RBC Morphology
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
A. Hypochromic Red Blood Cell,
B. Bigger central area of pallor
C. Hypochromasia
D. Microcytic hypochromic anemia
A. Identify the pointed cell
B. Describe the striking feature
C. Increased number of this cell in the peripheral smear is termed as?
D. Give associated condition
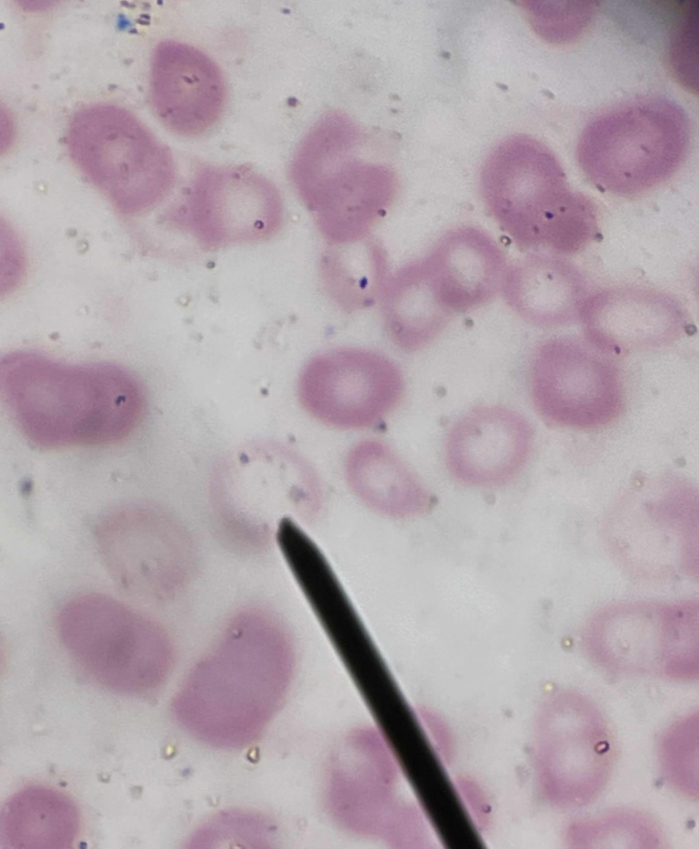
A. Red Blood Cell with Cabot Ring
B. Dark blue or reddish-blue to purple thin ringlike structure
C. Remnants of mitotic spindle
D. Megaloblastic Anemia, Lead poisoning, Dyserythropoiesis
A. Identify the pointed cell
B. Describe the striking feature
C. What represents the inclusion of this cell?
D. Give associated condition
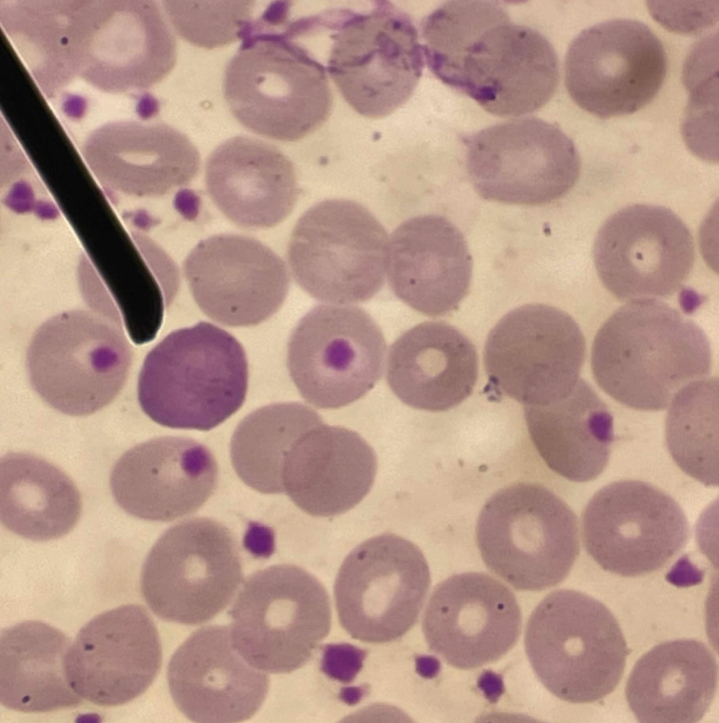
A. Echinocyte
B. Evenly distributed uniform-sized blunt spicules
C. True
D. Artifact
A. Identify the pointed cell
