Sports Science Test - Muscles and Bones!
1/87
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
superior
upward of, above the head.
inferior
downward, away from the head.
anterior
forwards, in front of.
posterior
backwards, back of.
medial
toward the middle.
lateral
toward the side.
proximal
towards the attachment (limb).
distal
away from the attachment (limb).
superficial
near to the surface.
deep
deep, further away from the surface.
ipsilateral
on the same side.
contralateral
opposite side.
simple
single crack across the shaft of a bone.
greenstick
when a bone bends or breaks partially (mainly in children).
hairline
a very small/fine break that sometimes can’t be seen in an x-ray.
complex
bone is broken in a complicated way.
compound
when the bone sticks out of the skin.
depressed
when a bone is pushed inward.
comminuted
where the bone is shattered into multiple pieces.
avulsion
when muscles or ligaments can generate enough force to break the bone and tear the attachment off.
closed
when the break is contained within the skin.
stress
partical crack due to repeated stress.
complicated
when the bone pierces through the skin and comes into contact with outside environment.
abduction.
moving limb away from midline.
adduction.
limbs move to midline.
flexion.
reducing angle of limb/joint.
extension.
increase angle of limb/joint.
medial rotation.
rotation to middle.
lateral rotation.
rotation to side.
supination.
palm facing sky.
pronation.
palm facing ground.
plantarflexion.
foot moves away from leg.
dorsiflexion.
foot moves toward leg.
functions of muscles.
generate heat, enable movement, provide structure.
ligaments.
strong, flexible bands of connective tissue, connecting bones to bones.
tendons.
tough fibrous cords of connective tissue, connecting muscles to bones.
involuntary.
don’t think about it.
voluntary.
conscious.
How many bones are in the axial section of the body?
80 bones.
How many bones are in the appendicular section of the body?
126 bones.
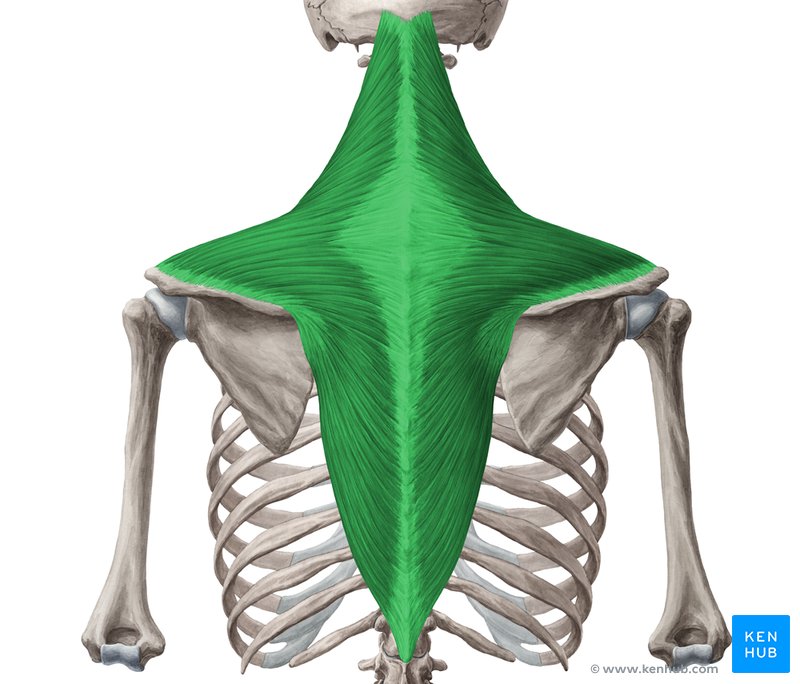
What muscle is this?
Trapezius.
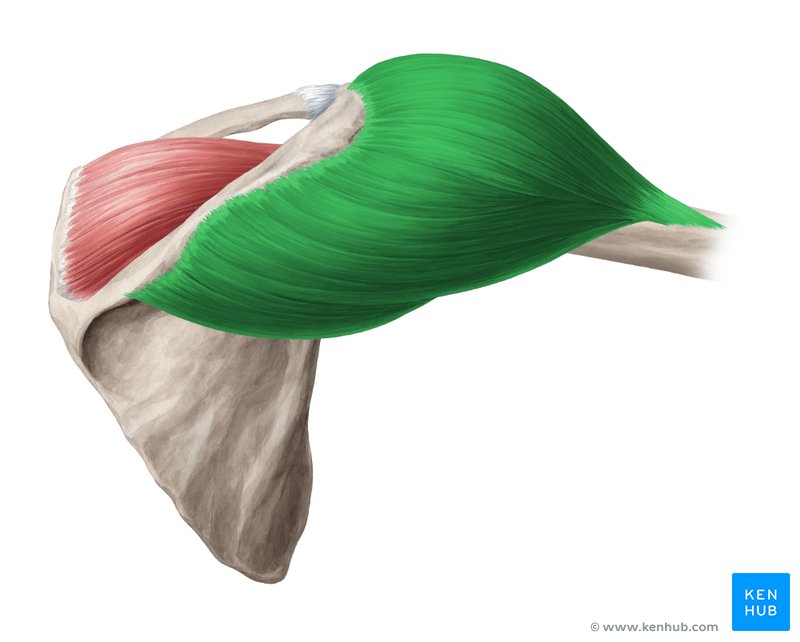
What muscle is this?
Deltoid.
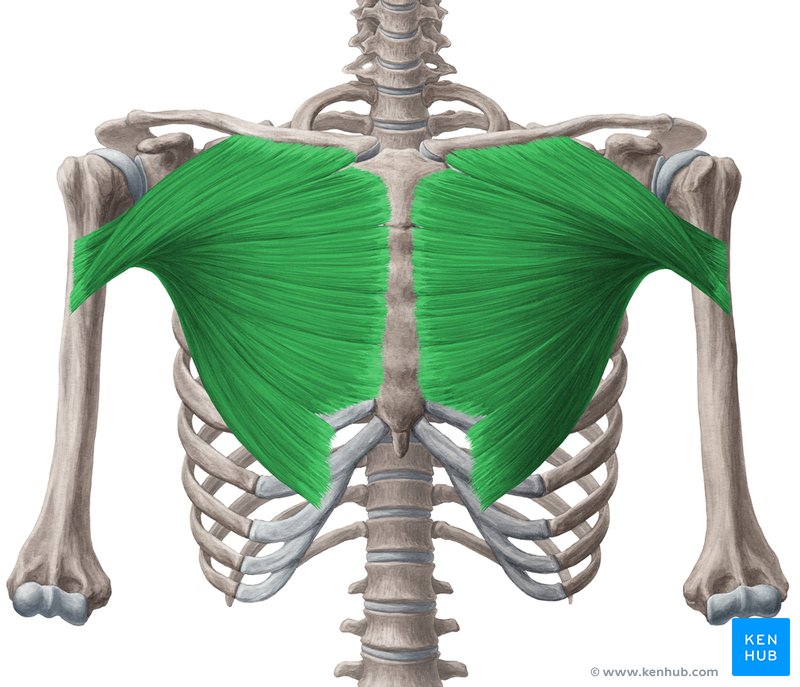
What muscle is this?
Pectoralis major.
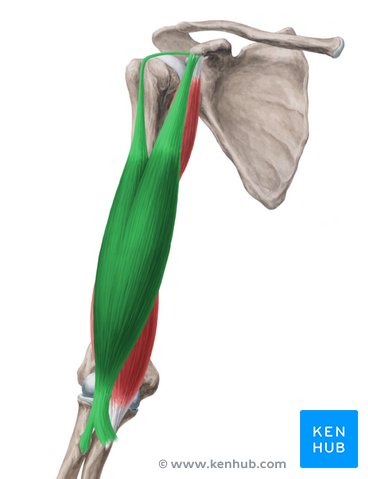
What muscle is this?
Biceps brachii.
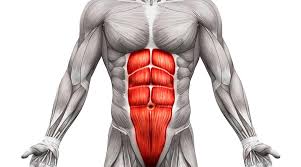
What muscle is this?
Rectus abdominis.
