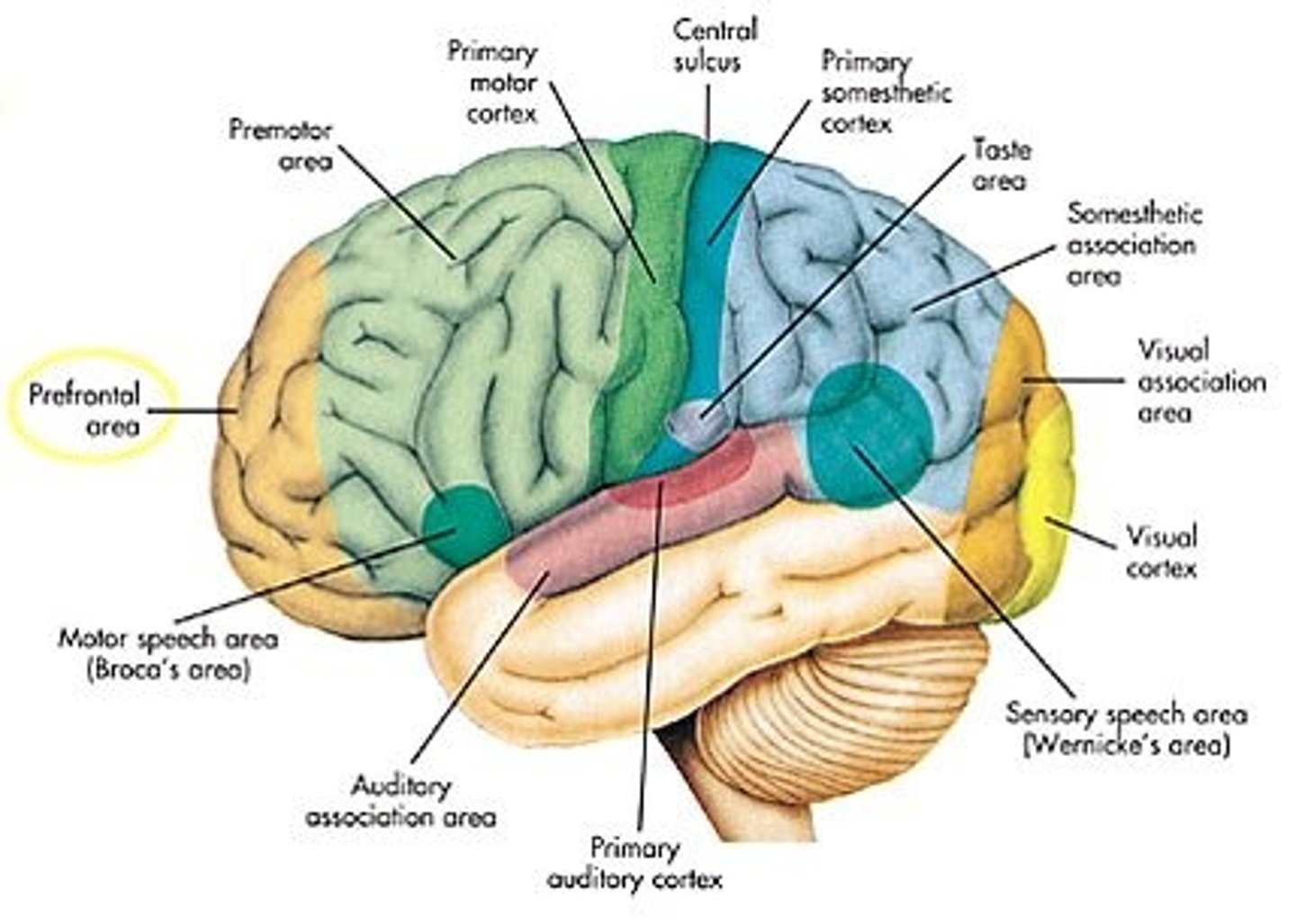
Functional Topography
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
Primary sensory cortex general function
•discriminate qualities of sensory information (basic processing)
Sensory association cortex general function
•complex analysis of sensation from thalamus and primary sensory areas (higher level processing & identifying)
Primary motor cortex general function
selective motor control
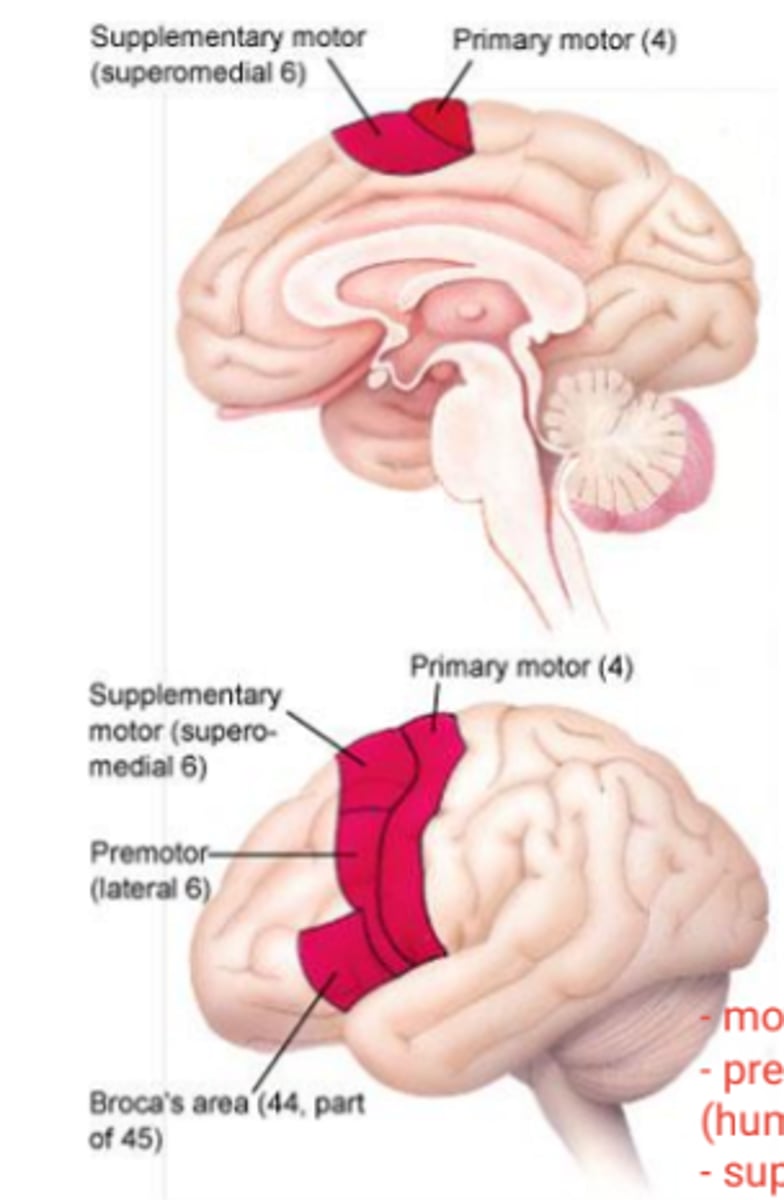
Motor planning areas general function
organizes movements
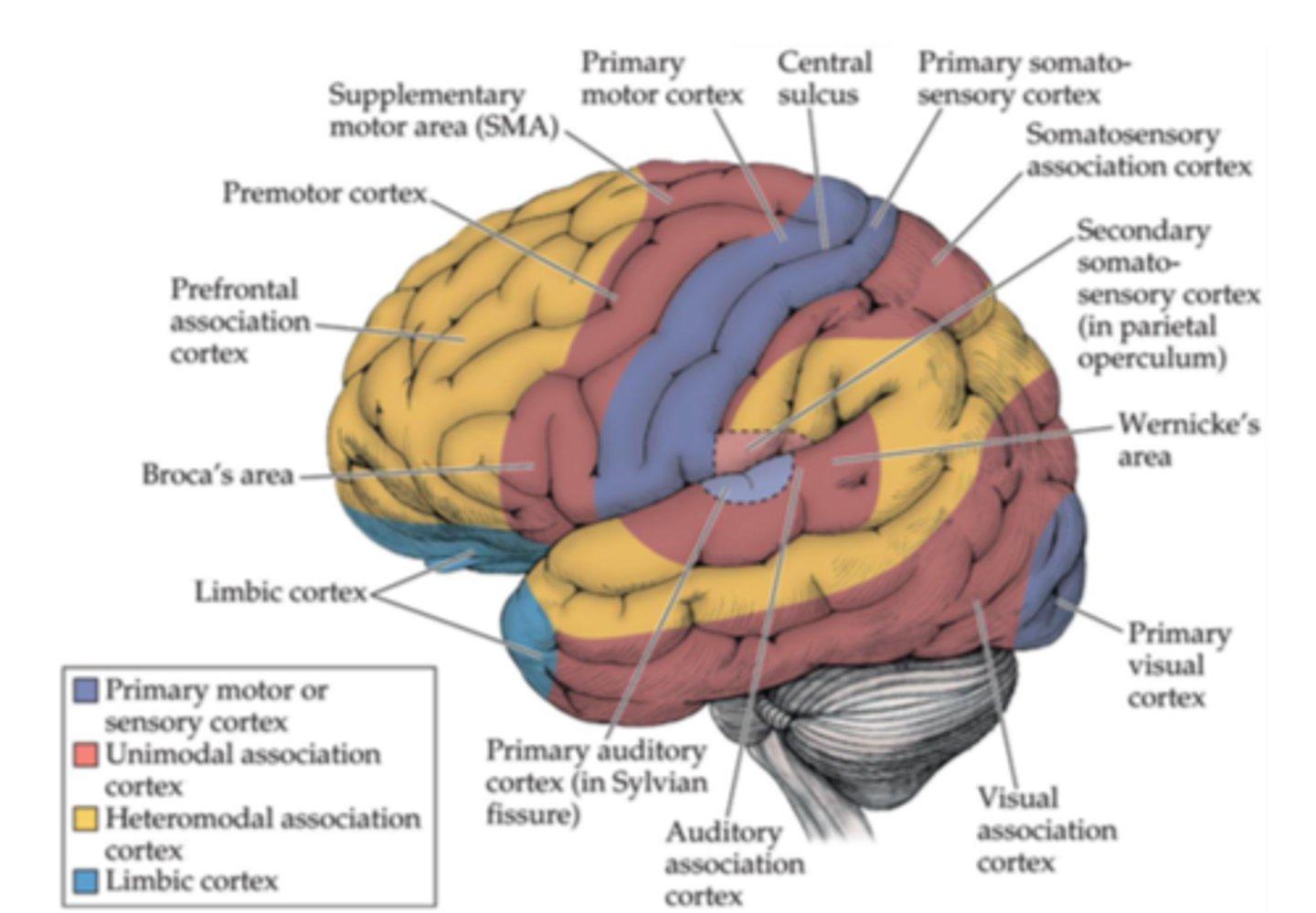
Association cortex general function
controls behavior, interprets sensation, processes emotions and memory
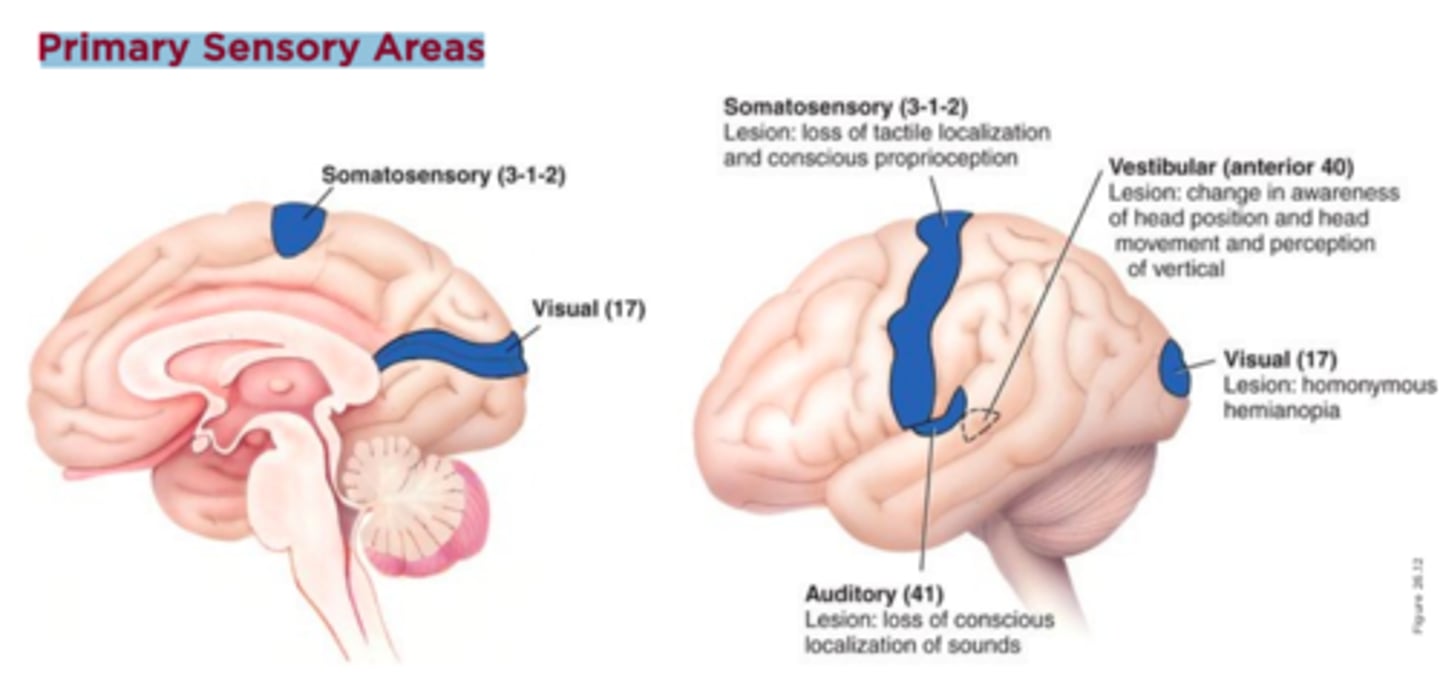
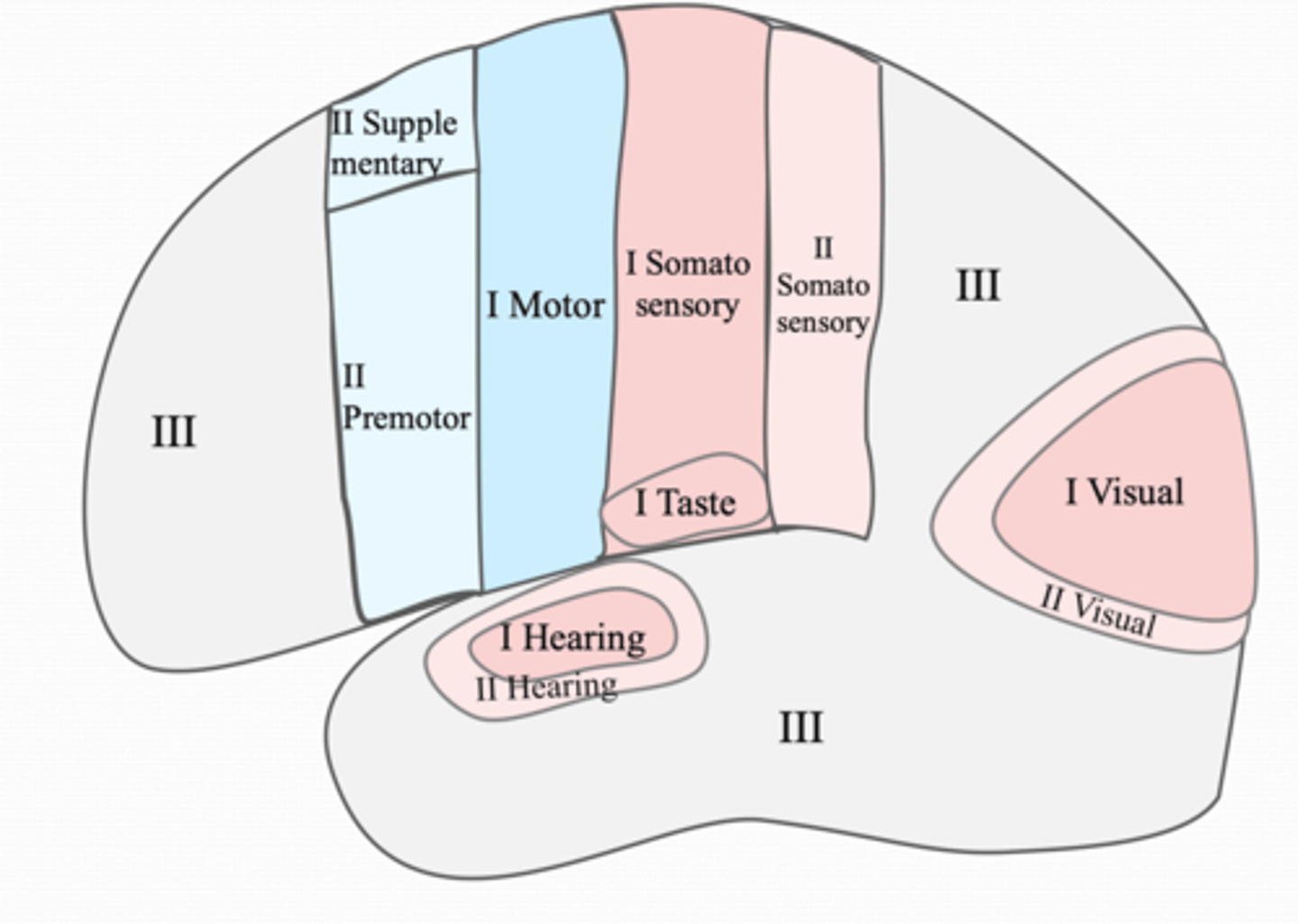
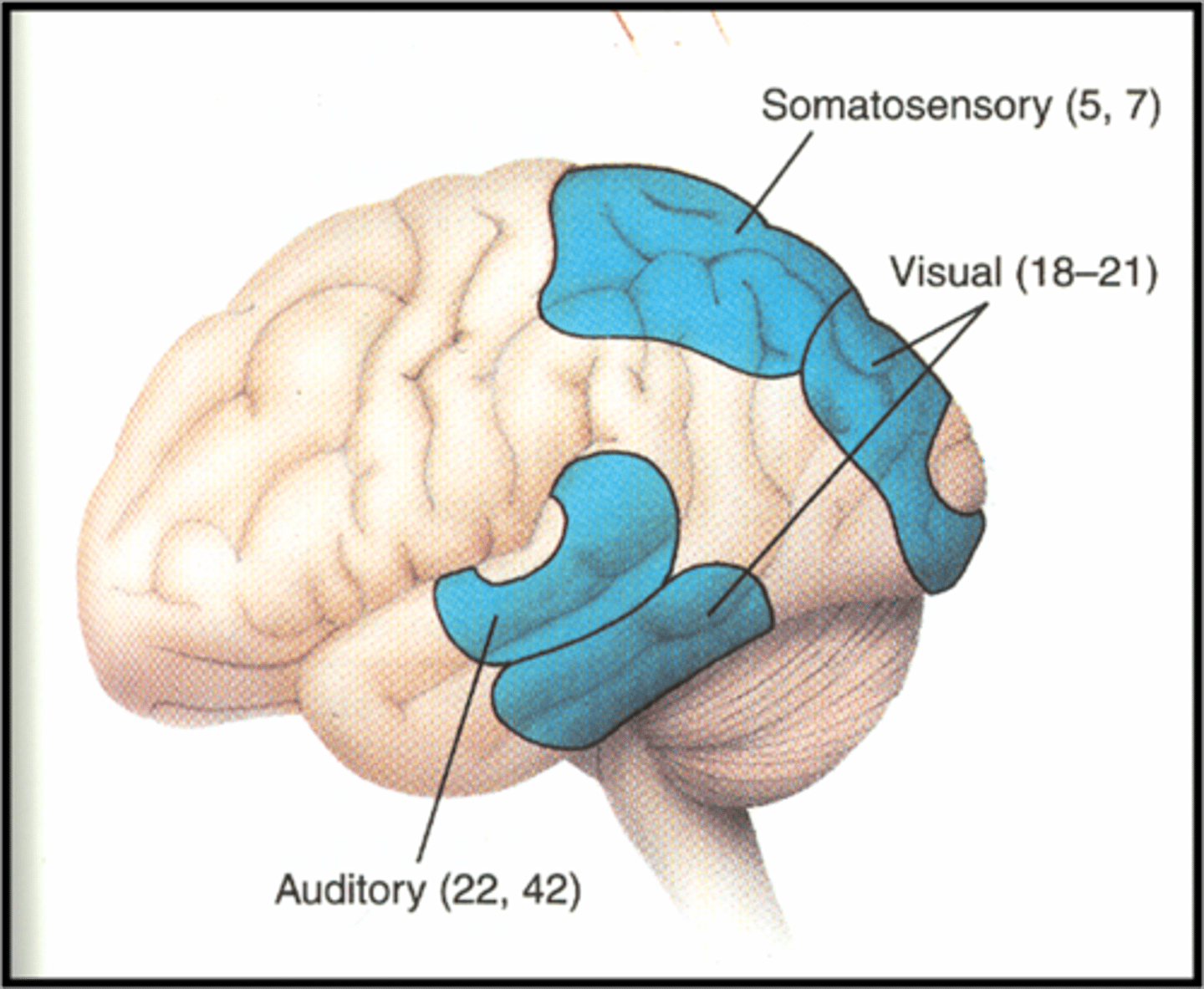
Primary Sensory Areas include
primary somatosensory
primary auditory
primary visual
primary vestibular
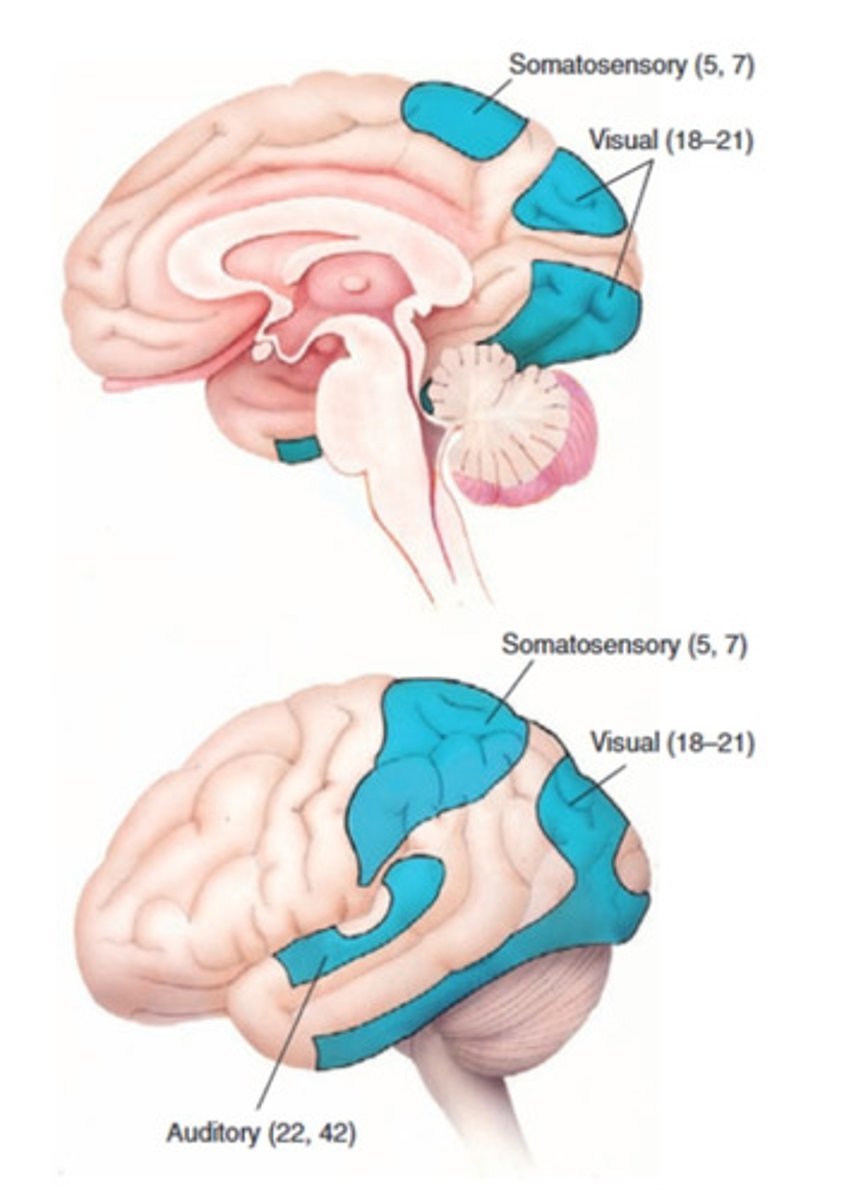
Secondary Sensory Areas include
secondary somatosensory
secondary auditory
secondary visual
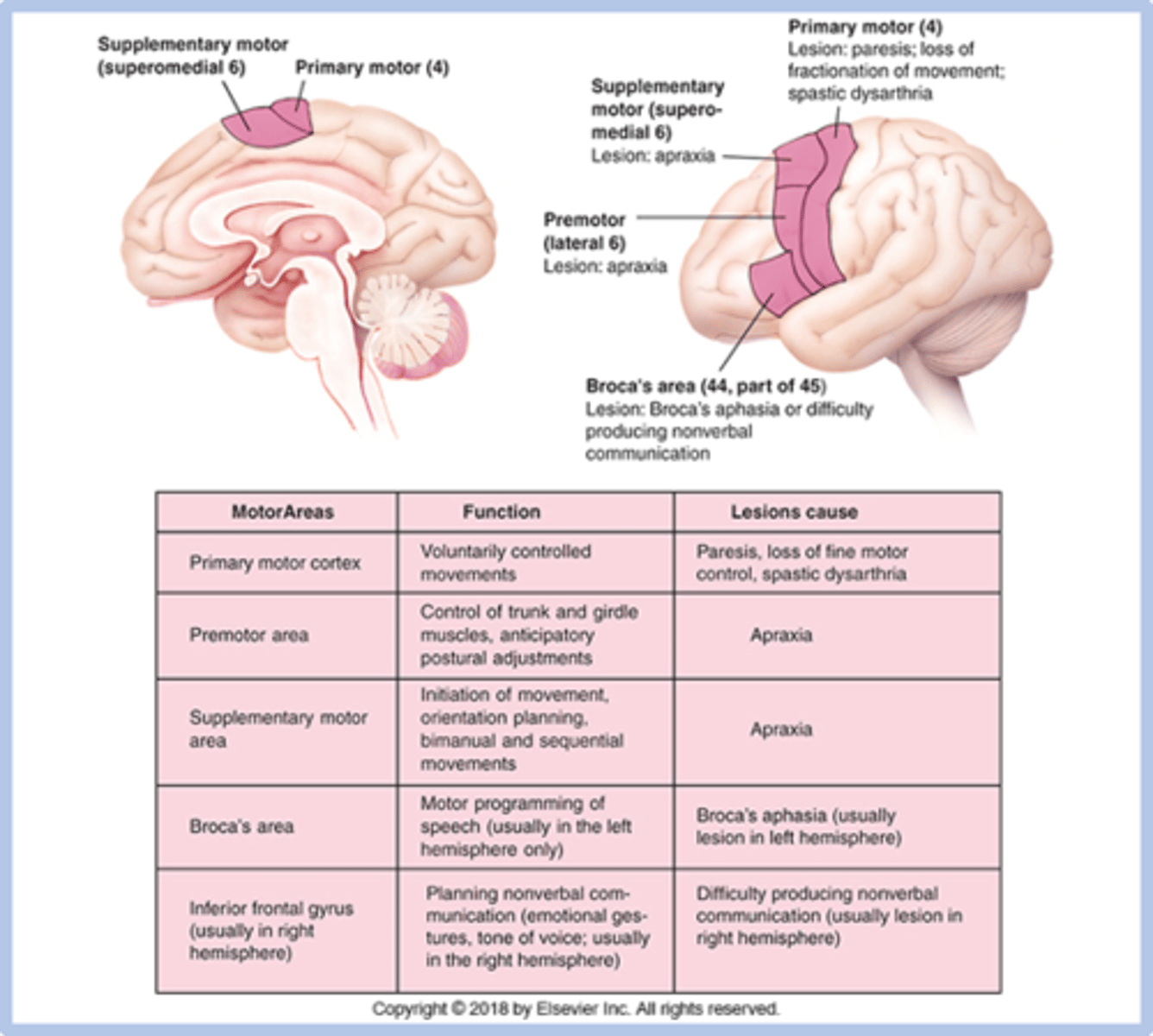
Motor planning areas include
premotor, supplementary motor, Brocas, Area corresponding to Broca's in the opposite hemisphere
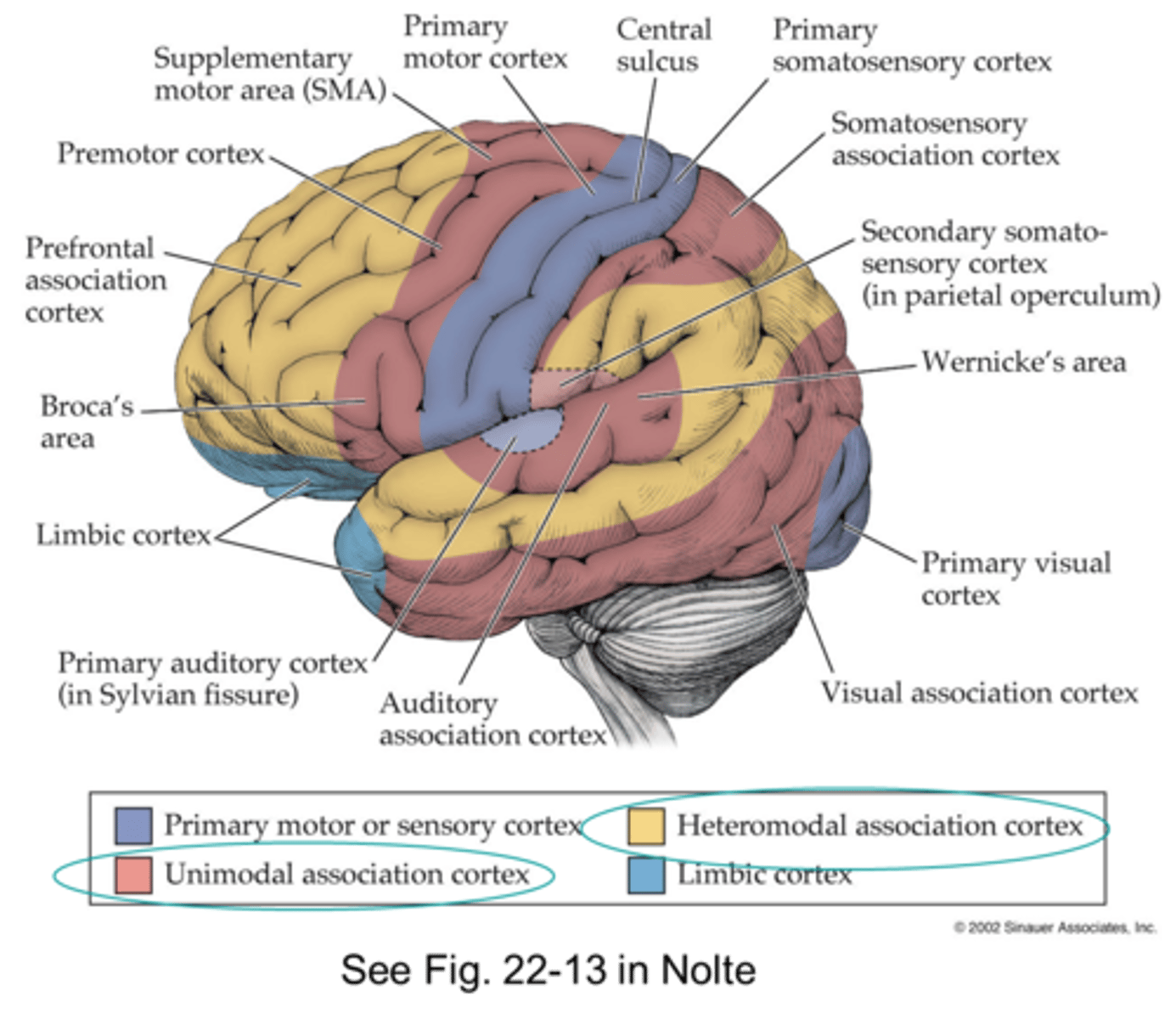
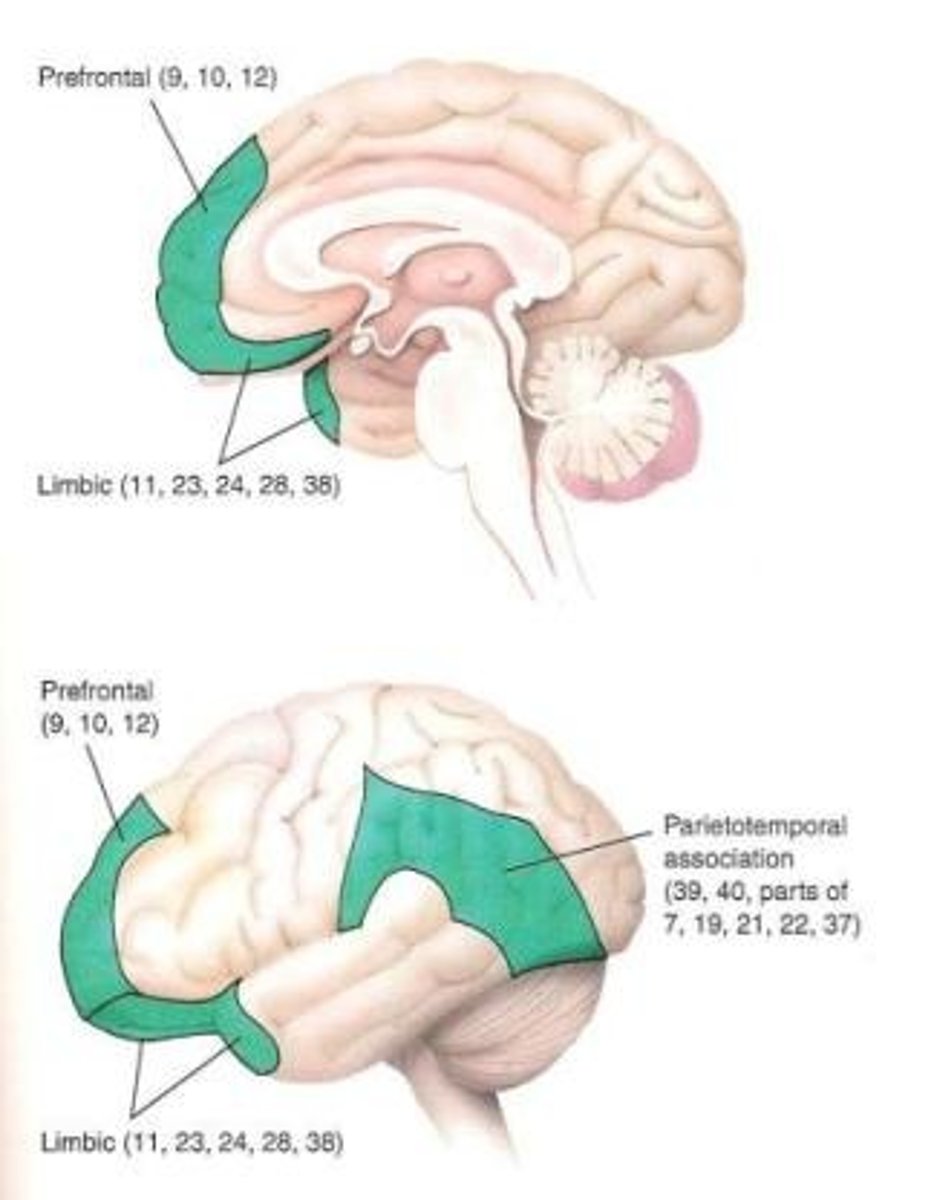
Association cortex includes
Prefrontal
Parietotemporal
Limbic
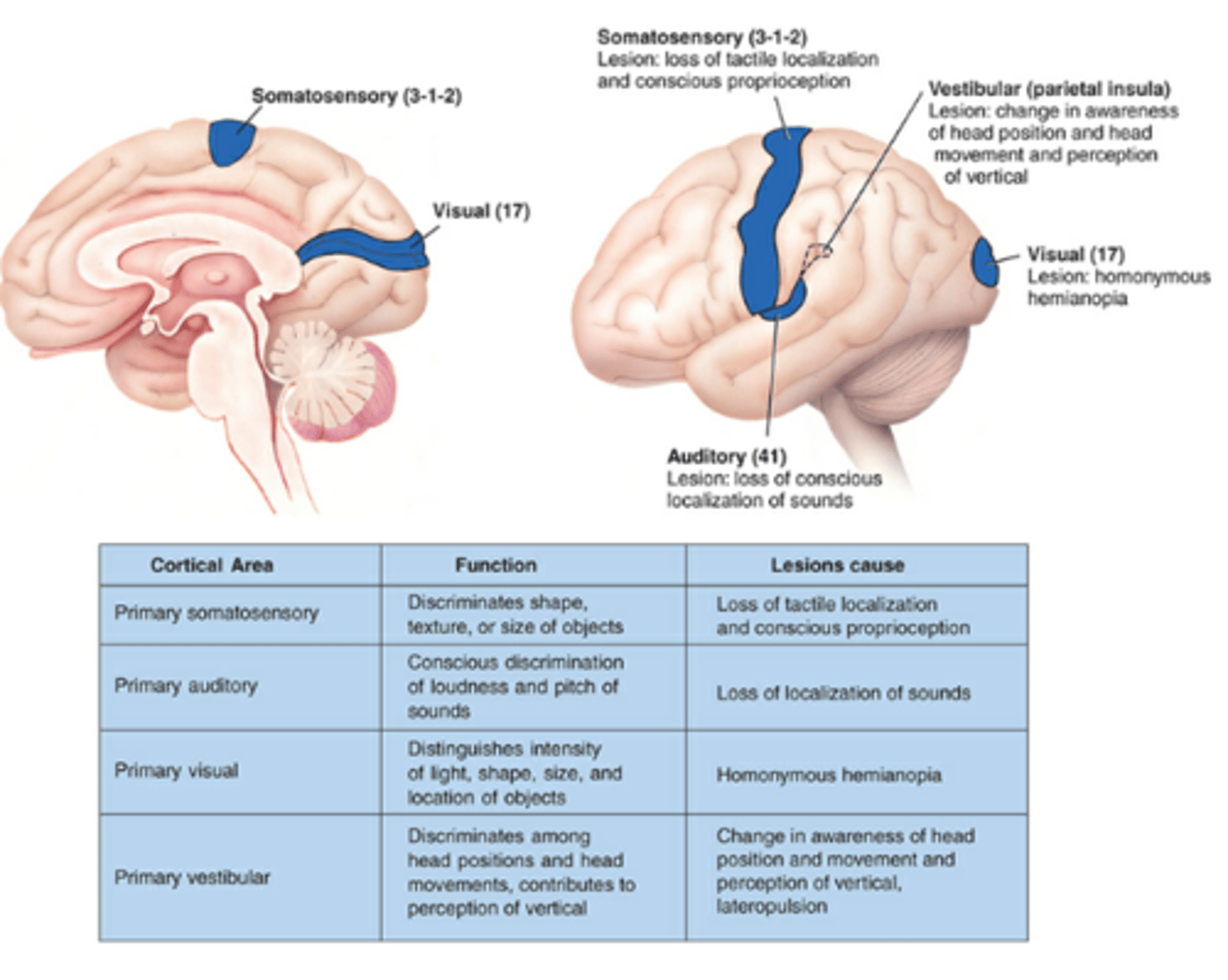
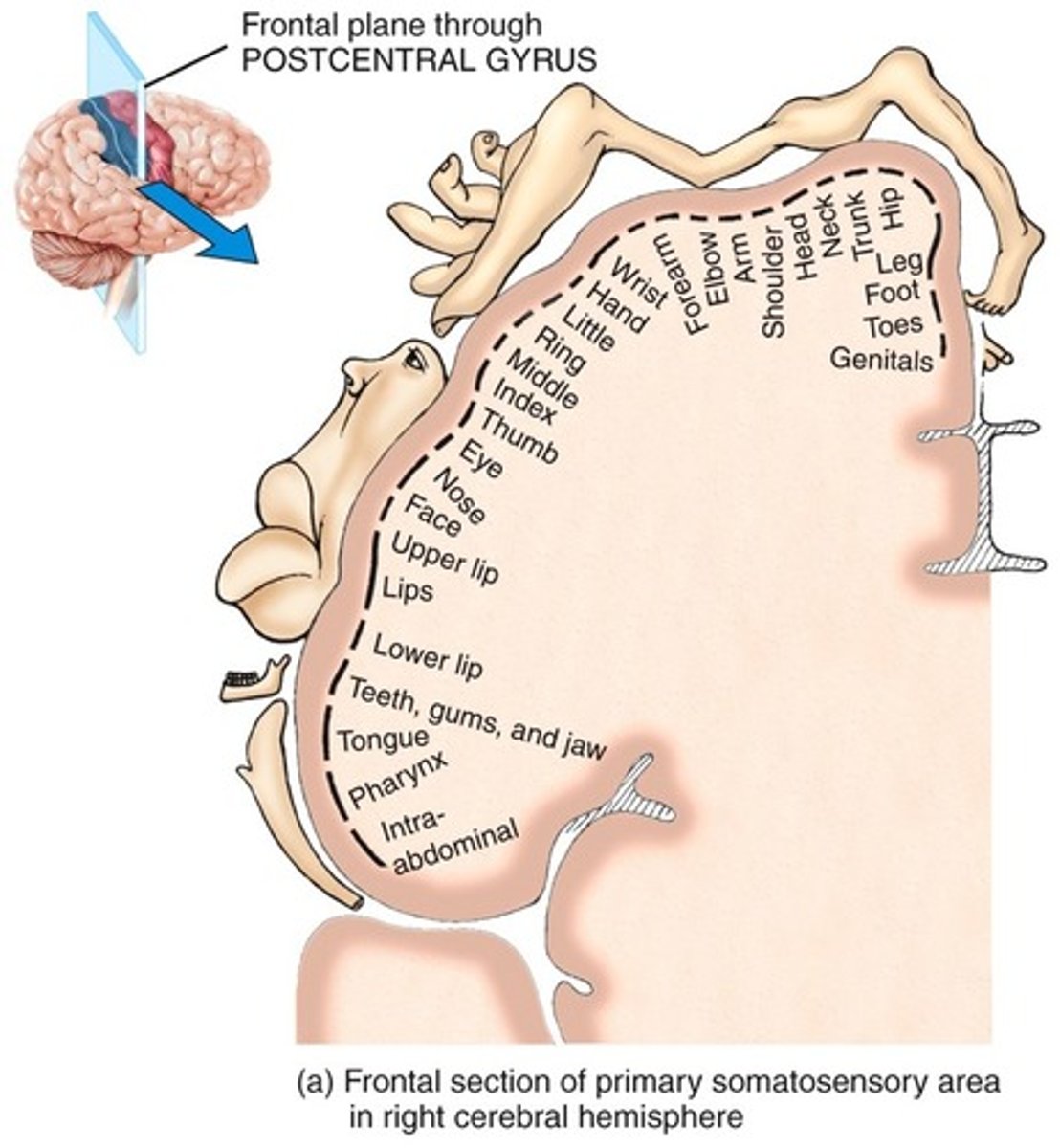
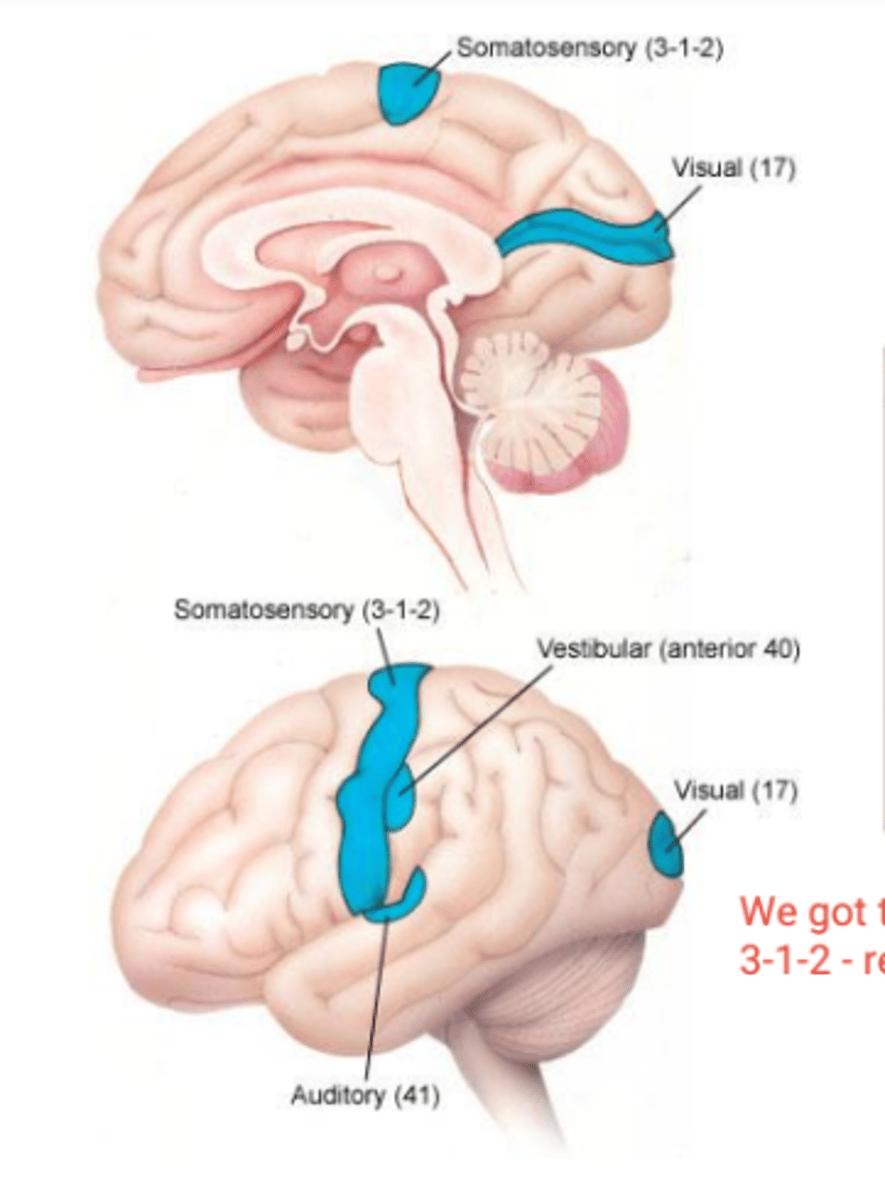
