The periodic table
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
What is periodicity?
the repeating pattern of chemical and physical properties of the elements
What does each period represent?
a new energy level
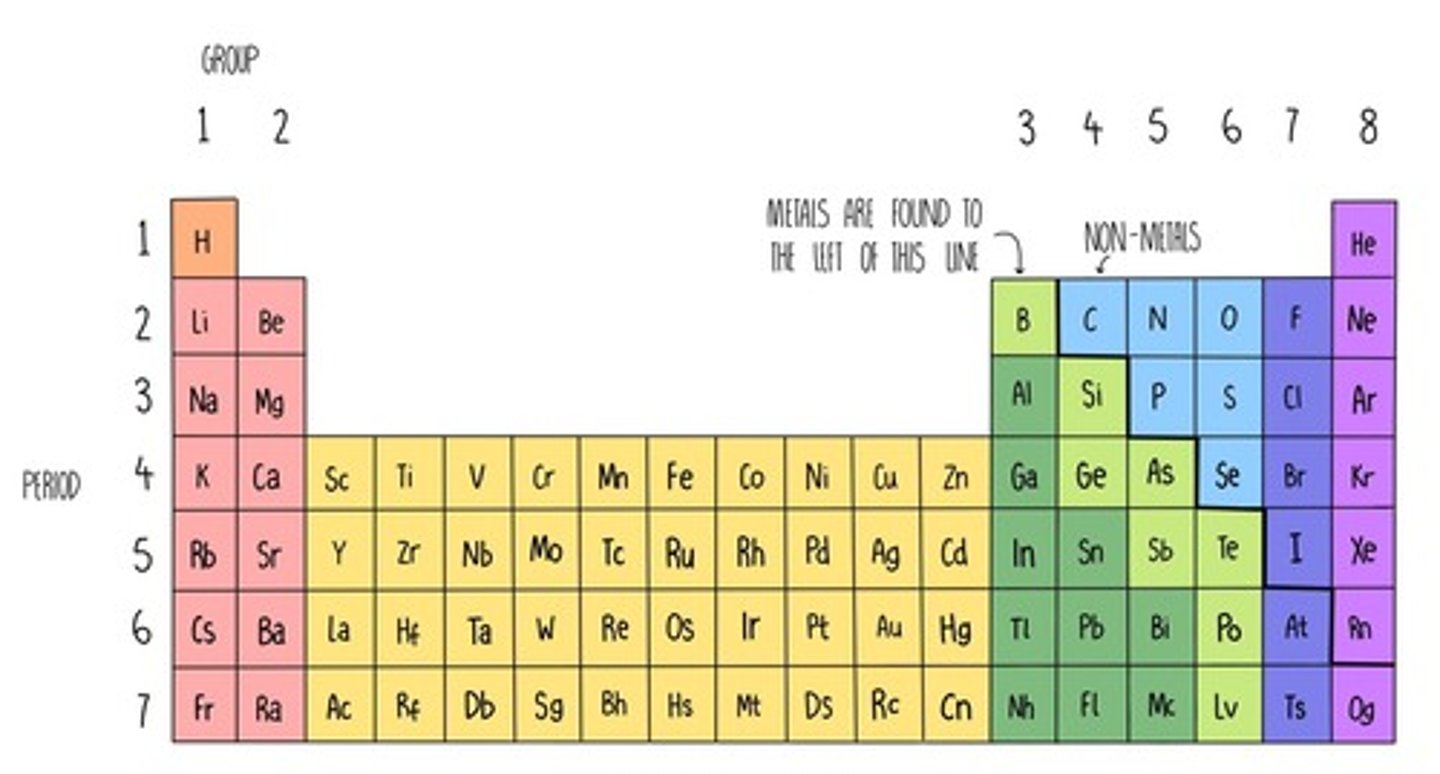
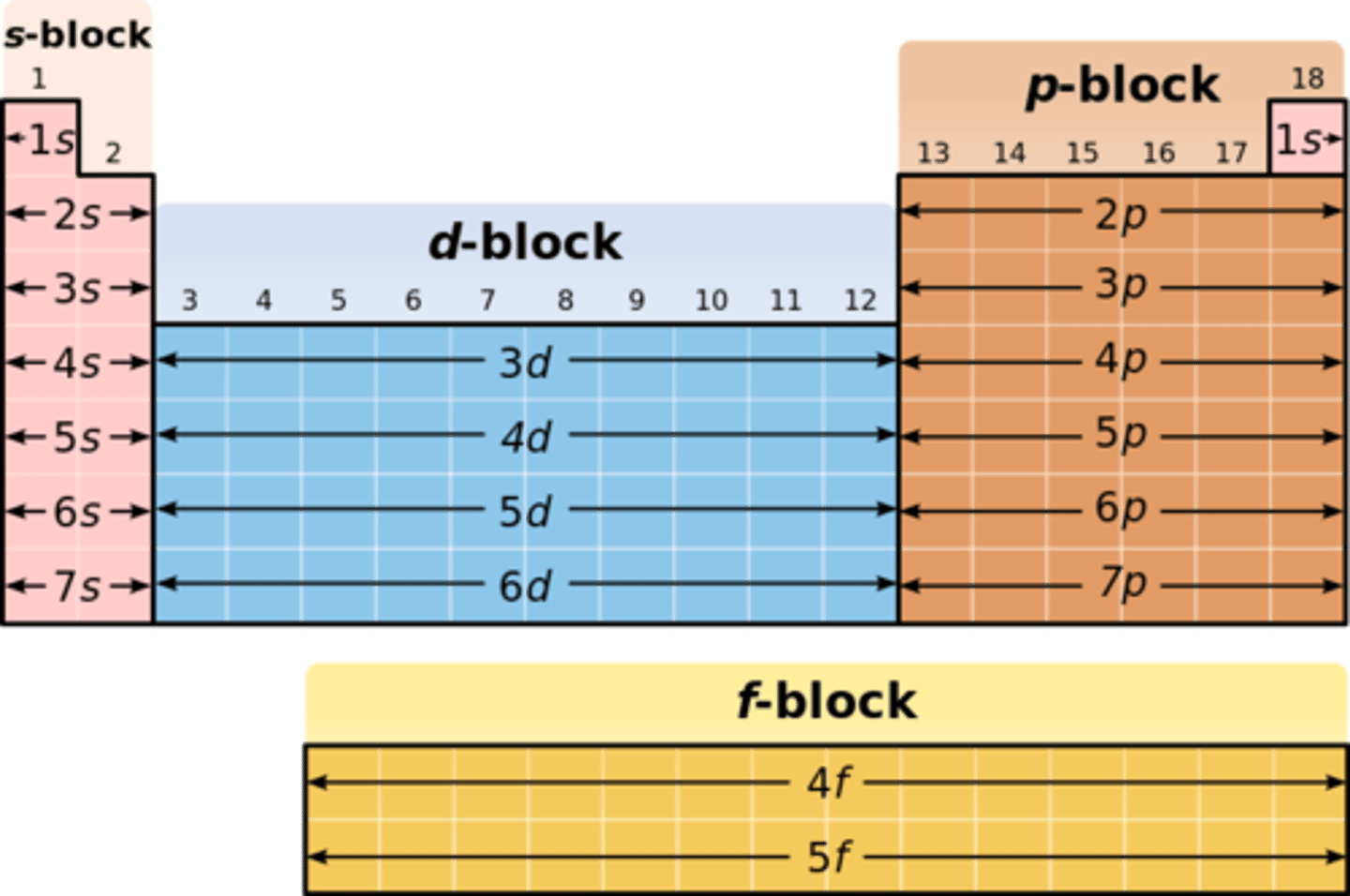
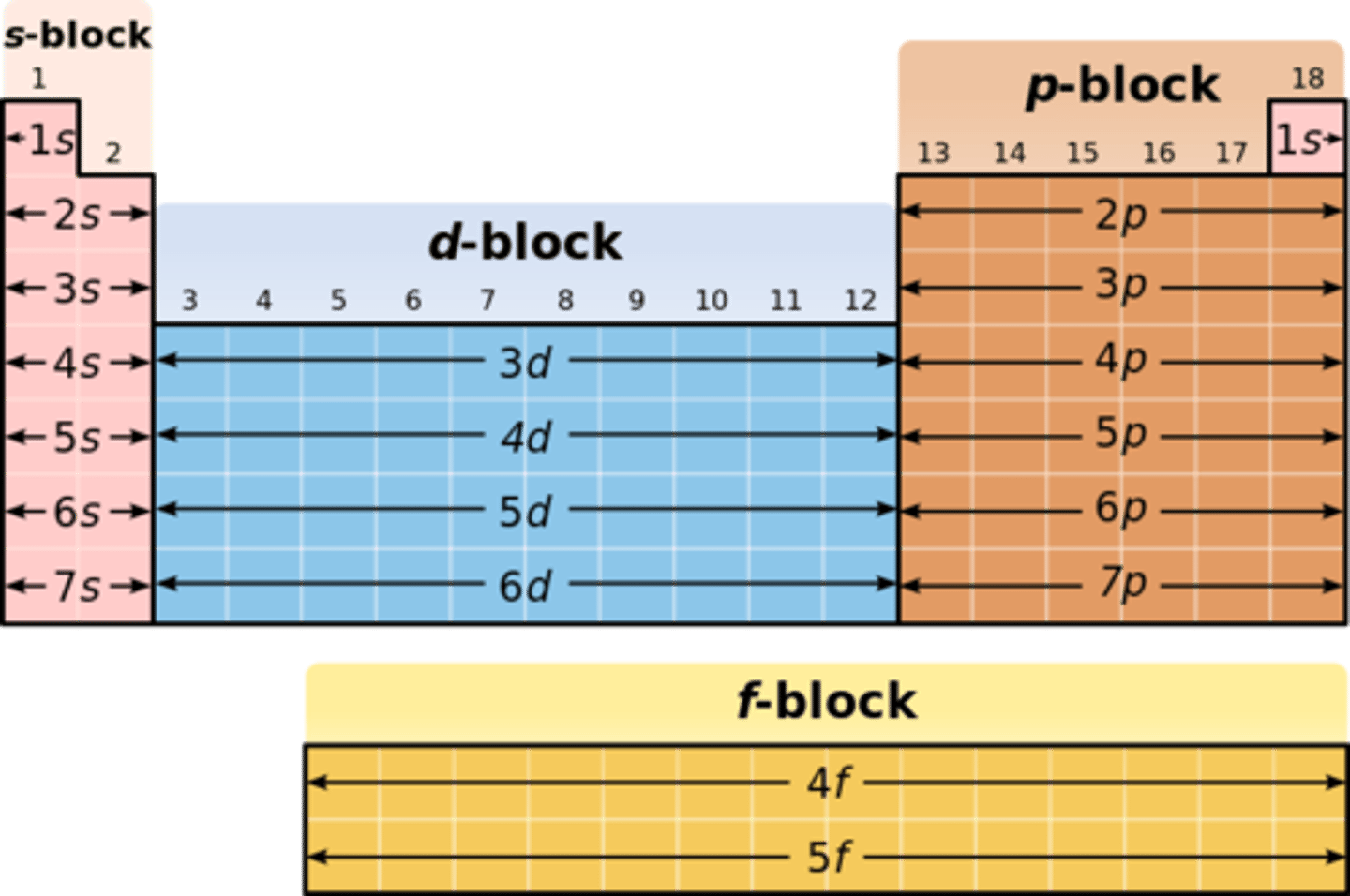