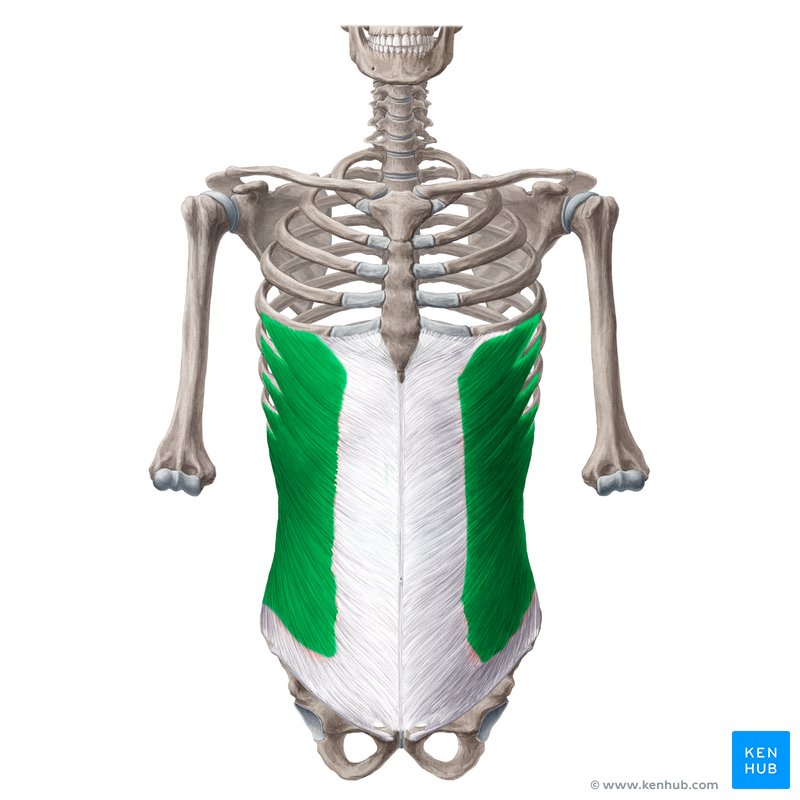
What muscle is this?
External obliques.
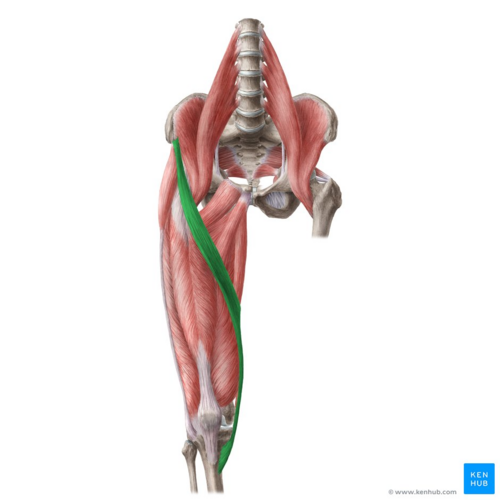
What muscle is this?
Sartorius.
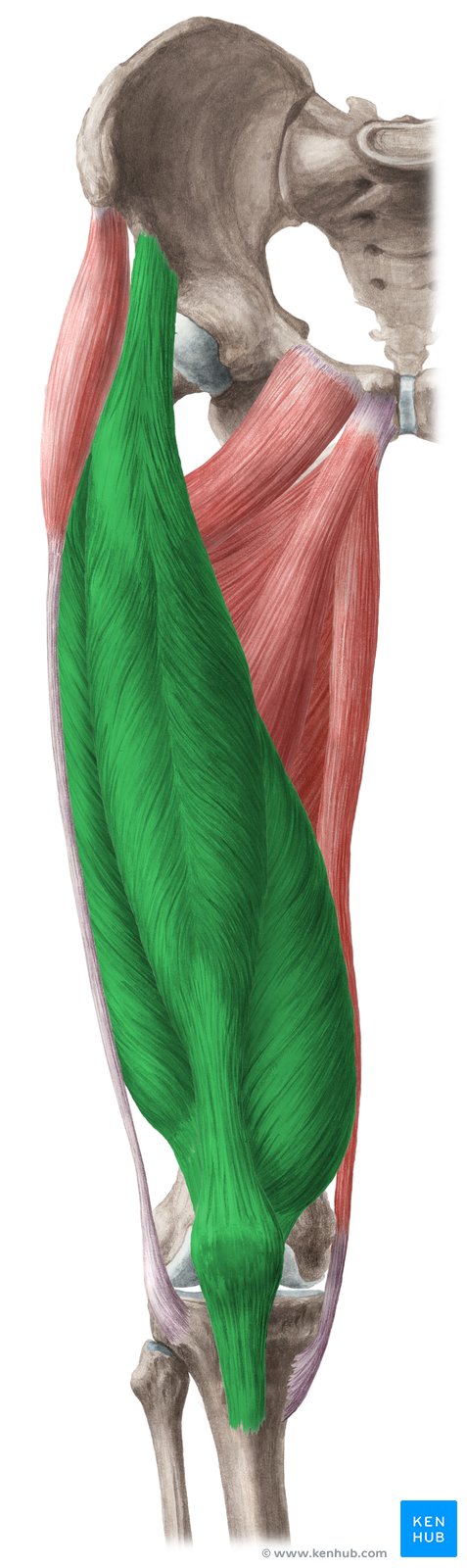
What muscle is this?
Quadriceps.
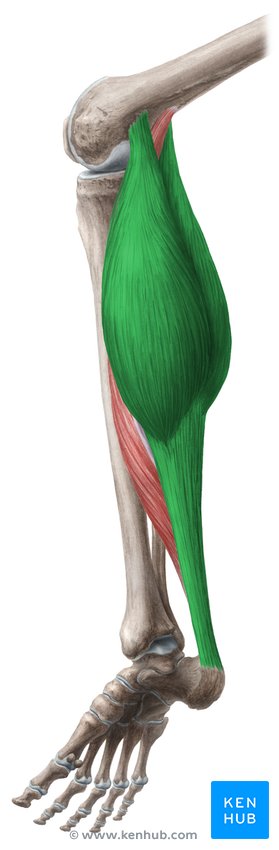
What muscle is this?
Gastrocnemius.
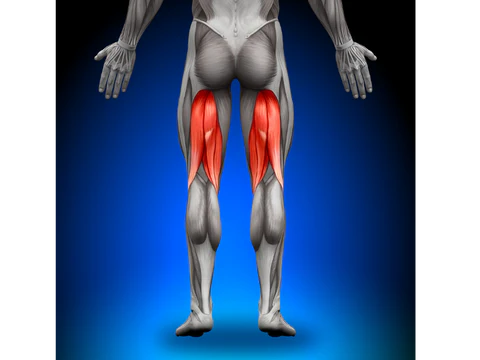
What muscle is this?
Hamstrings.
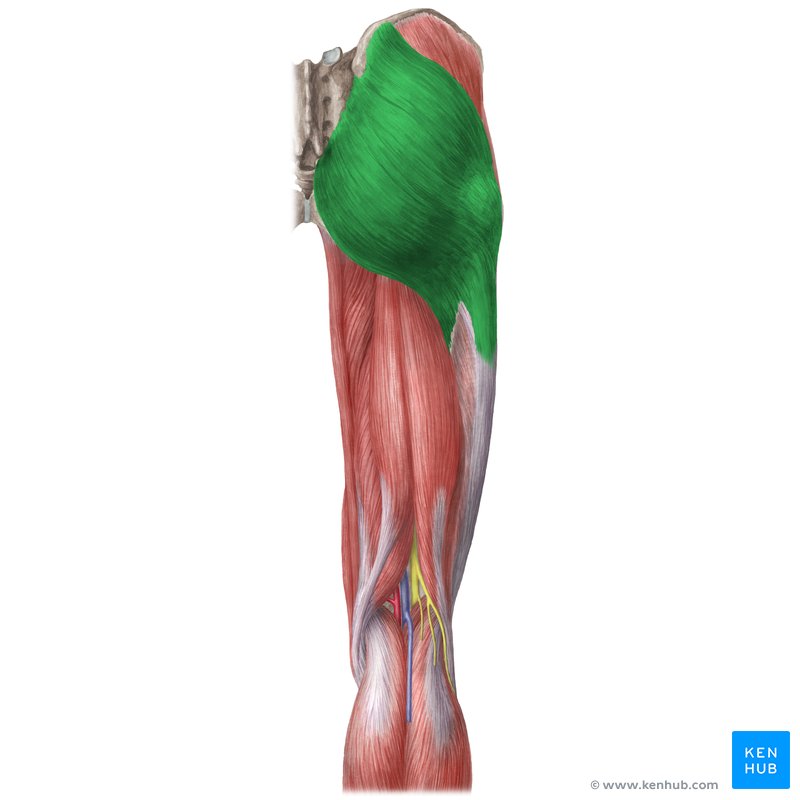
What muscle is this?