B. Describe the striking feature
C. Is not associated with pathological condition (True or False)
D. What formation can be seen from this cell?
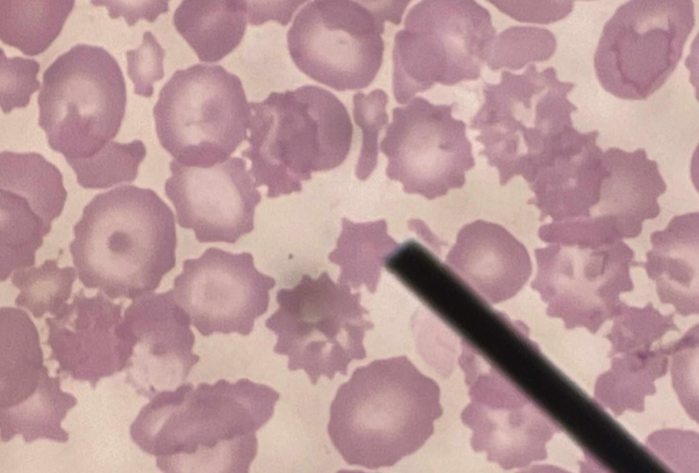
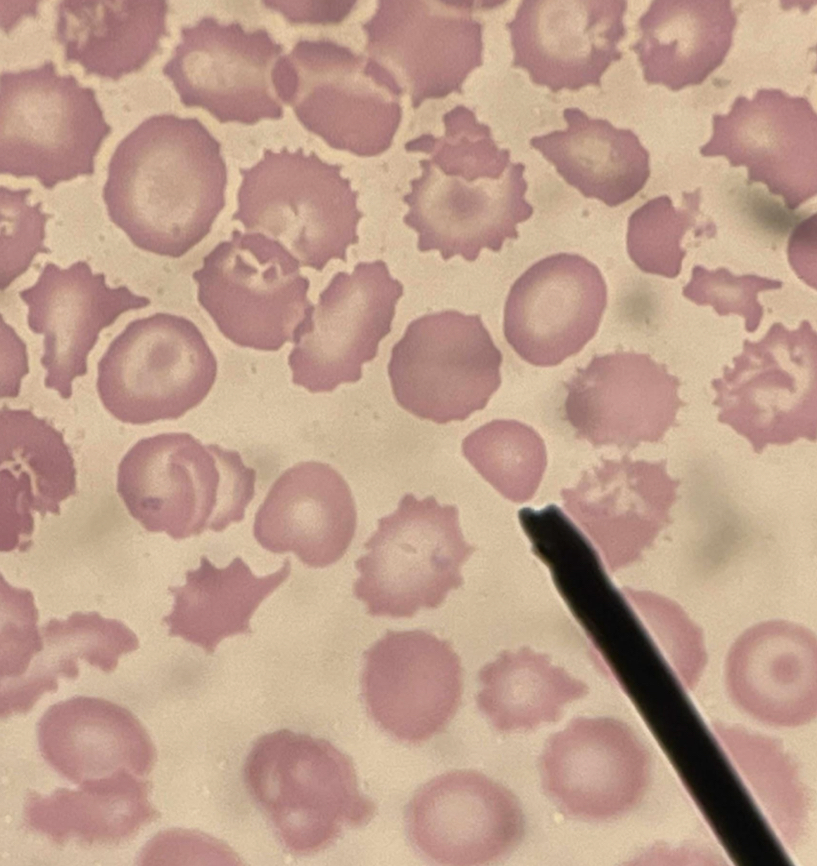
A. Burr Cell
B. Irregularly sized and unevenly spaced blunt spicules
C. Renal Insufficiency; Azotemia (increased in BUN)
D. Gastric carcinoma, Liver disease, Pyruvate kinase deficiency
A. Identify the pointed cell
B. Describe the striking feature
C. Associated with what pathological findings?
D. Other associated conditions
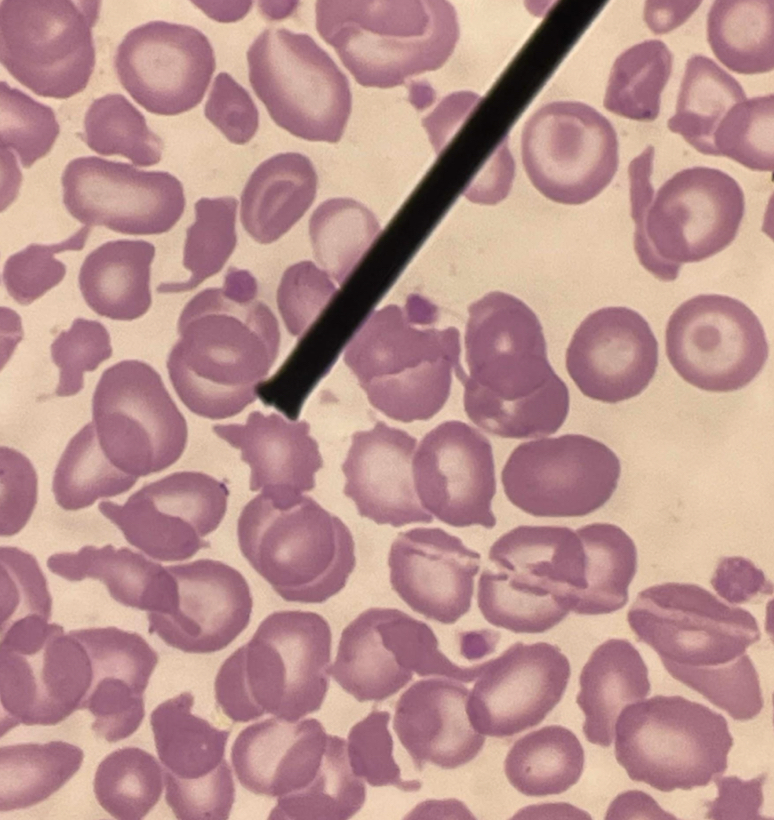
A. Schistocyte
B. Helmet, triangular and variety of irregular shapes
C. Microangiopathic hemolytic anemia
D. Helmet cell, Bite cell, Blister cell
A. Identify the pointed cell
B. Describe the striking feature
C. Associated with what pathological findings?
D. What are the other categories under this cell?
A. Sickle cell
B. Thin and elongated cell with pointed end
C. Sickle cell anemia
D. Polymerization of Hgb S (sickling hemoglobin)
E. Sodium metabisulfite and Hemoglobin solubility
F. Valine instead of glutamine
A. Identify the pointed cell
B. Describe the striking feature
C. Associated with what condition?
D. what is responsible for the characteristic shape of this cell?
E. What screening tests can be done ?
F. What is the main defect of this cell?
A. Stomatocyte
B. Slit-like central area of pallor
C. Hereditary stomatocytosis
D. Stomatin Deficiency
A. Identify the pointed cell
B. Describe the striking feature
C. Associated with what condition?
D. What is the main defect of this cell?
A. Agglutination
B. Clumping of red blood cells
C.Hemolytic anemia, Cold agglutinin disease, Trypanosomiasis, Atypical pneumonia, Staphylococcal infections