Primary somatosensory area function
discriminates shape, texture, size of object
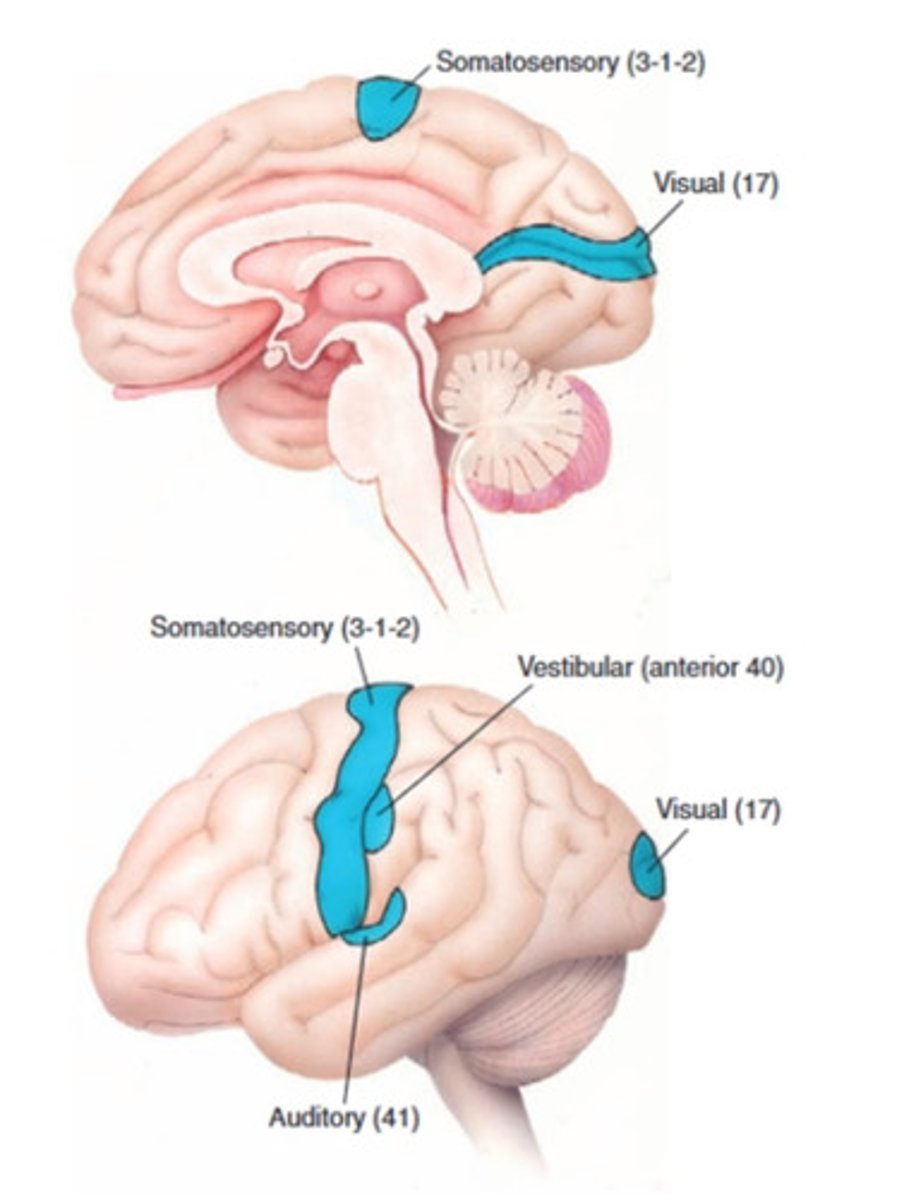
Primary somatosensory area lesion
loss of tactile localization and conscious proprioception
(impairs ability to discriminate intensity or assess quality)
Primary somatosensory area lesion -not affected significantly
Crude awareness and thermal stimuli (because it occurs in the thalamus)
Nociception (Pain): information is also processed in sensory association cortex
Primary somatosensory area receives
•Receives tactile, proprioceptive, and pain/temperature
Primary auditory area function
conscious discrimination of loudness and pitch of sounds
Primary auditory area lesion
loss of localization of sounds
Primary auditory cortex location
-lateral fissure on adjacent superior temporal gyrus
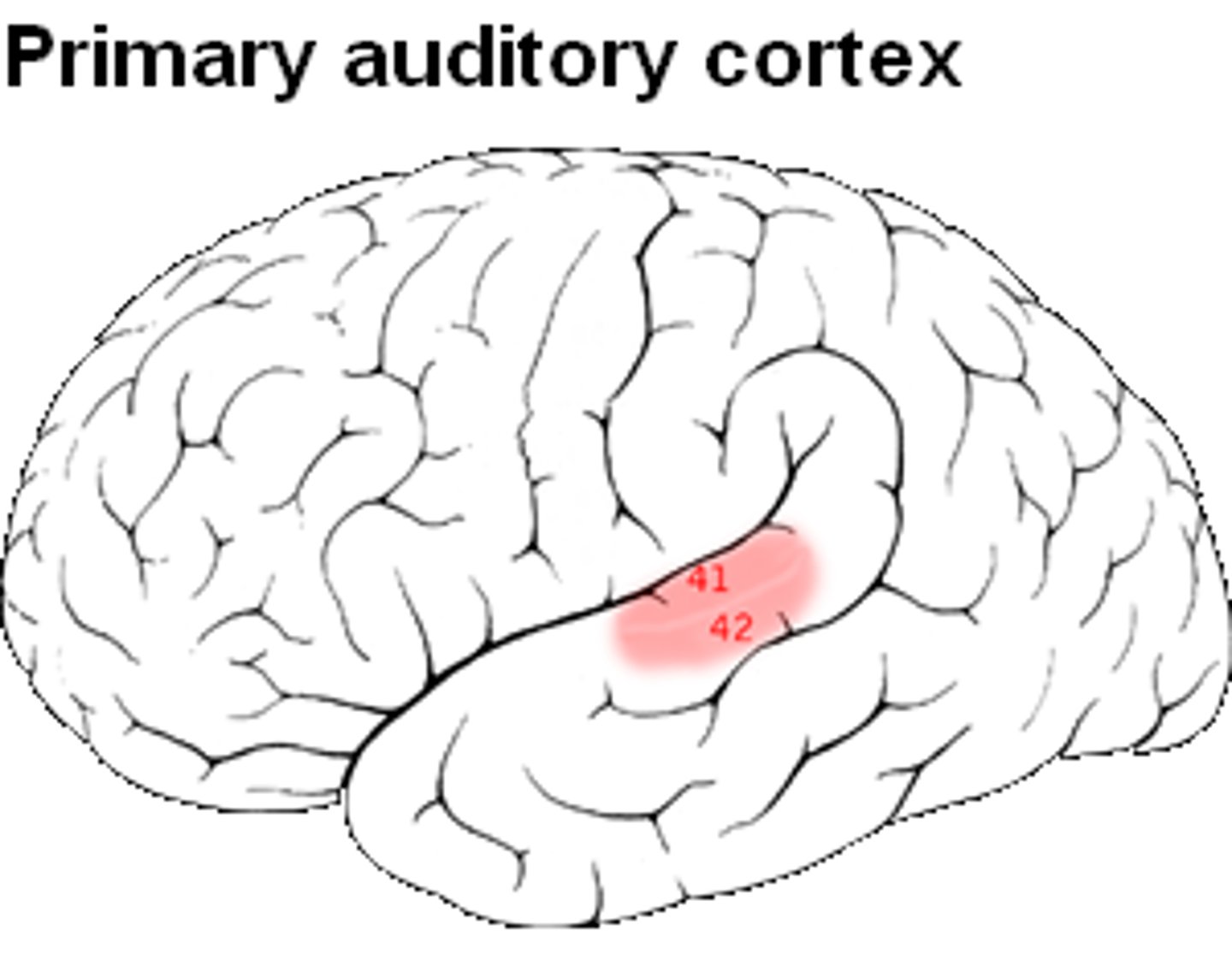
Primary auditory cortex receives info from
the cochlea of both ears
Primary auditory cortex
•Low frequency:
•High frequency:
•Low frequency: anterolateral
•High frequency: posteromedial
Primary visual area function
distinguishes intensity of light, shape, size, and location of objects
Primary visual area receives information from
•Receives information from lateral geniculate body (geniculocalcarine tract)
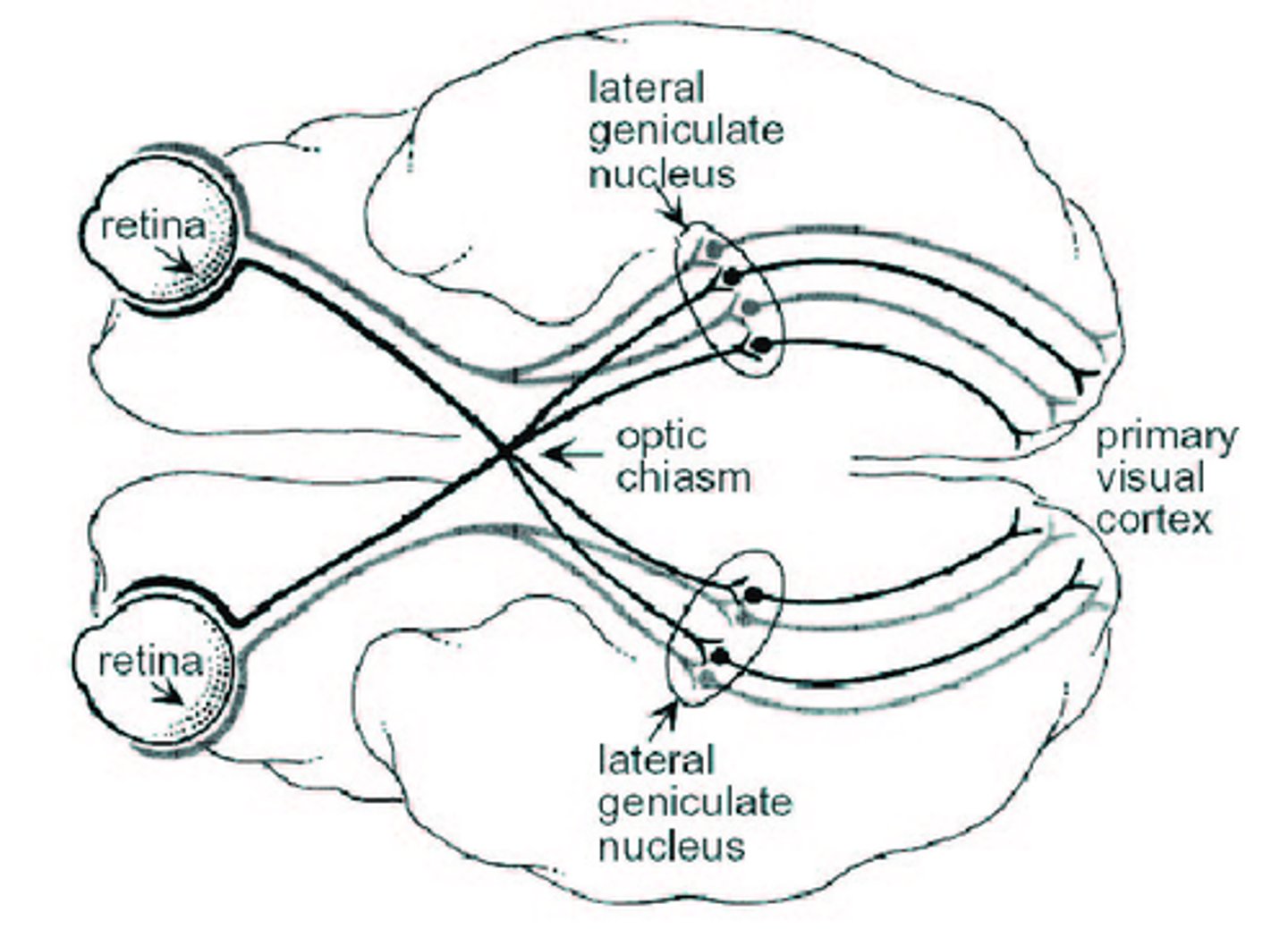
Primary visual area location
-within calcarine sulcus and adjacent gyri
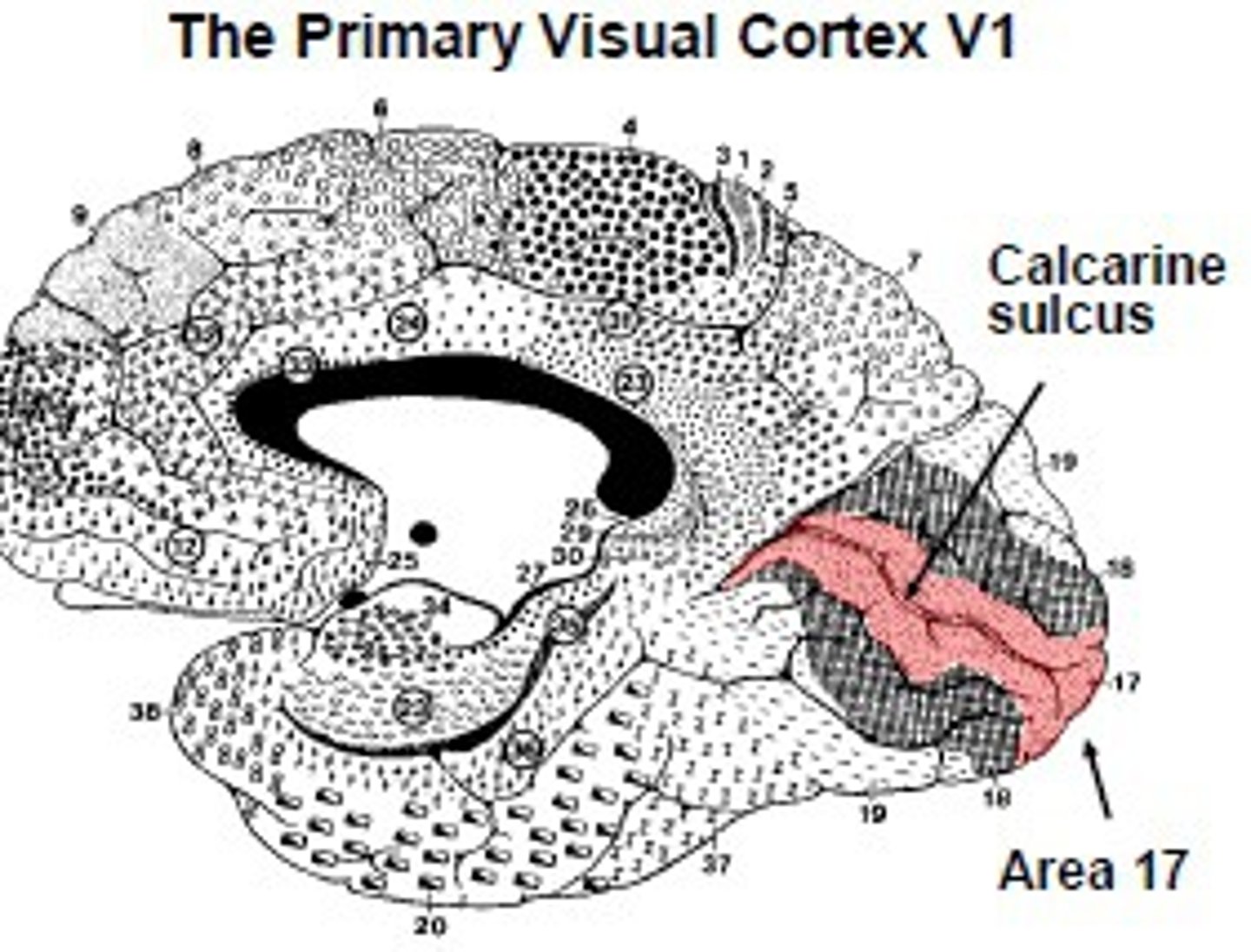
•Upper field of vision: _____ wall of the sulcus
•Lower field of vision: _____ wall of the sulcus