What elements are in the s-block of the periodic table?
groups 1 and 2
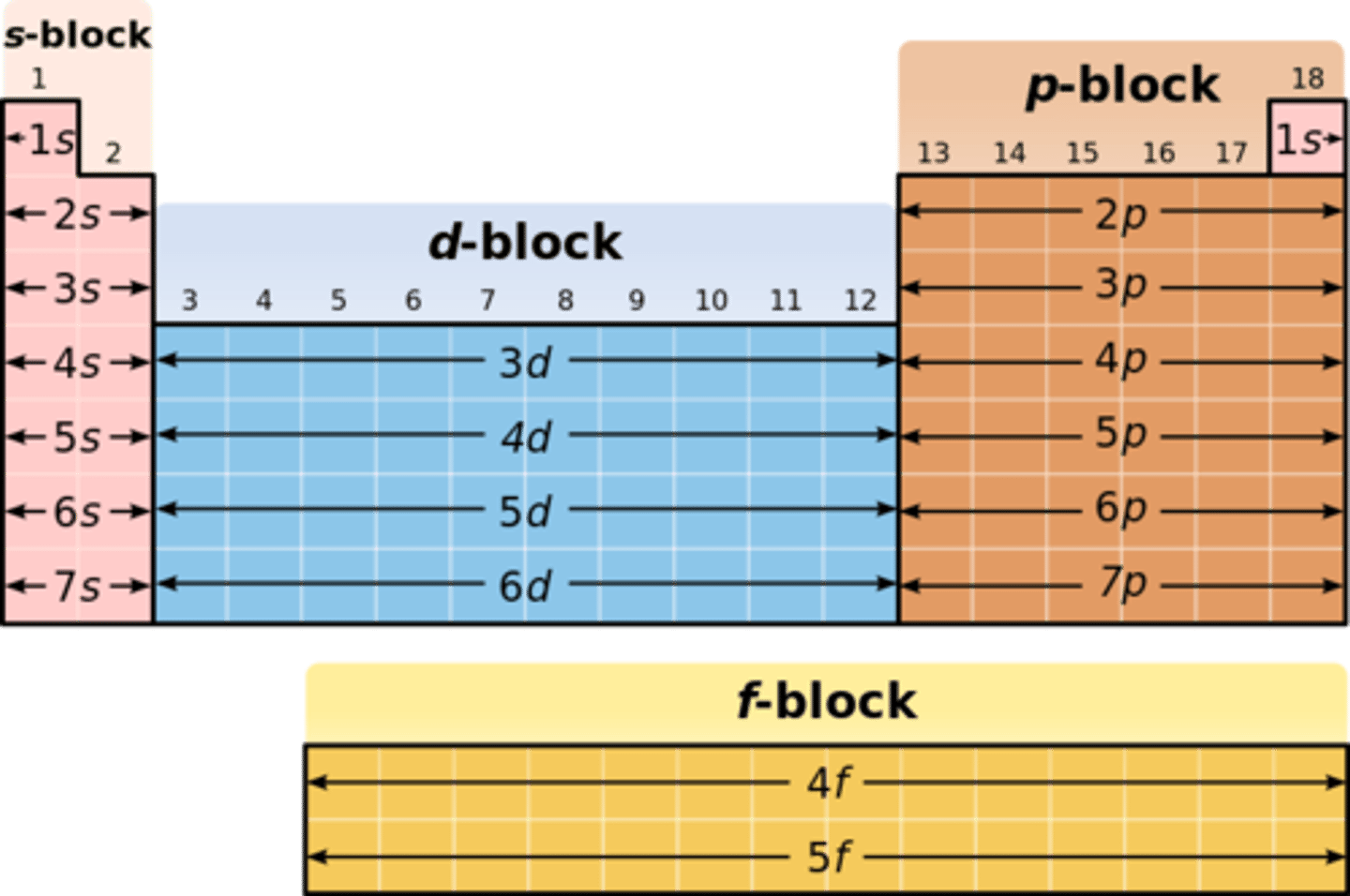
What elements are in the p block of the periodic table?
groups 3 to 0
