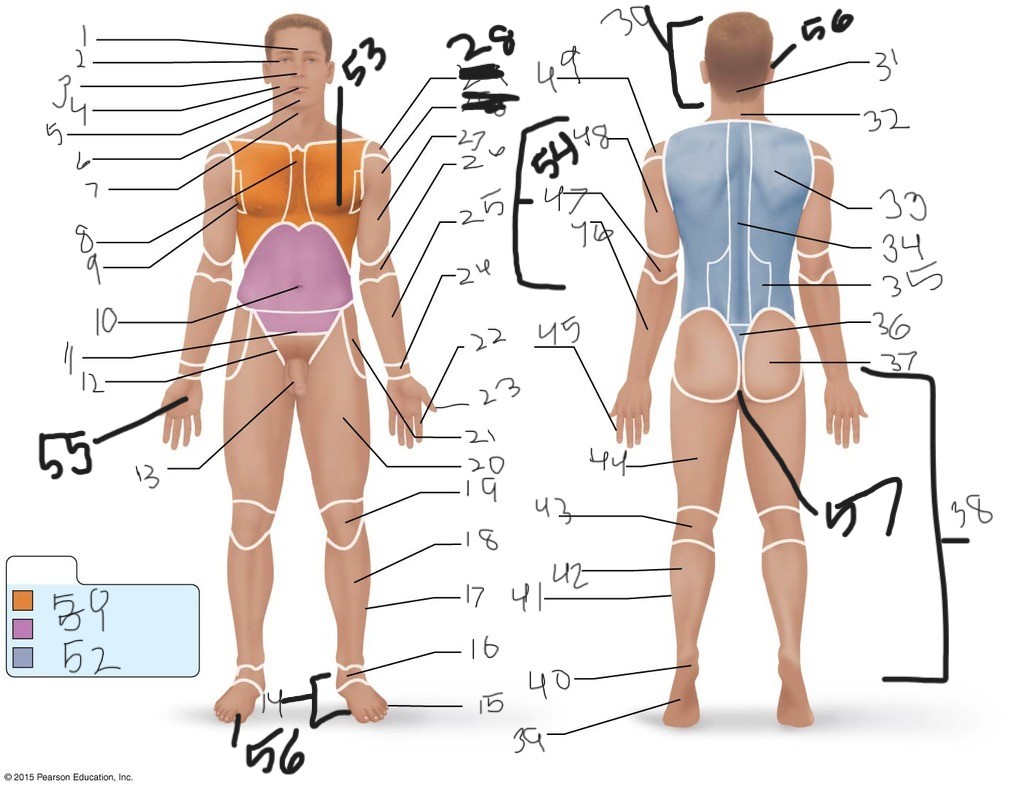
16. \
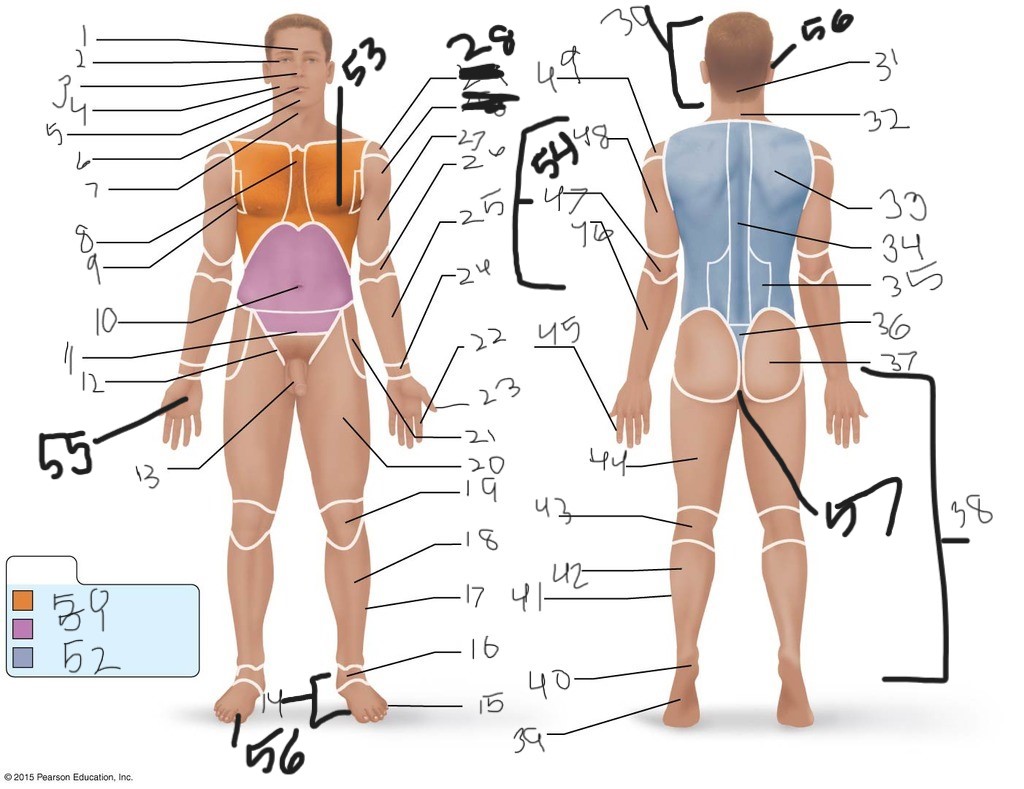
17. \
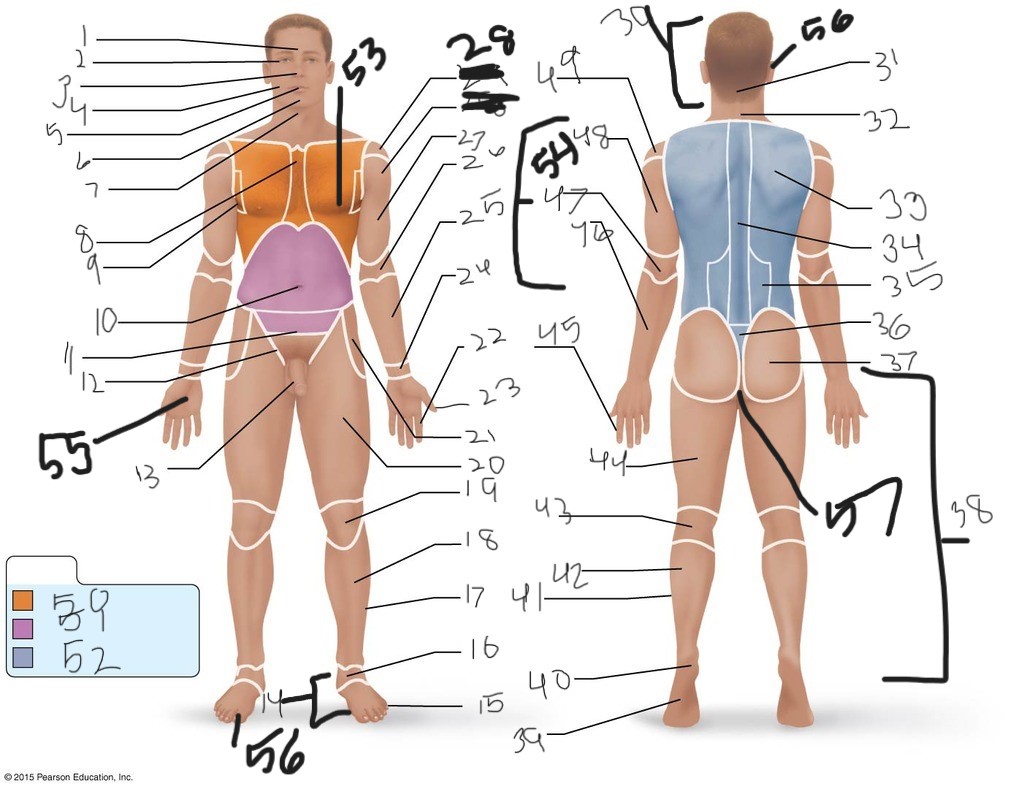
18. \
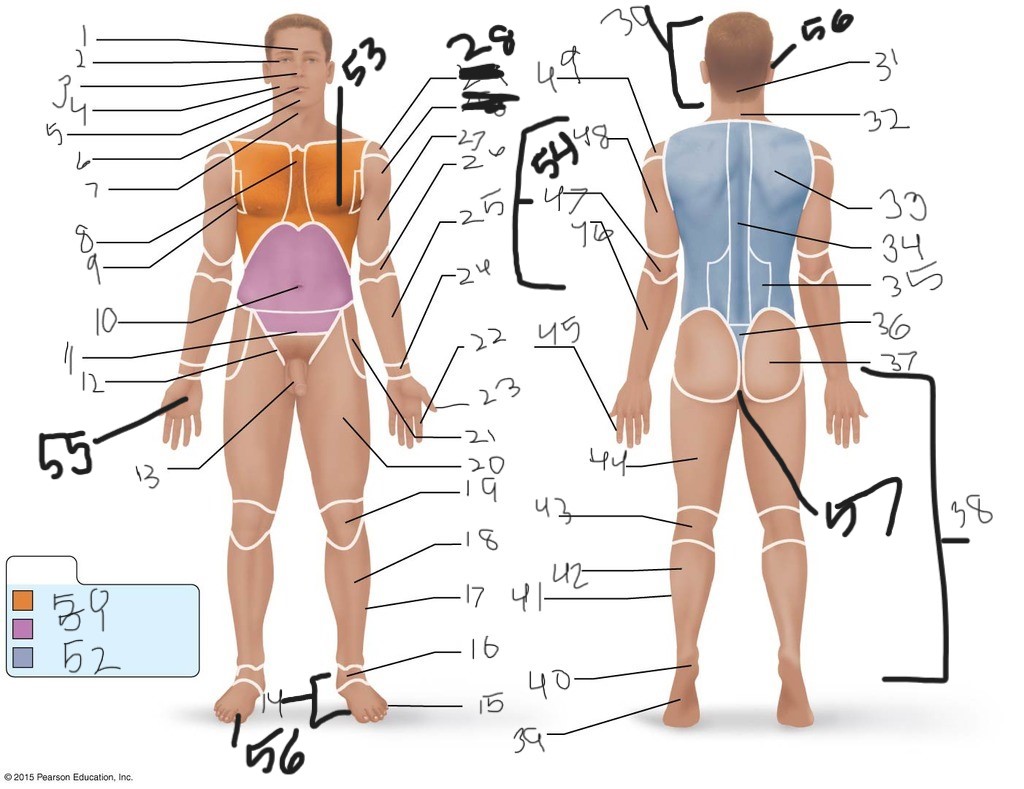
19. \
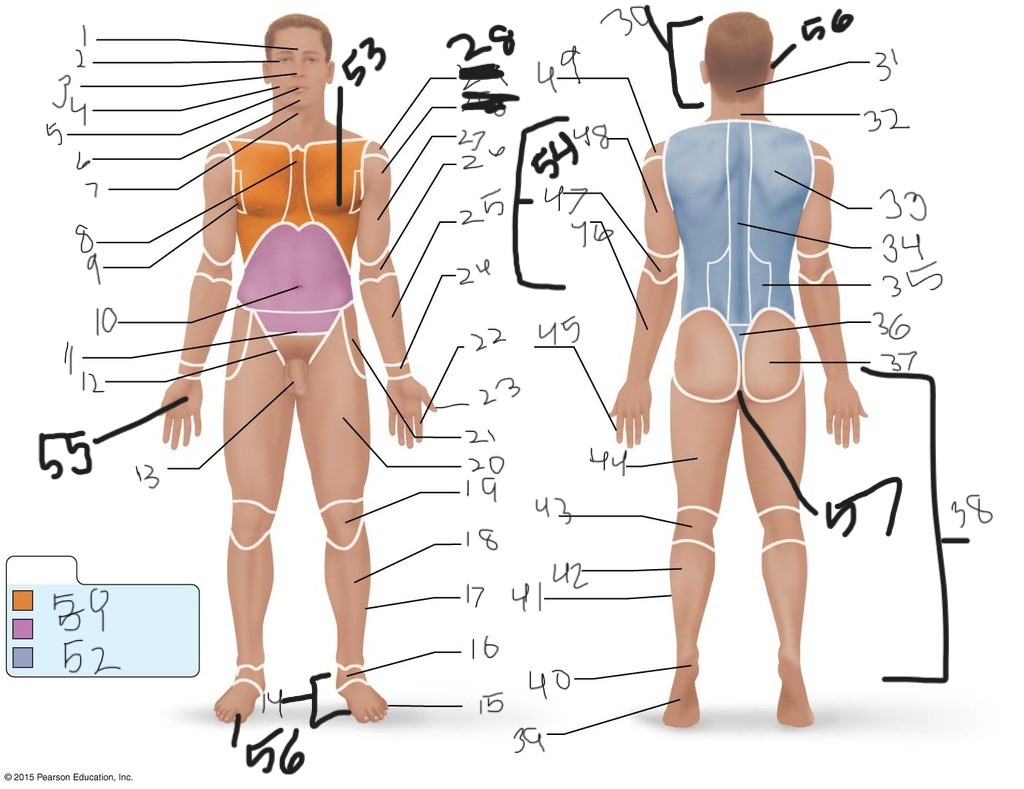
20. \
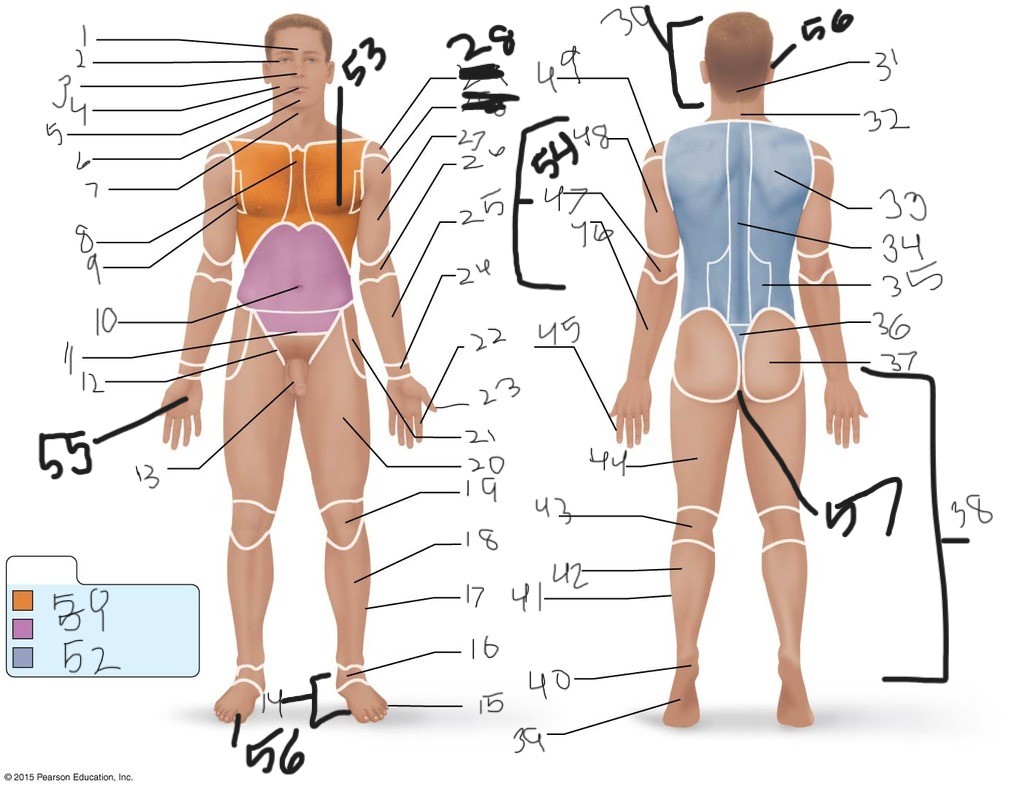
21. \
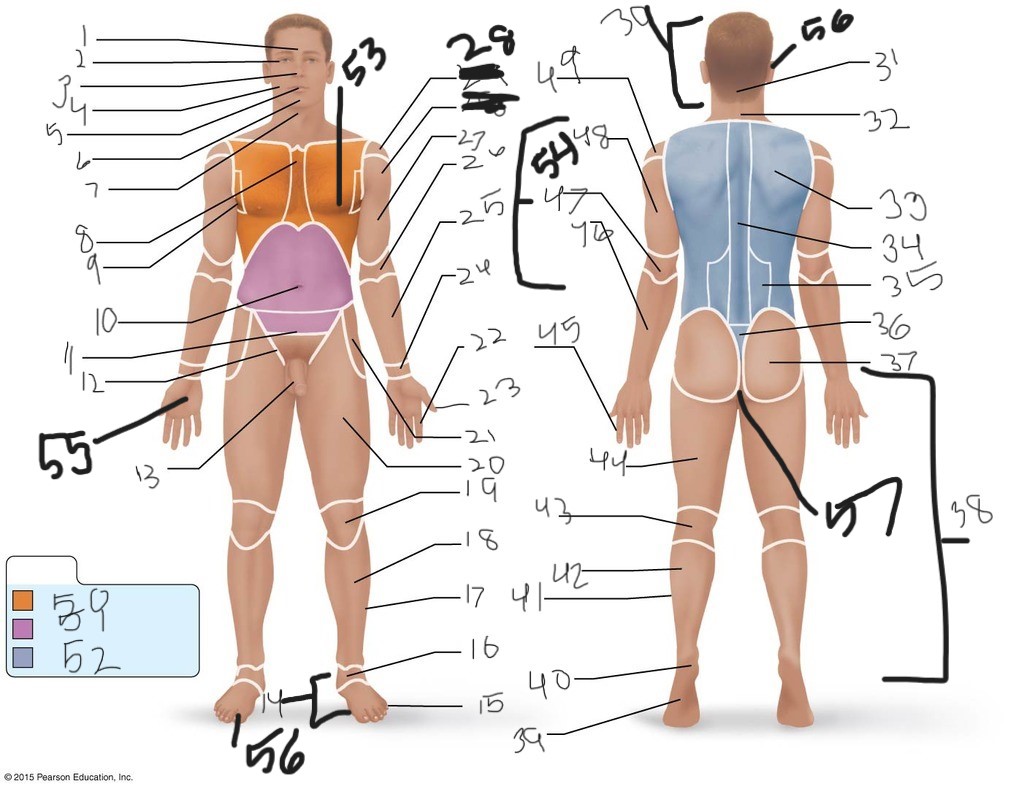
22. \
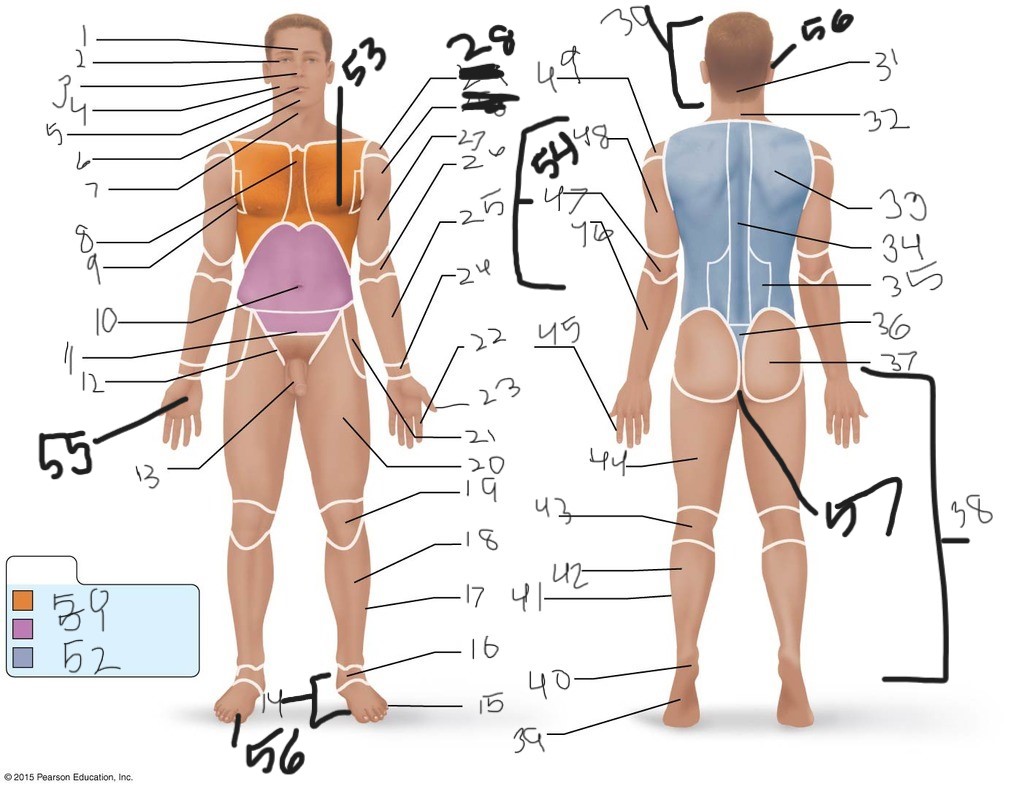
23. \
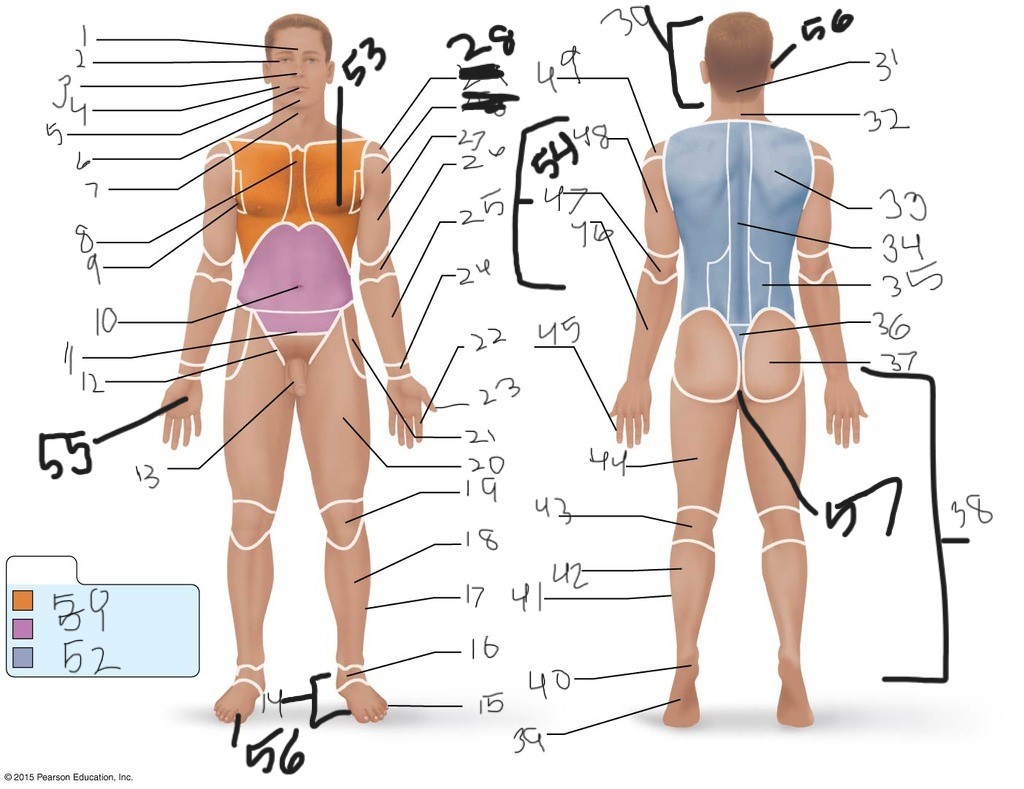
24. \
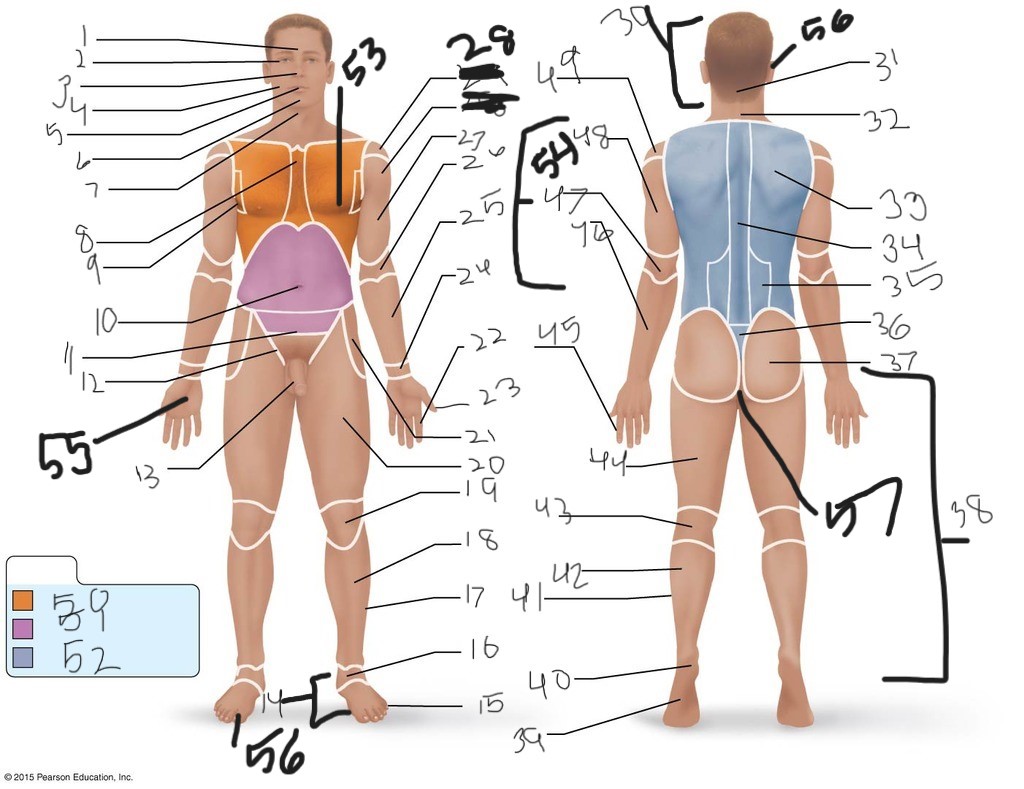
25. \
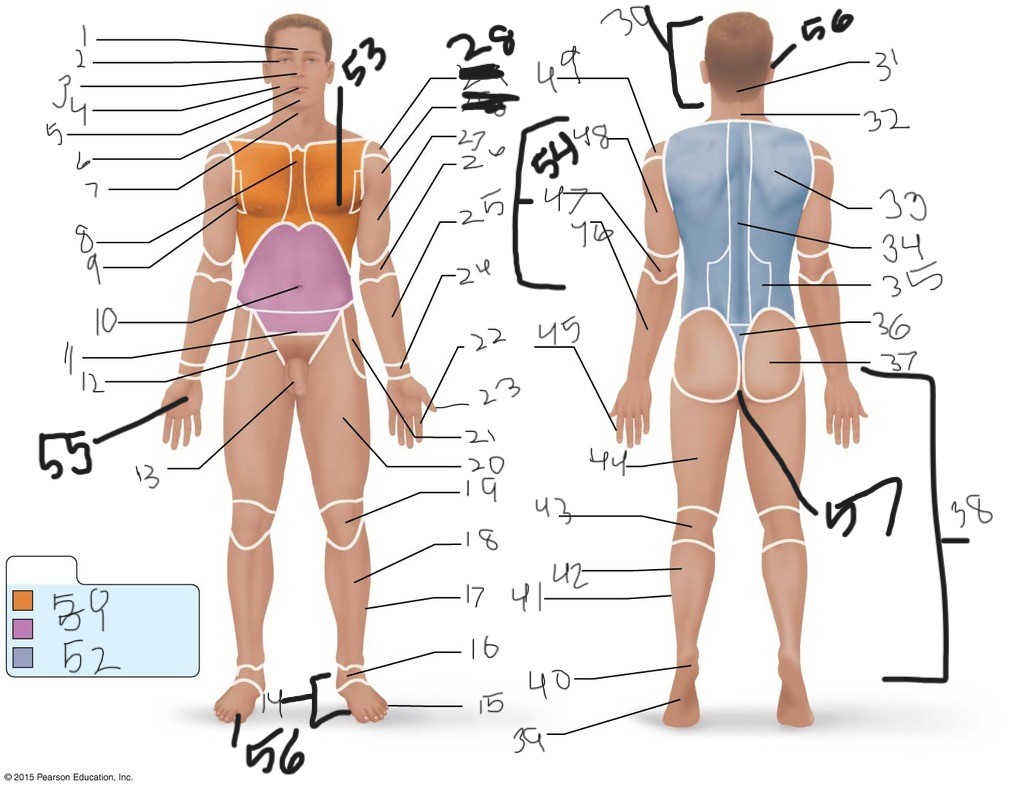
26. \
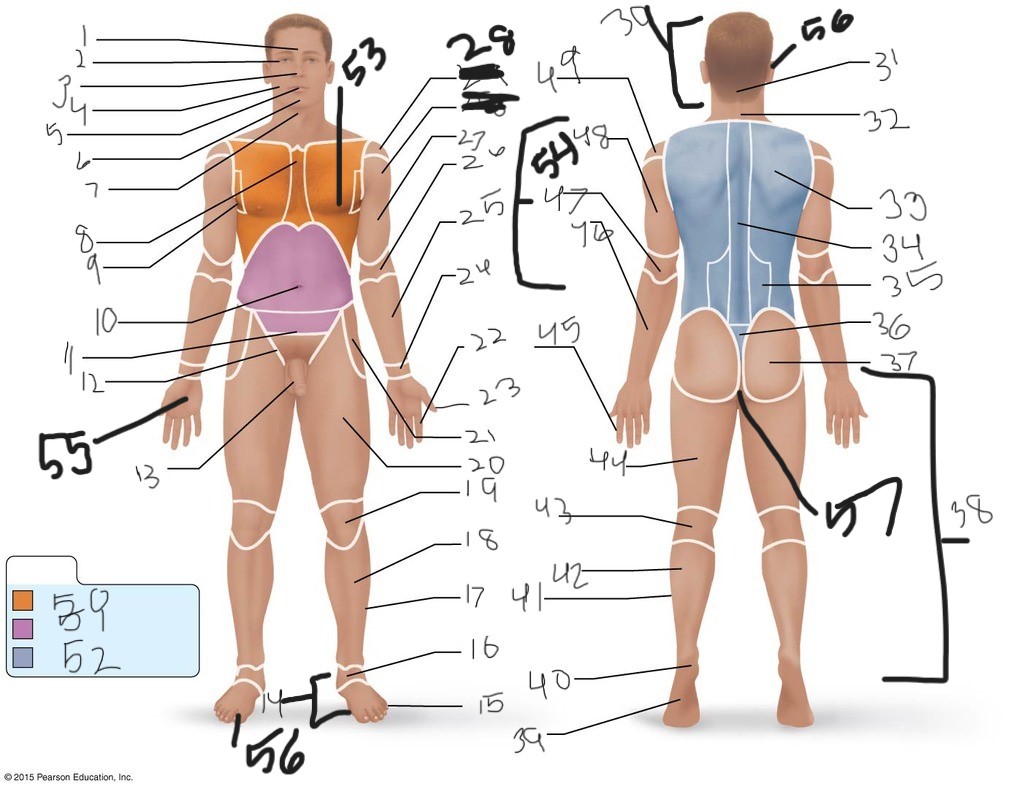
27. \
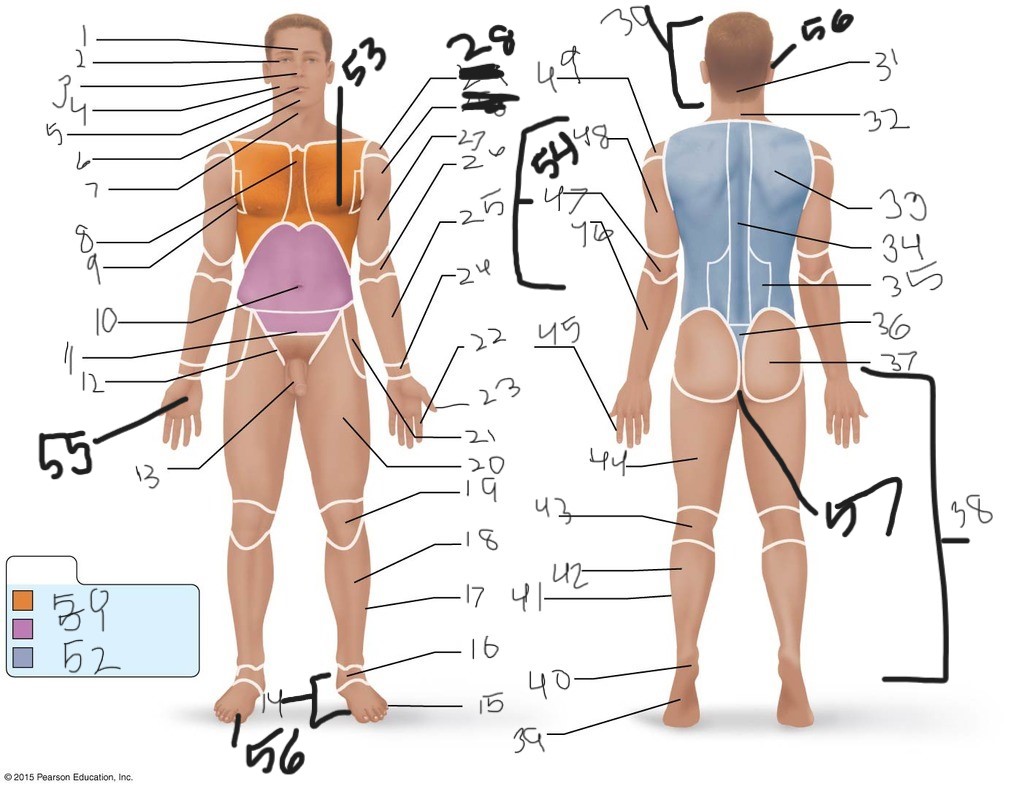
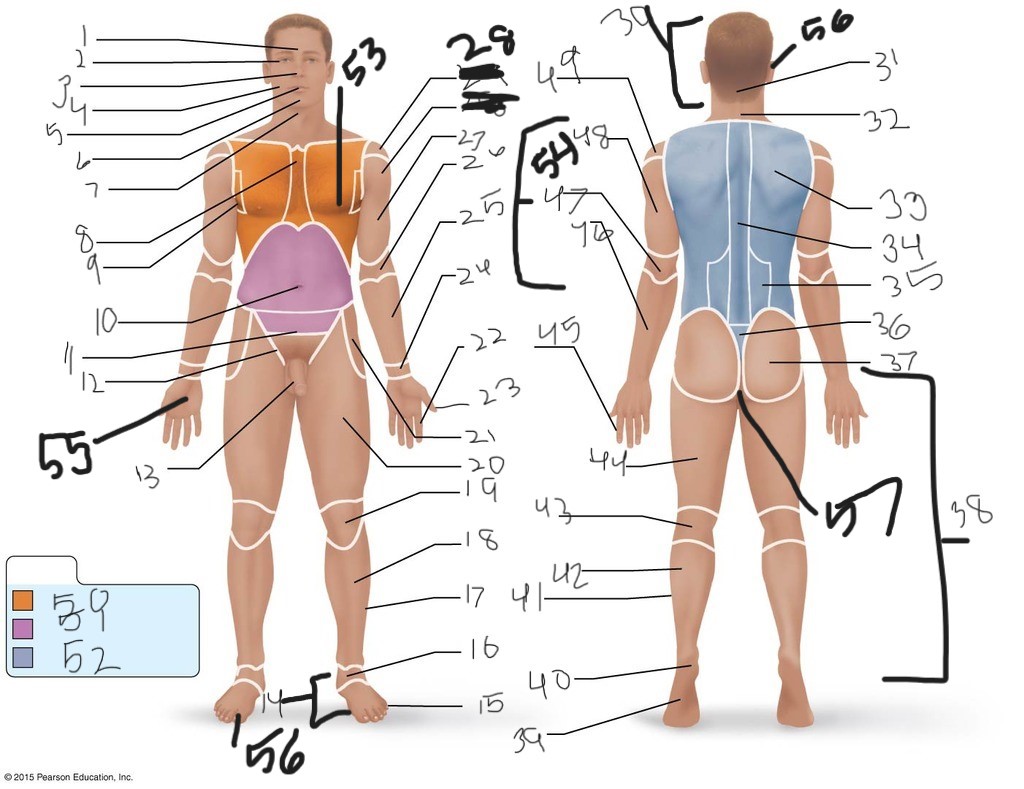
30. \
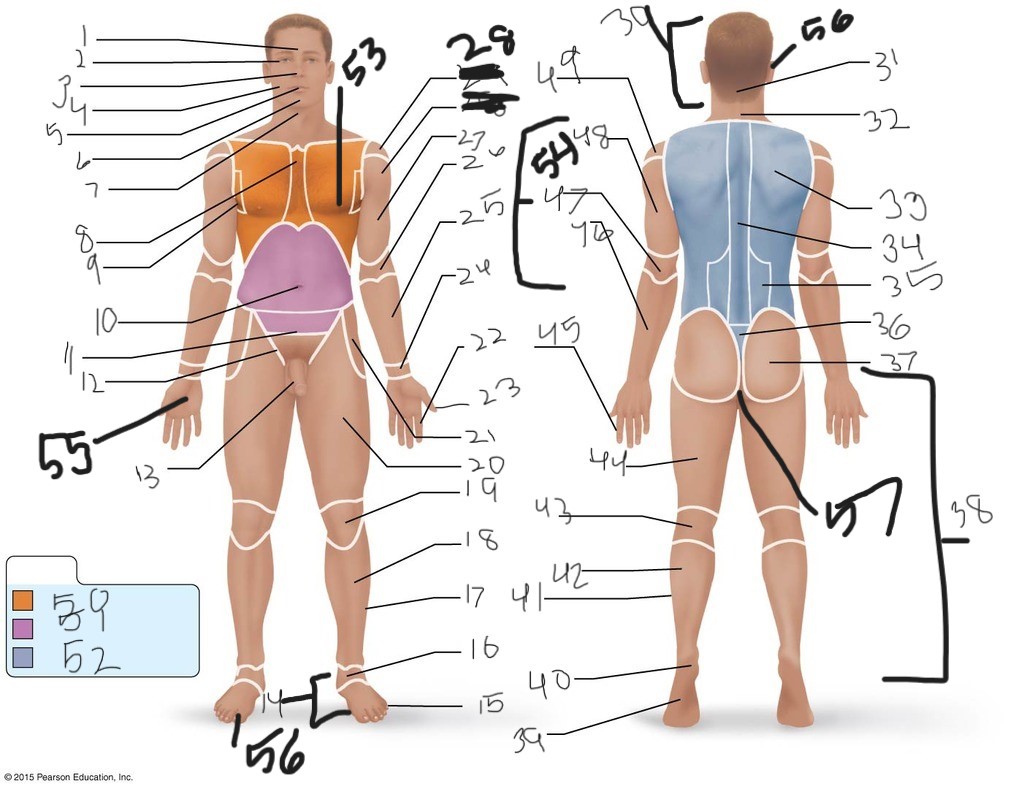
31. \
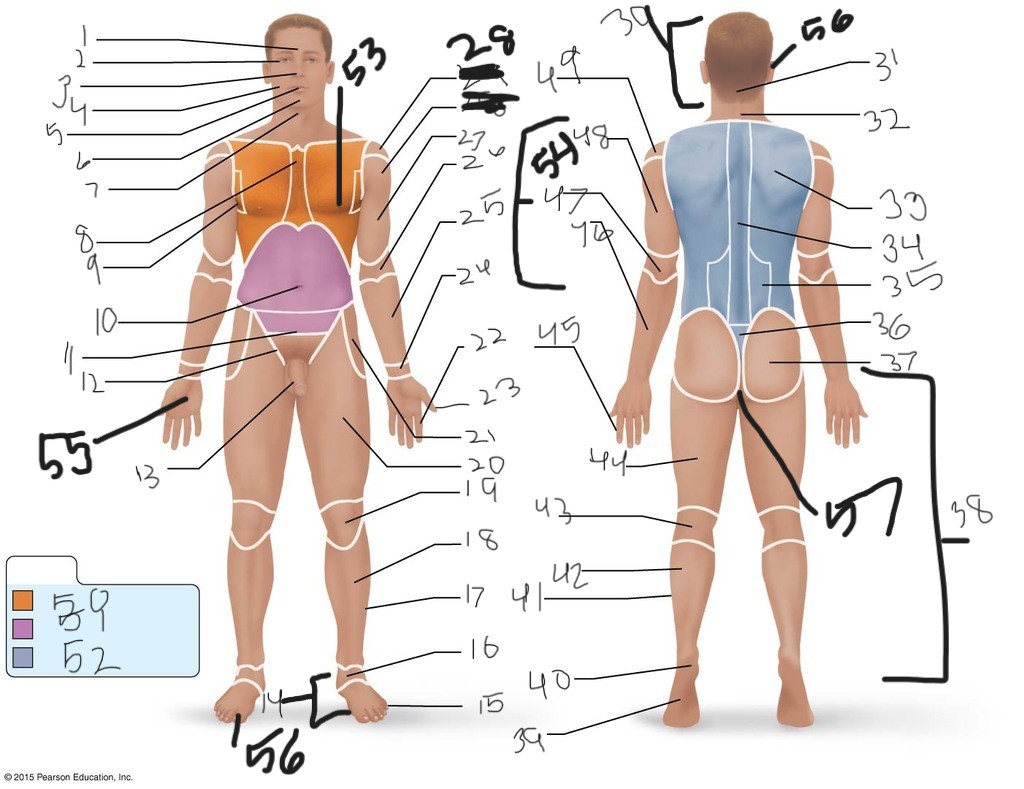
33. \