•Upper field of vision: lower wall of the sulcus
•Lower field of vision: upper wall of the sulcus
Primary visual area lesion
homonymous hemianopsia
•blindness of the opposite visual field
Primary vestibular area function
discriminates among head positions and head movements, contributes to perception of vertical
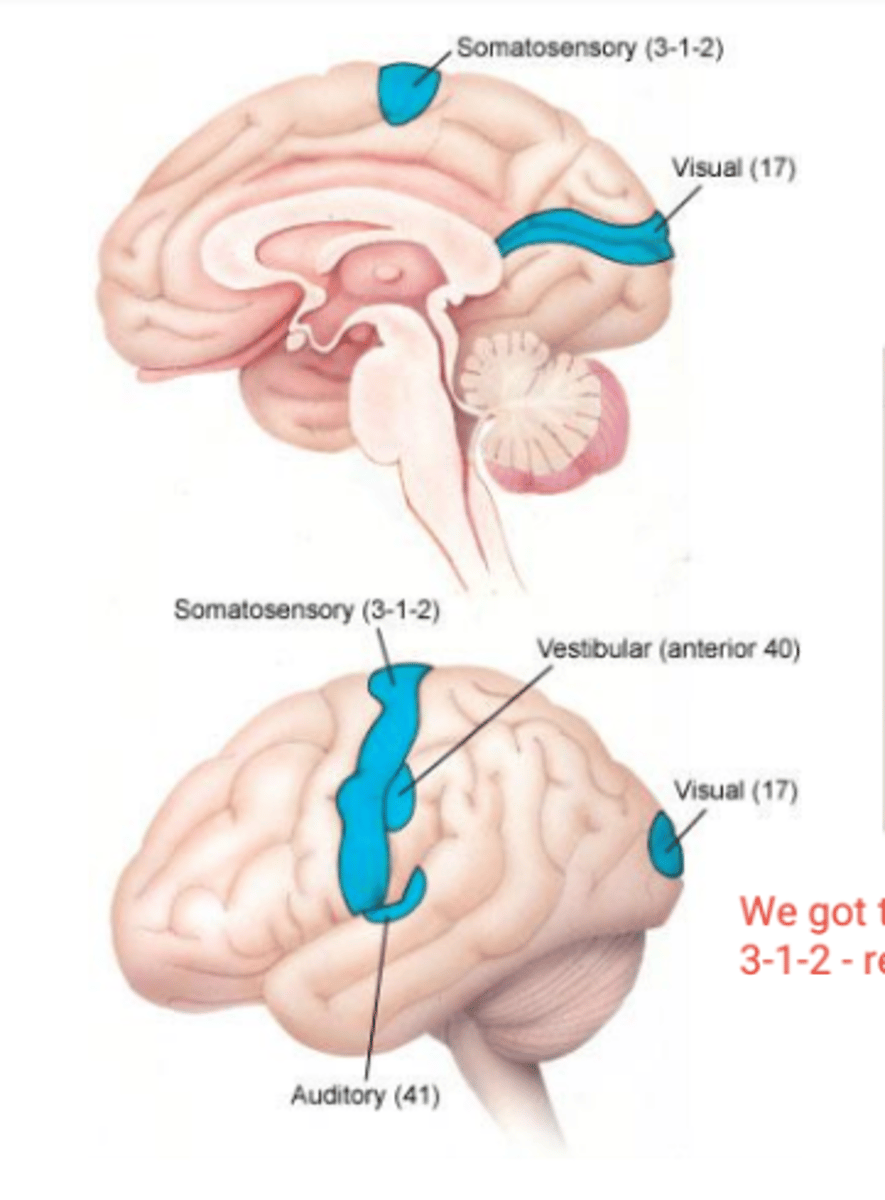
Primary vestibular area location
-posterior to primary somatosensory cortex

Primary vestibular area lesion
change in awareness of head position and movement and perception of vertical (= lateropulsion)
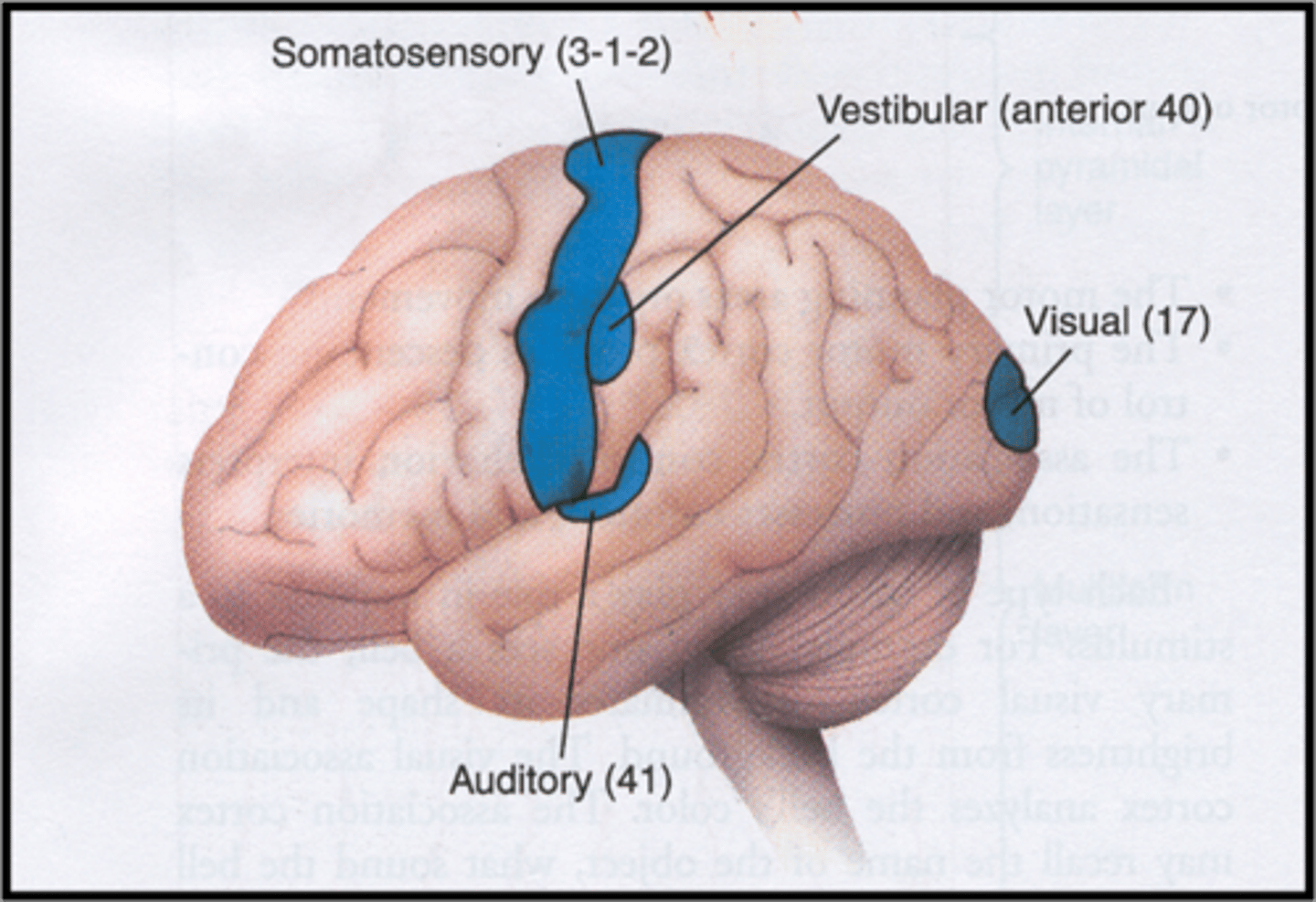
Secondary somatosensory area function
stereognosis (identification of object) and memory of the tactile and spatial environment
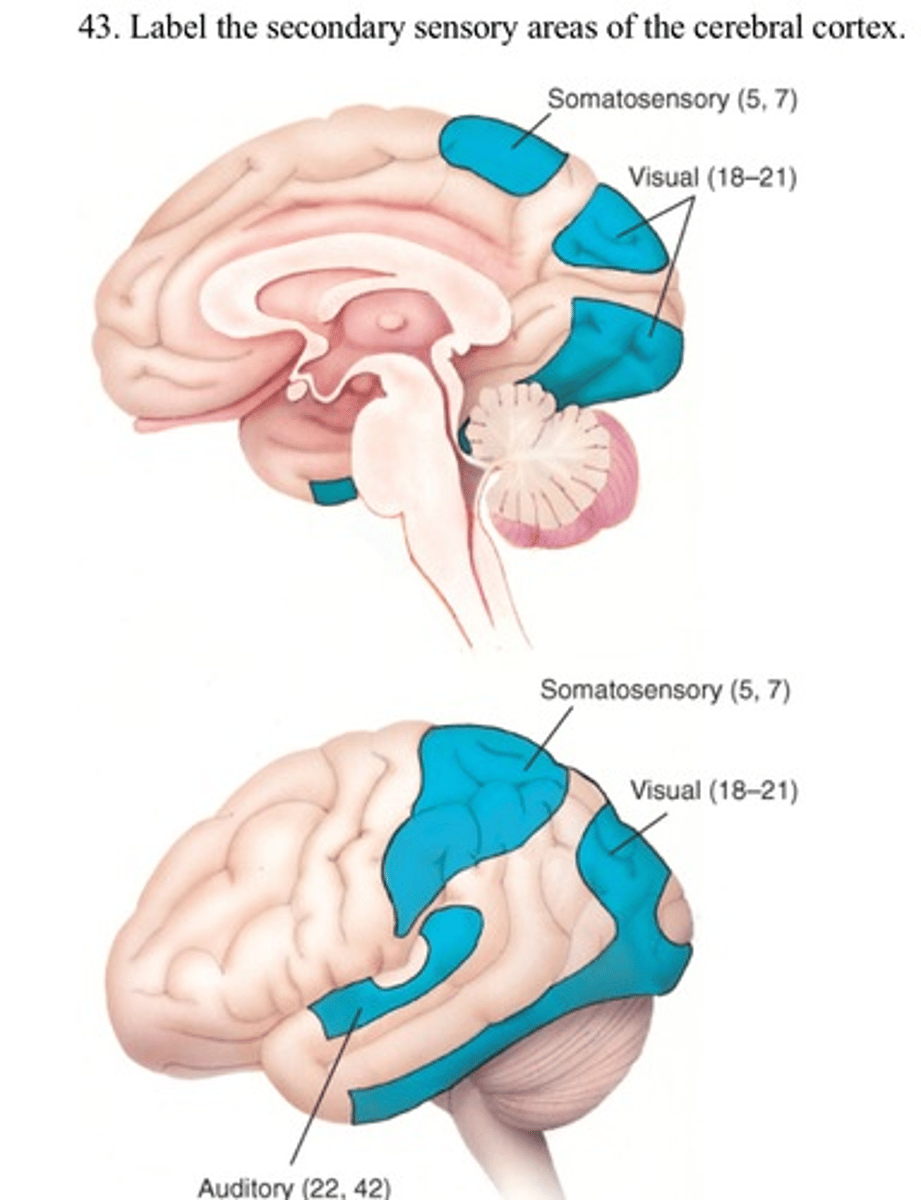
Secondary somatosensory area location
-superior aspect of parietal lobe posterior to SI
Secondary somatosensory area lesion
Astereognosis-
inability to discriminate shape and size by touch and the inability to recognize objects by touch
(& cortical neglect)
Secondary visual area function
analysis of motion, color; recognition of visual objects; understanding of visual spatial relationships; control of visual fixation
(& recognition of faces)
Secondary visual area location
surrounds primary visual area
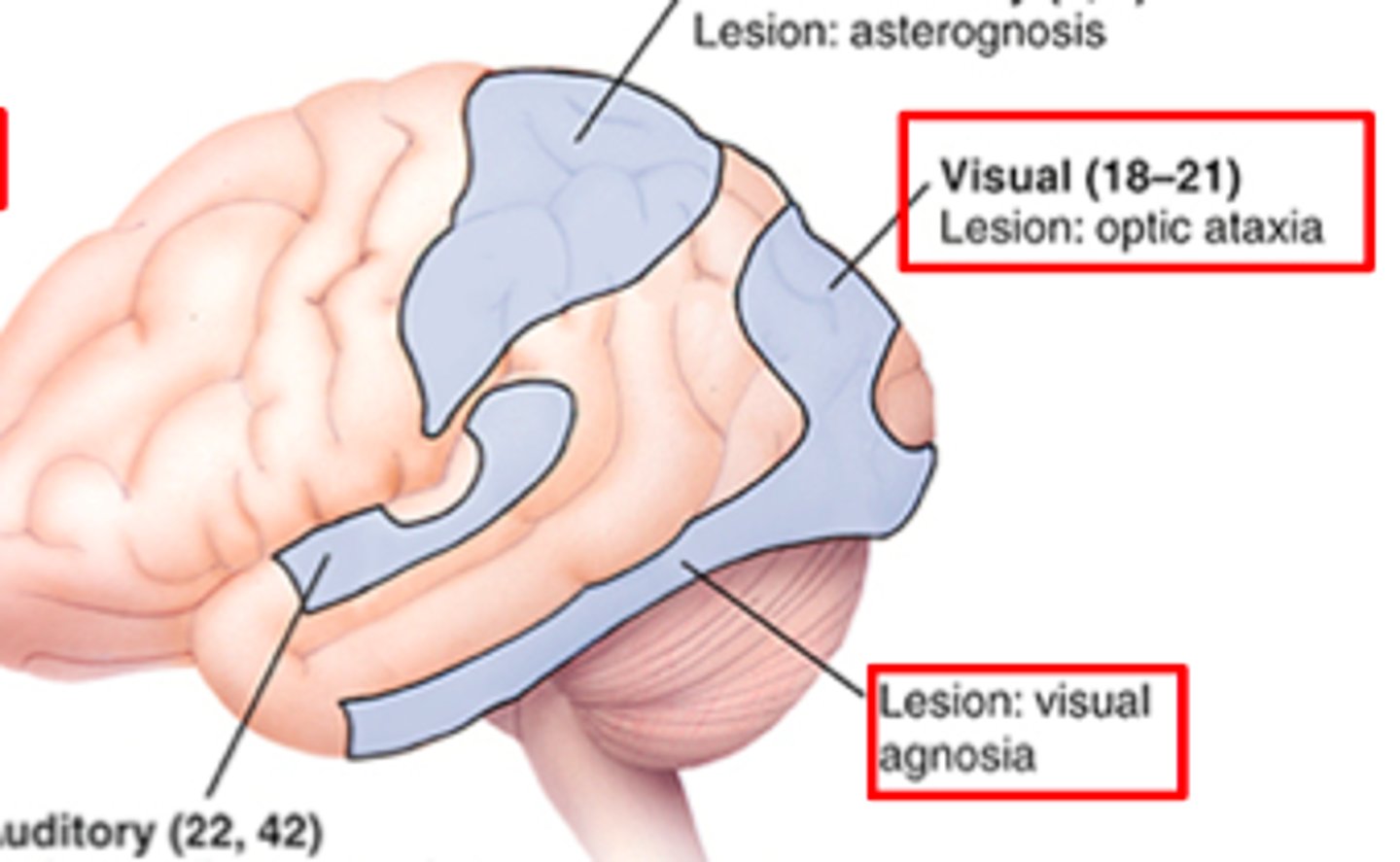
Secondary visual area lesion
–Visual agnosia: inability to recognize objects in the contralateral visual field
