EM E1: Wound Management
1/91
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
Which stage of wound healing:
initiated at time of injury, compression of small bleeding vessels, plts aggregate
hemostasis
Which stage of wound healing:
stimulated by chemotactic factors from plts, complement cascade begins, vasodilation
inflammation
Which stage of wound healing:
inflammatory response stimulates cell division in stratum germinativum -24hrs post injury
Epithelialization
Which stage of wound healing:
vital, new vessel growth 72 hrs post
Angiogenesis
Which stage of wound healing:
collagen synthesis and breakdown of old/damaged collagen (peak at 7 days)
Fibroplasia
Which stage of wound healing:
occurs of next several months, contraction modifies cosmetic appearance
Wound contraction & scar remodeling
Which stage of wound healing:
collagen remodeling, balance between new and removal of old, peaks 60 day post, only reaches 80% strength of old skin, remodeling begins ~21 days after injury, can last indefinitely
Maturation
What wound are at a high risk of infection?
bite wounds (check for presence of a FB)
visible contamination also inc risk (soil contains fungal spores, bacteria, fecal matter)
What injury is more susceptible to infection?
crush injuries
What is directly related to the growth of bacterial inoculum?
time interval from injury to repair
After how many days of open wound management does the risk of infection after closure substantially dec?
4 days
What areas of the body have low density for bacterial colonization?
upper arms, legs, torso
What areas of the body have a high density for bacterial colonization?
moist areas (axilla, perineum, intertriginous, toe webs)
In addition to bacterial flora, plays a role in determining the likelihood of infection?
regional blood flow -highly vascular areas are less likely to be infected
Who is more prone to keloids?
AA & Asian populations, hx keloid formation
What are keloids?
grow beyond the original wound boundaries, often larger and more pronounced
What are hypertrophic scars?
stay w/in wound boundaries, d/t tension during healing
What can epinephrine containing anesthetic solutions be helpful with if not contraindicated?
stopping wound bleeding (small bleeds)
What test is used for wooden FB and organic material?
US
What materials are visible on XR?
*radiodensity varies on the material
metal, bone, teeth, pencil, plastics, gravel, sand, fish bones, aluminum, glass > 1 mm thick
What imaging is good for all foreign substances?
CT
*but is $$ and significant exposure to radiation
What do you use to disinfect the skin surrounding the wound?
Betadine or chlorhexidine (Hibiclens)
*apply from wound edge outwards
What do you need to minimize the wounds exposure to?
undiluted Betadine and Hibiclens
*disastrous if eye is exposed
What is the most crucial step for wound healing and minimizing infection risk?
debridement
Which wound cleanser:
most widely used iodophor; lower free iodine (free iodine is toxic to tissues); available in 10% solution (1% free iodine) OR 1% solution -safe and effective
Povidone-iodine (Betadine)
Which wound cleanser:
effective when used w/ high-pressure irrigation
NaCl 0.9% (NS)
Which wound cleanser:
nonionic surfactant, NO toxicities, does NOT interfere w/ wound healing, impedes the development of infection, loosens debris, suitable for delicate tissues (mucous membranes & eyes)
Poloxamer 188 (Pluronic F-68)
What is the most effective form of wound cleansing?
high pressure irrigation (> 7 psi)
What is the most commonly used wound irrigation solution d/t safety and physiologic factors?
normal saline
Why is it better to create incisions or lacerations parallel to skin tension lines?
less likely to create widened scars than those perpendicular
What helps identify skin tension lines?
follow natural wrinkles/fold, pinch test, Langer’s lines, muscle orientation
What is primary closure?
wound is immediately closed by approximating its edges → reduced healing time, bleeding, and discomfort
What is secondary closure?
wound is left open and allowed to close on its own; suited for highly contaminated or infected wounds, and pts at high risk of infection → low risk of infection, but is slow and uncomfortable
What is tertiary closure?
(delayed primary)
combines advantage of primary & secondary; wound is left open for 4-6 days after which it may be closed if no infection supervenes
What is the preferred closure method for linear lacerations?
can be closed by any method as they are subject to tension (expect joints)
What is the preferred closure method for low-tension irregular lacerations?
ex: cut on thumb
sutures → allow greatest degree of precision and accurate wound approximation
What is the preferred closure for high tension lacerations?
deep dermal sutures and wound immobilization
What is the strongest wound closure device?
sutures
Which sutures are absorbable?
Catgut, polyglycolic acid (PGA), polyglactin 910 (Vicryl), poliglecaprone (Monocryl), polydioxanone (PDS)
Which sutures are non-absorbable?