D. Cold agglutinin
E. Another blood sample is extracted using sodium citrate as anticoagulant
A. Identify the pointed cell
B. Describe the striking feature
C. Associated with what conditions?
D. Common cause of the cell’s formation?
E. Remedy of this finding.
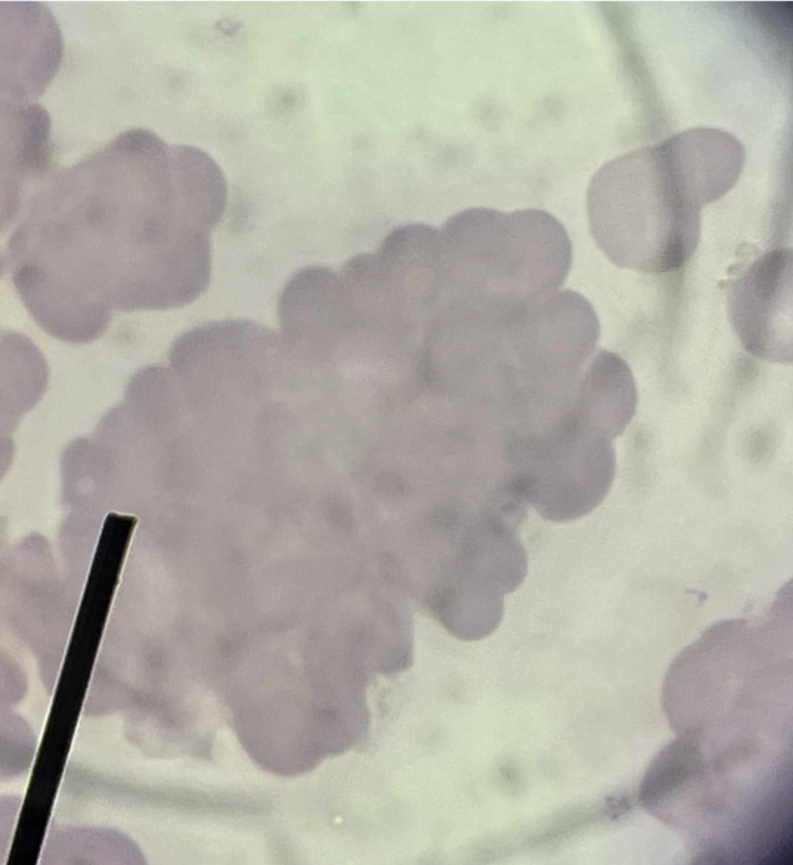
A. Rouleaux
B. Stacks of coin
C. Acute and chronic inflammatory disorders, multiple myeloma, hyperproteinuria
D. Increased concentration of plasma proteins
E. ESR
F. Decreased