–Prosopagnosia: inability to recognize people’s faces – usually associated with bilateral damage to the inferior visual association areas
Secondary auditory area function
classification of sounds (as language, music, or noise)
Secondary auditory area lesion
auditory agnosia (cannot recognize/ differentiate between sounds)
-Destruction of left auditory association cortex: unable to understand speech
-Destruction of right auditory assoc. cortex: unable to interpret noises
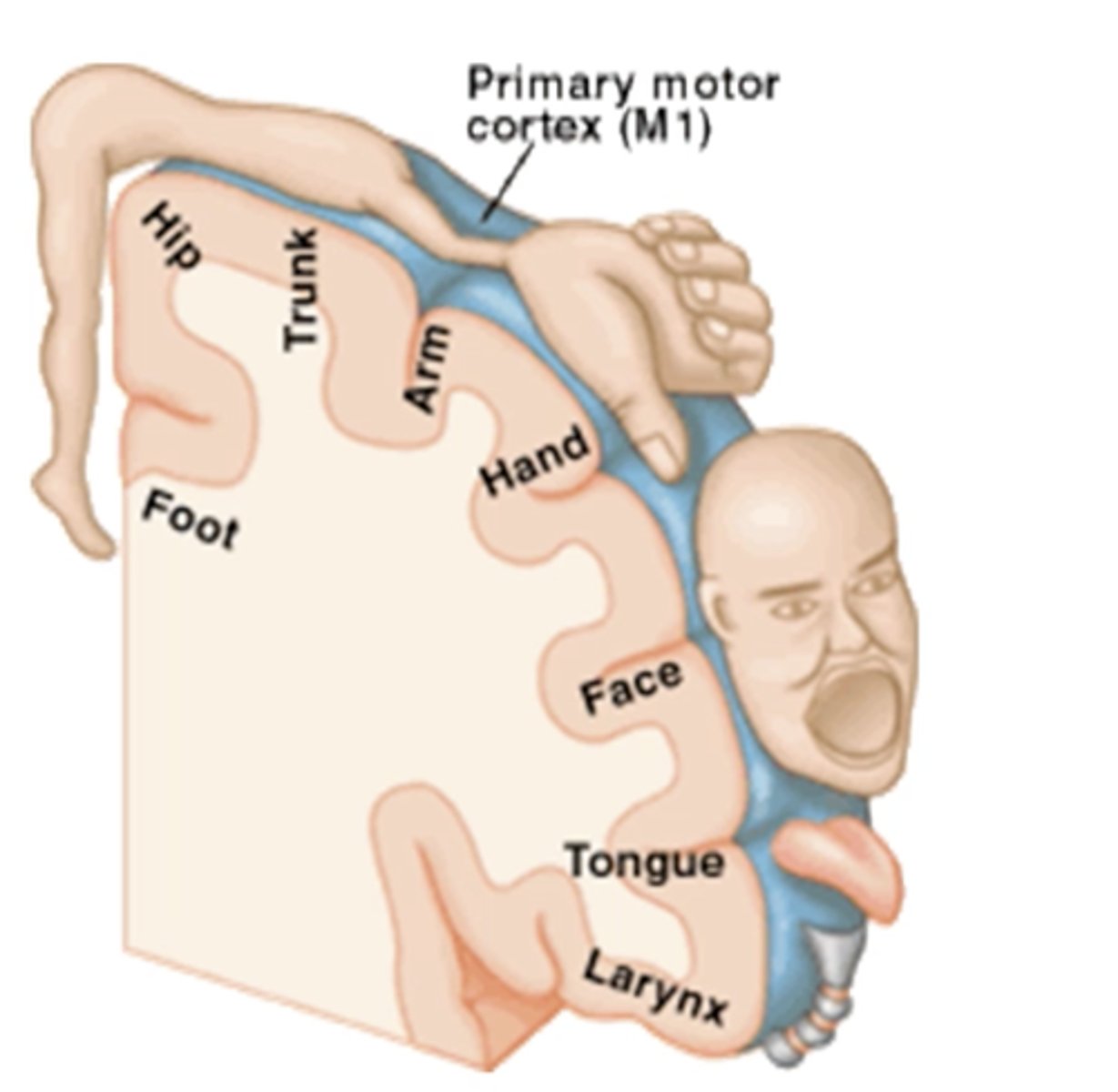
primary motor cortex function (generalized)
selective motor control
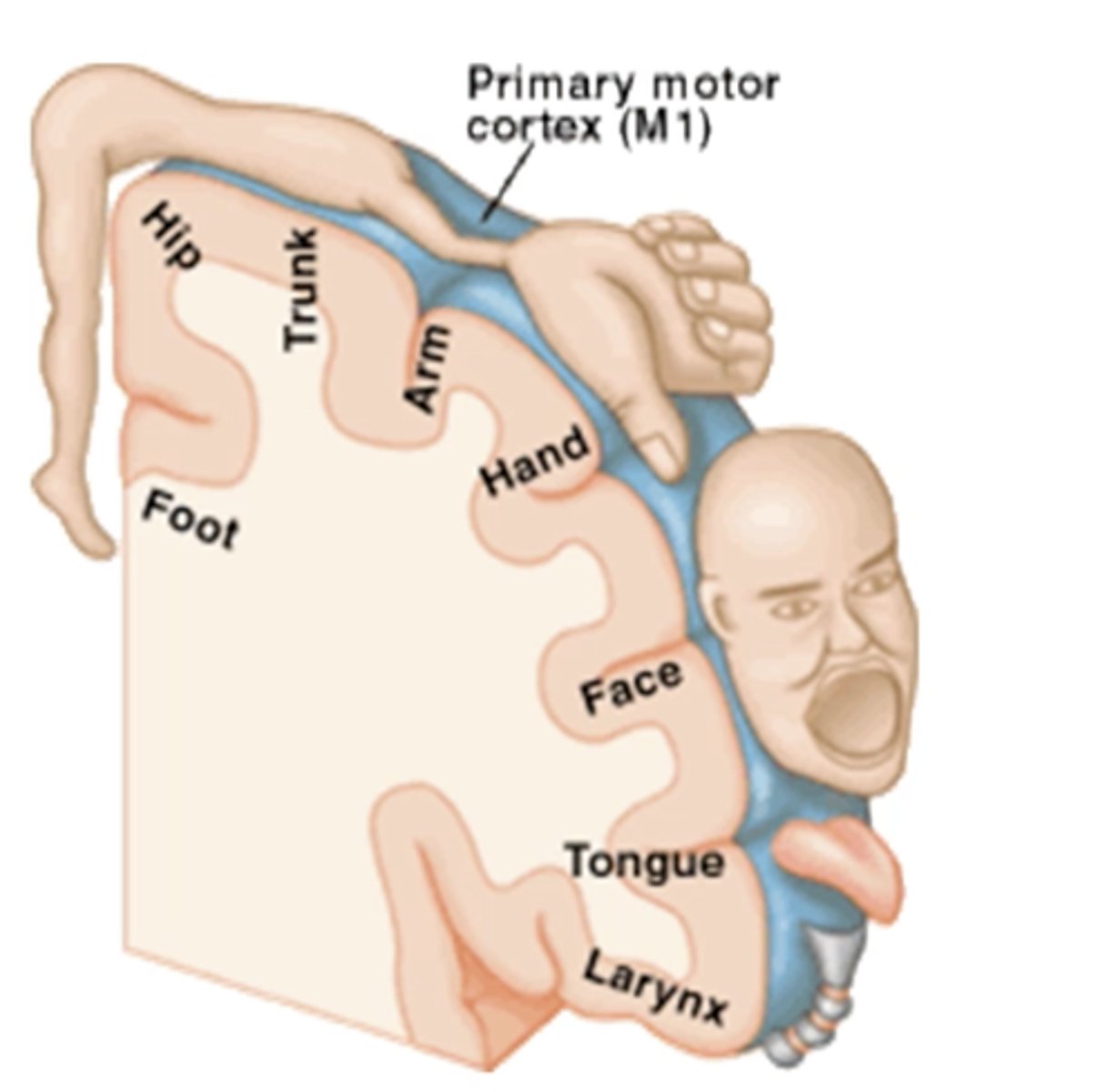
primary motor cortex function (detailed)
-source of many UMN (CorticoBulbar) & controls contralateral movement (CorticoSpinal)
-Fine movements
-Bilateral projections: upper face and back muscles
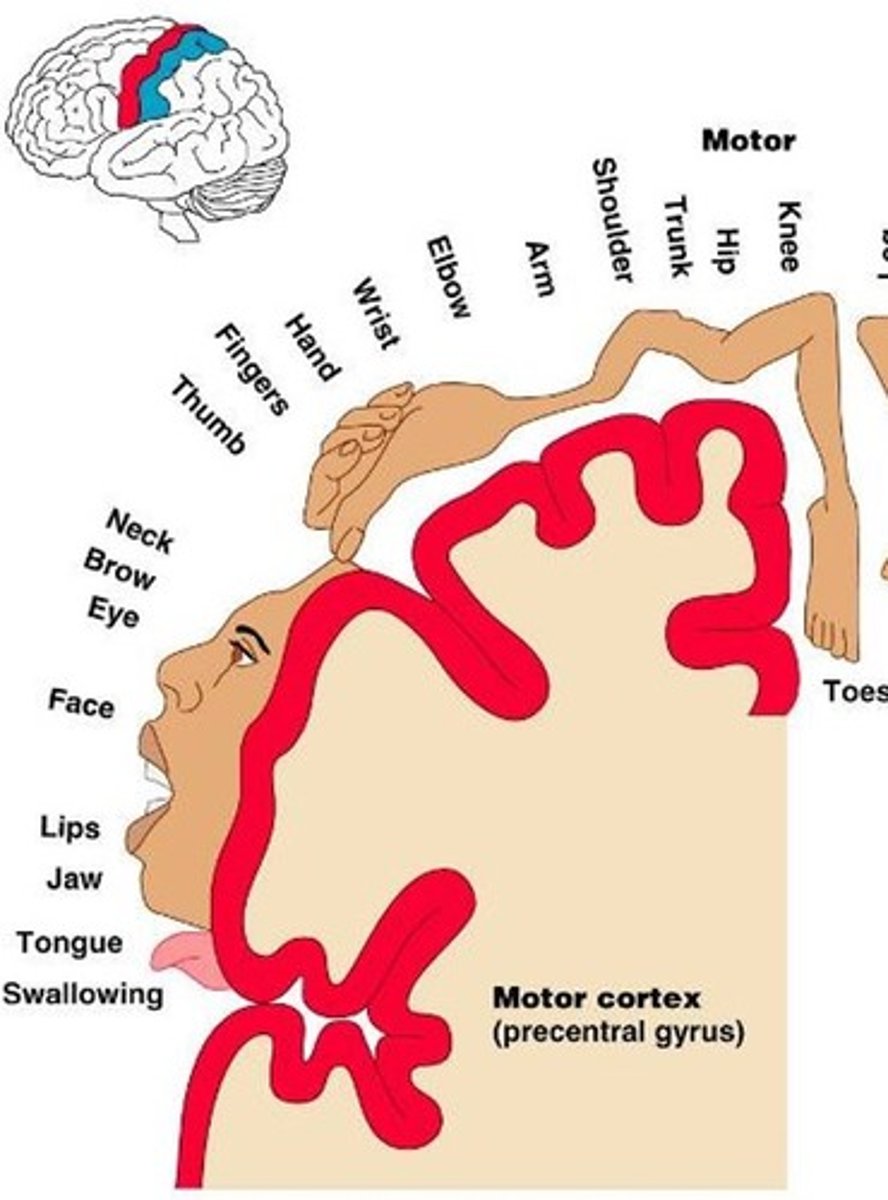
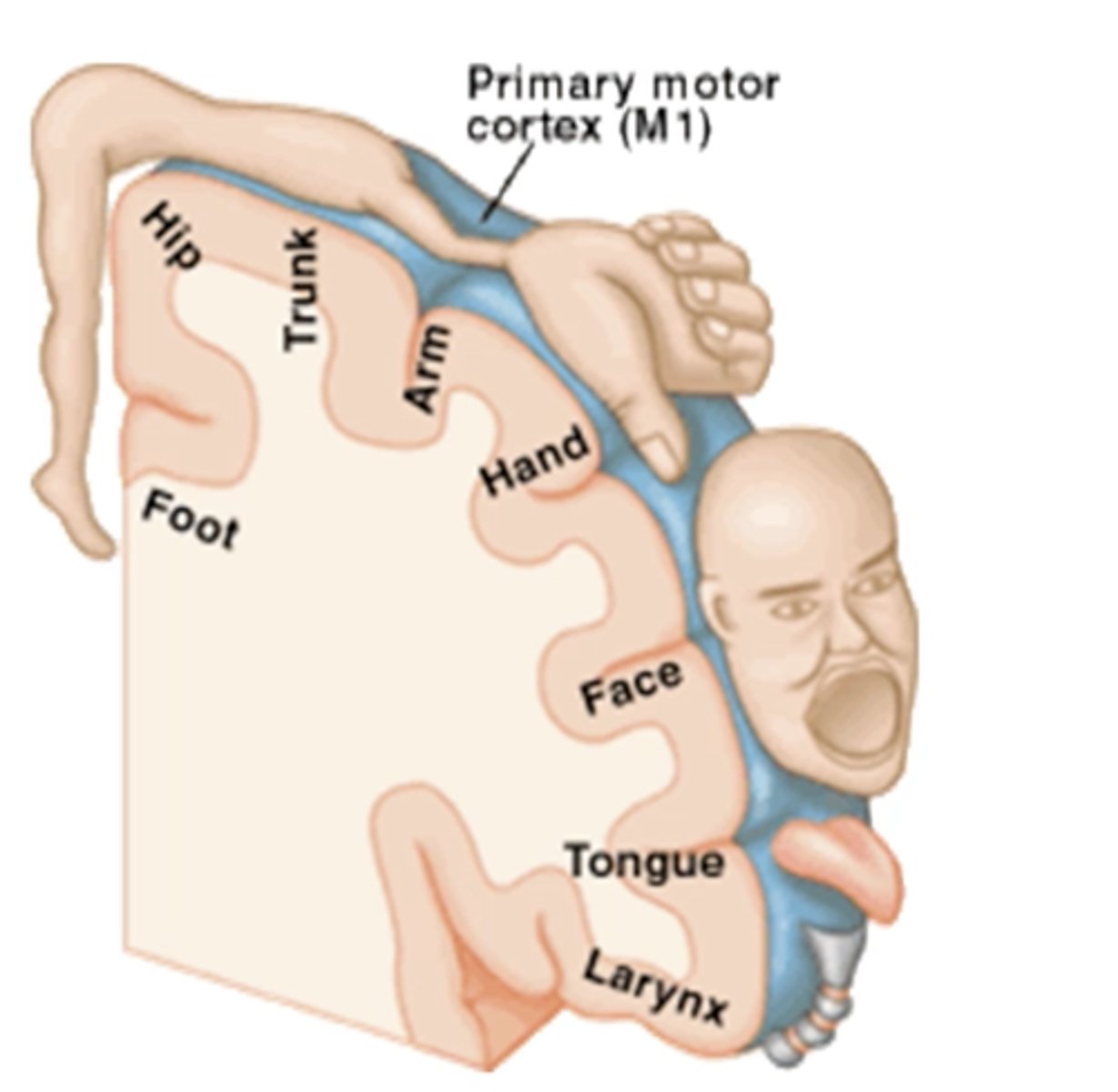
motor homunculus
largest area:
smaller:
largest area for hands and face (fine movements) - smaller representation for trunk and proximal limbs (gross motor)
primary motor cortex lesion (general)
paresis, loss of fine motor control, spastic dysarthria (harsh/awkward speech)
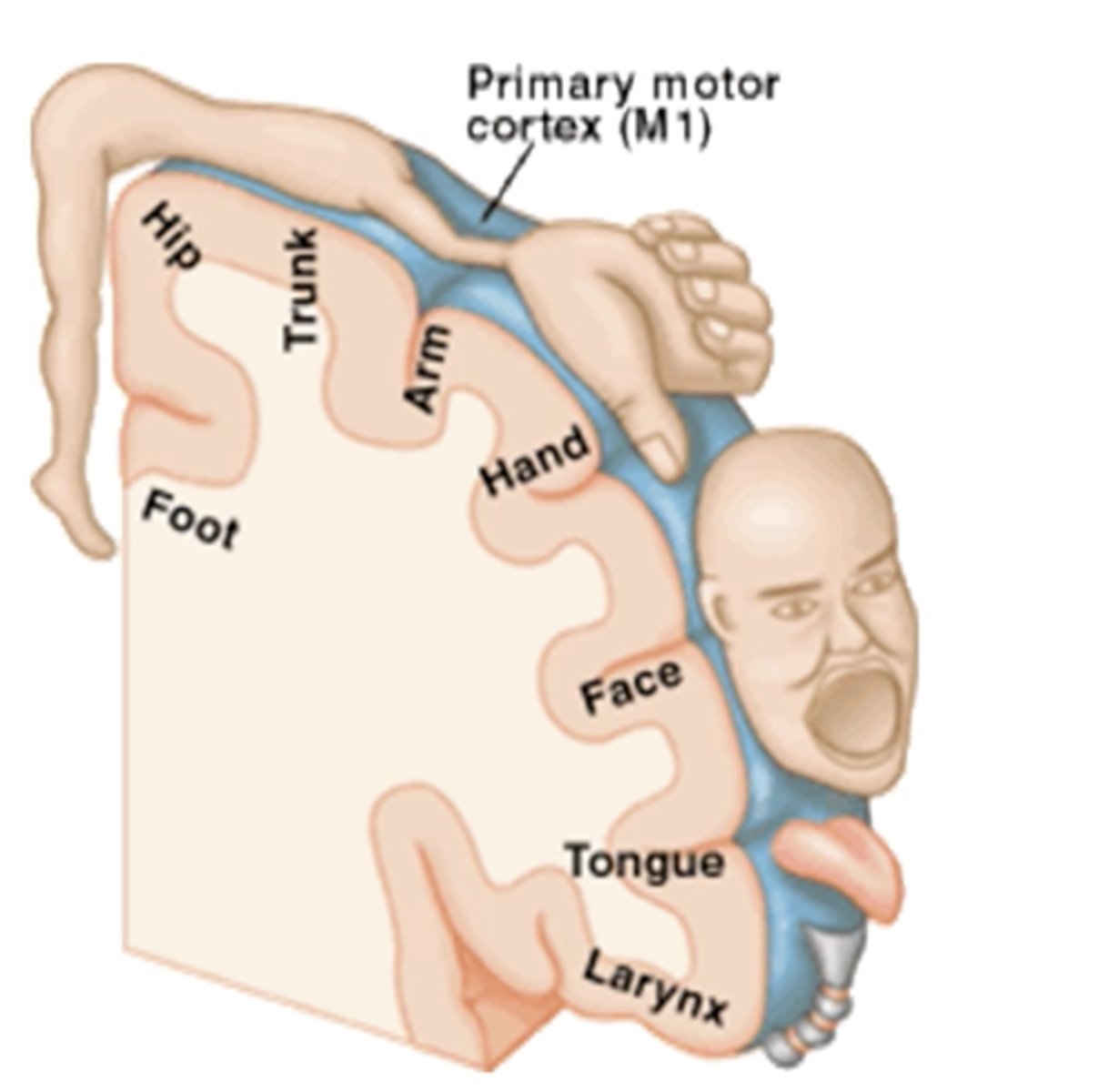
primary motor cortex lesion (detailed)
•Contralateral paresis and loss of fractionation of movement
•Complete destruction: cannot voluntarily move contralateral hand, lower face, and/or foot
•Spastic Dysarthria: speech disorder resulting from spasticity of the muscles used for speaking
(damage to UMN> Harsh, awkward speech)
