DNA Replication and Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
DNA Polymerase
Enzyme that replicates DNA during cell division.
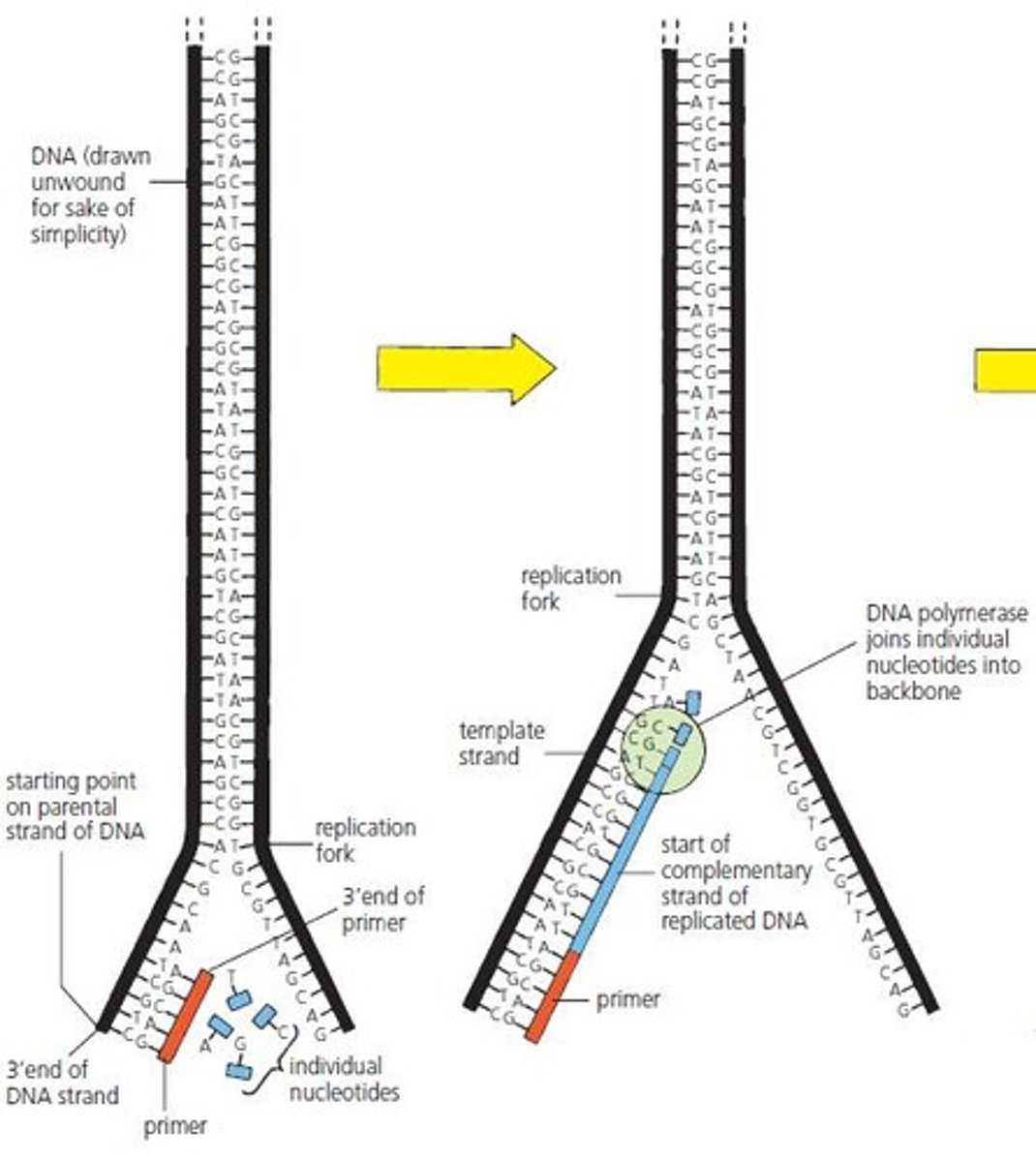
Primers
Short nucleotide strands initiating DNA replication.
Template DNA Strand
Original DNA strand used for replication.
Leading Strand
Continuously replicated DNA strand during replication.