A. Identify the pointed cell
B. Describe the striking feature
C. Associated with what conditions?
D. Primary stimulus of this formation?
E. What laboratory test increases in this formation?
F. What happens to the zeta potential?
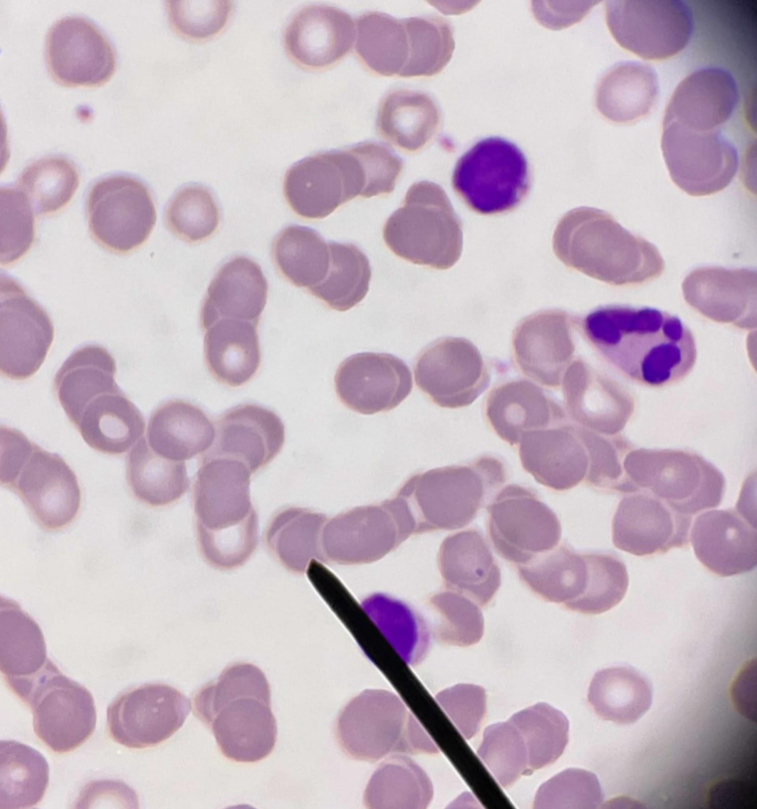
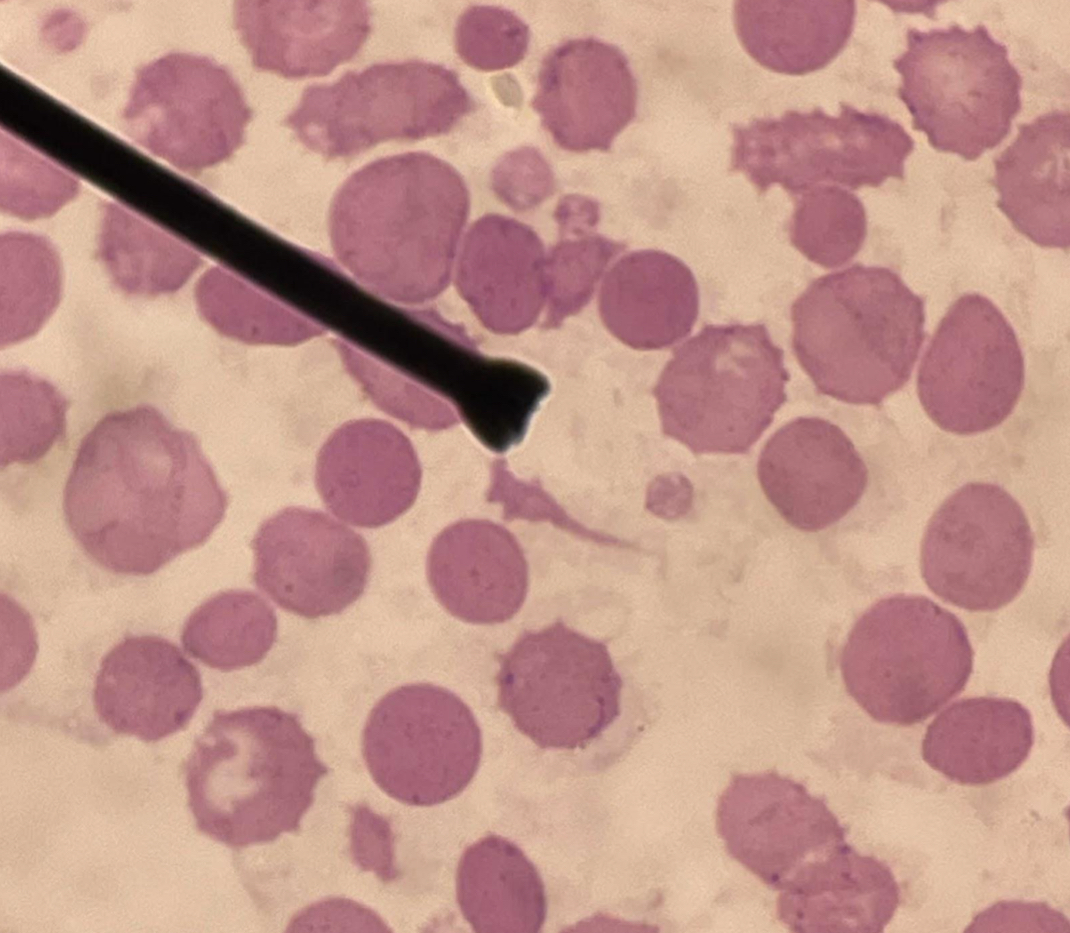
A. Macrocyte
B. Larger than normocyte
C. Megaloblastic anemia
D. Sideroblastic anemia, Myelofibrosis, Pure red cell aplasia , Aplastic anemia
A. Identify the pointed cell