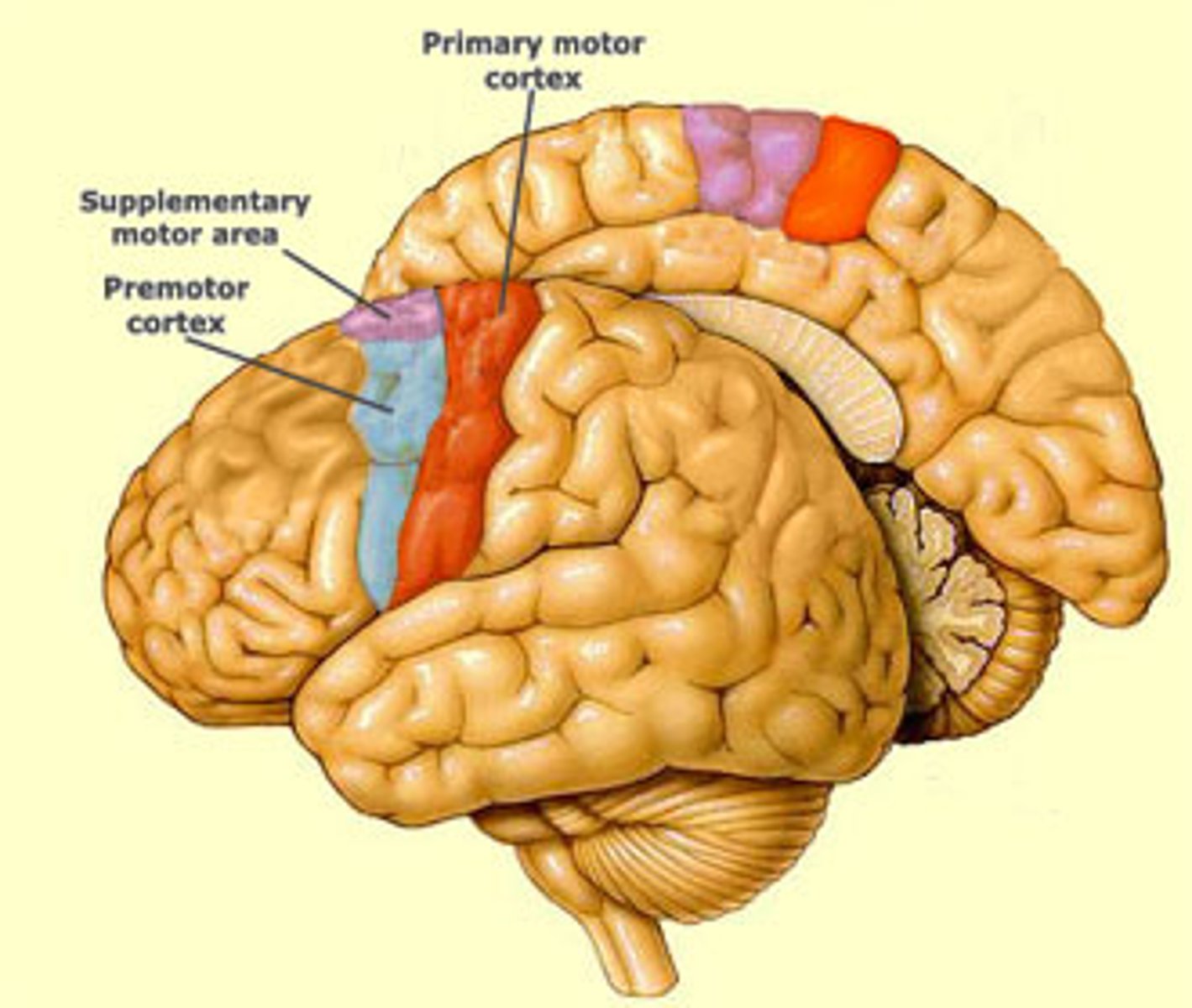
premotor cortex function
control of trunk and girdle muscles, anticipatory postural adjustments
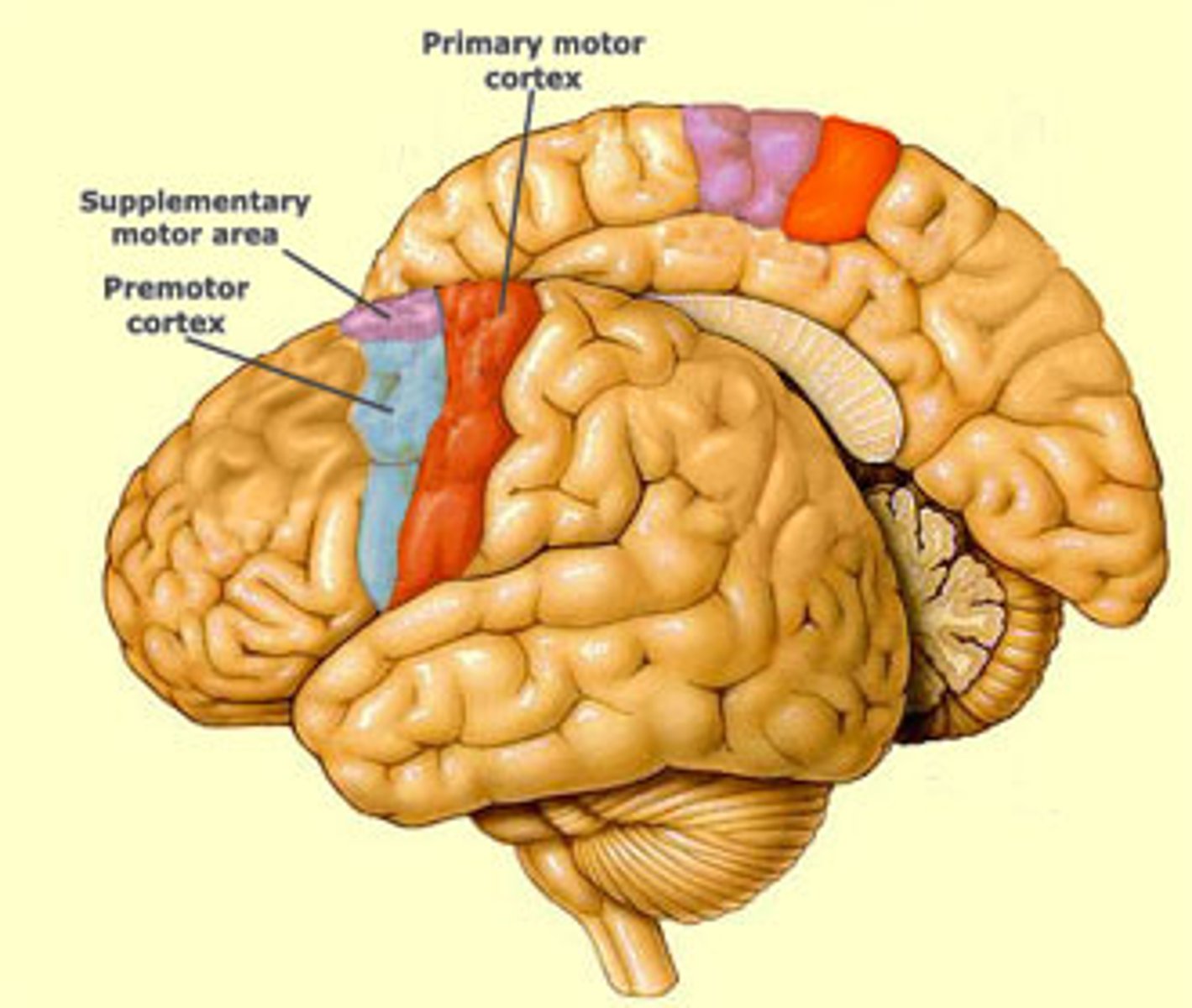
pre motor cortex lesion
apraxia
pre motor cortex location
-anterior to the upper body representation in M1
supplementary motor cortex function
initiation of movement, orientation planning, control of bimanual and sequential movements
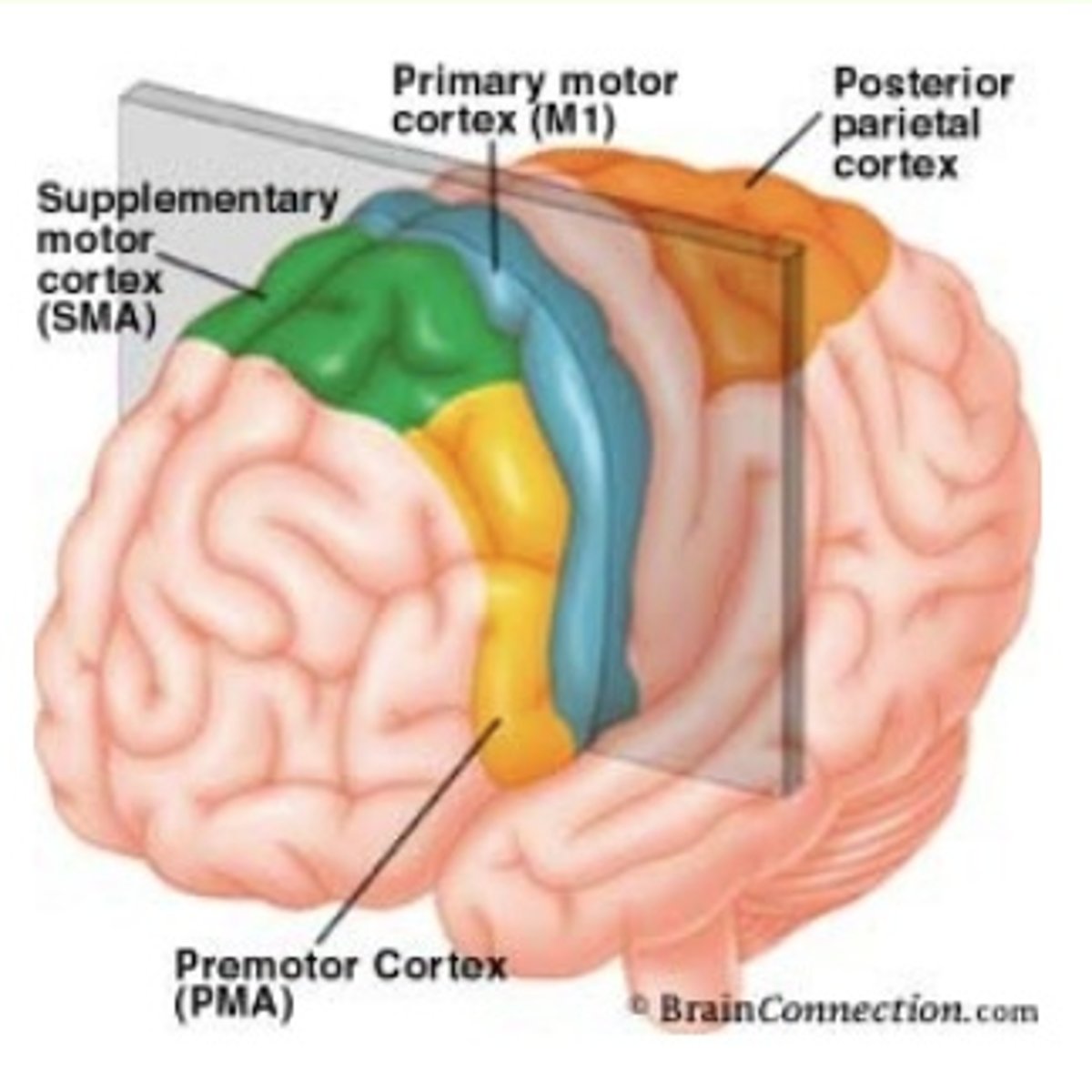
supplementary motor cortex lesion
apraxia
supplementary motor cortex location
anterior to the lower body represent in M1
broca's area function
motor programming of speech (usually in the left hemisphere only)
brocas area lesion
Broca's aphasia
Area corresponding to Broca's in the opposite hemisphere function
planning nonverbal communication (& gestures; adjusts tone of voice)
Area corresponding to Broca's in the opposite hemisphere lesion
difficulty producing nonverbal communication
Apraxia
Premotor or supplementary motor damage> inability to perform movement or sequence of movements
Prefrontal location
anterior part of the frontal lobe
Prefrontal functions
self-awareness and executive functions (deciding on a goal, planning how to accomplish, executing the plan, and monitoring execution)
Prefrontal impairments
-Loss of executive functions and divergent thinking
-Apathy, lack of initiative, lack of goal-directed behavior
-Difficulty choosing goals, planning, executing plans, and monitoring plans
-Difficulty conceiving of many possibilities [(uses of a stick)]