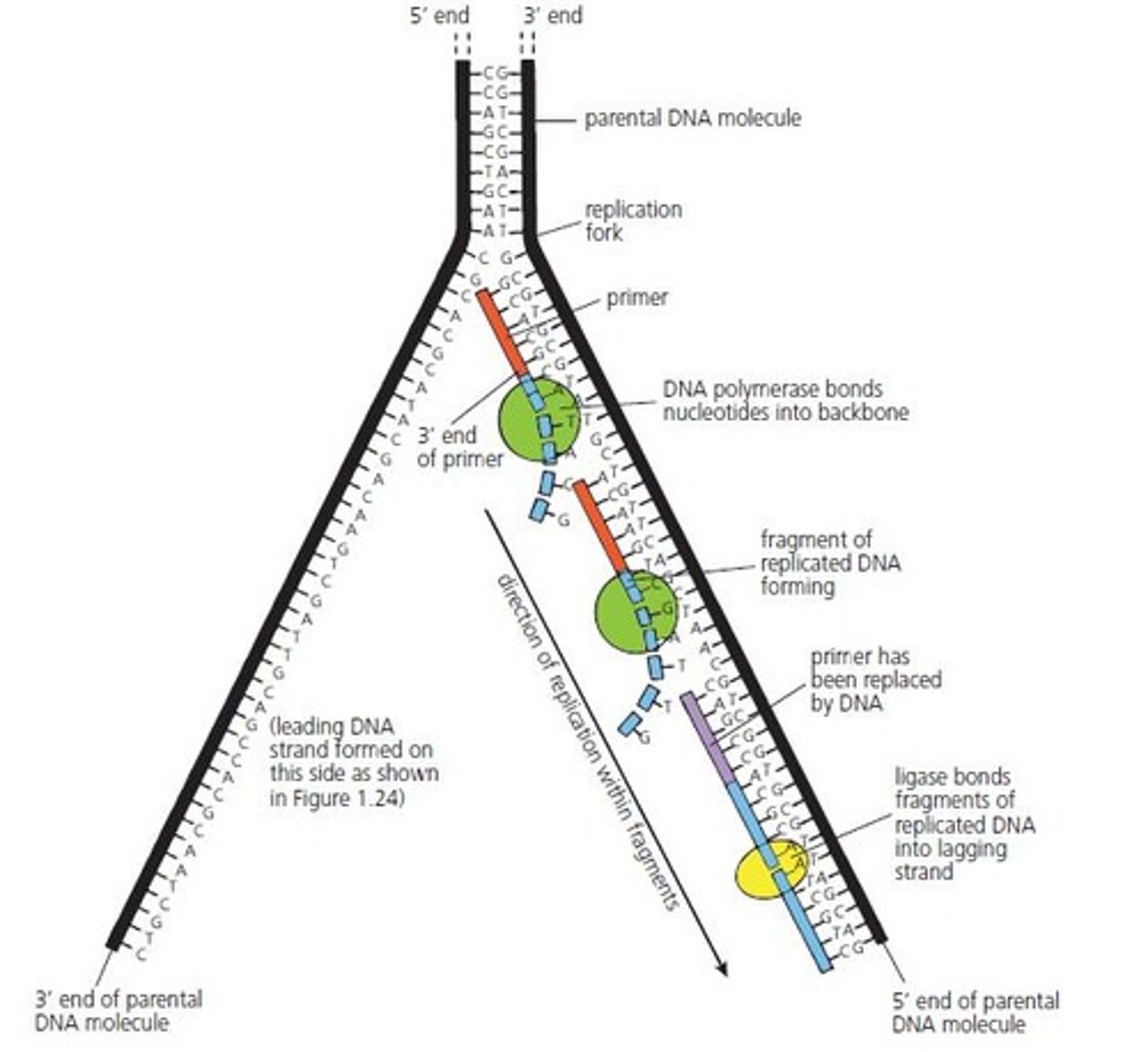
Lagging Strand
Discontinuously replicated DNA strand in fragments.
DNA Ligase
Enzyme joining fragments on the lagging strand.
Complementary Base Pairing
Specific pairing of DNA bases (A-T, C-G).
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
Technique to amplify specific DNA sequences.
Heating in PCR
Separates DNA strands at 92-98°C.
Cooling in PCR
Allows primers to bind at 50-65°C.