Gluteus maximus.
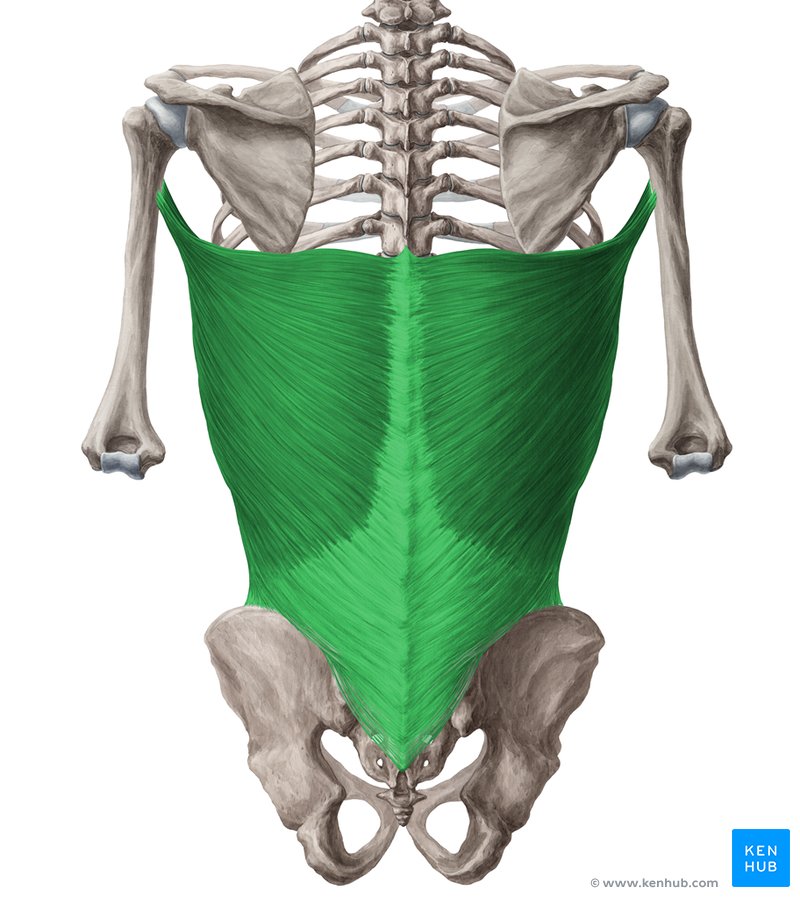
What muscle is this?
Latissimus dorsi.
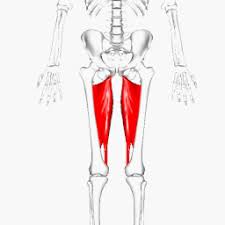
What muscle is this?
Adductors.
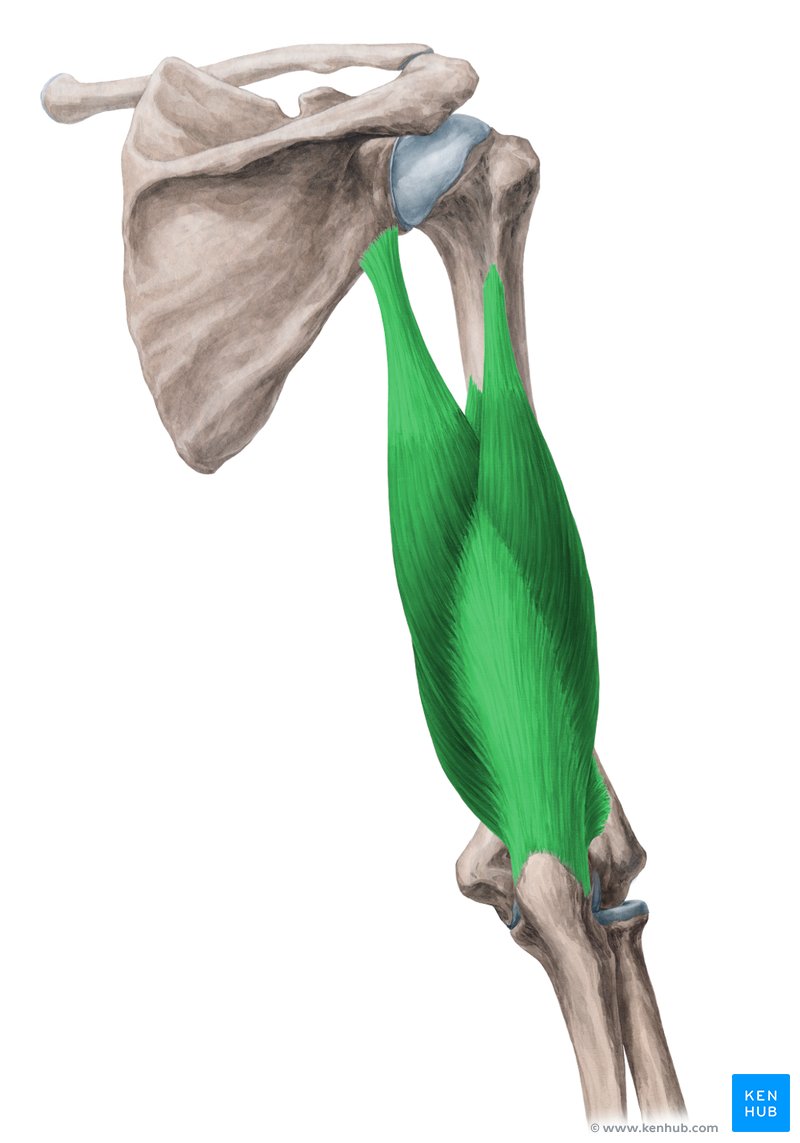
What muscle is this?
Triceps.
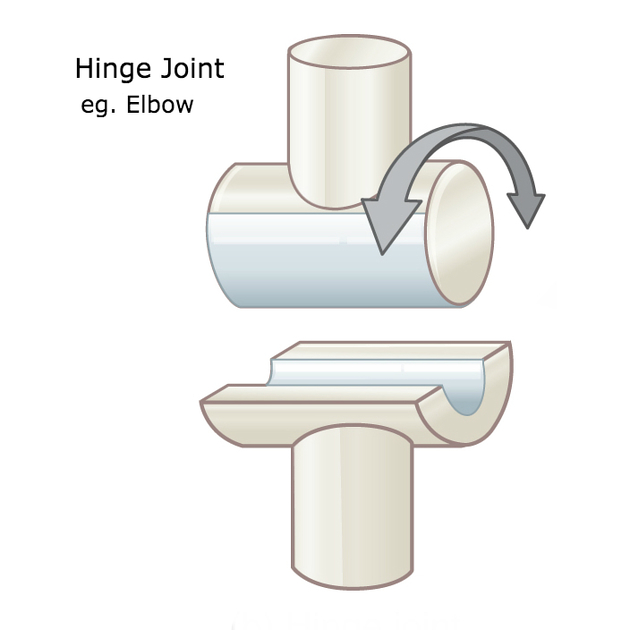
What joint type is this?
Hinge (example: elbow or knee)
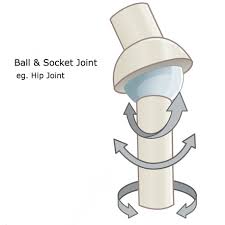
What joint type is this?
Ball and socket (example: shoulder or hip)
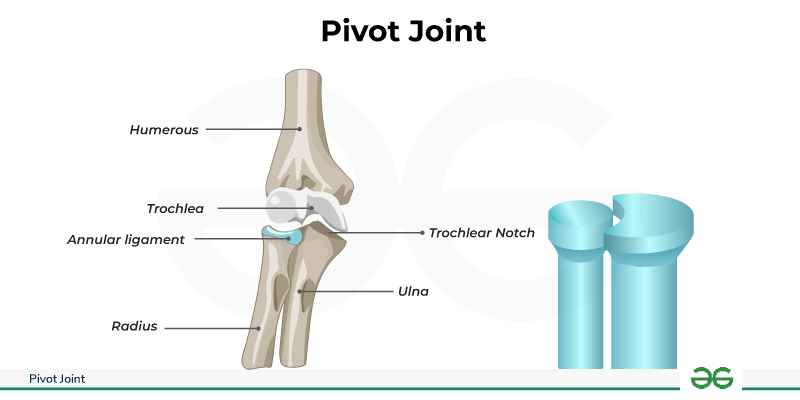
What joint type is this?