Polypropylene (Prolene), Nylon (polyamide), Silk, Polyester
Which suture is used for:
internal soft tissue approximation, ligation
Catgut
Which suture is used for:
general soft tissue approximation, ligation
Polyglycolic Acid (PGA) & Polyglactin 910 (Vicryl)
Which suture is used for:
subcuticular skin closure, soft tissue approximation
Poliglecaprone (Monocryl)
Which suture is used for:
fascia closure, pediatric cardiovascular surgery
Polydioxanone (PDS)
Which suture is used for:
vascular anastomosis, skin closure
Polypropylene (Prolene)
Which suture is used for:
skin closure, ophthalmic surgery, neurological surgery
Nylon (Polyamide)
Which suture is used for:
general soft tissue approximation, ligation
Silk
Which suture is used for:
cardiovascular surgery, tendon repair
Polyester
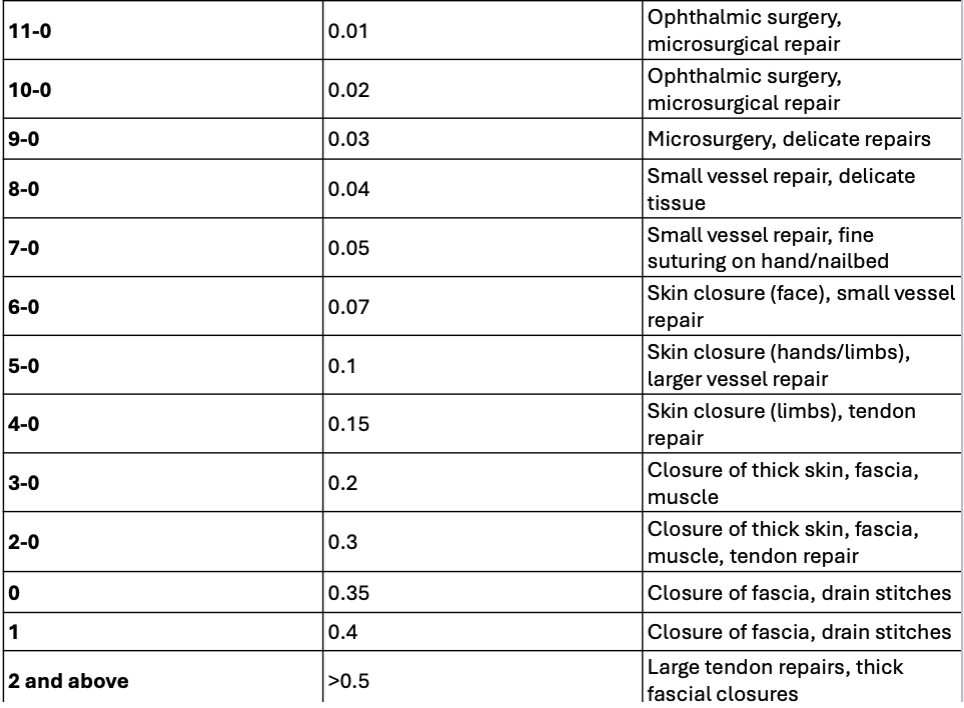
Reference slide 68
more 0 = smaller suture
How long do non-absorbable sutures retain their tensile?
at least 60 days
What are non-absorbable sutures used for most often?
close outermost layer of skin
Which non-absorbable sutures have lowest rate of infection and are the most non-absorbable ones used in the ED?
Monofilament synthetic: nylon or polypropylene
How long do absorbable sutures retain their tensile?
lose most of their strength < 60 days
What are absorbable sutures best for?
closure of deep structure: dermis and fascia
Which size suture should you used for laceration in the hand/fingers?
4-0/5-0
Which size suture should you use for facial lacerations?
6-0/7-0
Which size suture should you use for most locations?
4-0
Which closure device has the least precision in wound approximation?
staples
What should staple closure use be limited to?
linear, non facial lacerations; particularly helpful for scalp lacerations
Which closure device is the least reactive, inexpensive, and easy to use?
Adhesive tapes
What is closure with adhesive tape limited to?
very low-tension simple wounds or closure of fragile skin subject to low tension
How should adhesive tapes be applied?
perpendicular to wound edges ~2-3 mm apart, first strip should be placed across the center of the wound
What type of closure polymerizes into a stable bond when in contact with moisture to form an occlusive dressing?
Liquid monomers
What are the limitations of liquid monomer closure?
use w/ caution around eyes, should not be used alone for high-tension wounds bc of its strength
Which typed of tissue adhesive is stronger, more flexible, and OCA-based?
Dermabond
Which tissue adhesive is butyl-cyanoacrylate based?
Indermil
What should a wound be cleaned w/ post-op?
normal saline
If an injury is closed ____ hours after occurrence, infection rates inc exponentially w/ closure.
12 hours
What wounds need prophylactic abx?
human bites, cat bites, certain dog bites, intraoral alcerations, open fxs, wounds w/ exposed joints or tendons
What pts need prophylactic abx?
lymphedema, prosthetic joints or permanent hardware, grossly contaminated lacerations & prone to infective endocarditis
What is the abx of choice for prophylactic tx?
Cephalexin/Keflex OR Dicloxacillin
PCN allergy: Tetracycline
What is the abx of choice for intraoral wounds?
PCN or Clindamycin
What is the abx of choice for animal bite wounds?
Augmentin
What is the abx of choice for open fractures or joints?
Cephazolin + aminoglycoside (gentamicin, tobramycin)
If TD update is within 5 years is another shot needed?
nope
If TD update is btwn 5-10 yrs is another shot needed?
not for superficial laceration and minor injuries
If TD update is > 5yrs old and the injury is significant is another shot needed?
yes
What NEEDs to be done for bite wounds?
irrigation
Where are bites most likely to be infected?
hands
If a pt presents w/ an animal bite and is not previously vaccinated what should be done?
clean wound, HRIG, and rabies vax
If a pt presents w/ an animal bite and is previously vaccinated what should be done?
clean wound, rabies vax
Which bites develop infection faster: cats or dogs?
cats
What is the MC bacteria infecting cat bites?
Pasteurella species
Dog bites usually cause what type of wound?
crush-type wound d/t high pressure
What is the MC & most serious type of human bite injury?
closed-fist injury “fight bite”→ closed fist strikes the teeth of another individual and creates a small wound
What causes 90% of osteomyelitis cases from a foot puncture wound?
Pseudomonas
What is the tx for a foot puncture wound?
Cipro
What is the tx for shark bites?
Cipro
When should face sutures be removed?
3-5 days, replace w/ steri-strips
When should scalp & trunk sutures be removed?
7-10 days
When should arm or leg sutures be removed?
10-14 days
When should joint sutures be removed?
14 days