Classical AS Model, BoP and the Exchange Rate
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Classical AD/AS Model
A macroeconomic model/graph which shows both AD and AS (which is split into SRAS and LRAS) in the economy at each respective price level (PL) over a given period of time. Real GDP/income (Y) is shown on the x-axis.
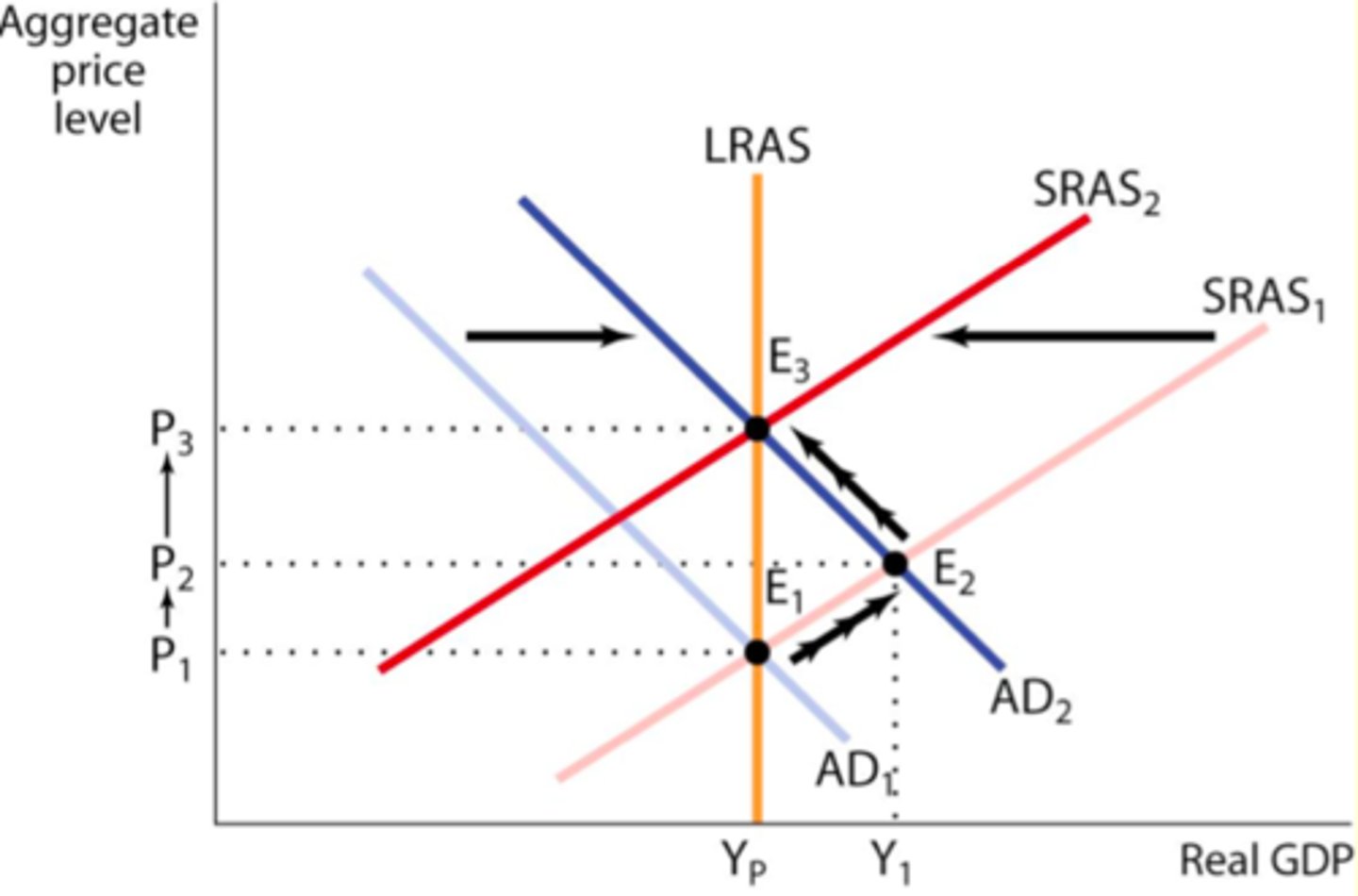
SRAS
Sloping, Aggregate supply that varies with the demand for goods and services, and that is shifted by changes in costs of factors of production
LRAS
Vertical. The total Quantity and Quality of resources available within an economy.