-Little effect on intelligence
Parietotemporal functions
•intelligence, problem solving, comprehension of communication, and spatial relationships
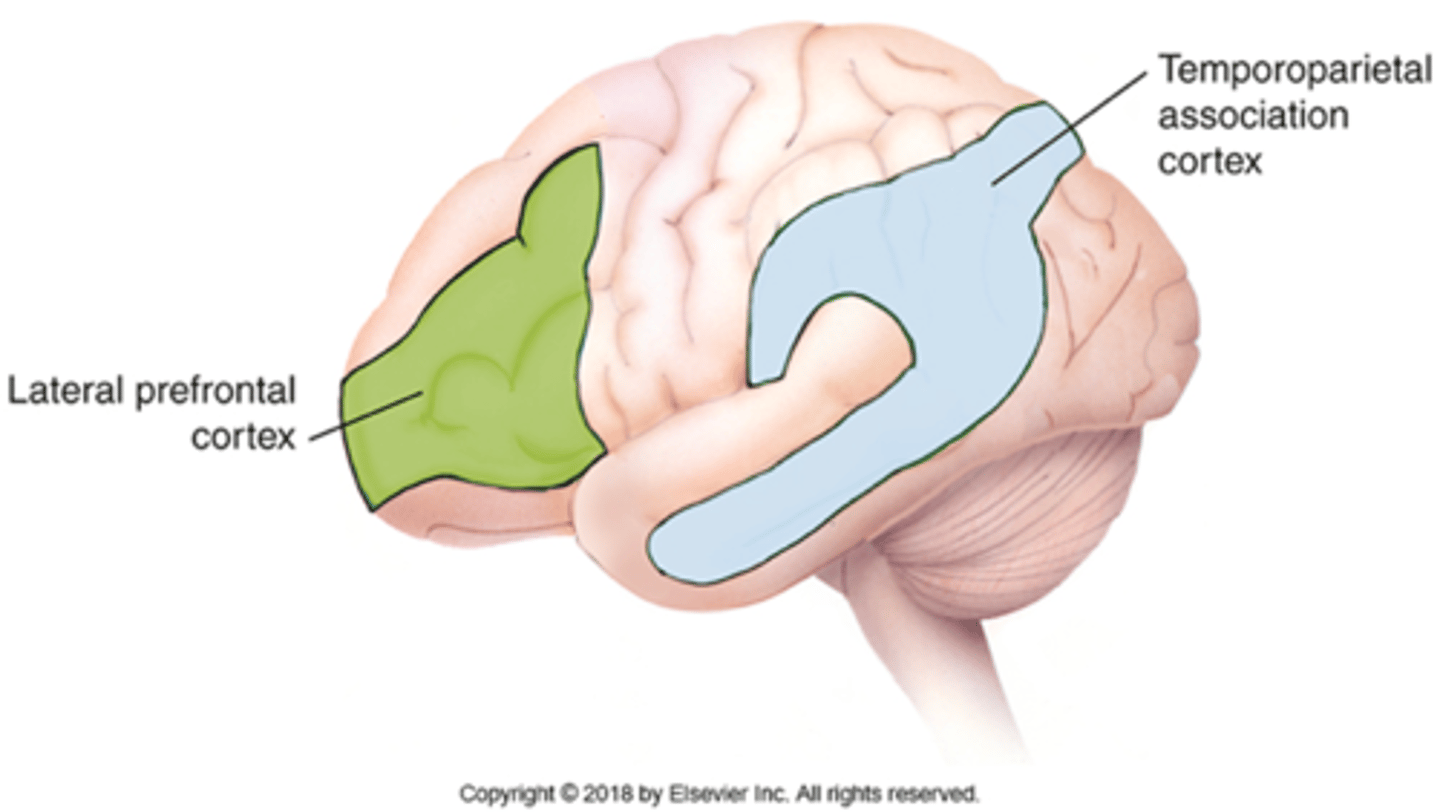
Parietotemporal impairments
-Problems with communication, understanding, and directing attention
-Wernicke's aphasia (receptive aphasia): inability to understand written and spoken language
(same place on right hemisphere= deficits in directing attention, comprehension of space, and understanding nonverbal commands)
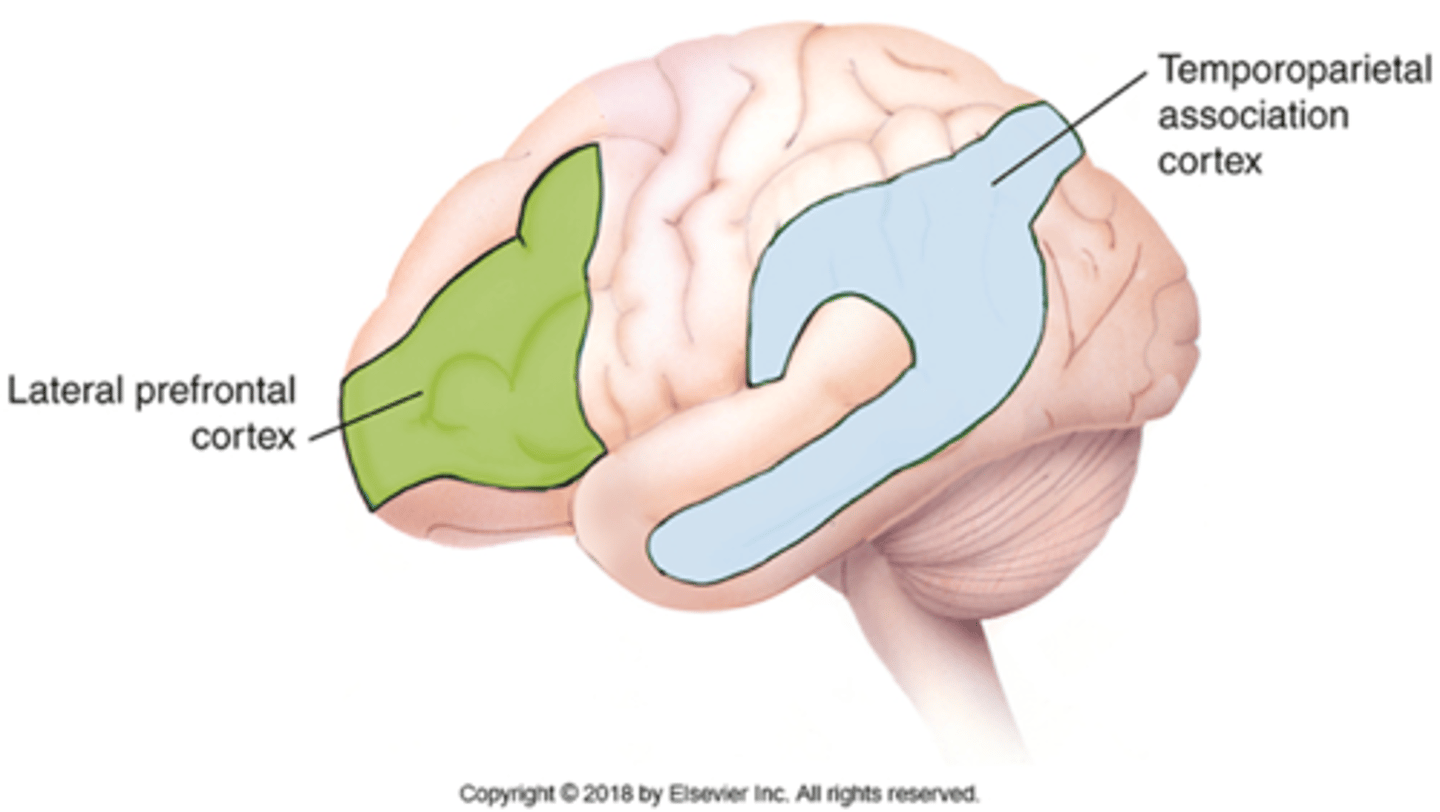
Limbic functions
•regulates mood (subj. feelings), affect (observable demeanor), and processing memory
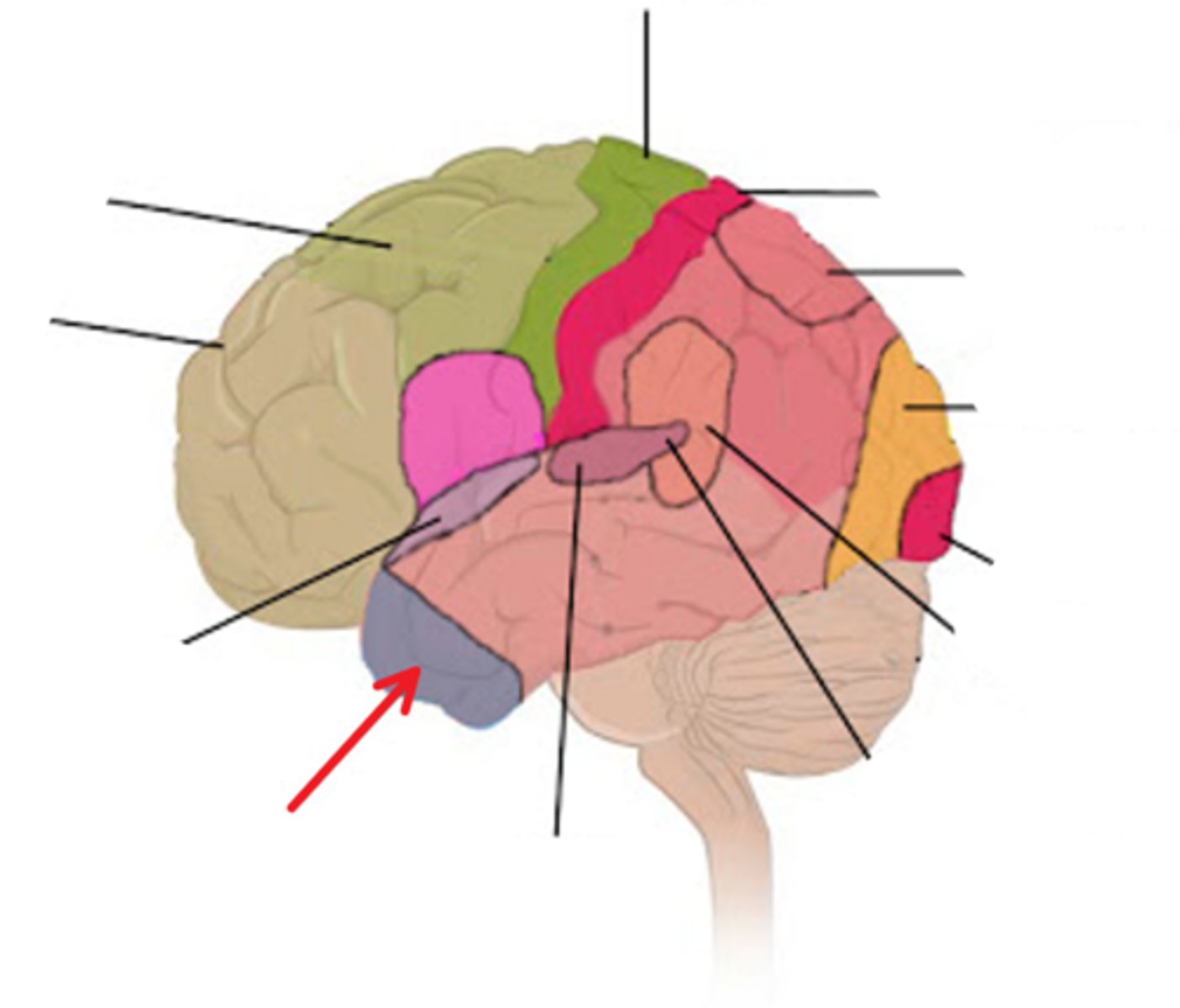
Limbic impairments
-Personality and emotional changes
-Damage to orbitofrontal cortex: inappropriate or risky behavior, poor judgement but intact intellect; saying or doing things that are socially unacceptable
Limbic location
-anterior temporal and orbitofrontal/inferior frontal cortex
damage to cortex --> what type of symptoms
"A" words
•Thalamic Injury
-Relay nuclei involvement:
-Relay nuclei involvement: loss of sensation and proprioception
•Thalamic Injury
-Thalamic pain:
-Thalamic pain: involving severe contralateral pain with/without provoking stimulus
•Internal capsule(IC) common injury results from
occlusion or hemorrhage of lenticulostriate vessels supplying IC are common - even small lesion may have severe consequences
Injury to posterior limb of internal capsule results in