What elements are in the d block of the periodic table?
transition metals
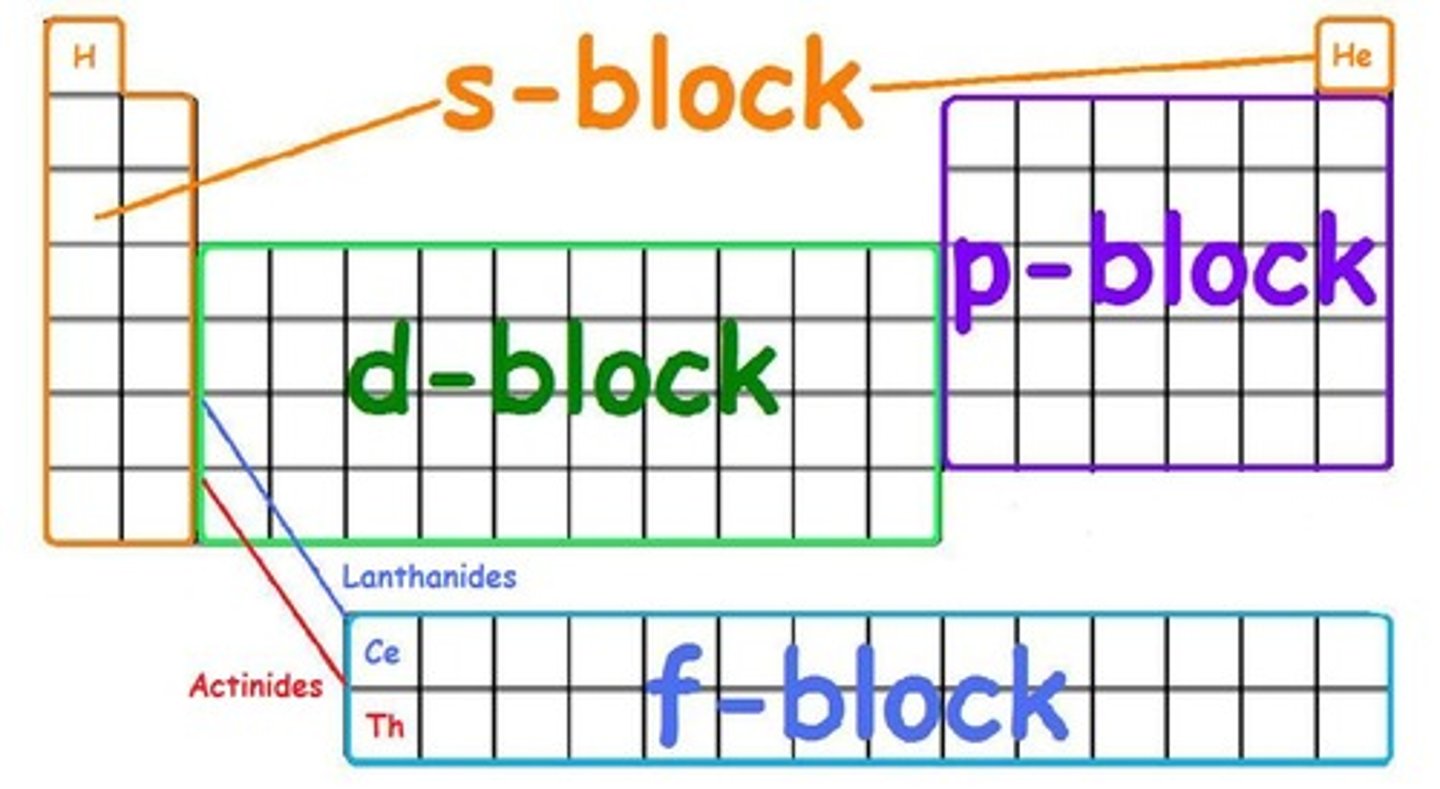
What elements are in the f block of the periodic table?