Three accounts of the balance of payments
current account, financial account, capital account
Balance of payments
the difference between the amount of money that comes into a country and the amount that goes out of it, the record of all international transactions into and out of the country.
Current Account
In the balance of payments, records transactions involving the flow of income, export or import of goods and services, net primary and secondary income.
Net Primary Income
Part of the current account of the balance of payments, it measures the net flow of profits (Reward for factor of productions), interest and dividends from investments in other countries (inflows of money) and net remittance flows from migrant workers (outflows of money).
Capital Account
national account that records transactions involving the purchase and sale of assets and debt forgiveness
Financial Account
In balance of payments, transactions that involve hot money flows, FDI and portfolio investments (Stocks and Shares)
Visible Trade
Component of the current account; The import or export of physical goods such as cars, clothing and food.
Invisible Trade
Component of the current account; The import or export of services such as tourism, financial services and information services.
Net secondary income
Part of the current account of the balance of payments, payments flowing between countries in forms such as foreign aid and contributions to international institutions.
Financial Capital
The funds a firm uses to acquire its assets and finance its operations
Balancing Item
Since records of transactions are imperfect the accounts never exactly balance. For this reason the government's statisticians add in a balancing item (a figure) to bring the total to zero.
Foreign Direct Investment
Component of Financial Account: Investment by a multinational corporation headquartered in one economy, in a foreign country's economy.
Portfolio Investment
Component of Financial Account: Investment in a foreign country via the purchase of stocks (equities), shares of foreign companies, bonds, or other financial instruments. Portfolio investors do not exercise managerial control of the foreign operation.
Reserve Assets
Component of Financial Account:Refers to foreign currency reserves that the central bank maintains and can buy or sell to influence the value of the country's currency exchange rate.
Credit
An inflow of income into the economy
Debit
Outflow of income from the economy
Types of services
Financial services, information services, consultancy, tourism, education
Bilateral Exchange Rate
The rate of exchange of one single currency for another single currency
Effective Exchange Rate
Otherwise known as Trade Weight Exchange Index; Measure of the exchange rate of a country's currency, usually against a basket of currencies of a country's major trading patterns.
Exchange Rate
The rate at which one country's currency can be exchanged for that of another in the FOREX market.
Floating Exchange Rate
An exchange rate policy under which a government permits its currency to be traded on the open market by the forces of demand and supply without direct government control or intervention. Examples include USA, Australia, the UK, the Eurozone, Japan and Russia.
Depreciation
A fall in the value of one currency in terms of another currency in a floating exchange rate system.
Appreciation
An increase in the value of a currency as measured by the amount of foreign currency it can buy, determined by the floating exchange rate.
Devaluation
a reduction in the value of a currency that is set under a fixed exchange rate regime through government policy or a central bank.
Revaluation
An increase in the value of a currency in a fixed exchange rate system due to government or central bank policy.
Forex Market
The market in which international buyers and sellers buy, sell or exchange currencies for hedging and speculative purposes. Forex is the largest financial market in the world and is made up of banks, commercial companies and central banks. It is where a currency's exchange rate relative to other currencies is determined.
Currency Demand
An inflow of money into an economy. This is a DERIVED demand, meaning it is derived from demand for a country's exports of goods and services.
Currency Supply
The outflow of money into an economy. We supply money into the FOREX market when we want foreign goods. It is determined by the level of domestic demand for foreign imports and goods.
Speculative purchases of currency
The most significant influence on a floating exchange rate. The purchase of currency by a hedge fund or a financial institution where they believe the value of the currency will appreciate, so they can then sell off the currency for a profit when the currency does.
Price Elasticity of Demand
a measure of how much the quantity demanded of a good responds to a change in the price of that good. Affects the effect to which a depreciation or appreciation of the exchange rate on a country's balance of trade.
J curve
Diagram showing the effect of currency depreciation on the trade deficit, which depends on PED for exports and imports. The country's trade deficit can worsen after depreciation as the PED of imports and exports is more likely to be inelastic, but improve in the medium term if the Marshall-Lerner condition holds.
