ET&P EKG
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
what is the normal pacemaker of the heart? where is it located?
the sinoatrial node
right atrium
where does depolarization spread from?
the SA node across atria and results in the P-wave
how many tracts within the atria conduct depolarization to atrioventicular node (AV)? where does conduction slow?
3
→ slows in the AV node to allow atria to empty blood into ventricles before ventricular systole
what connect the AV to the bundle branches?
Bundle of His
what are the Purkinje Fibers?
terminal bundle branches
what place on the EKG shows if someone had a heart attack?
ST segment
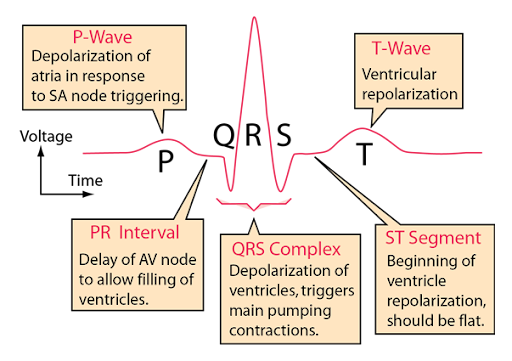
knowt how to label the EKG
slide r of ECG sldies
mV number that is instantly ahcieved upon depolarization
+30mV
what kinds of things can effect electrical reading tests?
skin prep
body composition
placement of nodes
know this
Phase 0 | Rapid Depolarization | Rapid Inflow of Na+ |