Pivot (example: forearm)
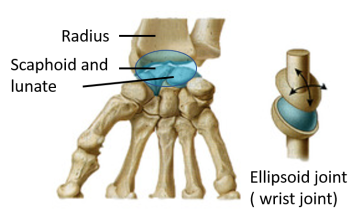
What joint type is this?
Elliposoid (example: wrist joint)
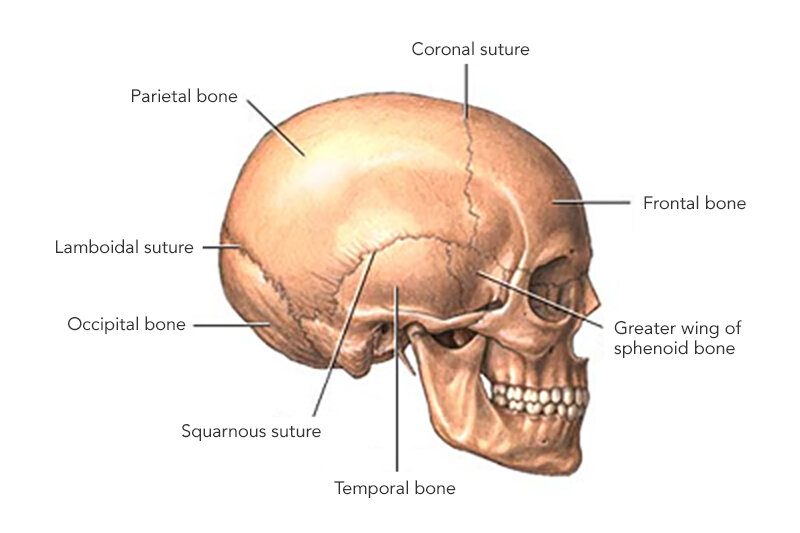
What bone is this?
Cranium (flat)
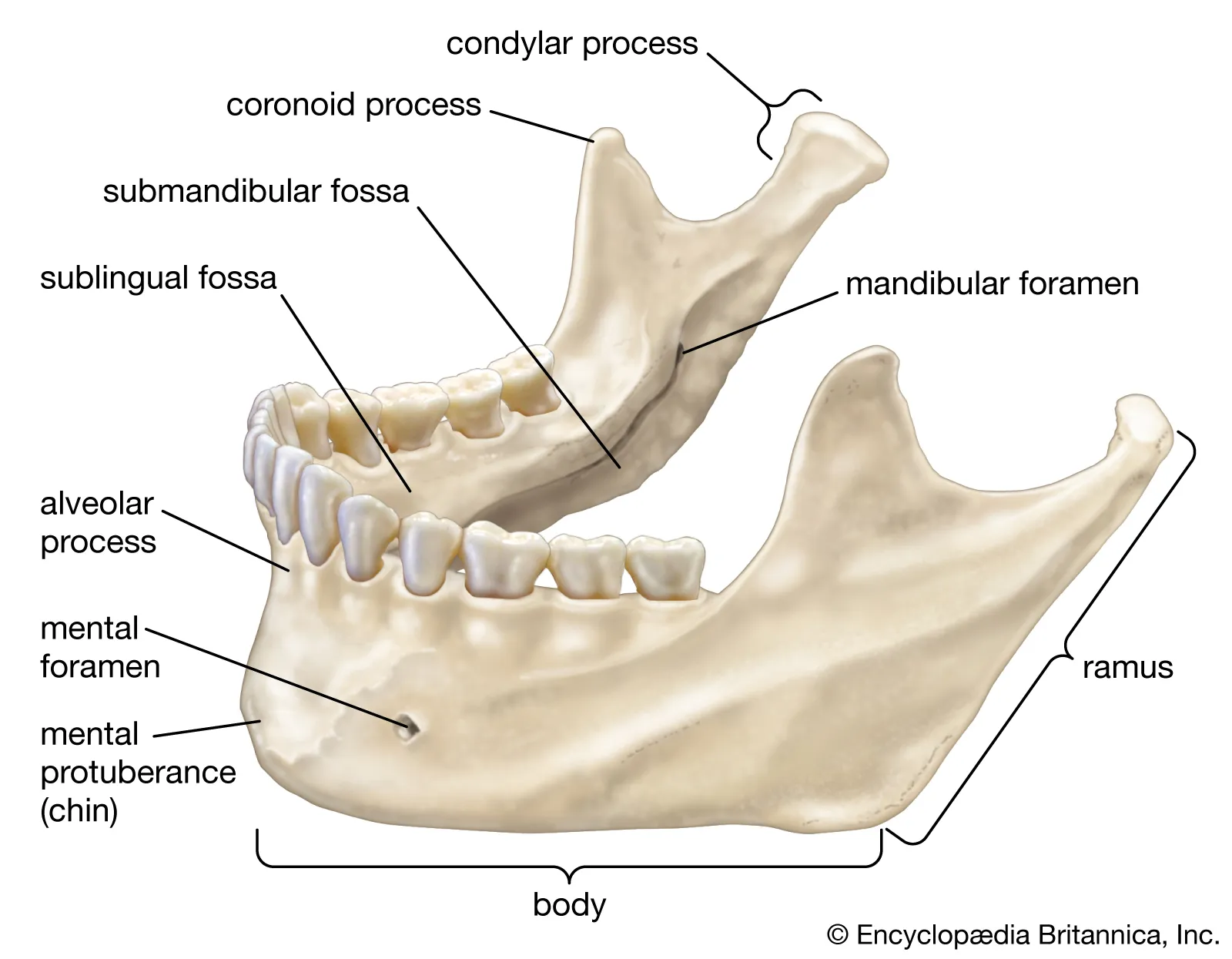
What bone is this?
Mandible (irregular)
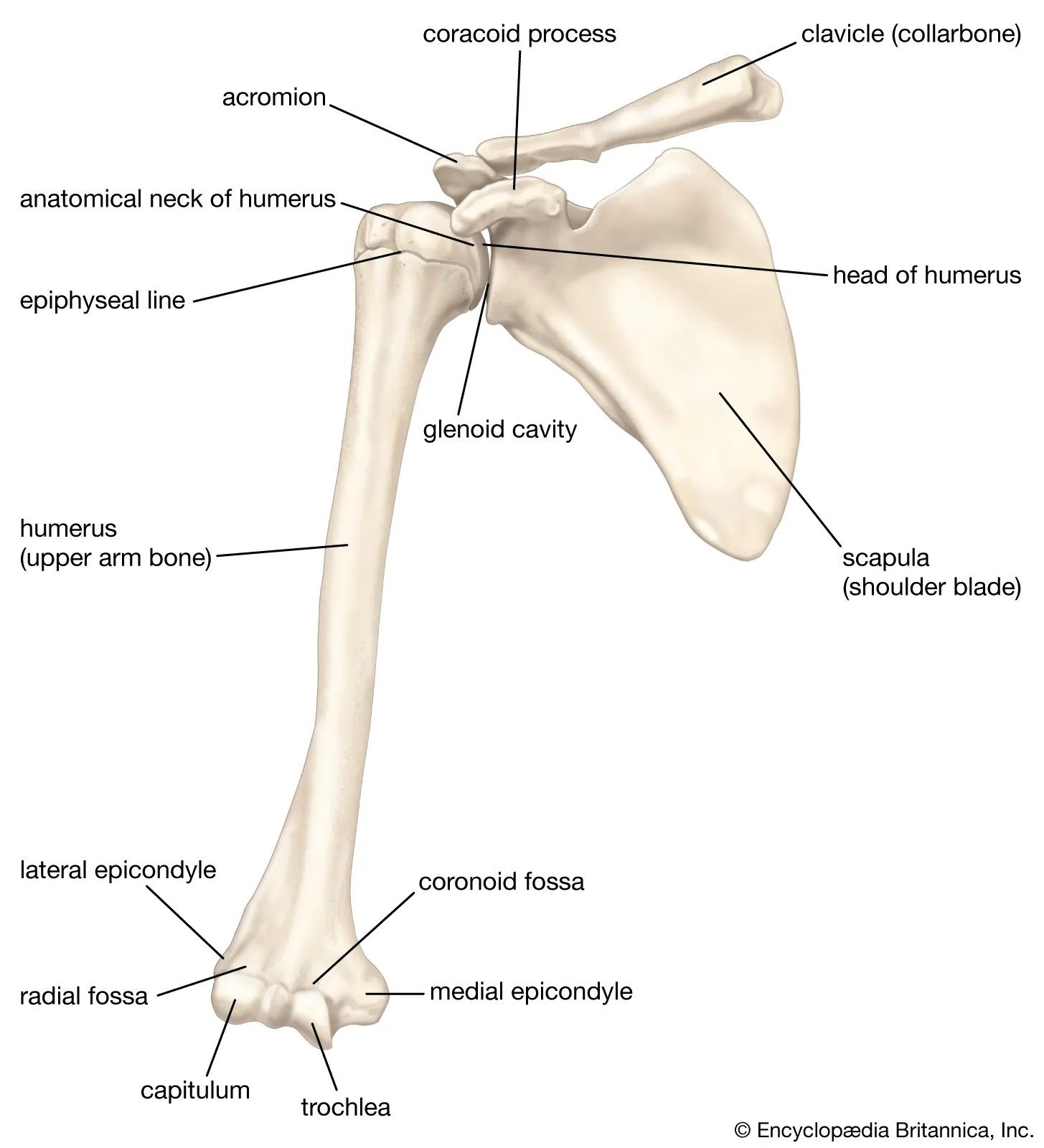
What bone is this?