-Contralateral loss of voluntary movement
-Contralateral decreased automatic movement control
-Contralateral loss of conscious somatosensation
-Visual & auditory radiations
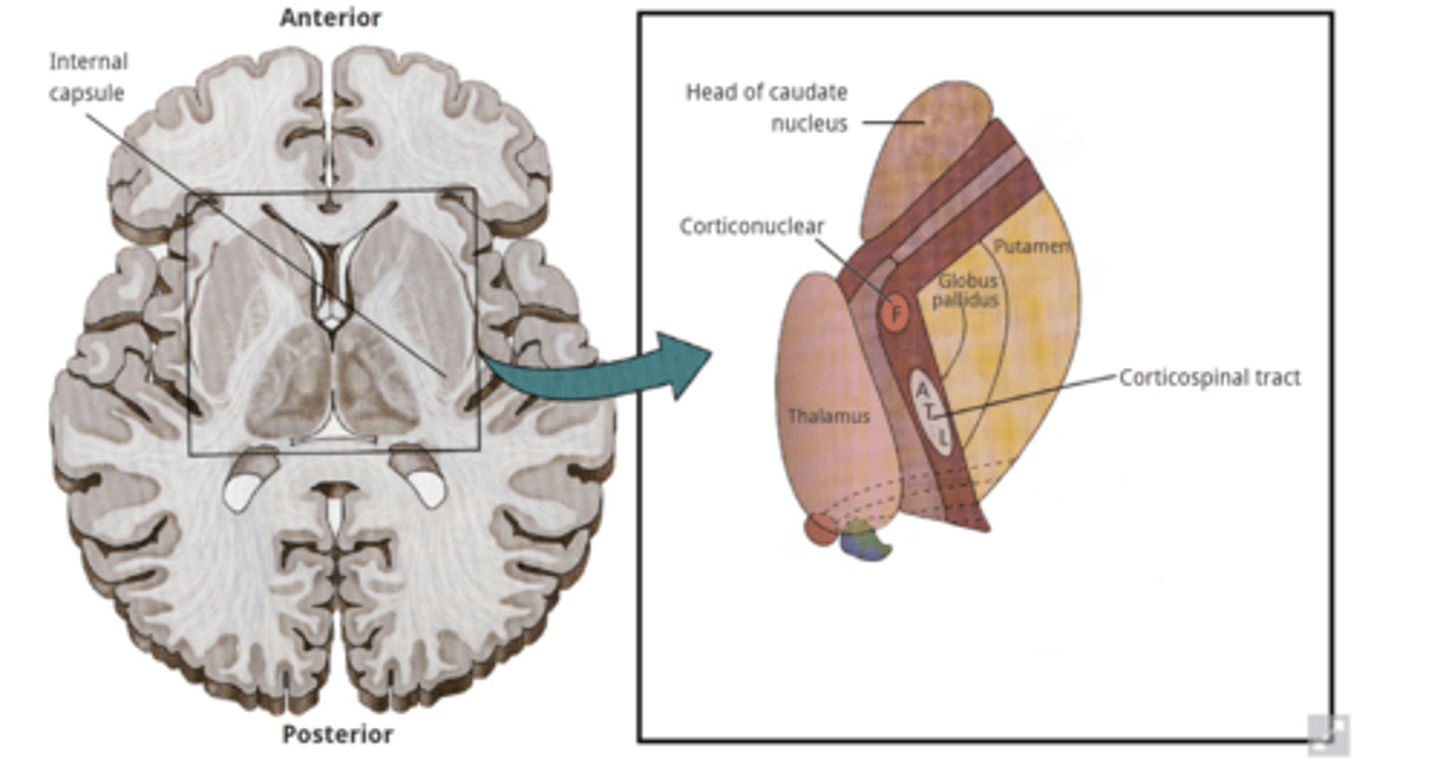
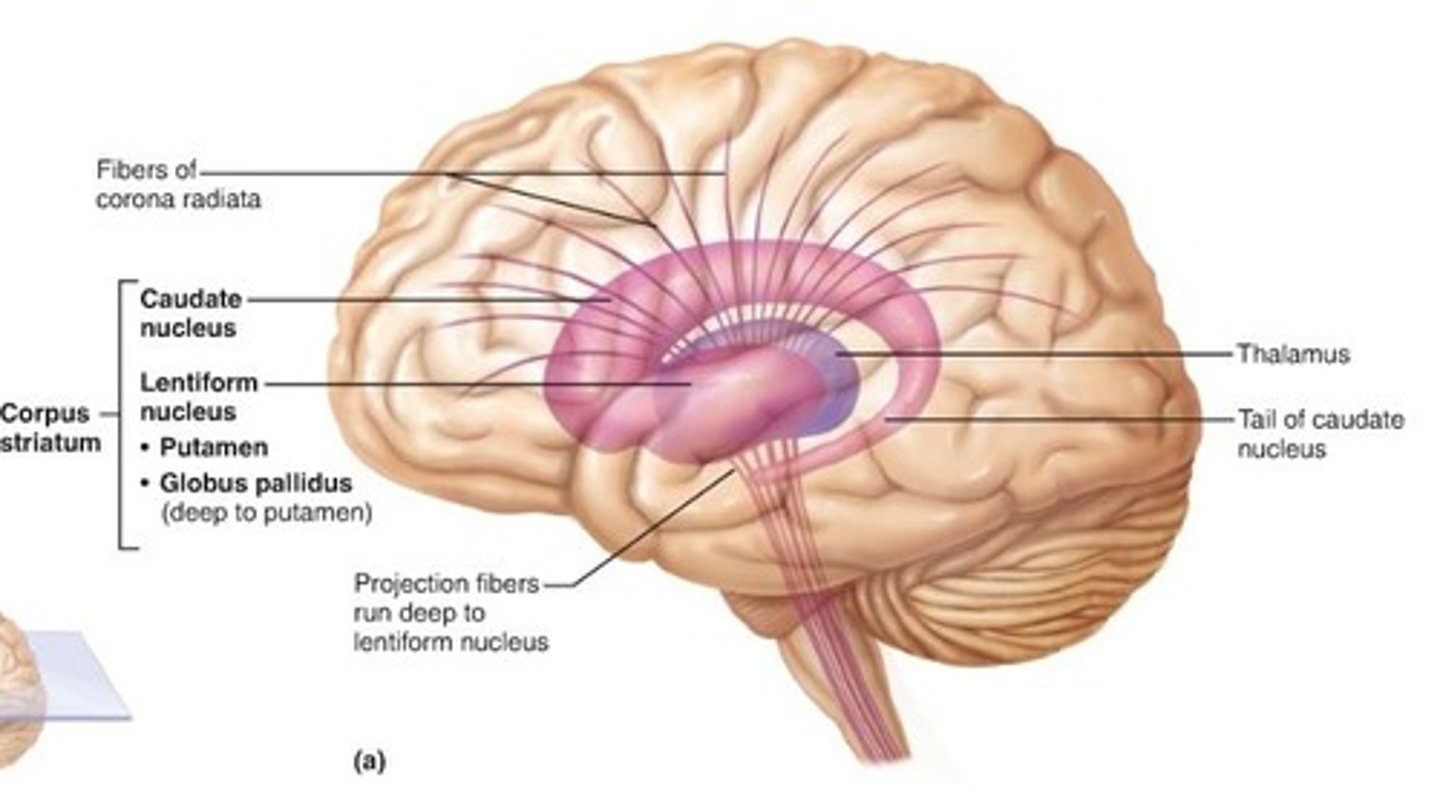
Basal Ganglia Disorders:
Lenticular dysfunction
-hypokinetic (Parkinson's) to hyperkinetic (Huntington's ds)
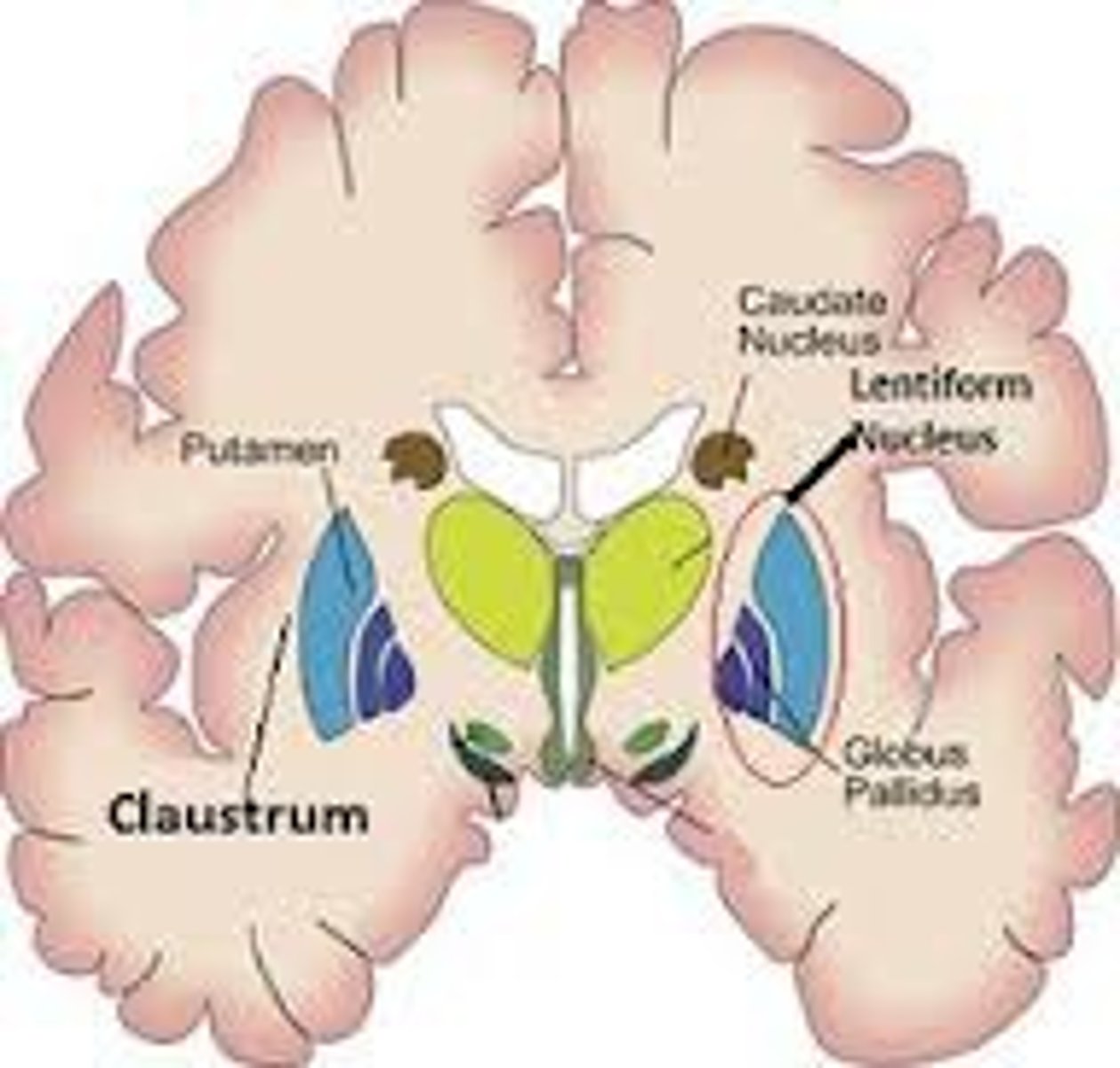
Basal Ganglia Disorders:
caudate lesions
•rarely causes motor disorders but does cause behavioral disturbances (e.g. apathy, loss of initiative, loss of spontaneous thought, and loss of emotional response)
•Acute cerebellar infarction:
-dizziness and /or vertigo, lack of balance, nausea, vomiting, dysarthria, HA, Ataxia, Hypotonia
primary somatosensory cortex = # area
3, 1, 2
primary auditory cortex= # area
41
primary vestibular cortex= # area
40
primary visual cortex= # area
17
primary motor cortex = # area
4
supplementary and pre -motor cortex = # area
6
Vascular insufficiency of the cerebral arteries: Anterior Cerebral Artery (ACA)
1. frontal lobe: Change personality / confusion
2. Medial S1 and M1: Contralateral strength and sensory deficits (LE>UE)(result in difficult with bimanual task) + urinary incontinence
3. Deep: putamen (basal ganglia) and anterior limb of IC: Motor dysfunction
4. secondary motor cortex: apraxia
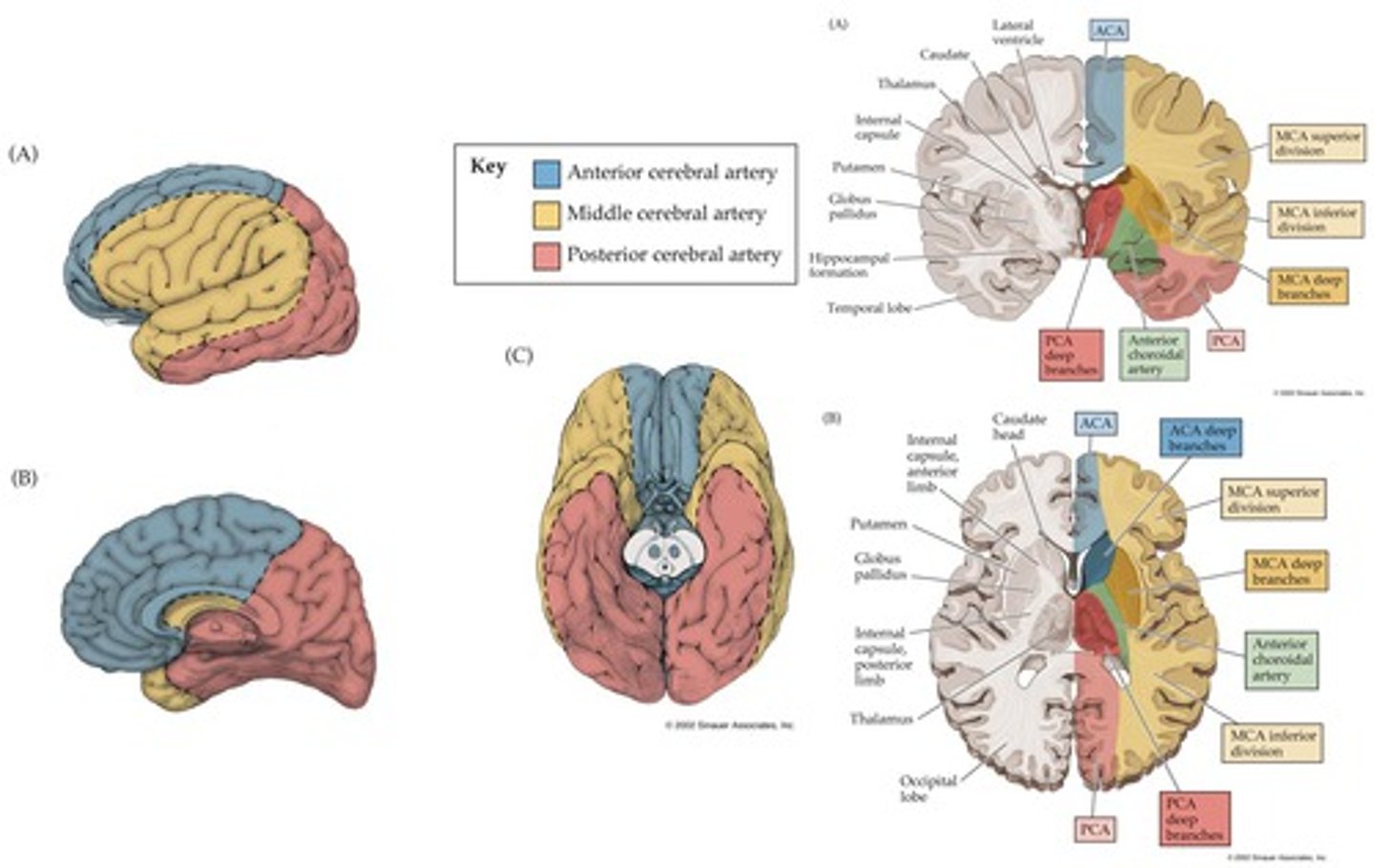
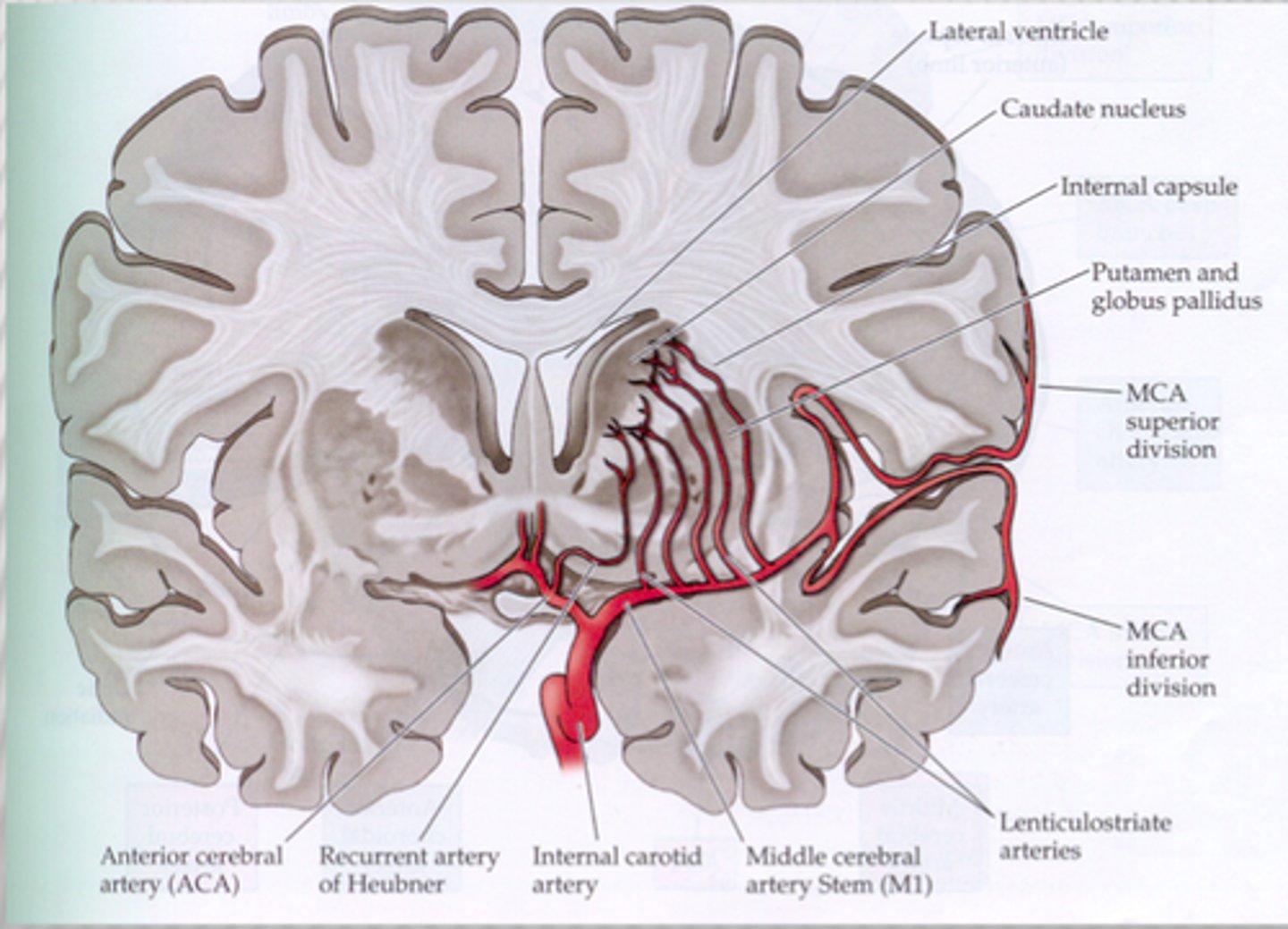
Vascular insufficiency of the cerebral arteries: Middle Cerebral Artery (MCA) deep