Phase 1 | Initial Repolarization | Rapid Outflow of K+ |
Phase 2 | Plateau State | Inward flow of Ca2+ |
Phase 3 | Final Rapid Repolarization | Inward flow of Ca stops Outward flow of K+ accelerated |
Phase 4 | Resting or Polarized State | Na+/K+ pump Return to Normal |
what is the normal mV threshold at beore depolarization?
-90mV
refractory periods; def and types
Ionic composition during different phases (allow differing RXN’s to stimuli)nothing can happen!/reset
Absolute refractory period- cells cannot respond to stimuli Phase 0,1,2 and ½ of 3
Relative Refractory Period- Repolarization is almost complete, a strong depolarization could occur second half of phase 3-close but may wait
Non-Refractory Period- Cells are in resting polarized state Phase 4
rate (R-R) represents:
between Rs (ex.beats per min)
looking at P-waves (PR interval length)
are they equal?
QRS complex (length of complex)
how high
how does fat % increase effect R?
makes it short
what to look for in EKGs
•Rate (R-R)
•Are there P-Waves (PR interval Length)
•QRS Complex (Length of Complex)
•T-Wave (QT Interval)
•Little boxes and big boxes
•ECG stripes are 6 seconds in length
•In 12-lead look at transition
know what normal sinus rhythym looks like
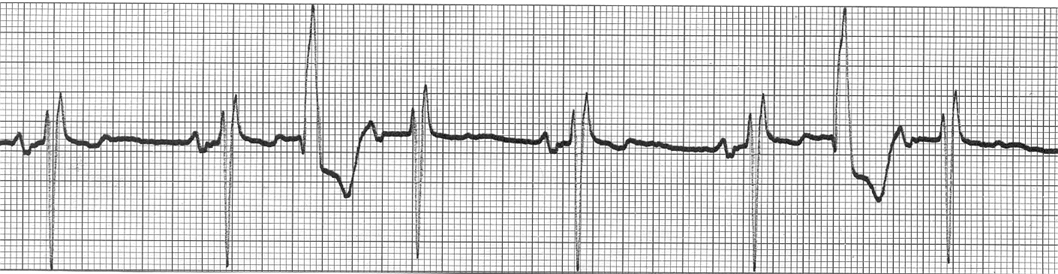
PVC-pre ventricular contraction- throws a QRS waves
multifocal PVC- (signals) originates in a different spot
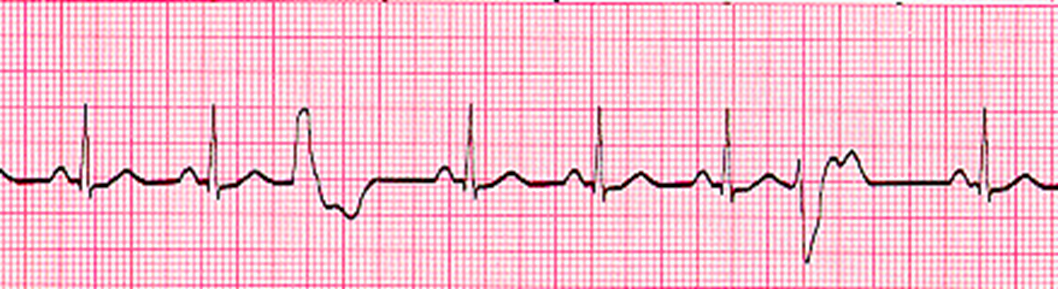