radioactive elements
What happens to the atomic radius as we move along a period?
It decreases
Why does atomic radius decrease across a period?
Number of protons in an atom increases while the electron shielding remains the same, resulting in greater nuclear attraction between the protons and electrons
What happens to atomic radius moving down a group?
it increases
Why does atomic radius increase down a group?
increasing number of energy levels
Define first ionisation energy
The energy required to remove one electron from each atom in one mole of gaseous atoms of an element to form one mole of gaseous 1+ ions
What is the general trend in ionisation energy across a period?
increases
Why does ionisation energy generally increase across a period?
Increased nuclear charge and decreased atomic radius
What is the exception to the trend in ionisation energy in period 3?
Aluminium as it has an electron in a higher energy level than magnesium, making it easier to remove
What are metalloids?
elements that have some properties like metals and some like nonmetals
Going across period 3, what is the general trend in melting and boiling points?
Increases then decreases
Why does the melting and boiling points increase from Na to Al?
metallic bonds become stronger
Why does the trend in melting and boiling points in period 3 peak at silicon?
Silicon has giant covalent structure - strong bonds
Why do melting and boiling points decrease from P to Ar?
Rely on vdw forces
Why does sulfur have a higher melting point than phosphorus?
it is the bigger molecule (S8) - more vdw forces
Why does argon have a very low melting point?
It exists as individual atoms (monatomic) resulting in very weak van der Waals forces
What are elements in Group 2 referred to as?
alkaline earth metals
Are group 2 metals reactive or unreactive?