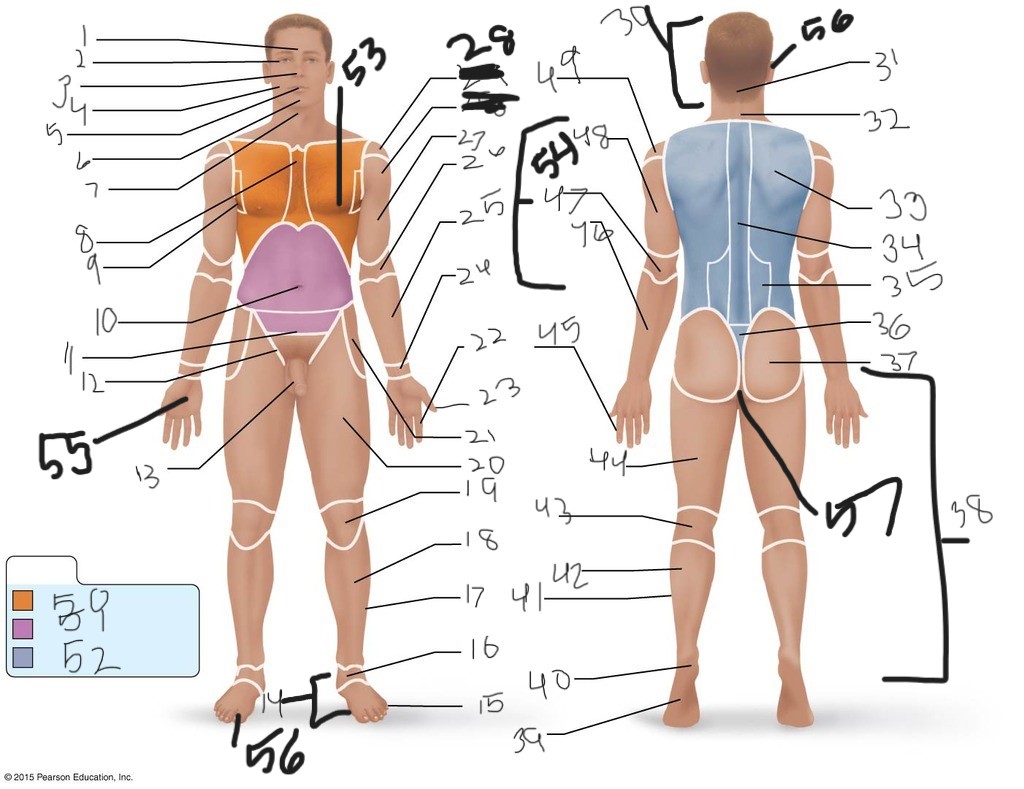
34. \
35. \
36. \
37. \
38. \
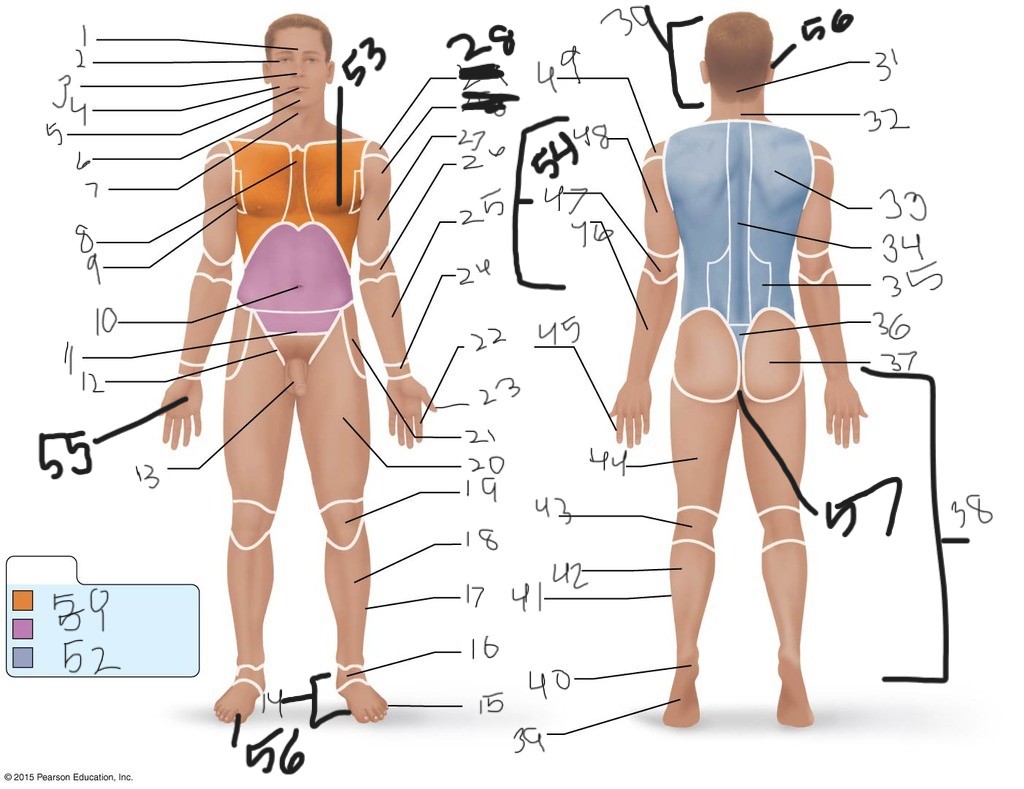
39. \
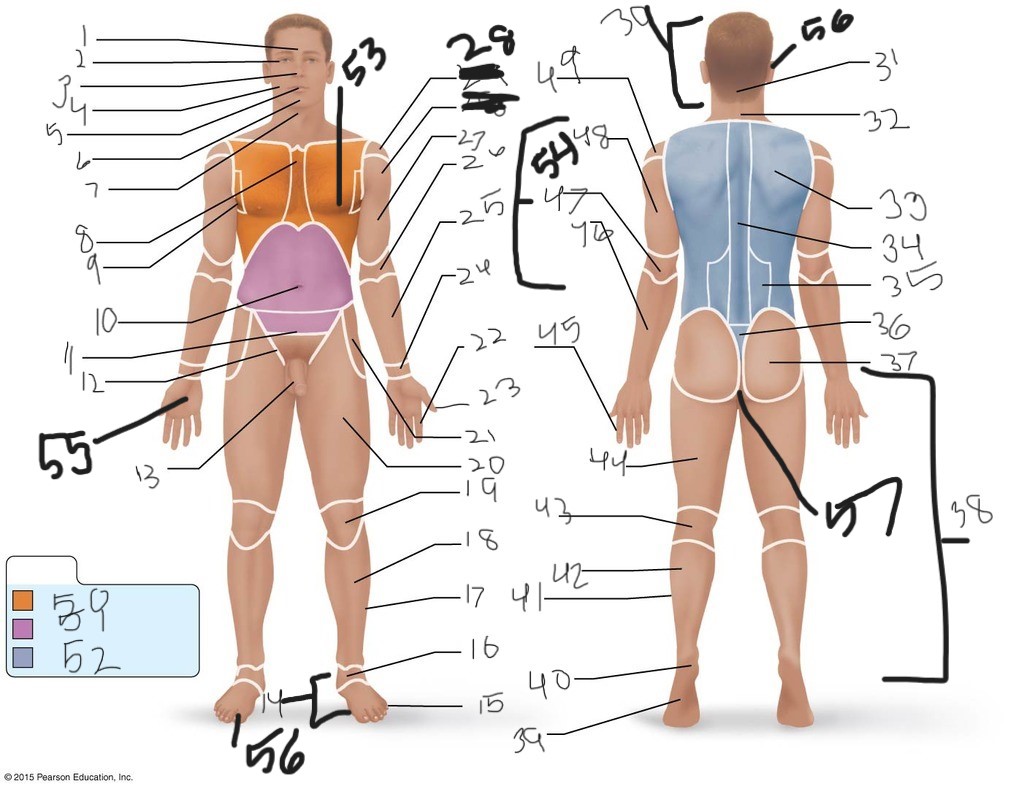
40. \
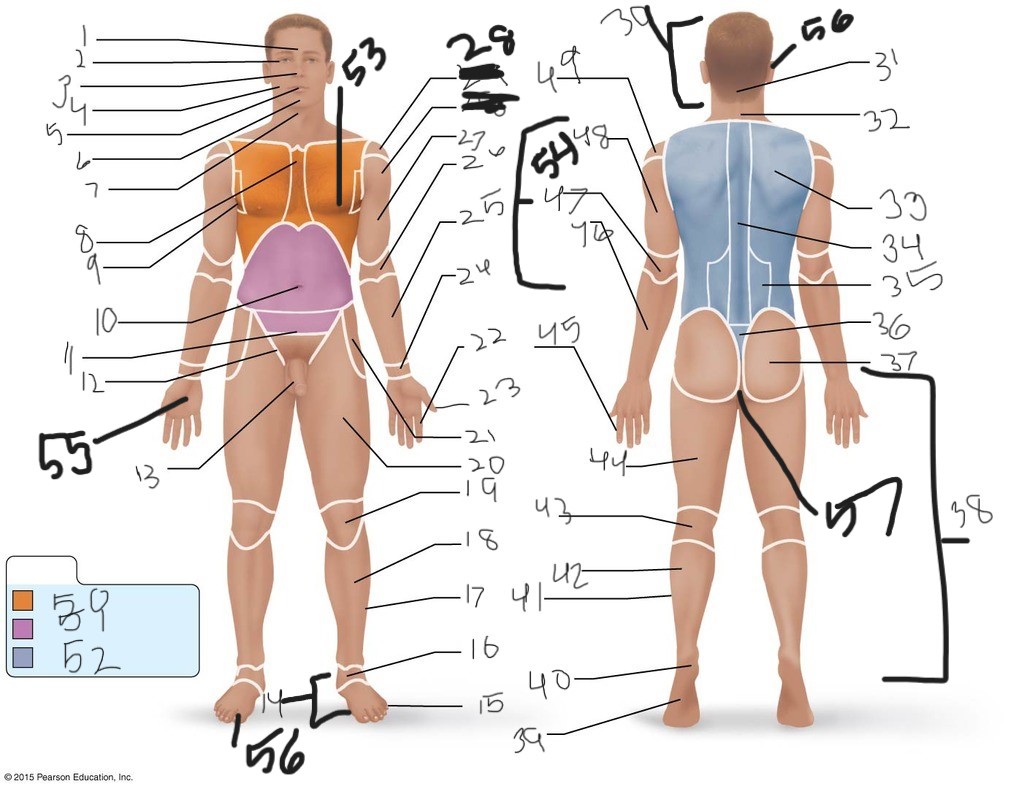
41. \
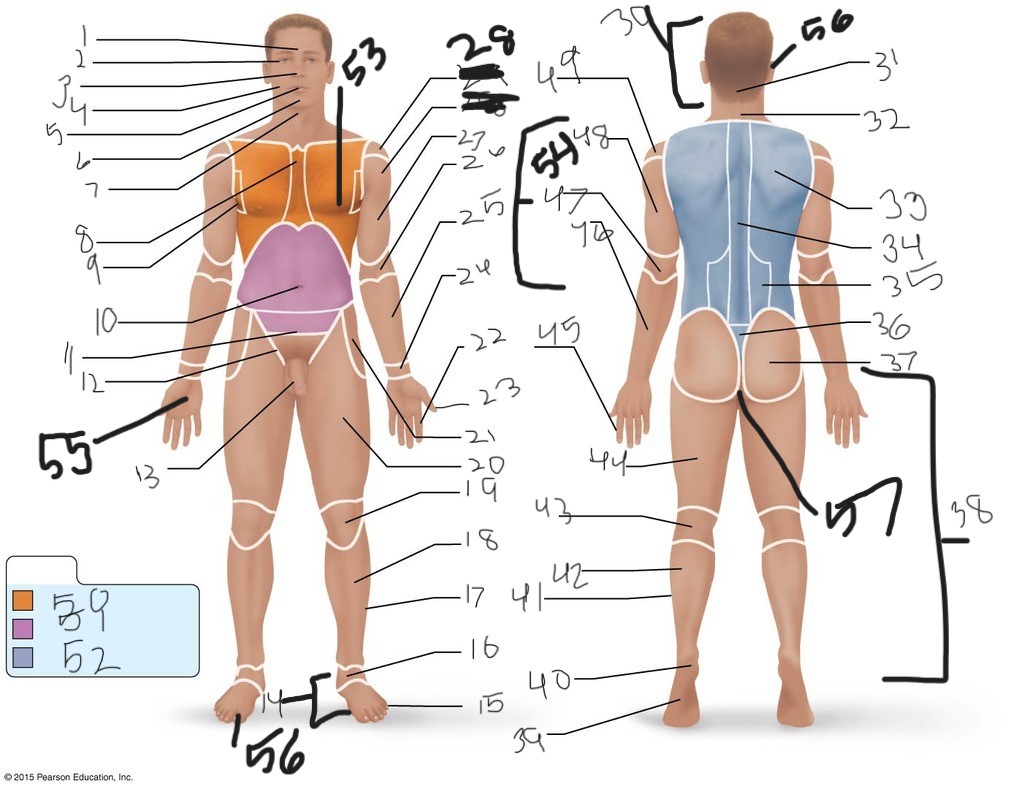
43. \
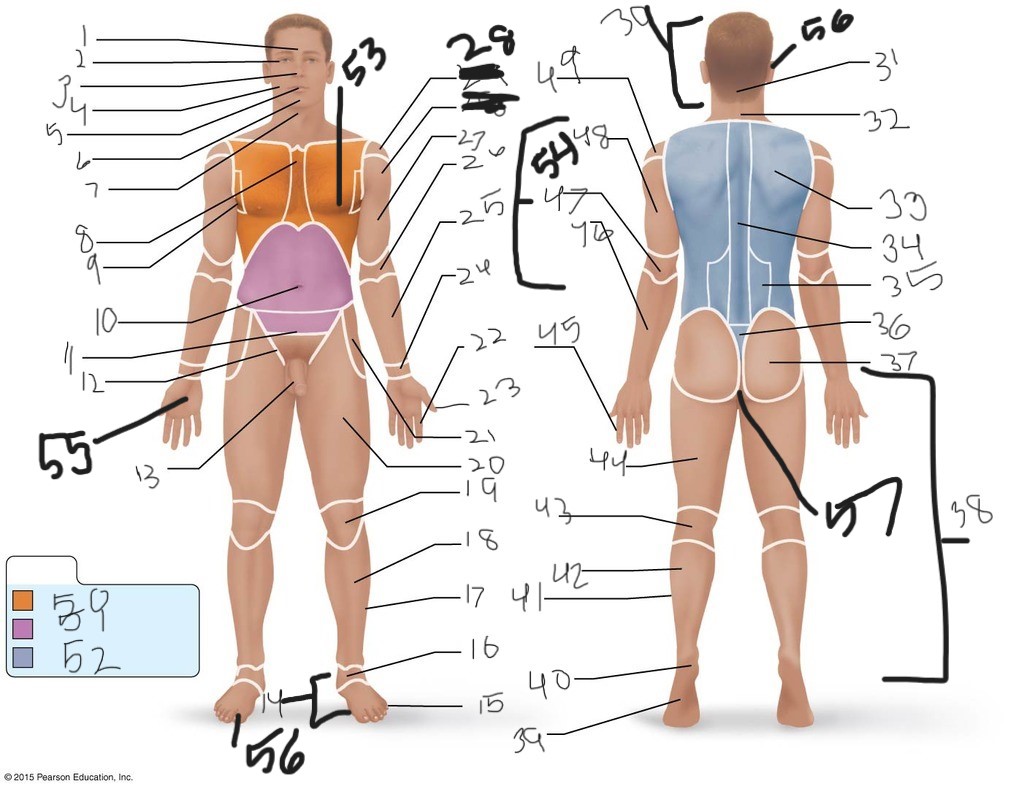
44. \
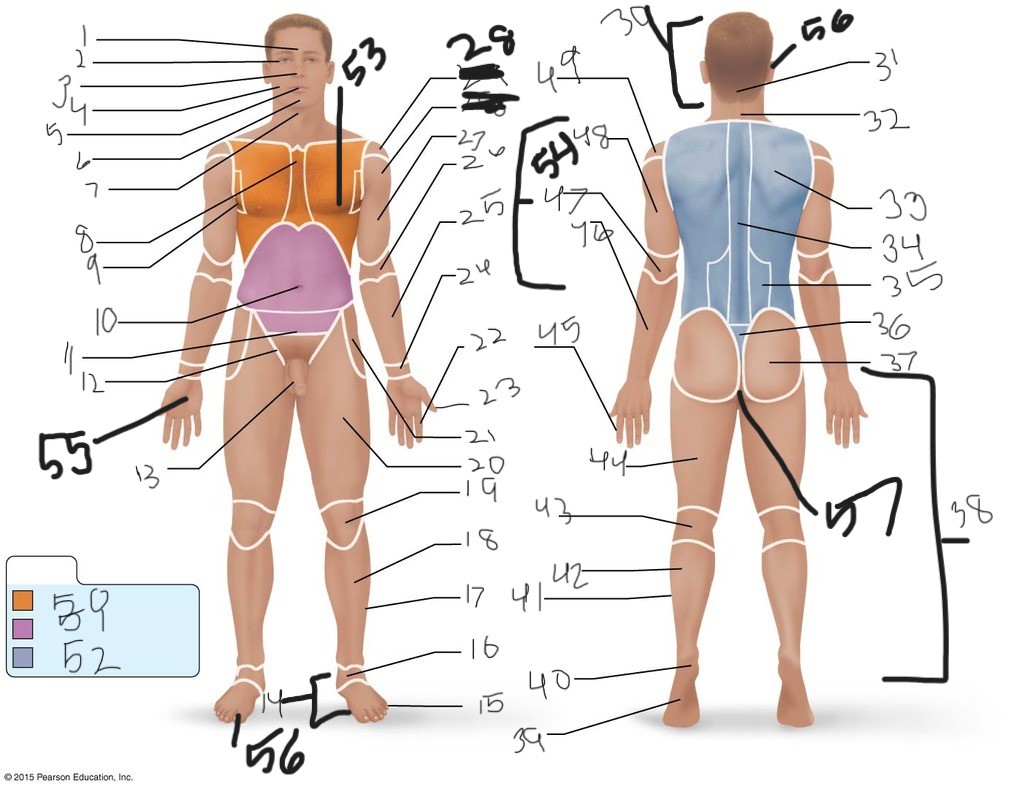
45. \
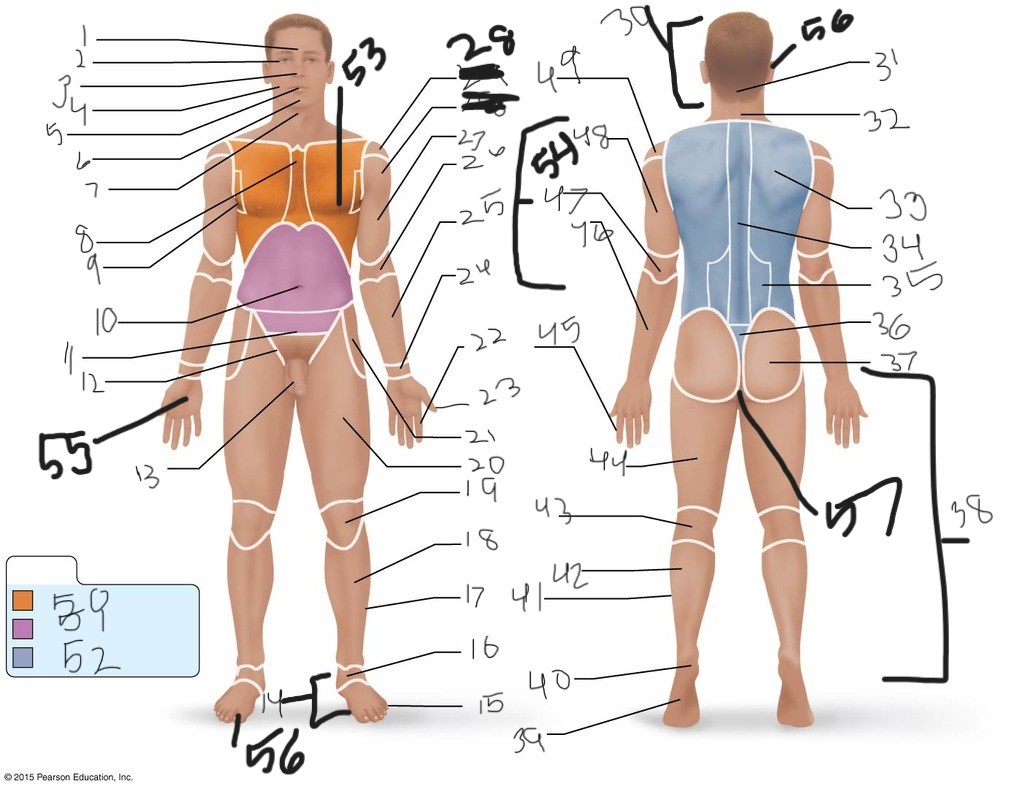
46. \
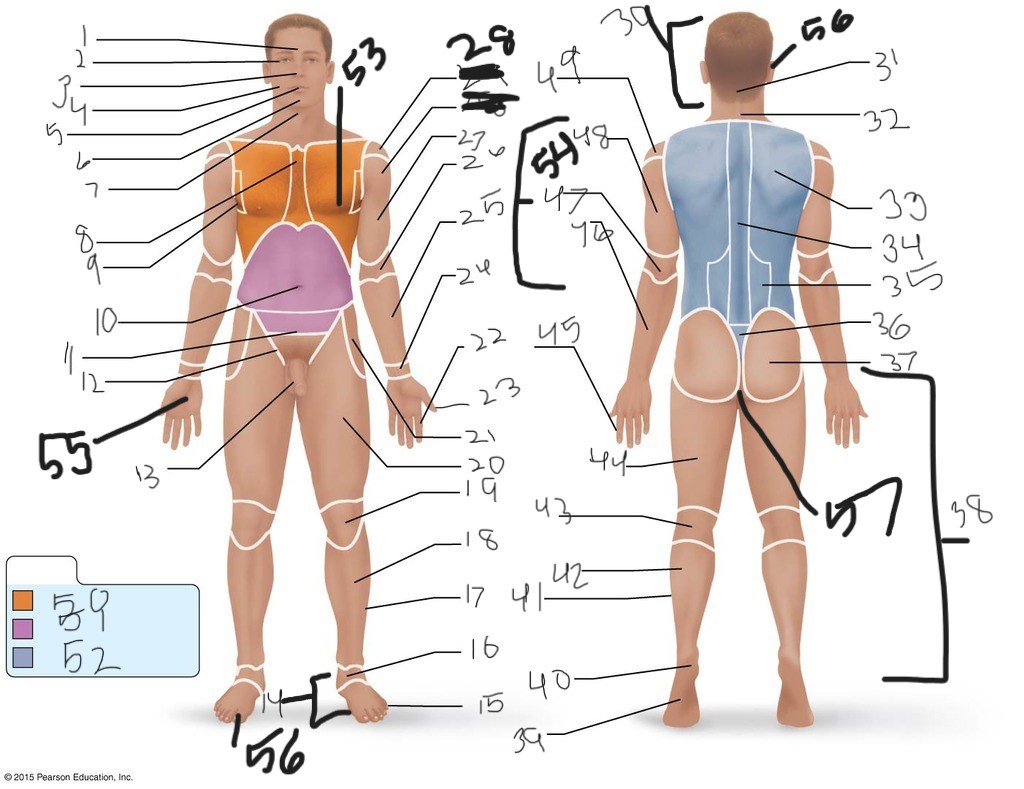
47. \
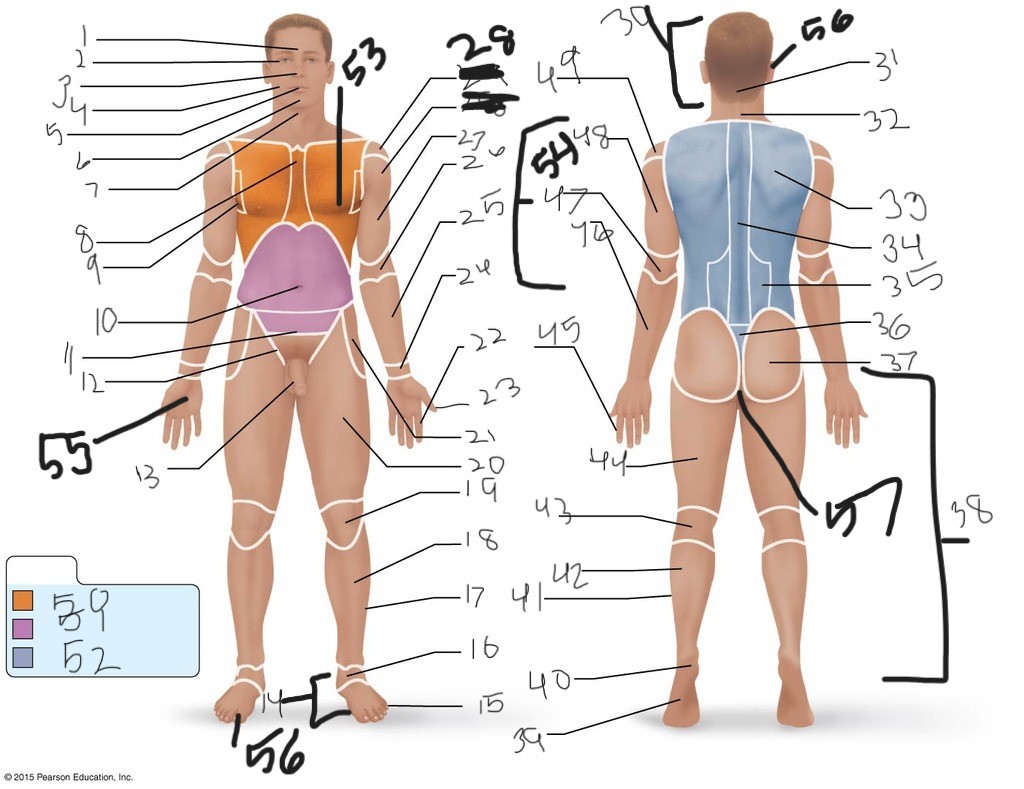
49. \
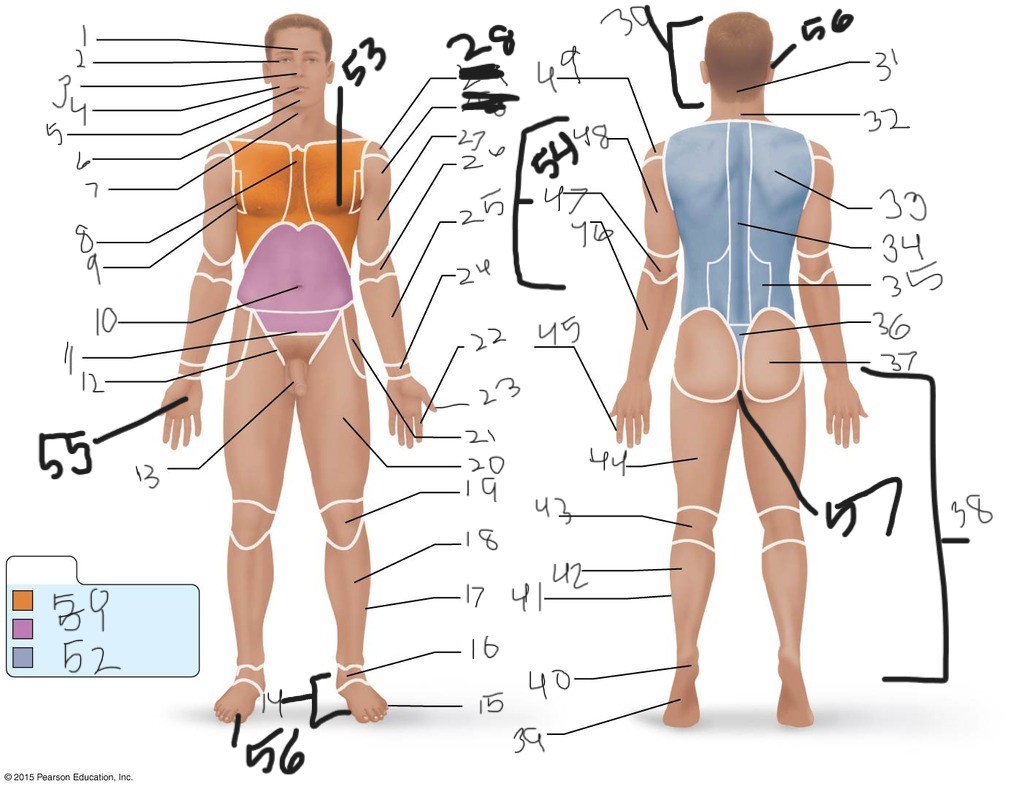
50. \
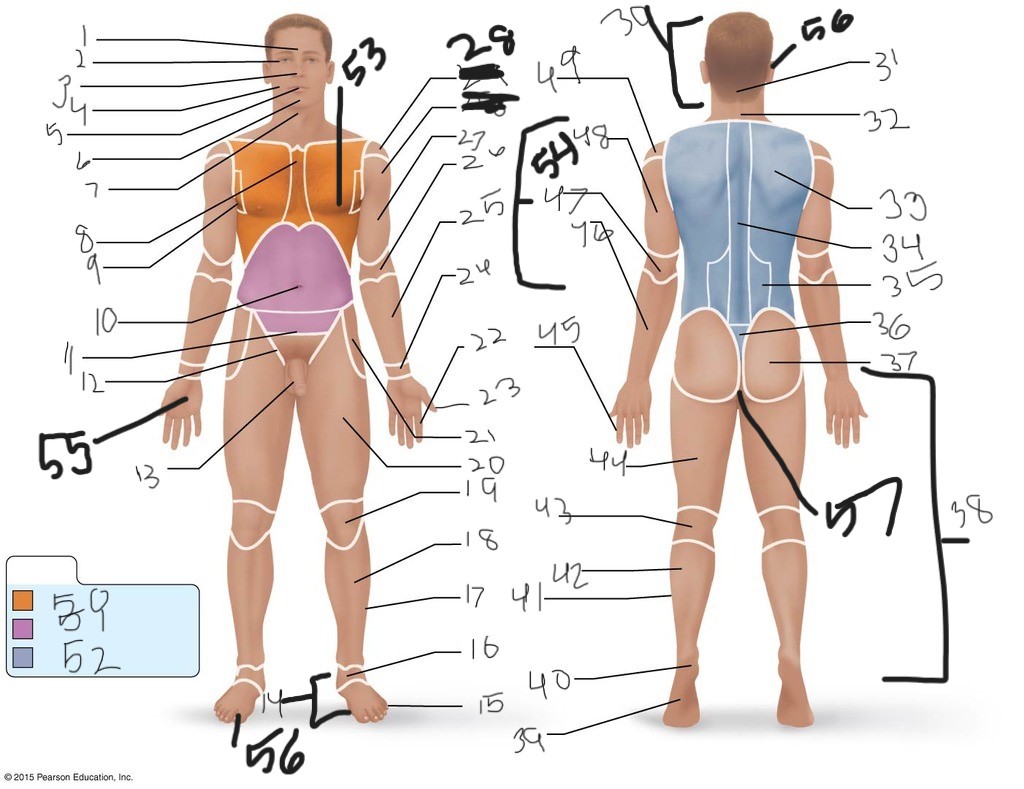
51. \
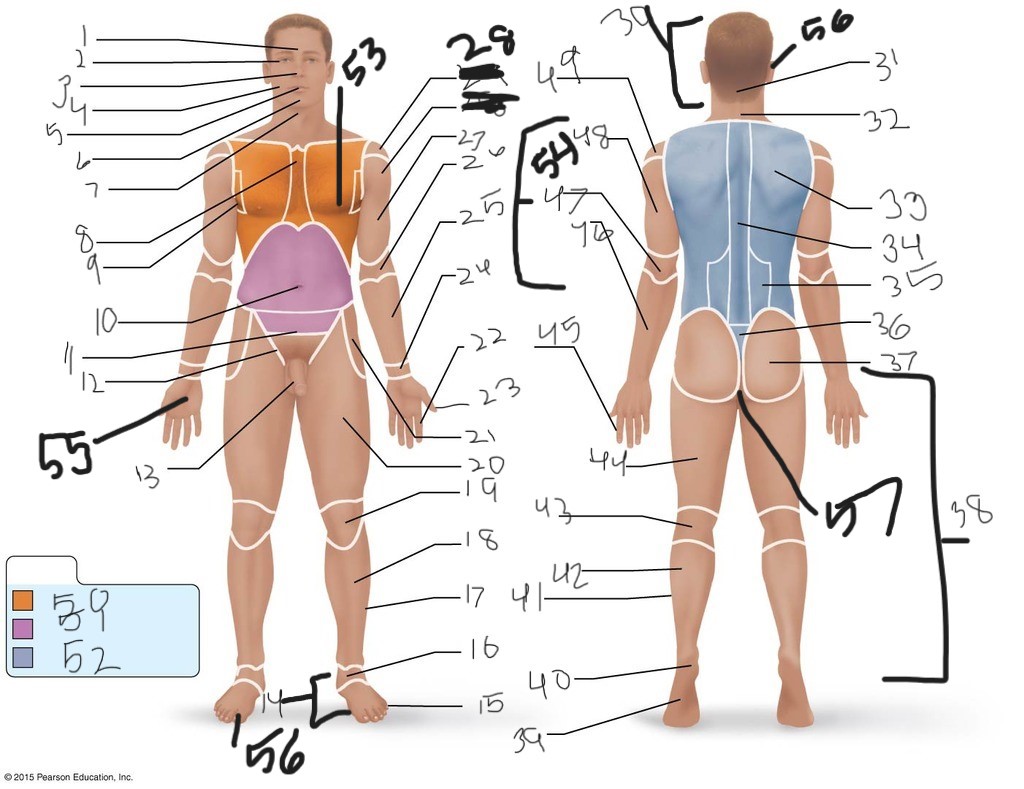
52. \
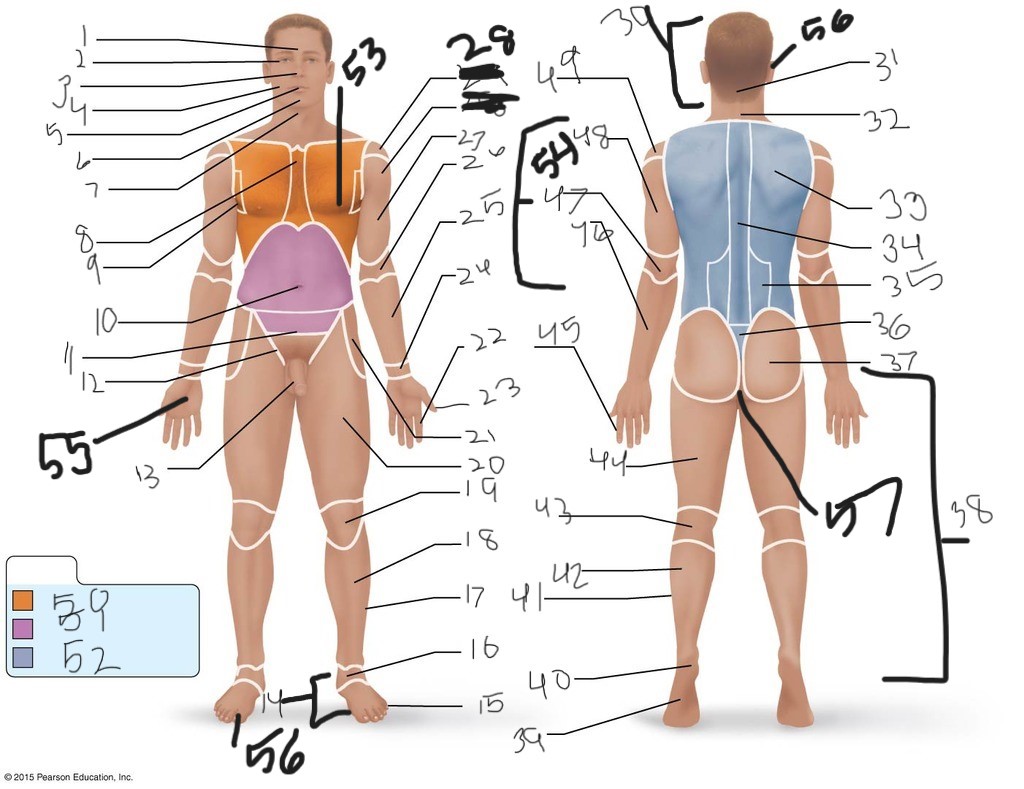
53. \
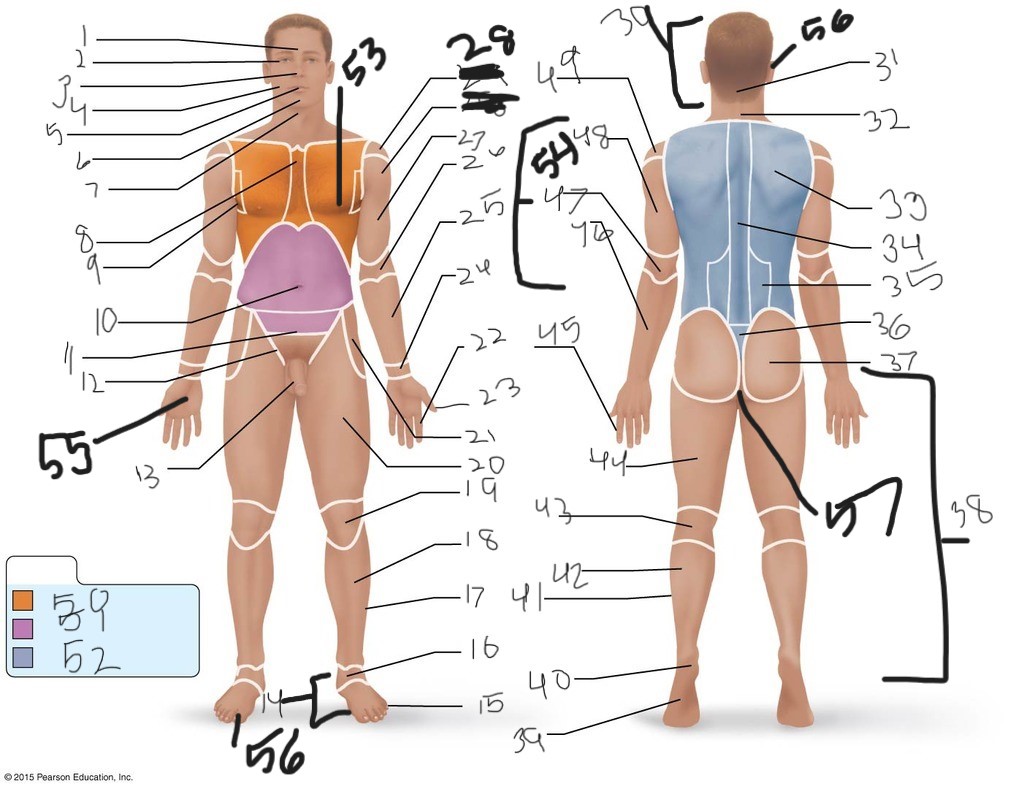
54. \
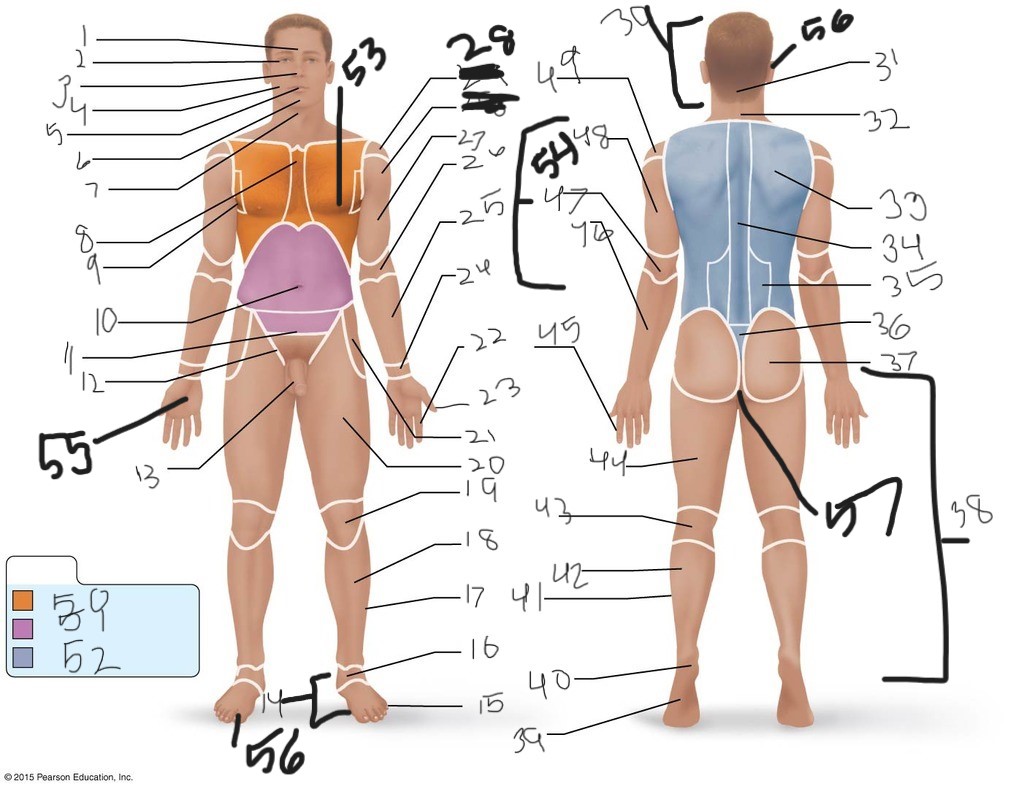
55. \