look at A-FIB
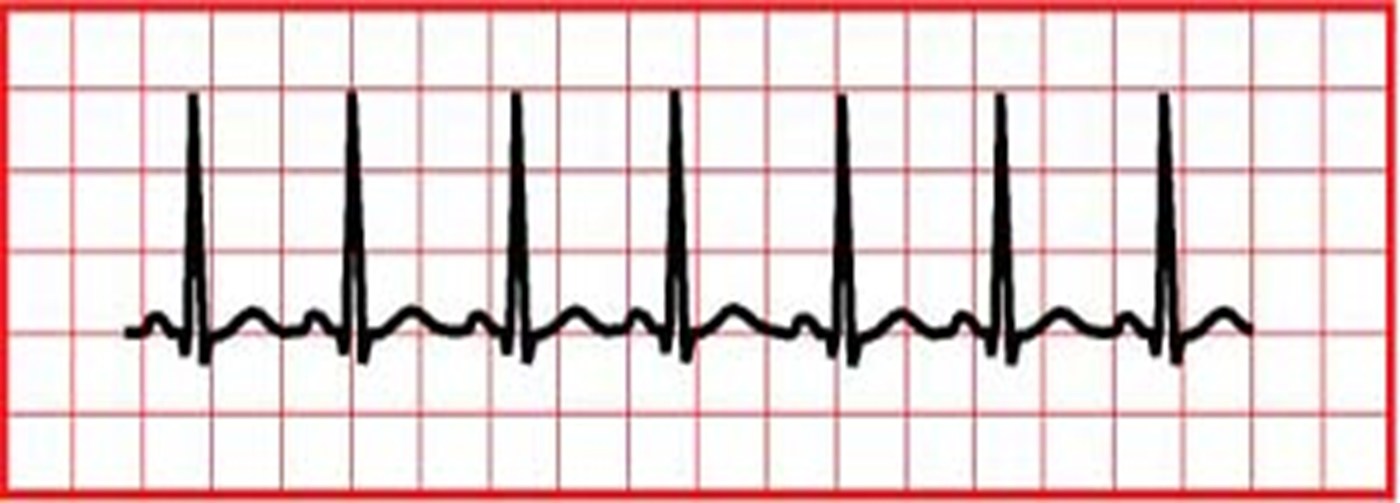
sinus tachycardia
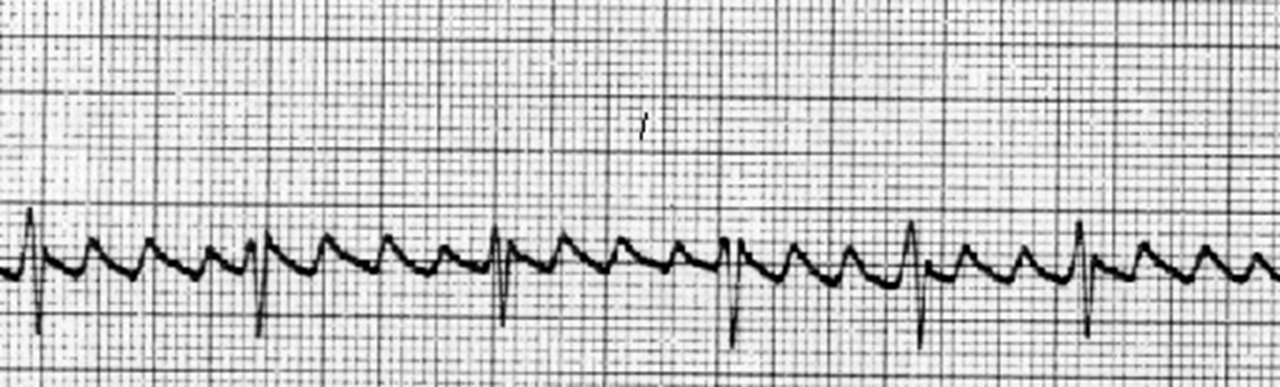
trial flutter- lots of P, not many QRS (travel in a loop). AV =more disorganized and faster (is worse)
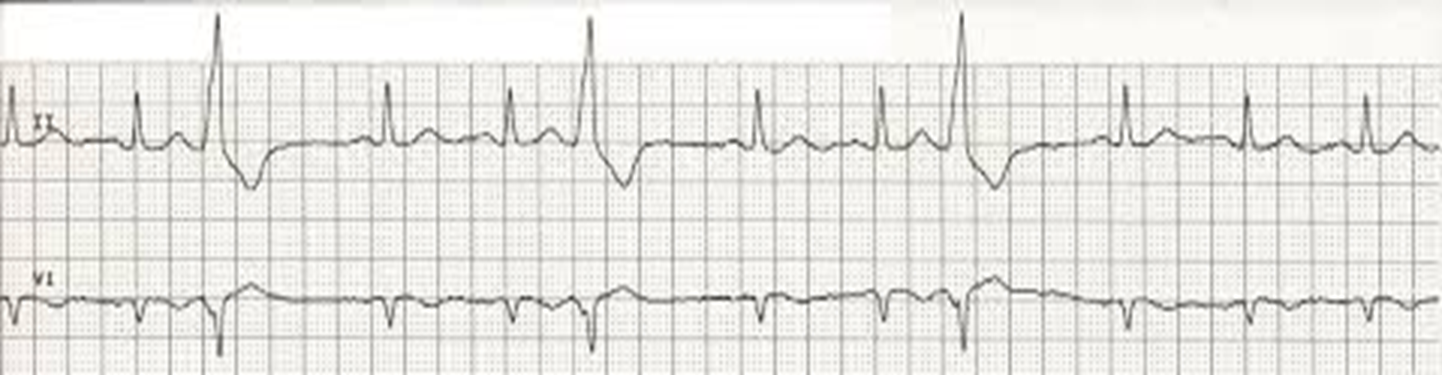
trigeminy (PVC occurs every third beat). rare. has QRS
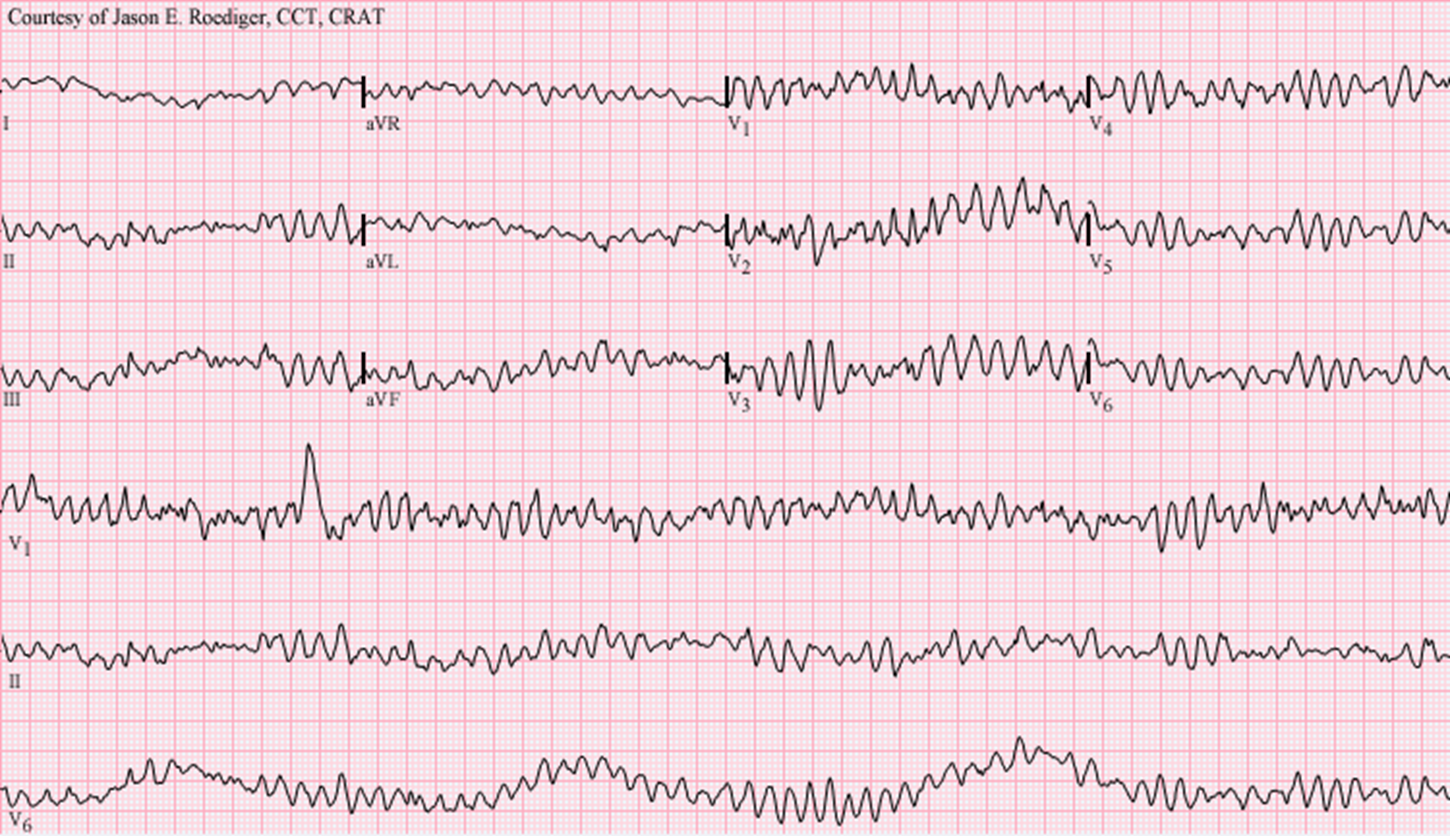
ventricular flutter(some QRS)
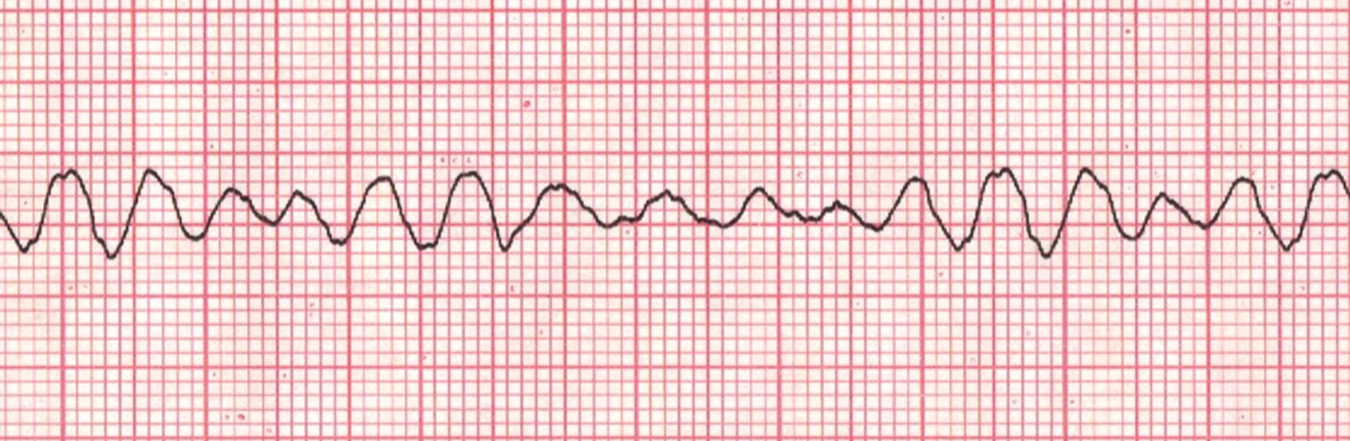
V-fib ventricular fibrillation-not quite as bad