reactive
What block are group 2 metals in the periodic table?
the s block
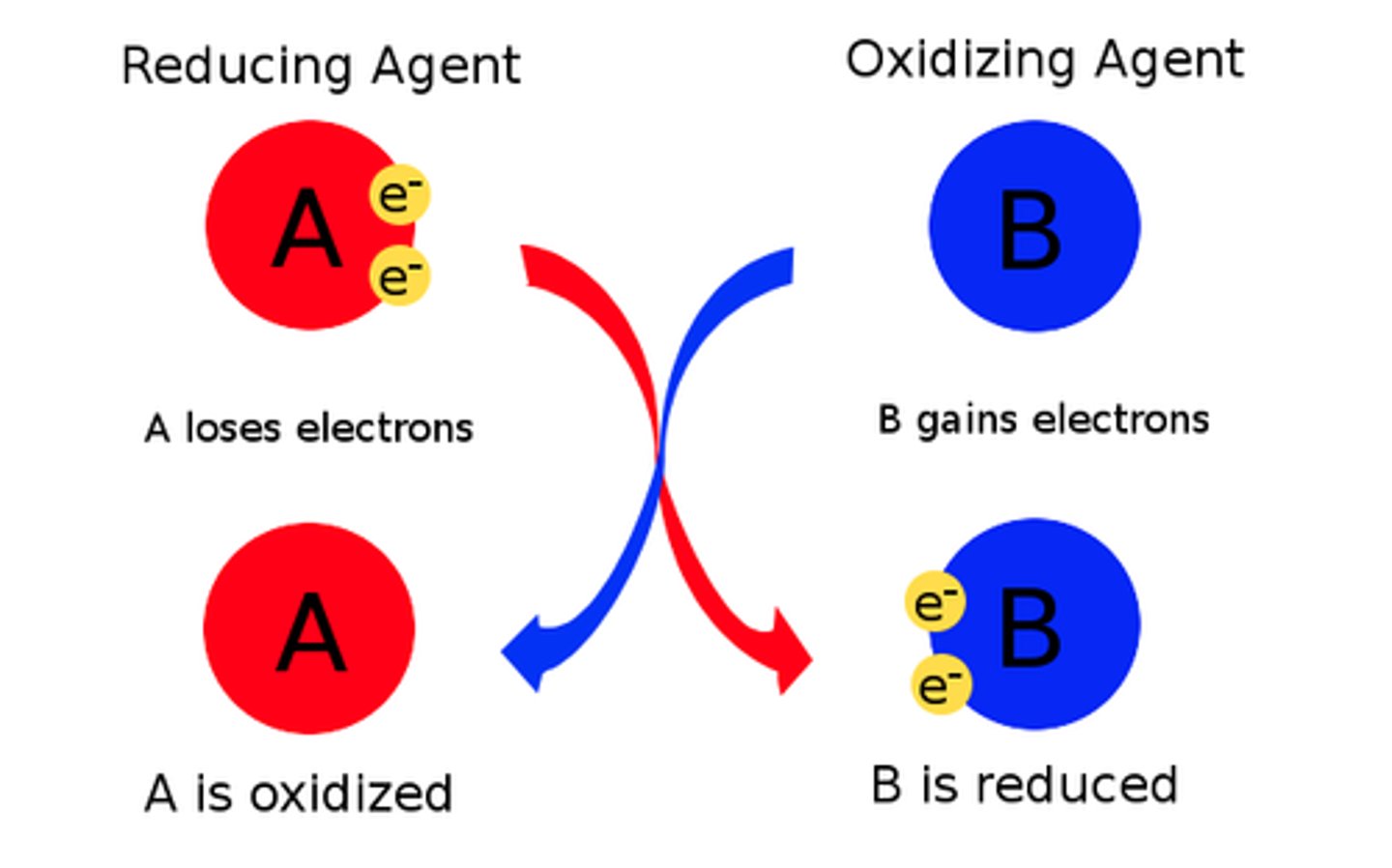
What agents do group 2 metals act as?
reducing agents
Why does the reactivity increase going down Group 2?
First ionisation energy decreases as there is more electron shielding
What does reacting a group 2 metal with water produce?
metal hydroxide and hydrogen

What happens to the Group 2 metal's oxidation number when reacted with water?
Goes from 0 to +2
How does the reactivity with water change going down Group 2?
Rate of reaction increases
What happens to the solubility of the Group 2 hydroxides going down Group 2?
It increases - less precipitate forms
What does the concentration of hydroxide ions determine?
The alkalinity of the solution
Which one has the higher pH, magnesium hydroxide or barium hydroxide?
Barium hydroxide as it has a higher concentration of hydroxide ions
What is calcium hydroxide (slaked lime) used for?
neutralising acidic soils
What is magnesium hydroxide (milk of magnesia) used for?
neutralises stomach acid
What happens to the solubility of Group 2 sulphates going down the group?
it decreases
Which group 2 sulfate is insoluble in water?
barium sulfate

What is barium sulfate used for?
Barium meal for X Ray's - lines the digestive tract so it shows up on x ray
How is barium chloride used to test for sulfate ions?
If barium chloride solution mixed with solution containing sulfate ions, barium sulfate is formed which is insoluble - forms white precipitate.
What has to be added to the barium chloride solution before testing for sulfates?
Either hydrochloric acid or nitric acid to react with any carbonate atoms preventing a false positive
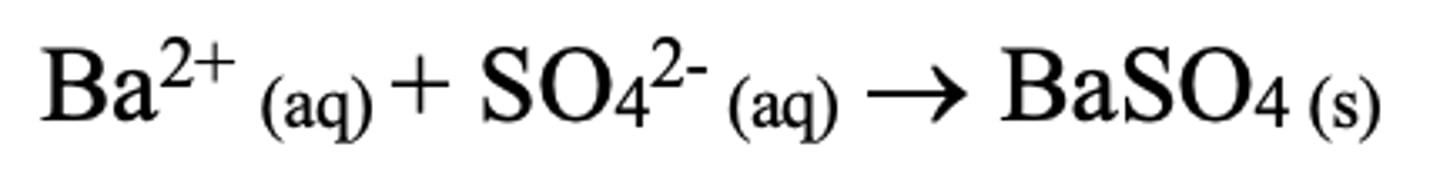
What happens to melting and boiling point going down group 7?