Pectoral girdle (flat)
What bone is this?
Clavicle (long)
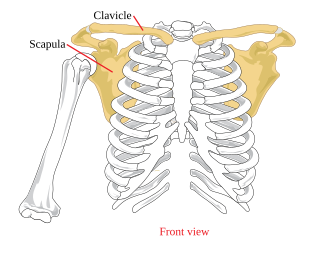
What bone is this?
Scapula (flat)
What bone is this?
Sternum (flat)
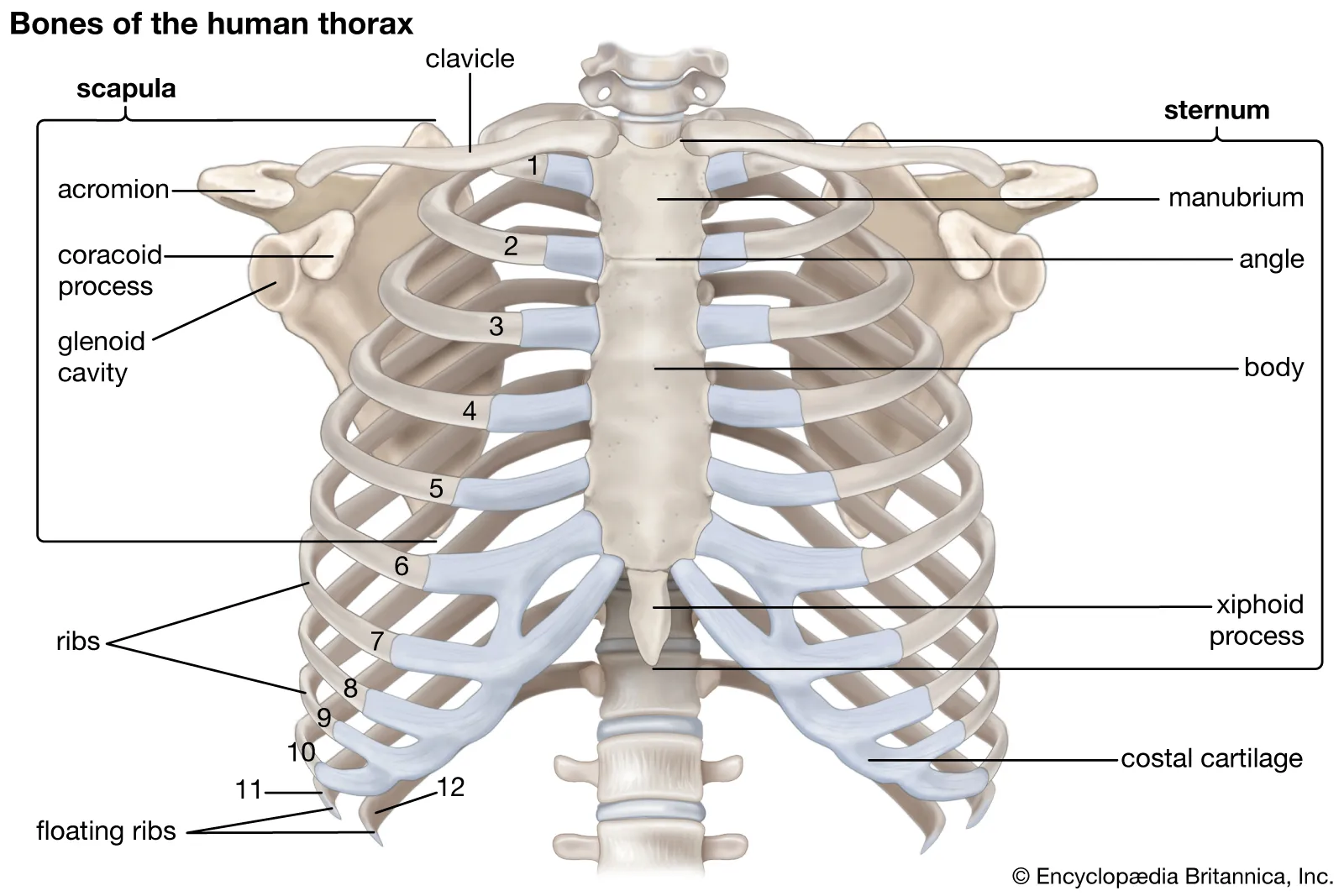
What bone is this?
Rib (flat)
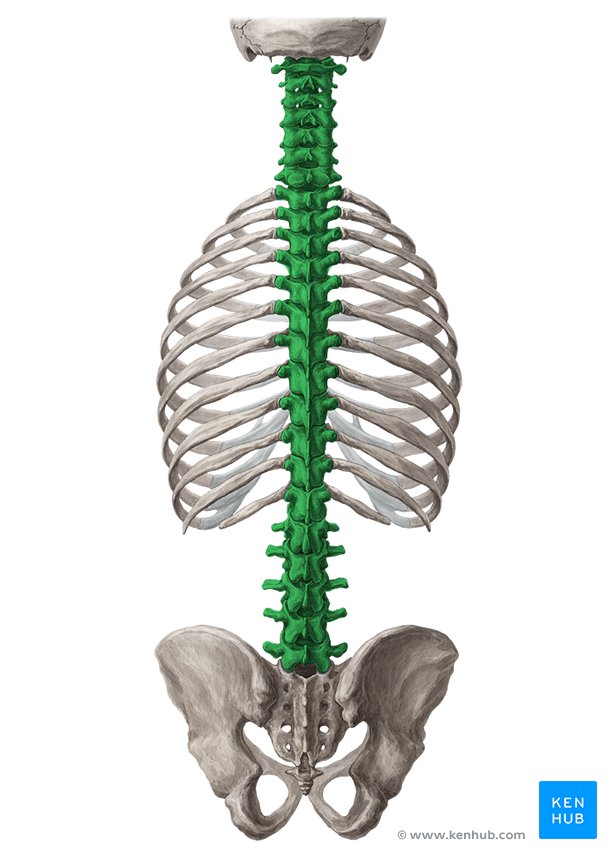
What bone is this?
Vetrebral column (irregular)
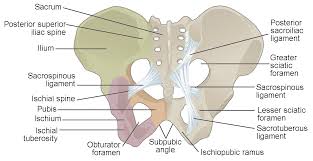
What bone is this?
Pelvic girdle (irregular)
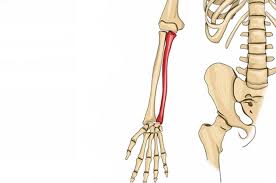
What bone is this?