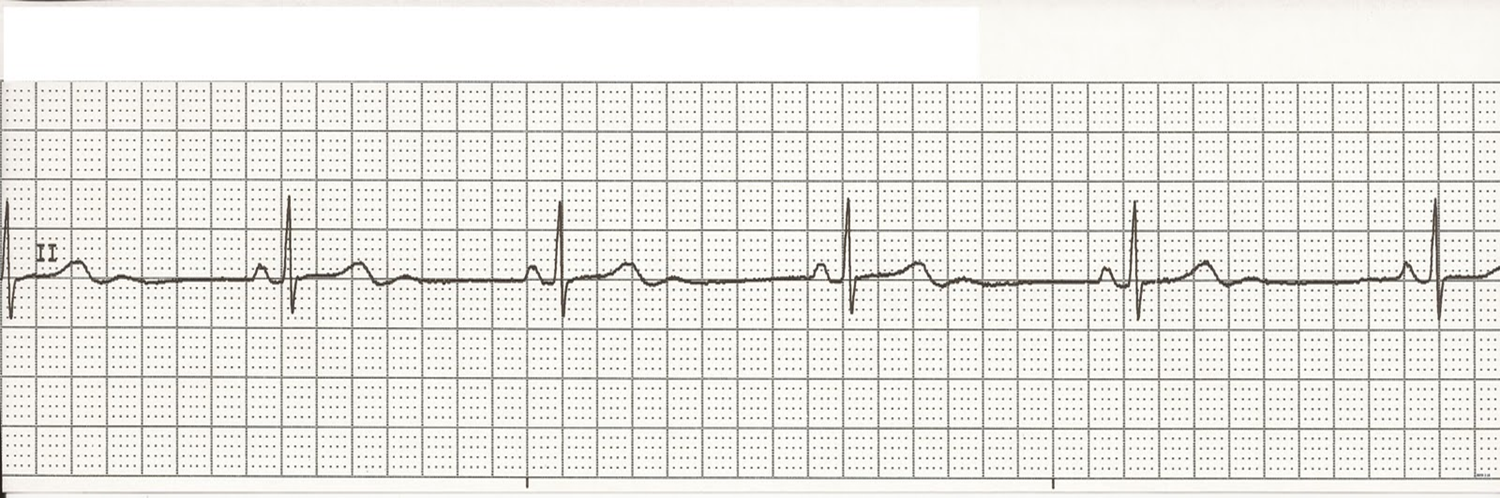
sinus bradycardia
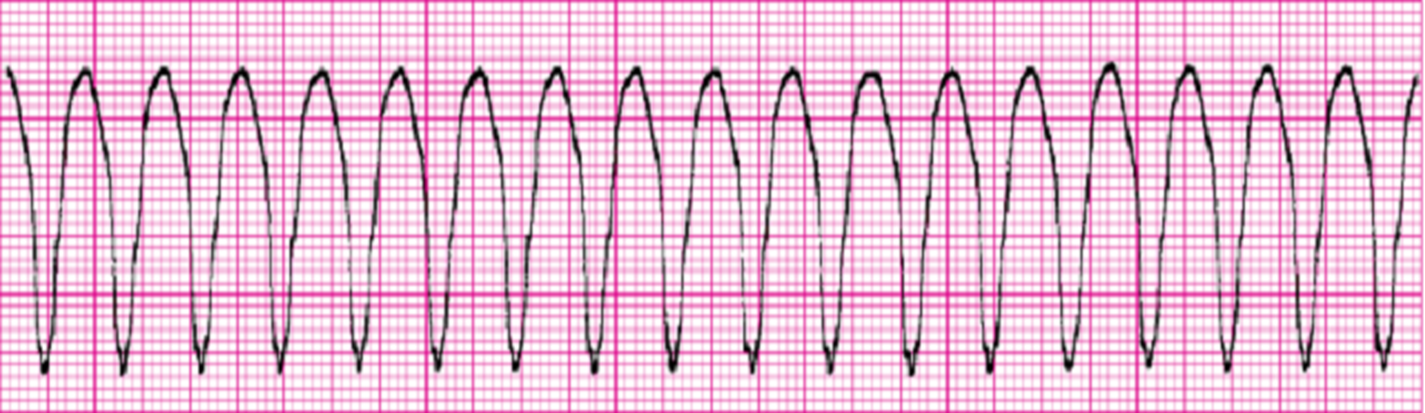
VT-ventricular tachycardia- no pwaves, all QRS
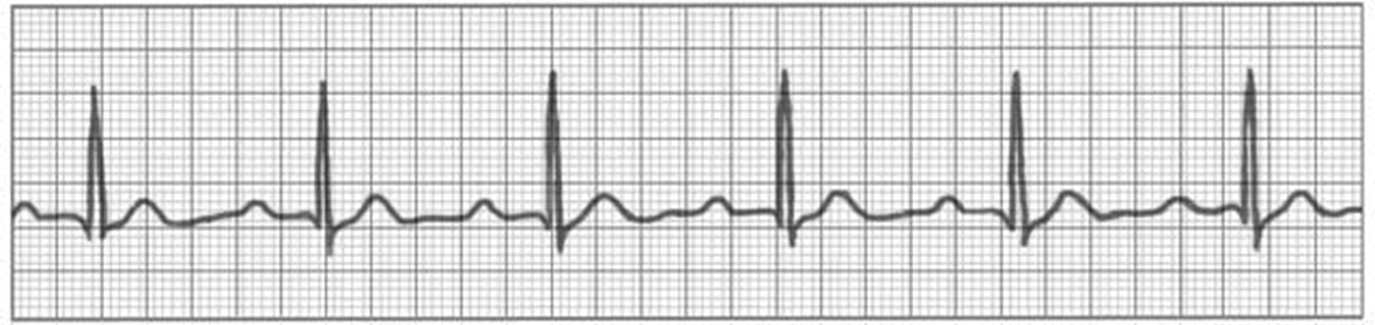
first degree block
AKA first degree AV block
AV- ventricles delayed
prolonged PR interval
more p than QRS
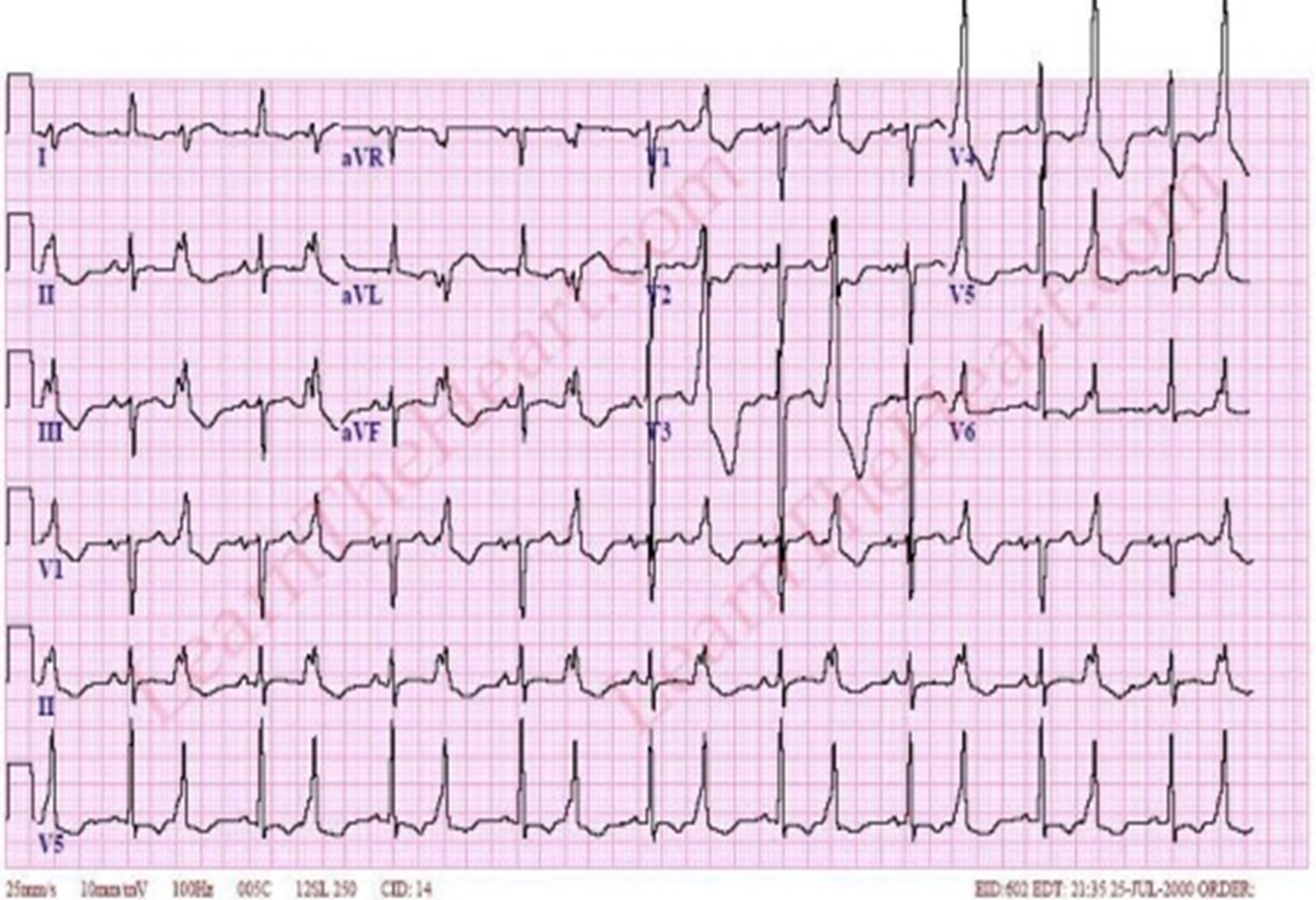
bigeminy (can be atrial or ventricular) every other beat extra contraction 9PVC or 9PAC)
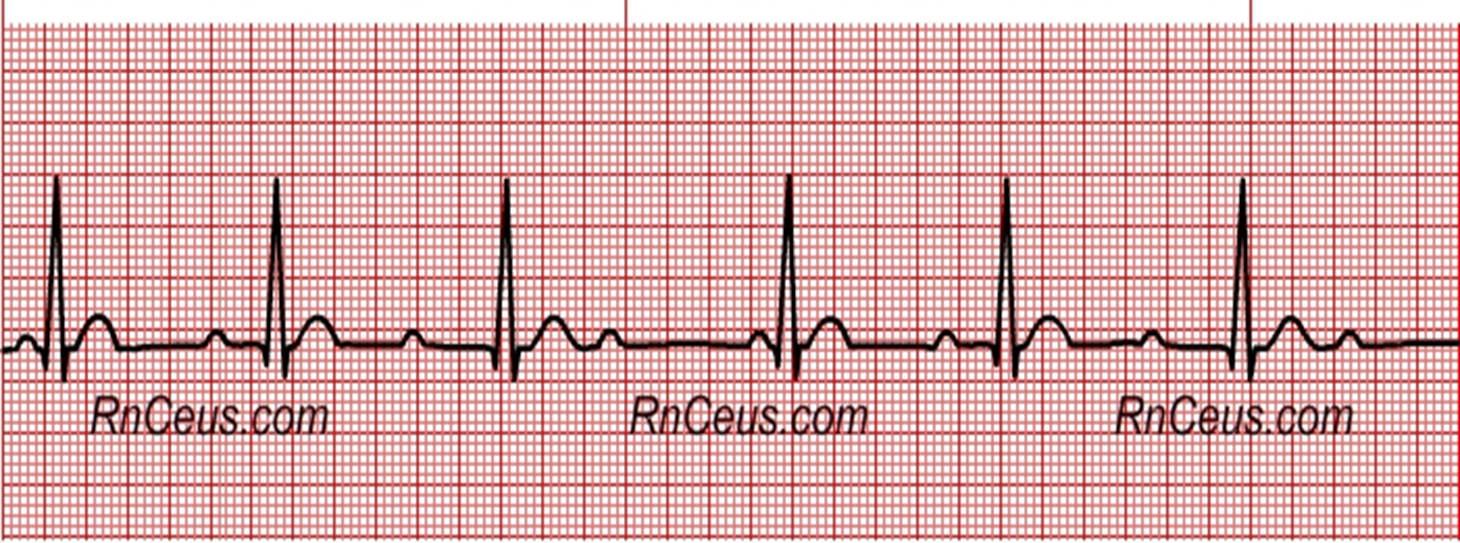