It increases - increased vdw forces due to more electrons
What happens to electronegativity going down Group 7?
It decreases - higher atomic radius and more electron shielding reduces nuclear attraction
What does a group 7 halogen act as in a redox reaction?
Acts as an oxidising agent - removes an electron
What happens to reactivity going down group 7?
it decreases - higher atomic radius and shielding means less nuclear attraction - harder to attract an electron
Which element in group 7 is the most powerful oxidising agent?
Fluorine
What happens to oxidising ability going down group 7?
decreases
What happens in a displacement reaction?
A more reactive metal displaces a less reactive metal from a compound
What is produced in a displacement reaction?
A halogen
What is one of the uses of chlorine?
Killing bacteria in water
What is the reaction between chlorine and water?
Cl2 + H2O -> HClO + HCl
What is a disproportionation reaction?
A redox reaction in which the same element is both oxidised and reduced
What are the risks of using chlorine in drinking water?
- Chlorine is a toxic gas
- Chlorine could react with hydrocarbons and create a carcinogen
Describe appearance of fluorine
Yellow gas
Describe appearance of chlorine
Green gas
Describe appearance of bromine
Red-brown liquid
Describe appearance of iodine
Dark grey solid
What do halide ions act as?
reducing agents - donate their electrons to other species
What happens to power of reducing agents going down Group 7?
Increases
Why is fluorine a weak reducing agent?
Small atomic radius and small amount of shielding means strong attraction of outer electrons to nucleus - harder to lose electron
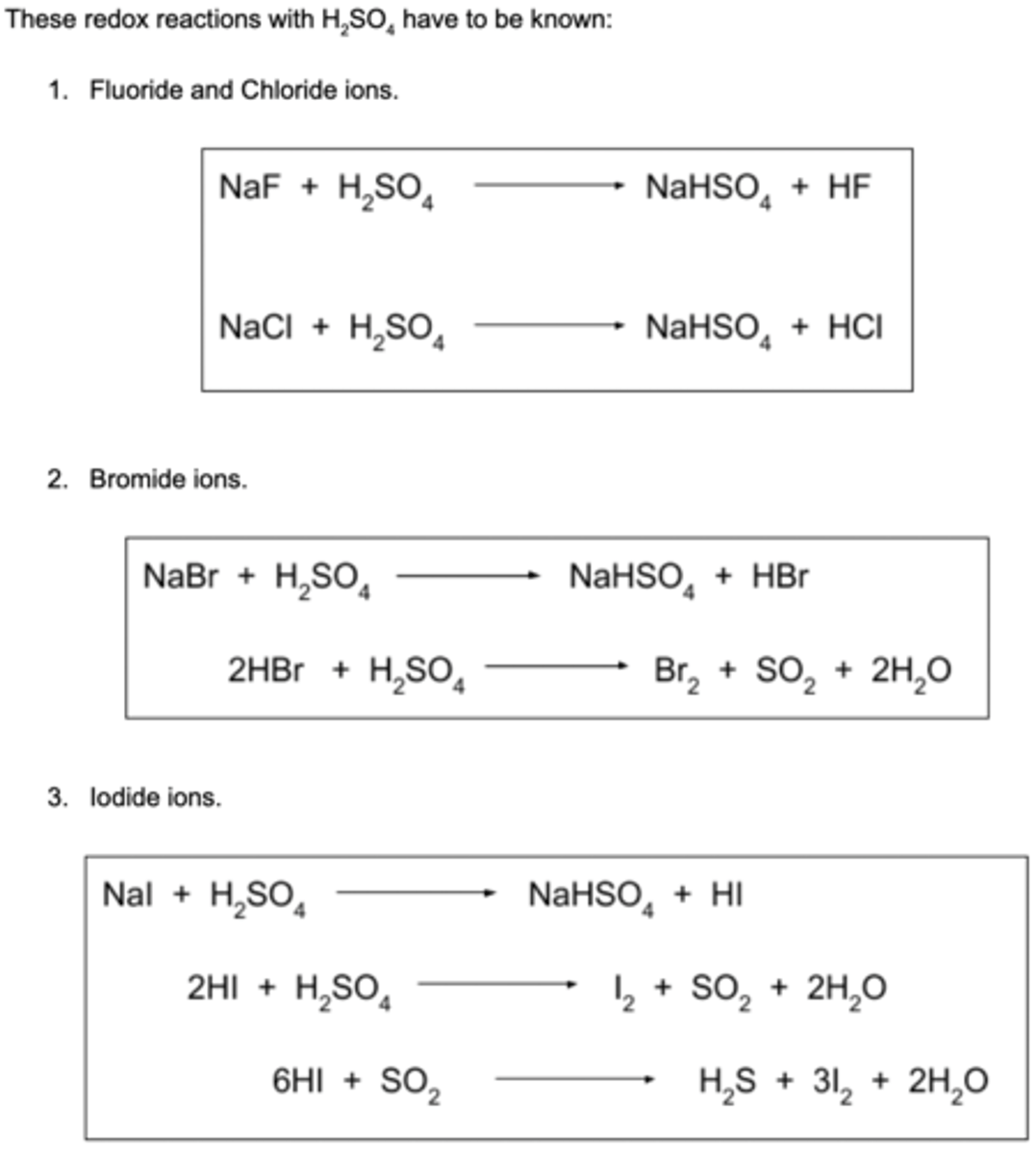
What products are formed when solid sodium chloride reacts with sulfuric acid?