Ulna (long)
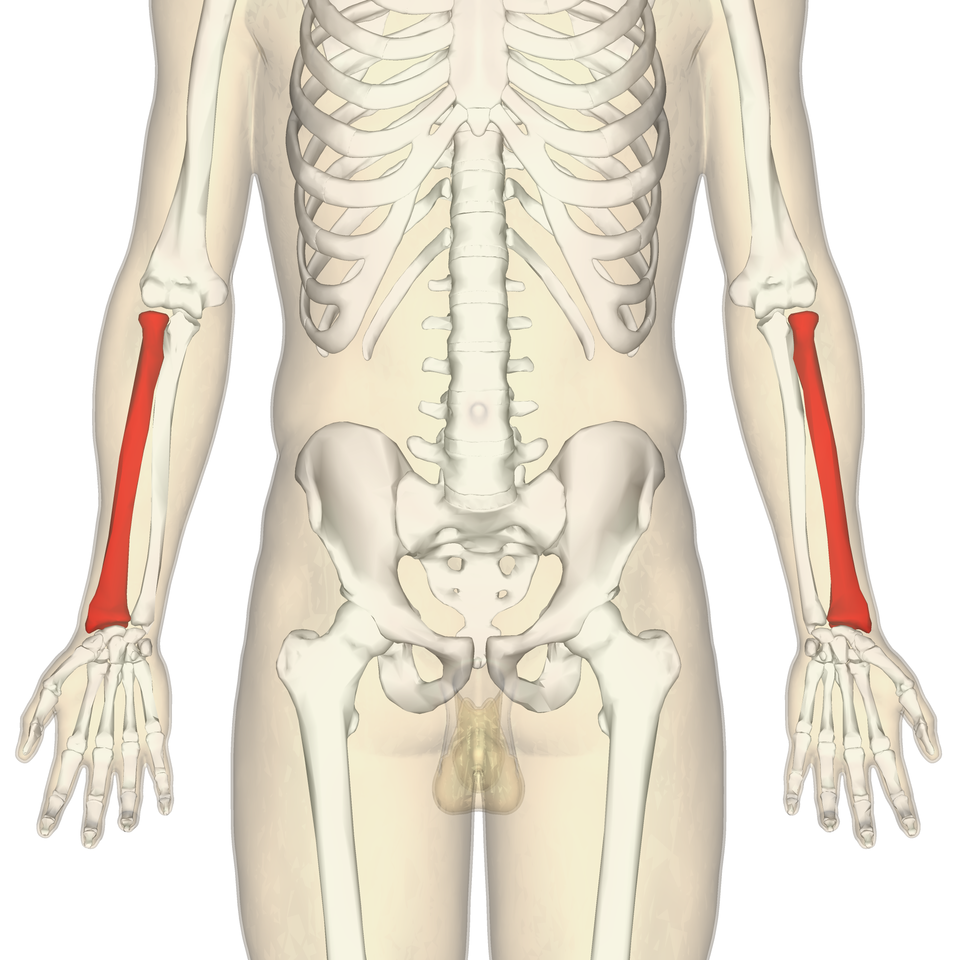
What bone is this?
Radius (long)
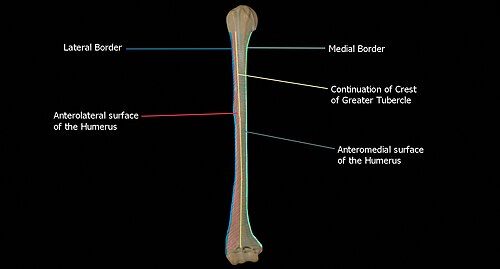
What bone is this?
Humerus (long)
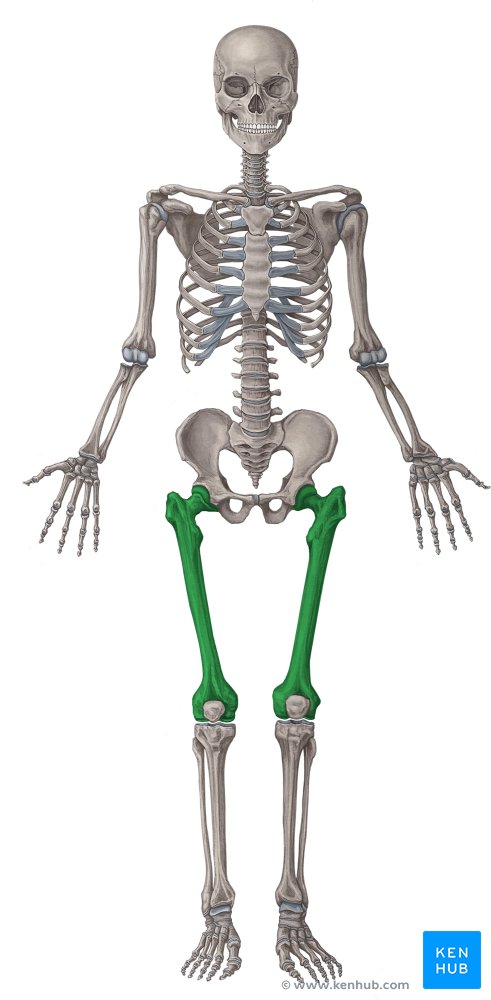
What bone is this?
Femur (long)
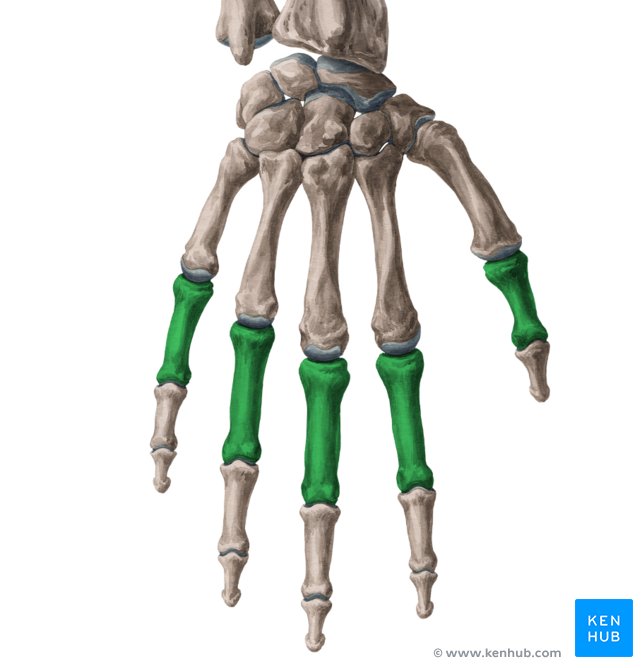
What bones is these?
Phalanges and metacarpals (long)
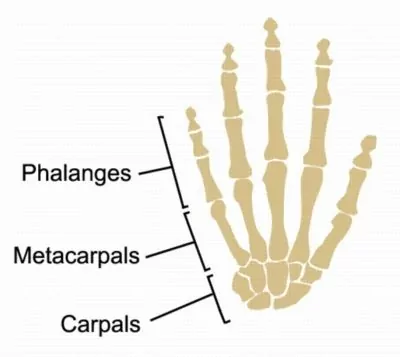
What bone is this?
Carpals (short)
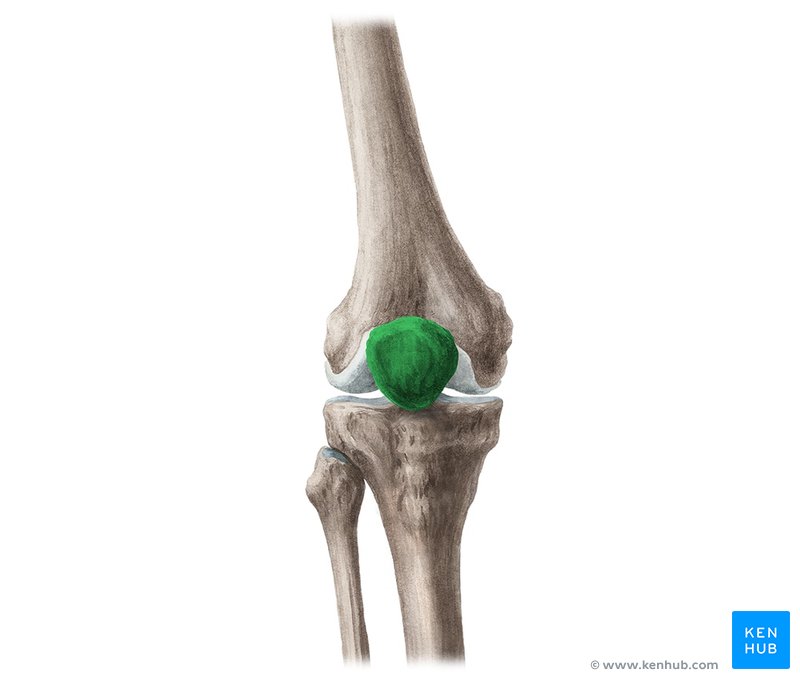
What bone is this?
Patella (sesamoid)
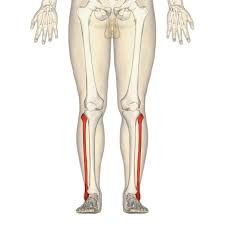
What bone is this?