second degree block (AV-ventricles is intermittently blocked
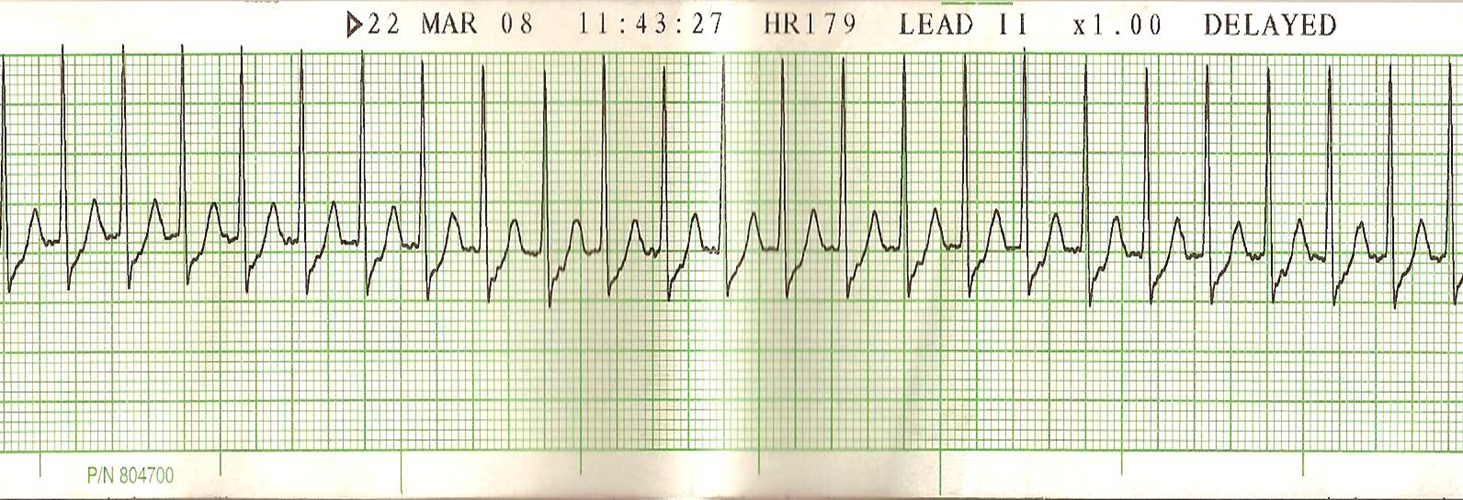
SVT- supraventricular tachycardia. impulse originates is above ventricular
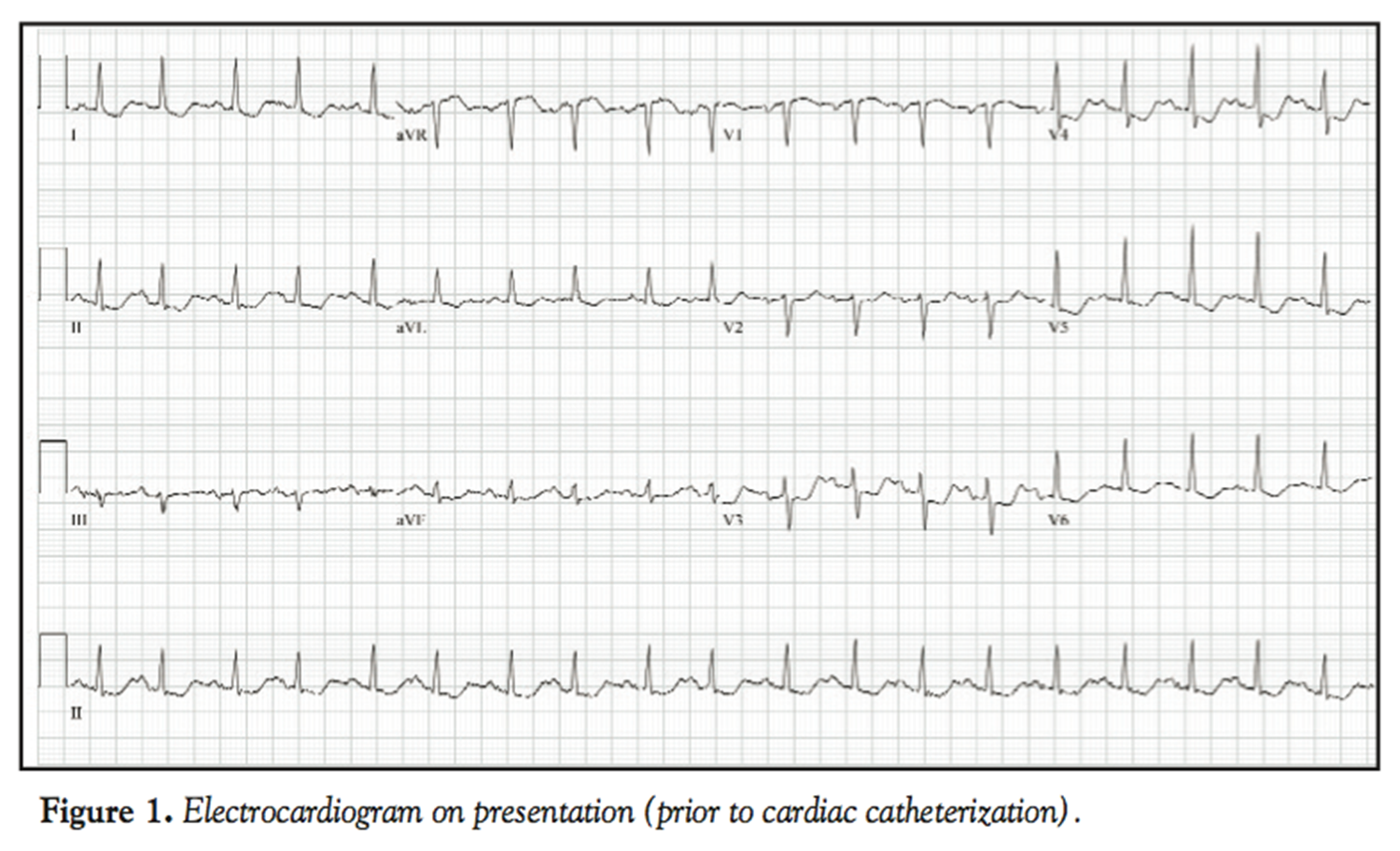
mild ST depression (lead II)partial or tempoary blockage needs immediate help

3rd degree AV block
absense of any conduction between atria andventricles
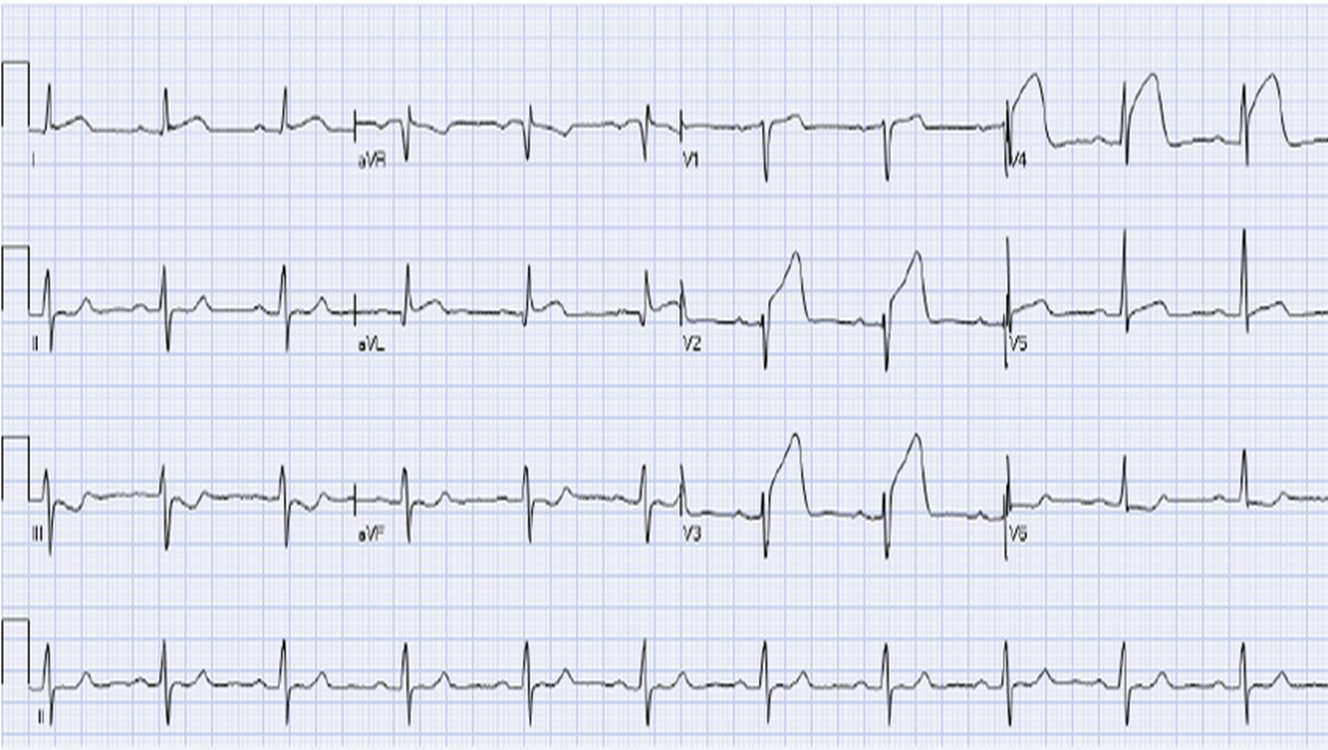
ST elevation- worst case tissue dealth from MI- (lead I and AVL and V2)