Sodium hydrogensulfate and hydrogen chloride
Why is sulfur not reduced in a reaction between sodium chloride and sulfuric acid?
Chlorine is a weak reducing agent
What is the reaction of sodium bromide with concentrated sulfuric acid?
NaBr(s) + H2SO4(l) → NaHSO4(s) + HBr(g)
2HBr + H2SO4(l) → SO2(g) + 2H2O(l) + Br2(l)
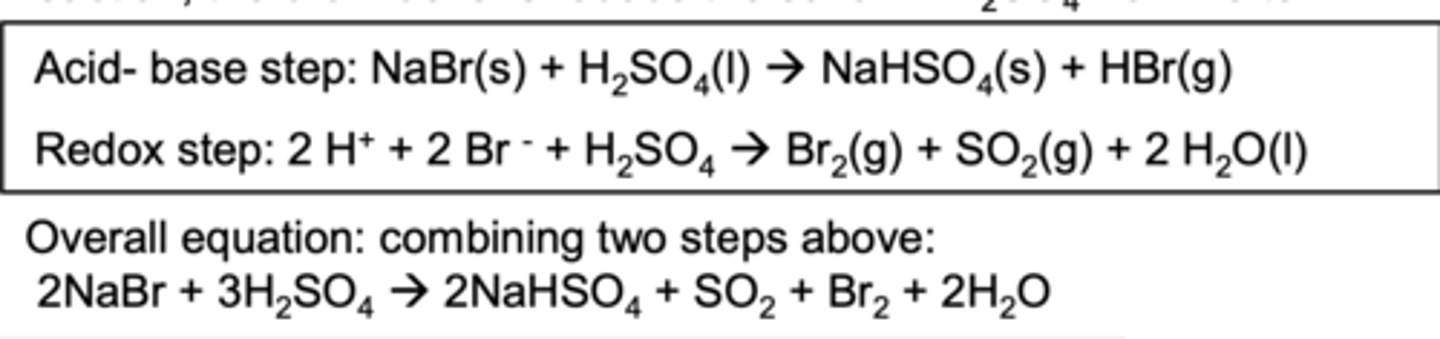
What type of reaction is the reaction of sodium bromide with concentrated sulfuric acid?
A redox reaction as the sulfur is reduced from +6 to +4
What is the reaction of sodium iodide with concentrated sulfuric acid?
NaI(s) + H2SO4(l) → NaHSO4(s) + HI(g)
2HI + H2SO4(l) → SO2(g) + 2H2O(l) + I2(s)
8HI + H2SO4(l) → H2S(g) + 4H2O(l) + 4I2(s)
What can iodine reduce sulfur to in a reaction with sulfuric acid?
- +6 to +4 - SO2
- +6 TO 0 - S8
- +6 TO -2 - H2S
What is used to test for halide ions?
Acidified silver nitrate (AgNO3)
What happens when a silver halide reacts with water?
It forms a precipitate as it is insoluble in water
What colour precipitate is produced when silver nitrate reacts with a chloride ion?
White
What colour precipitate is produced when silver nitrate reacts with a bromide ion?
cream
What colour precipitate is produced when silver nitrate reacts with a iodide ion?
pale yellow
What will silver chloride precipitate dissolve in?
dilute aqueous ammonia
What will silver bromide precipitate dissolve in?
concentrated aqueous ammonia
What will silver iodide precipitate dissolve in?
neither concentrated or dilute aqueous ammonia
Why is dilute nitric acid used in the test for halide ions using silver nitrate solution?
to remove any carbonates or hydroxides
What is produced when chlorine reacts with cold, dilute, aqueous NaOH?
sodium hypochlorate

What is sodium hypochlorite used for?
bleach