Heat-Tolerant DNA Polymerase
Enzyme replicating DNA at 70-80°C in PCR.
PCR Cycles
Repeated heating and cooling to amplify DNA.
DNA Amplification
Doubling of DNA amount with each PCR cycle.
DNA Template
Original DNA needed for PCR amplification.
DNA Nucleotides
Four types (A, T, C, G) required for replication.
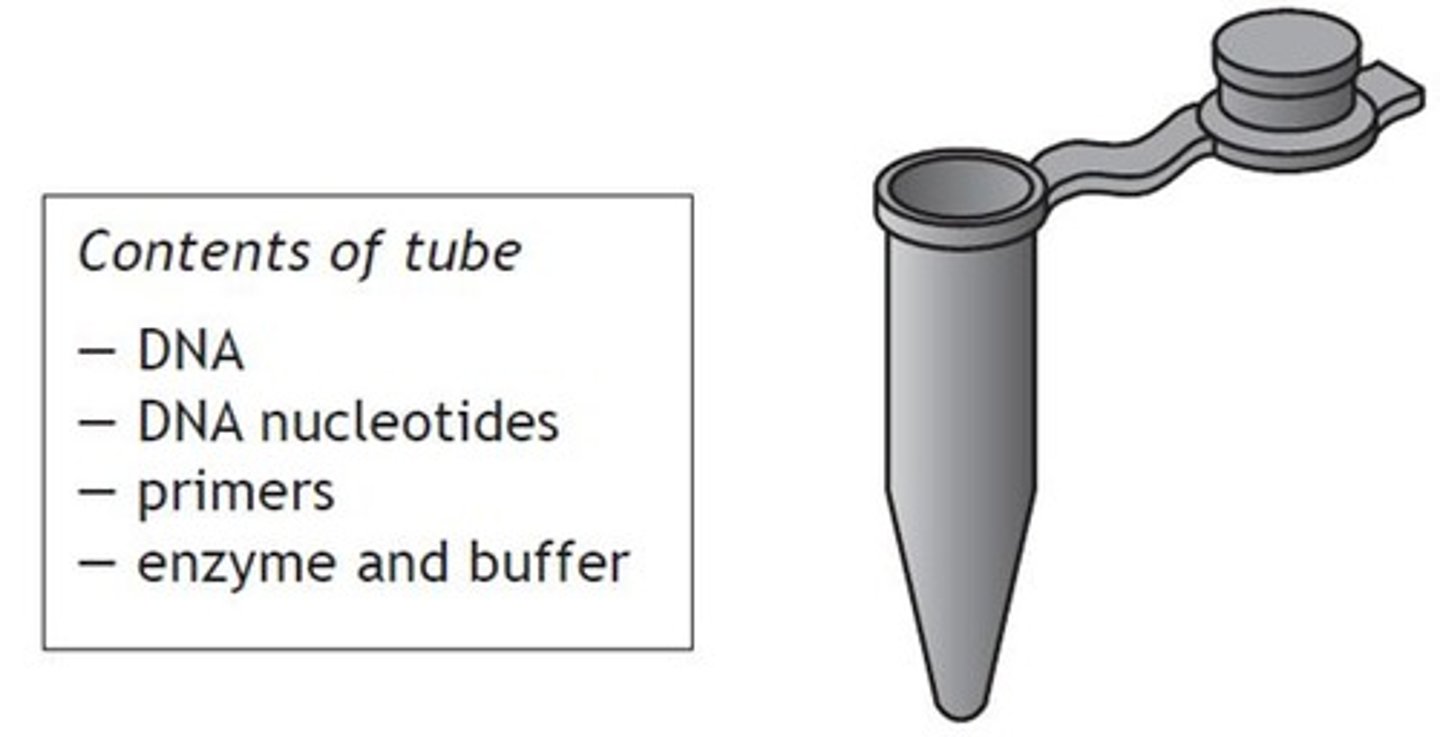
pH Buffer
Maintains optimum conditions for enzyme activity.
Forensic Evidence
PCR application for solving crimes.
Paternity Suits
PCR application for determining biological relationships.
Genetic Disorders Diagnosis
PCR application for identifying genetic conditions.
Hydrogen Bonds
Connections between DNA bases that are broken during unwinding.
Fragments
Short sections of DNA on the lagging strand.