striatum and IC (posterior limb):
Hemiparesis / hemisensory -Contralateral strength and sensory deficits
Optic radiation- loss of contralateral field of vision (homonymous hemianopia)
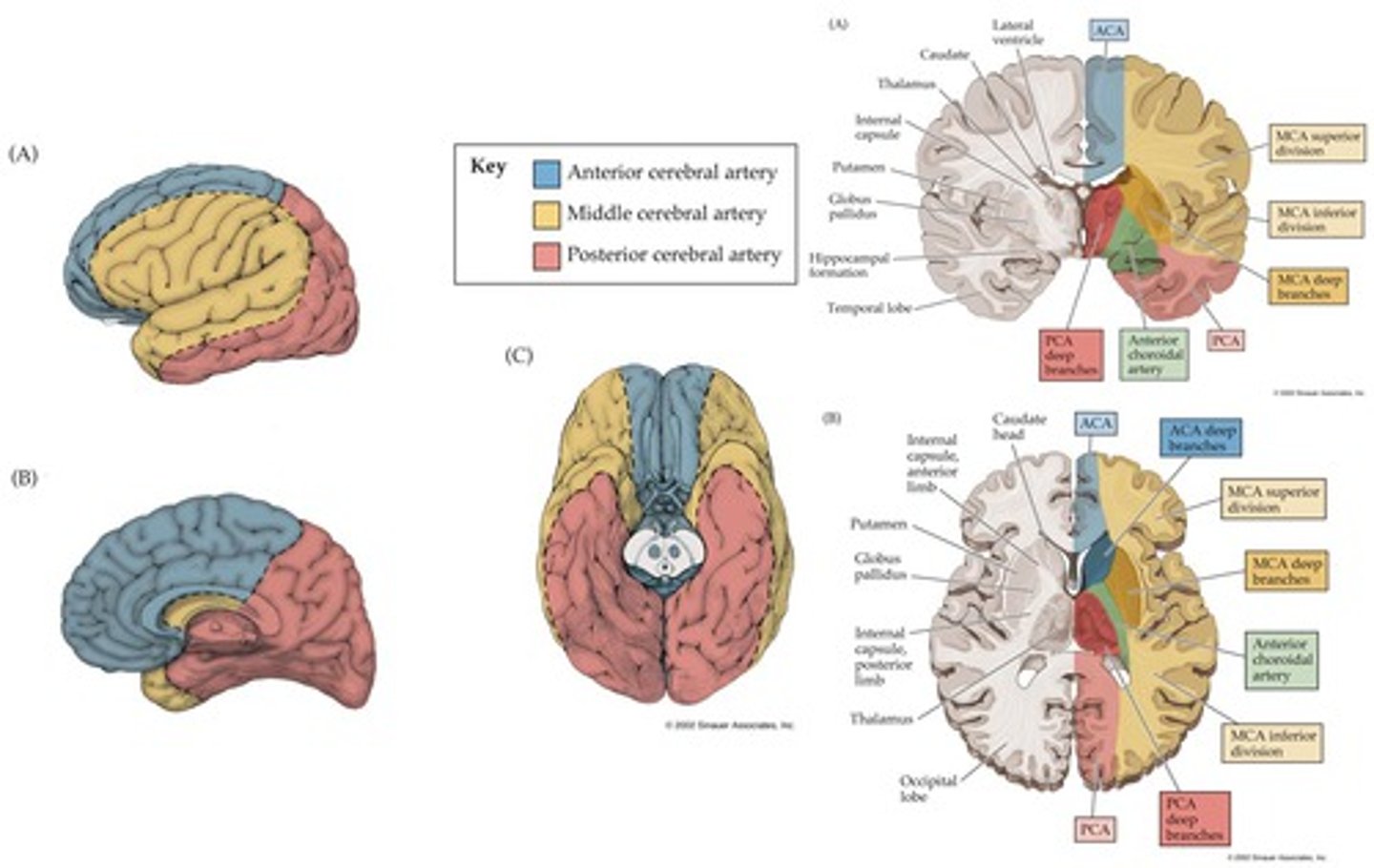
Vascular insufficiency of the cerebral arteries: Middle Cerebral Artery (MCA) superficial
1. ?: sterotyped posture
2. Lateral S1 and M1: Hemiparesis / hemisensory -Contralateral strength and sensory deficits (UE/face>LE)
3. a) Brocas/wernike's (if dominant hemisphere): Aphasia
OR b) alternative (if non dominant): Difficulty with nonverbal communication /spatial relationships
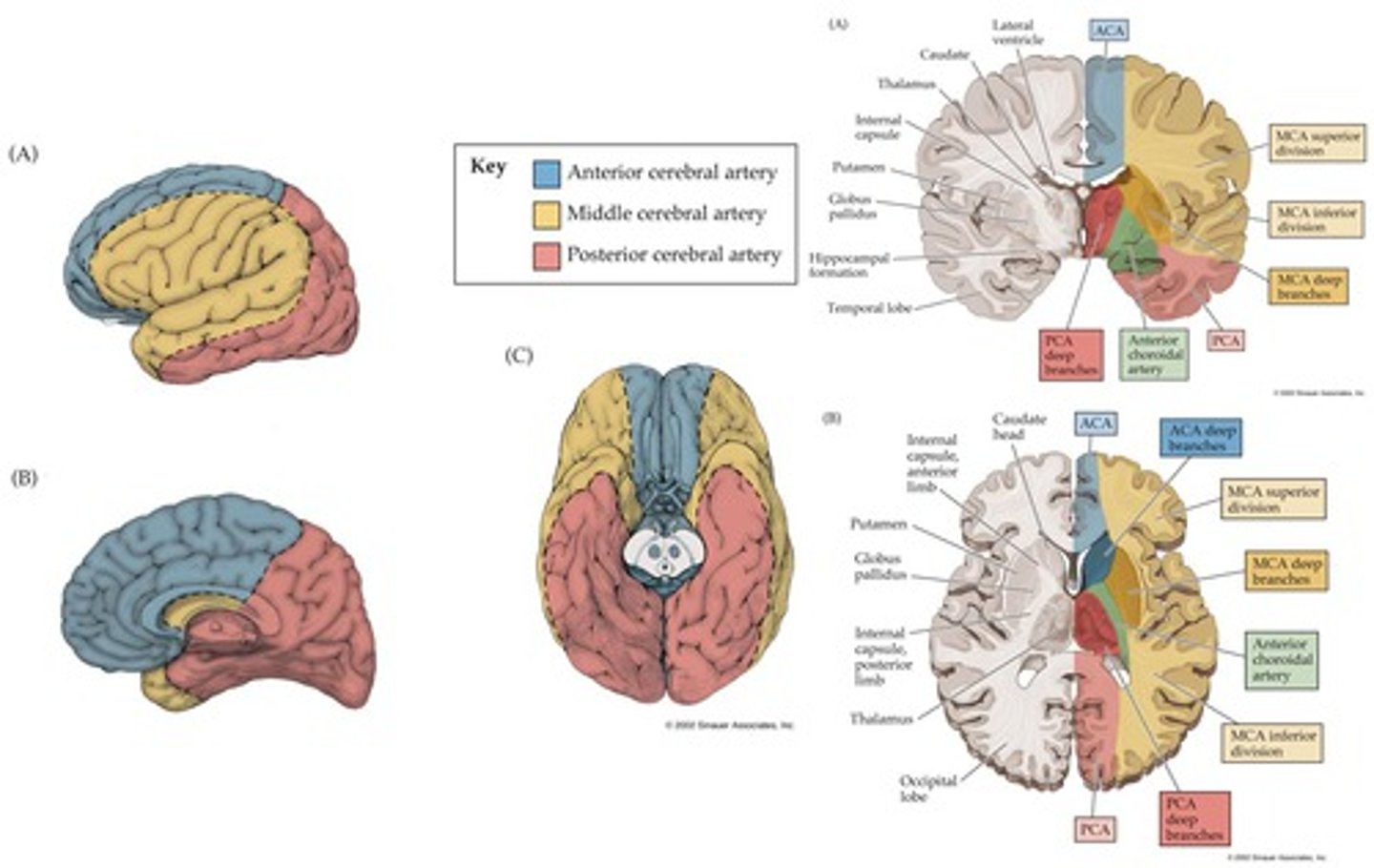
Vascular insufficiency of the cerebral arteries: Posterior Cerebral Artery (PCA)
1. Cerebral peduncle: Contralateral hemiparesis
2. ?= Eye movement
3. Calcarine branches: Blindness affecting contralateral visual field
Deep:
4. hippocampus: declarative memory
5. diencephalon (thalamus): thalamic syndrome
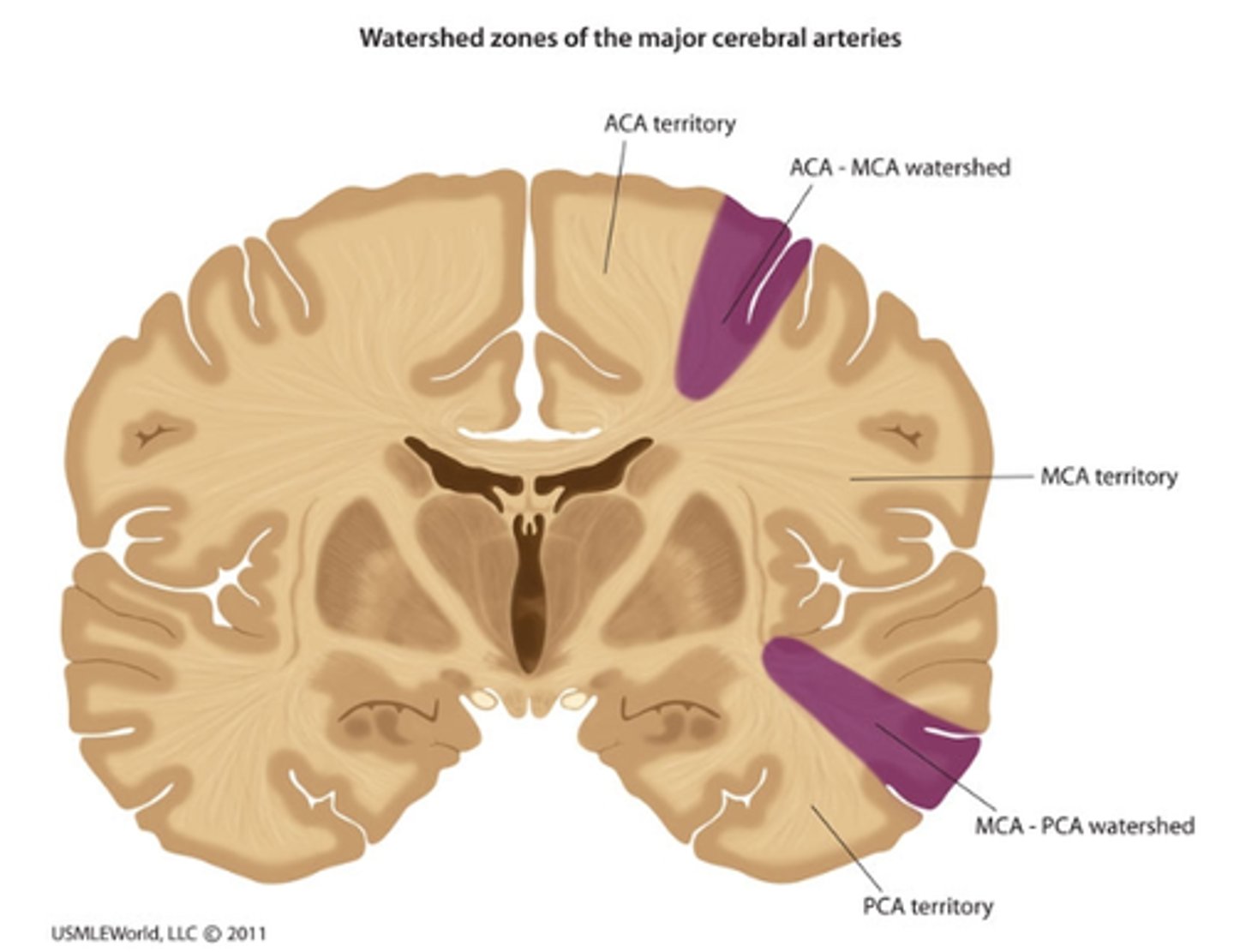
Vascular insufficiency of the cerebral arteries: Watershed area
(where distal cerebral arteries anastomose is vulnerable to ischemia)
· Impairments: upper limb paresis and paresthesias
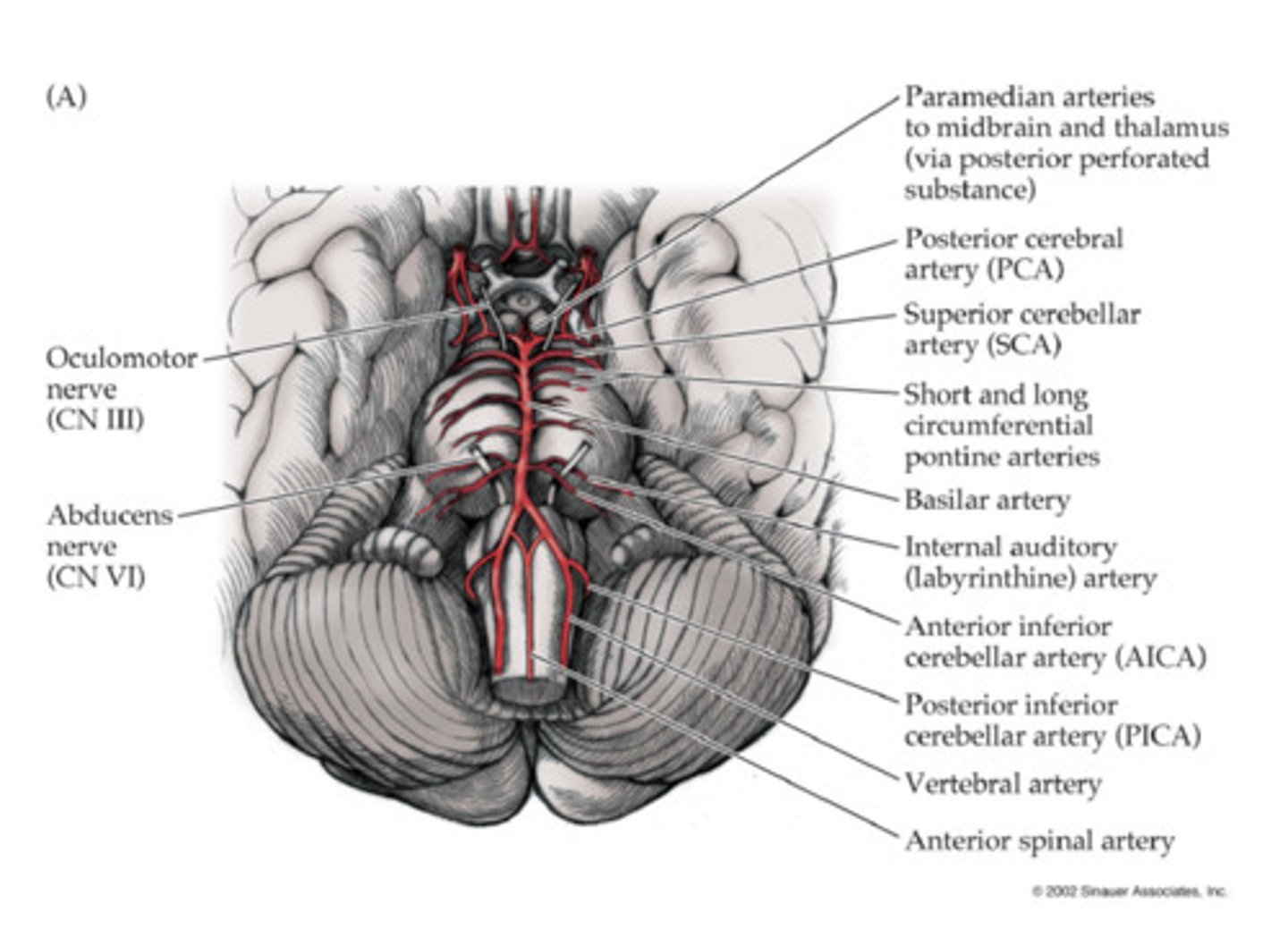
Vascular insufficiency of the cerebral arteries: Vertebral and Basilar Arteries
· Complete vs partial occlusion:
· Complete occlusion: death (vital functions of the brainstem)
· Partial occlusion: tetraplegia, loss of sensation, cranial nerves signs, and/or coma