Fibula (long)
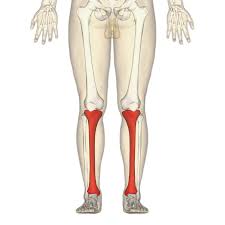
What bone is this?
Tibia (long)
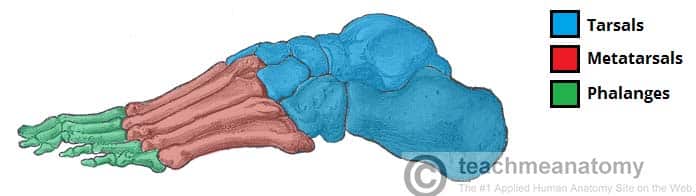
Foot phalanges.
Phalanges and Metatarsals (long), Tarsals (short)
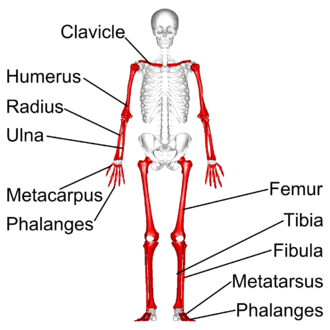
What are long bones?
Act as levers, facilitating movement, allowing absorption of stresses and body weight.

What are short bones?
Cube shaped, consist mostly of spongy bone.
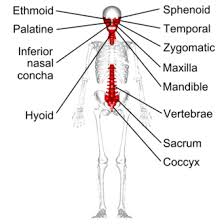
What are irregular bones?
Don’t fit into other categories, have a complex shape.
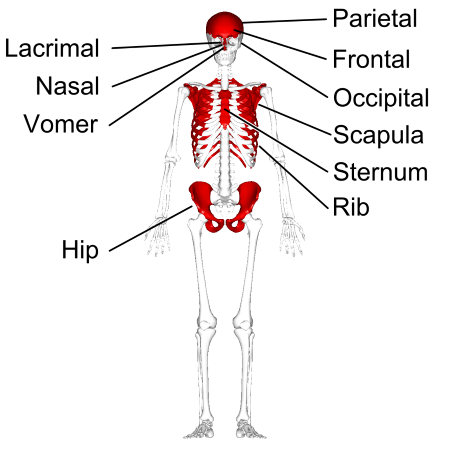
What are flat bones?
‘Protecting bones’, usually curved, thin.
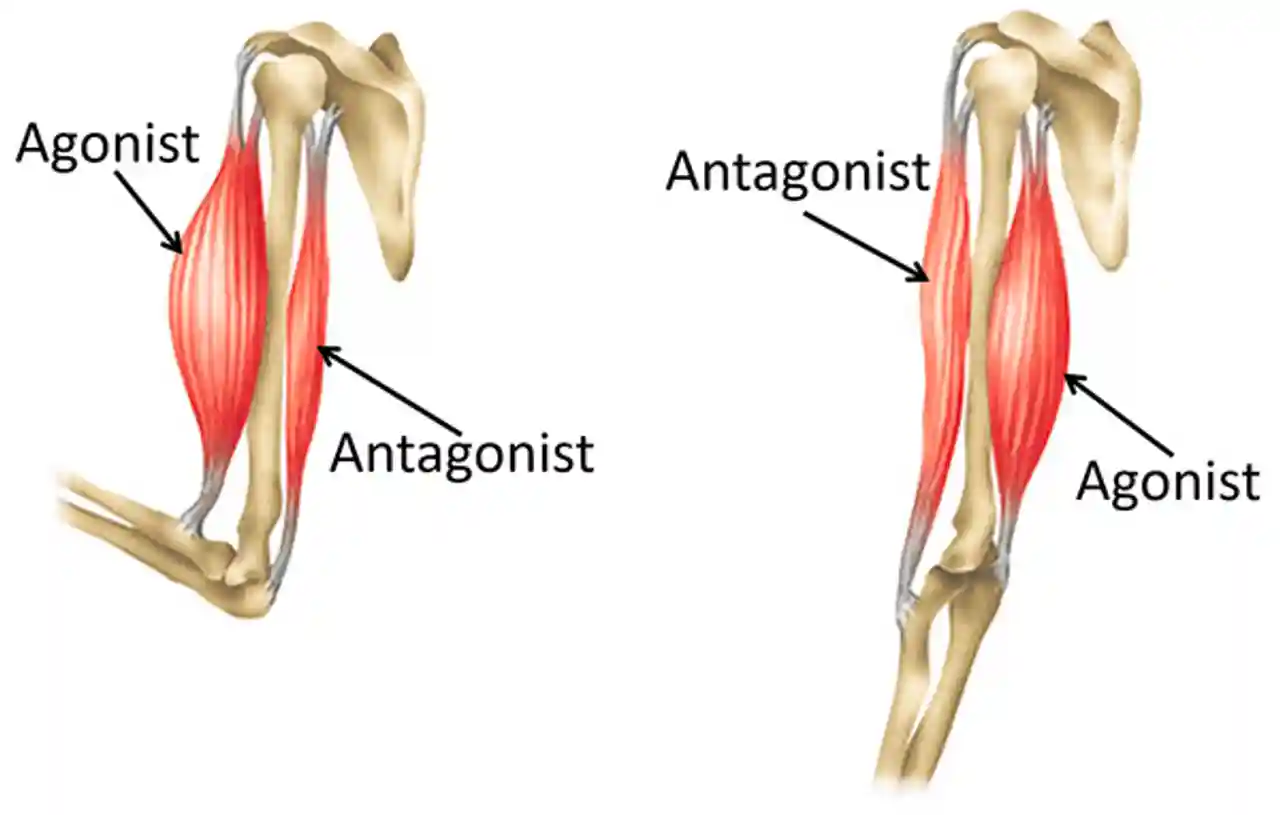
What is the agonist muscle?
Main muscle that generates movement of a bone around a joint.
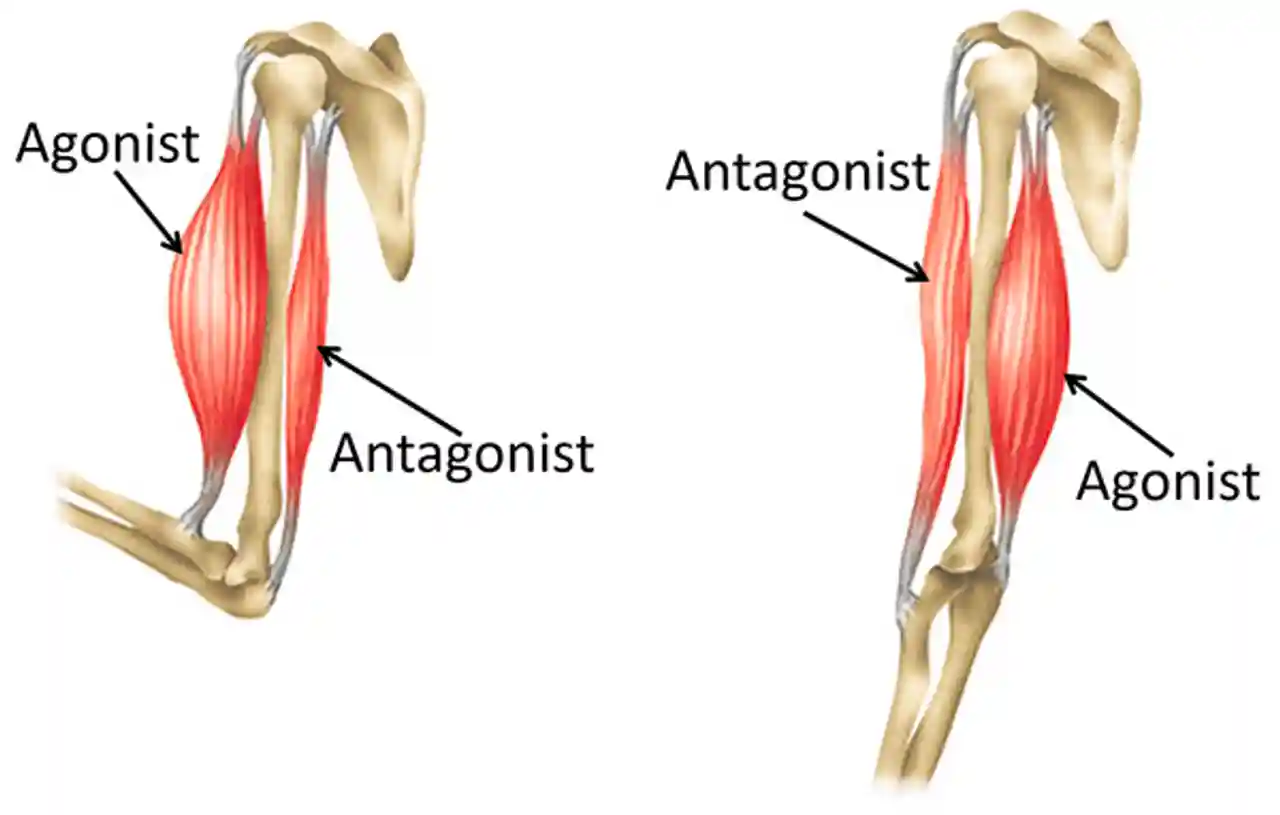
What is the antagonist muscle?