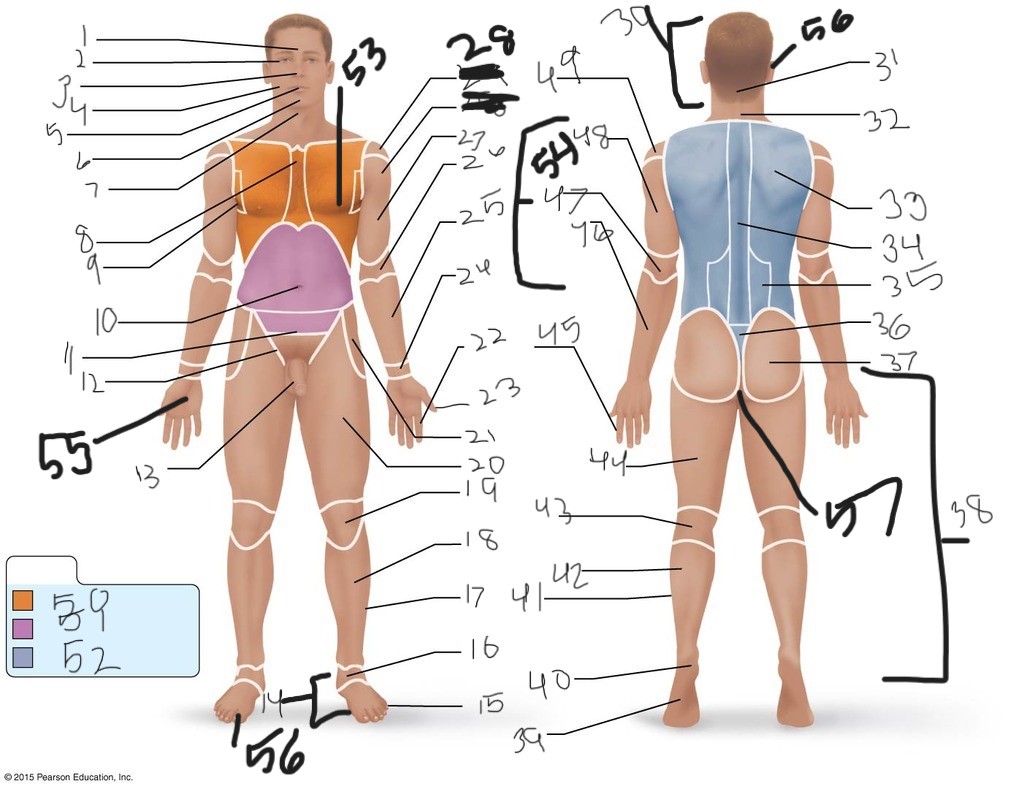
56. (bottom)
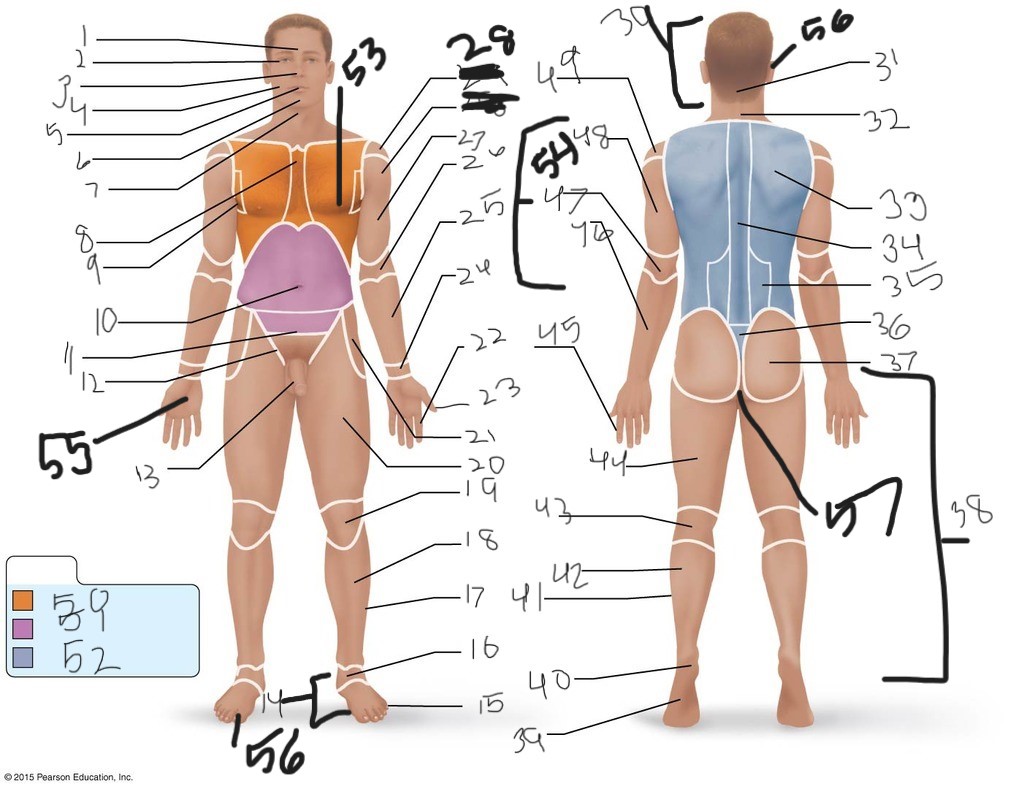
56. (top)
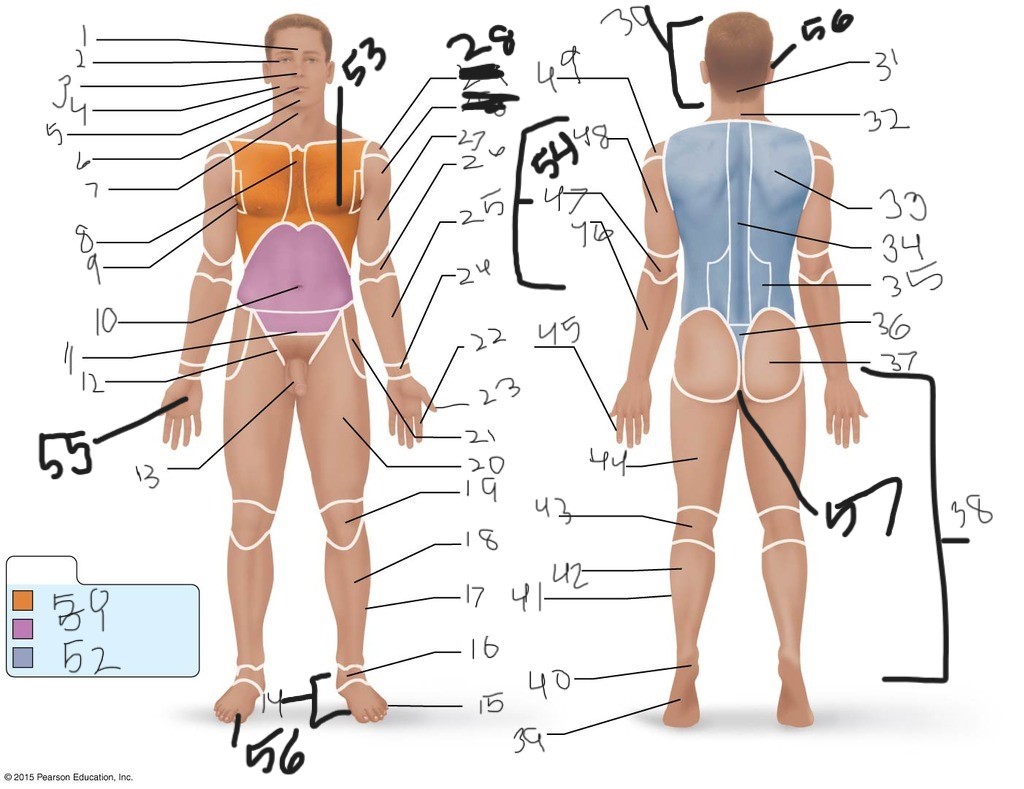
57. \
anatomy:
study of the structure of body parts and their relations to each other
study of structures that can be seen with the naked eye:
gross anatomy
study of all body structures in a given body region
regional anatomy
study of all structures in a body system
systemic anatomy
study of internal body structures as they relate to the overlying skin
surface anatomy
study of structures that are too small to be seen with the naked eye
microscopic anatomy
study of cells
cytology
study of tissues
histology
study of the change in body structures over the course of a lifetime
developmental anatomy