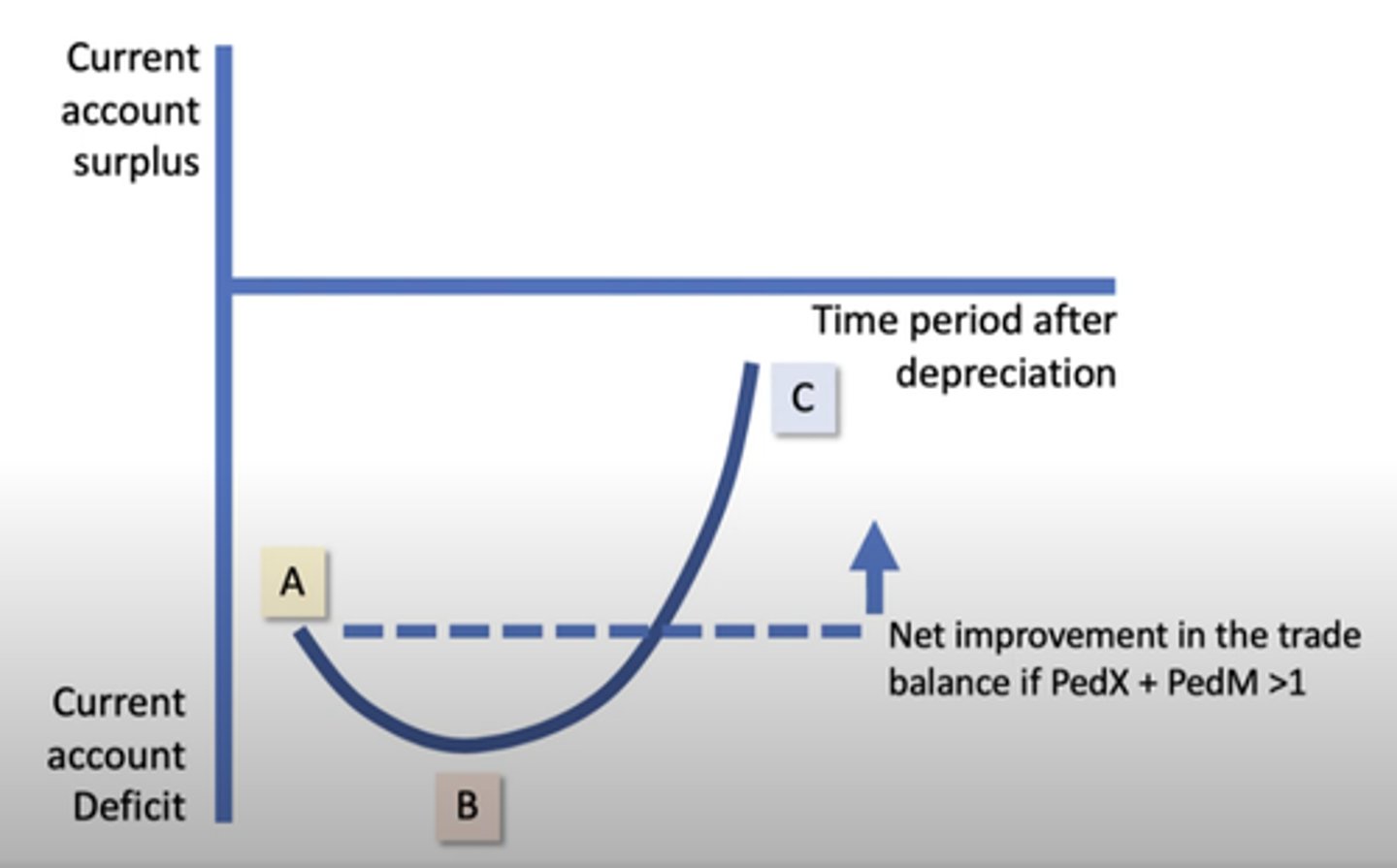
Marshall-Lerner Condition
States that a depreciation, or devaluation, of a currency will only lead to a net improvement in the current account balance if the PED of exports plus the PED for imports is greater than one. However, this does not always hold, as seen through oil.

Global Trade Imbalances
Occur when some countries have persistent large current account deficits while other countries have large current account surpluses
Savings ratio
Savings as a proportion of disposable income
Mercantilism
An economic policy under which nations sought to increase their wealth and power by having an excess of exports over imports (Trade surpluses and export-led growth)
Protectionism
The theory or practice of shielding a country's domestic industries from foreign competition by taxing imports. Can result in retaliation, inflation and reduced living standards.
Impact of a depreciation in the exchange rate on FDI
Reduces FDI and investment, as investors believe the value of their assets will decline under depreciation so will resist until the currency begins to climb again, reduces AD.
Reducing expenditure
Policy to reduce a current account deficit where a government puts quotas on the amount of imports allowed to be imported, in order to reduce the volume of imports.
Supply-Side Policies
economic policies designed to stimulate the economy and reduce the current account deficit by increasing production of exports.