Opposes action of the other muscle.
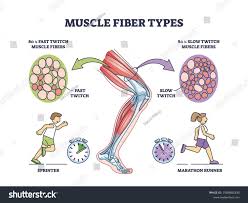
Describe a fast twitch muscle.
Fast, powerful contractions, tire quickly, burn oxygen quickly (meaning they are anaerobic), smaller white, short term, used for power and strength. (e.g. layup in basketball)
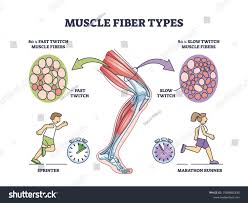
Describe a slow twitch muscle.
Contract slowly, weaker, aerobic, used in endurance activities. (e.g netball player in C, ironman, West Macs)
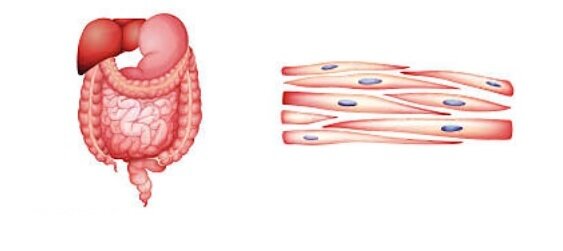
Smooth Muscles?
involuntary, found in between outer covering, inner lining (like bread and cheese), from the sphincter. (e.g. intensines, stomach, bladder)
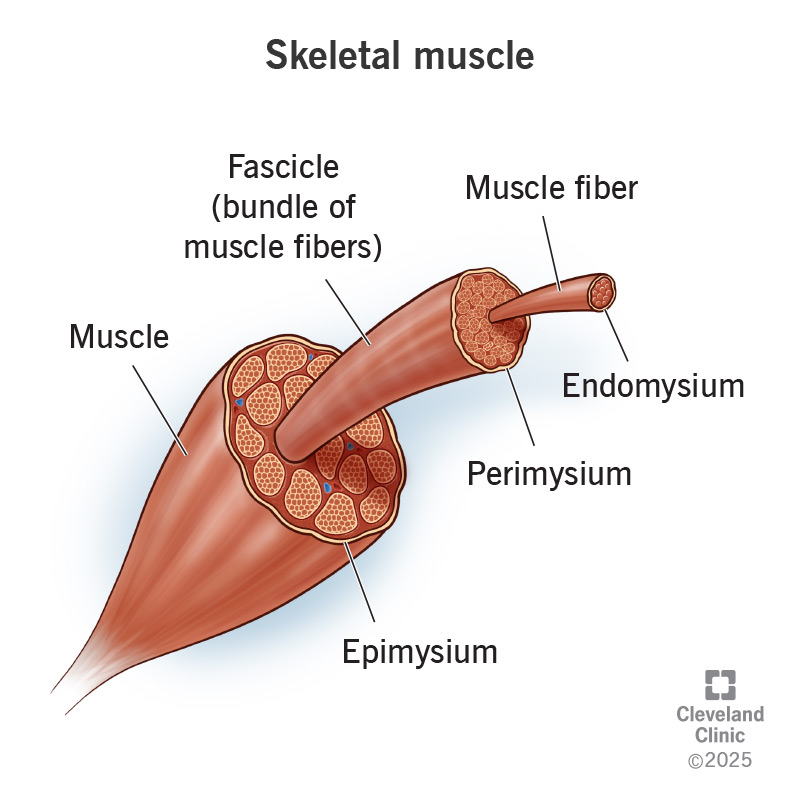
Skeletal Muscles?
voluntary movements, attached to bones via tendons (e.g. hamstring muscles, abdominal muscles, shoulder muscles)
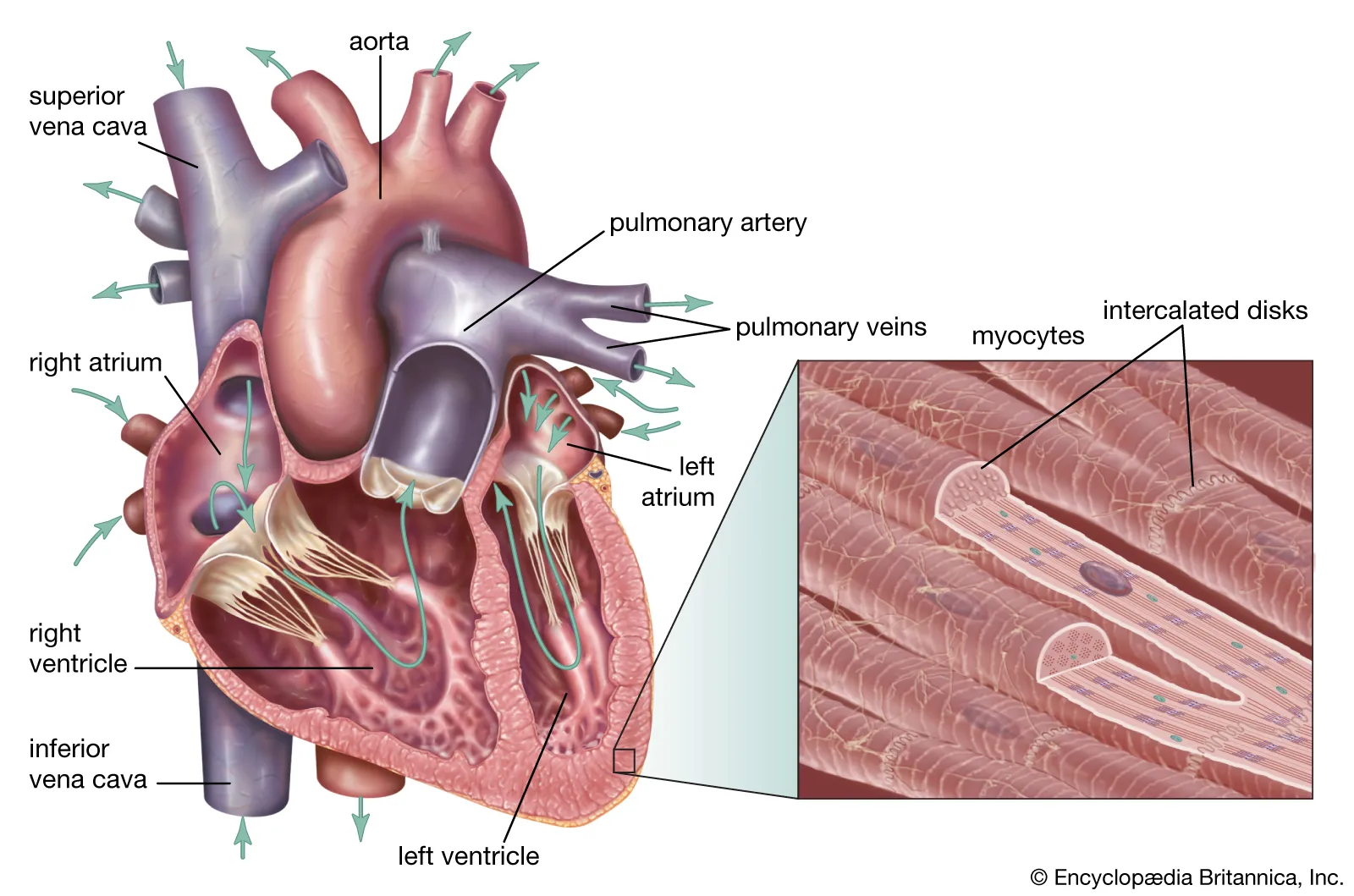
Cardiac Muscles?
heart related, involuntary (just your heart)