study of structural changes associated with disease
pathological anatomy
study of internal structures using specialized visualization techniques
radiographic anatomy
study of biological molecules
molecular biology
what does physiology rely on to explain body systems:
physics
The principle of complementarity of structure and function states:
function is dependent on structure, and the form of a structure relates to its function
levels of structural organization:
atoms, molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organisms
this necessary life function allows an organism to maintain separate internal and external environments, or separate internal chemical environments:
maintaining boundaries
this necessary life function allows organisms to travel through their environment:
movement
this necessary life function is the ability to detect changes in an organisms internal and external environments and respond to them:
responsiveness
this necessary life function is the process of breaking down food into molecules that can be used by the body:
digestion
this necessary life function is all the chemical reactions that occur in the body:
metabolism
this necessary life function is the process of removing waste:
excretion
this necessary life function is the process of producing more cells and organisms:
reproduction
this necessary life function is an increase in size:
growth
integumentary system:
external covering for body, vitamin D synthesis, cutaneous respiration, sweat & oil gland secretion
skeletal system:
protect & support deeper body tissues & organs, framework for movement, hematopoiesis, mineral storage
muscular system:
manipulation of environment, locomotion, facial expression, posture maintenance, heat production
nervous system:
fast-acting response to internal & external stimuli, activation of muscles & glands
endocrine system:
secretion of hormones which regulate growth, reproduction, & metabolism
cardiovascular system:
transportation of blood which carries oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, & wastes
lymphatic system:
returns leaked fluid to blood, disposes of debris, houses white blood cells for immunity
respiratory system:
maintains blood oxygen and removes carbon dioxide via lung air sacs
digestive system:
breaks down ingested food for absorption, eliminates undigested foods as feces
urinary system:
eliminates nitrogenous wastes; regulates water, electrolyte, and acid-base balance of blood
male reproductive system:
testes produce sperm and male sex hormones
female reproductive system:
ovaries produce eggs and female sex hormones, fertilization and development of fetus, mammary glands to nourish newborn.
mnemonic device used for the systems:
send mr. uric l
this survival need is used for energy and cell building:
nutrients
this survival need is used to release energy from food during chemical reactions:
oxygen
this survival need is the most abundant chemical substance in the body, provides an environment for chemical reactions & a fluid medium for secretions & excretions.
water
this survival need is required for the chemical reactions of the body to occur at the proper rate.
normal body temperature
this survival need must be within an appropriate range so that proper gas exchange occurs in the lungs
atmospheric pressure
this term is the tendency of biological systems to maintain relatively constant conditions
homeostasis
name the components of homeostatic control
variable, receptor, control center, effector
this component of homeostatic control is the regulated factor:
variable
this component of homeostatic control is the structure that recognizes a change and reports it to the control center:
receptor
this component of homeostatic control is the structure that coordinates a proper response to the change:
control center