B. Describe the striking feature
C. Associated with what conditions?
D. What are the other associated conditions?
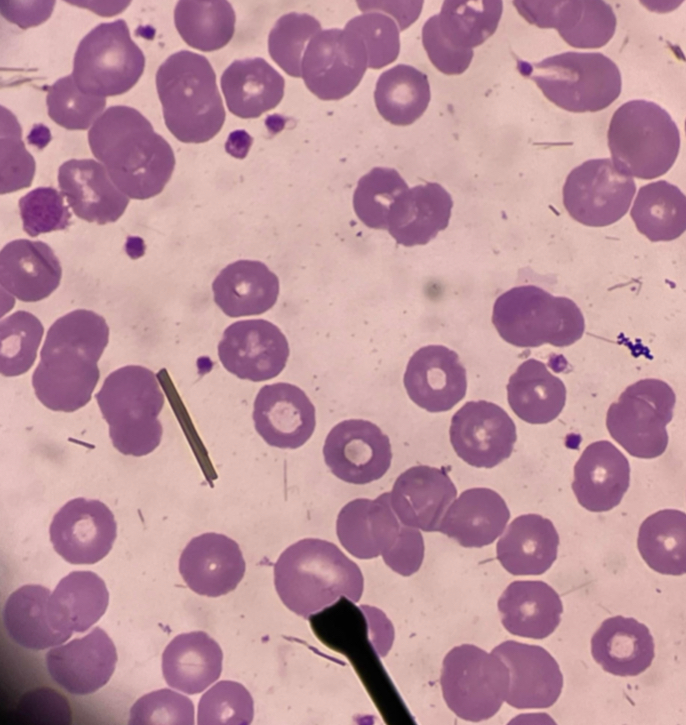
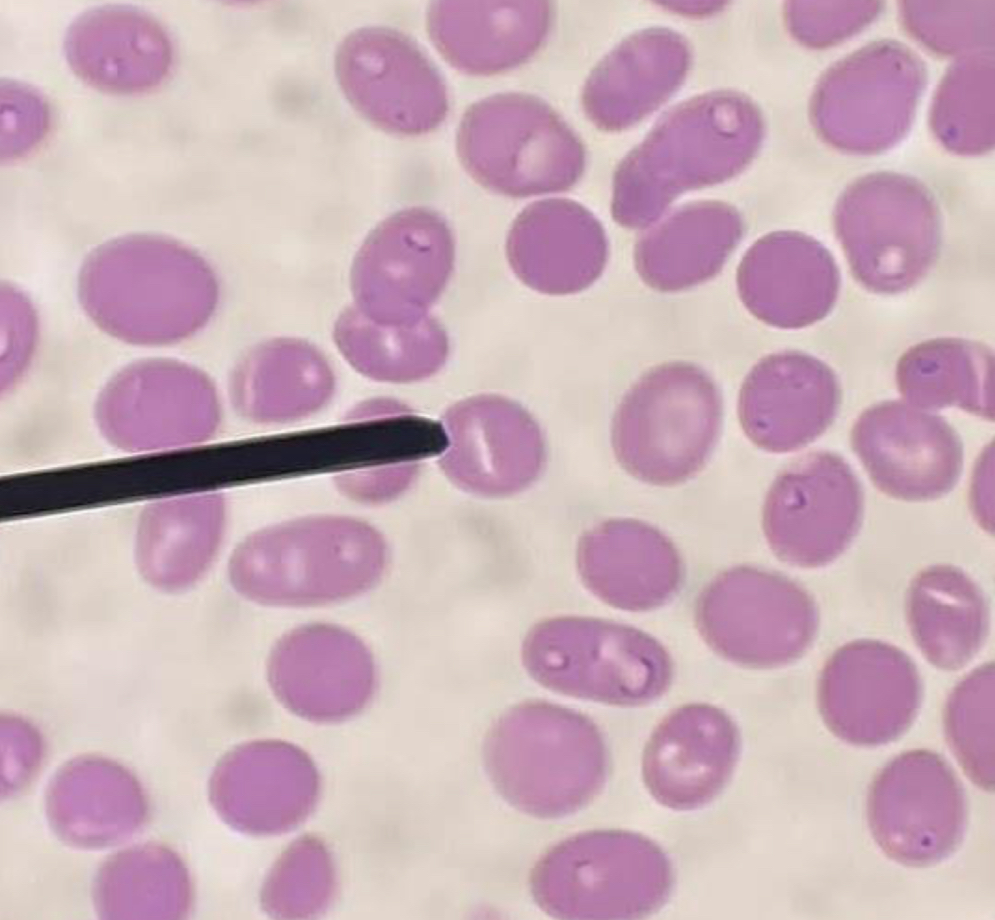
A. Target cell
B. Bull’s eye
C. Thalassemia
D. Increased membrane cholesterol and phospholipid content
E. Codocyte
A. Identify the pointed cell
B. Describe the striking feature
C. What is the characteristic finding?
D. What is the main defect of this cell?
E. Another term for this cell
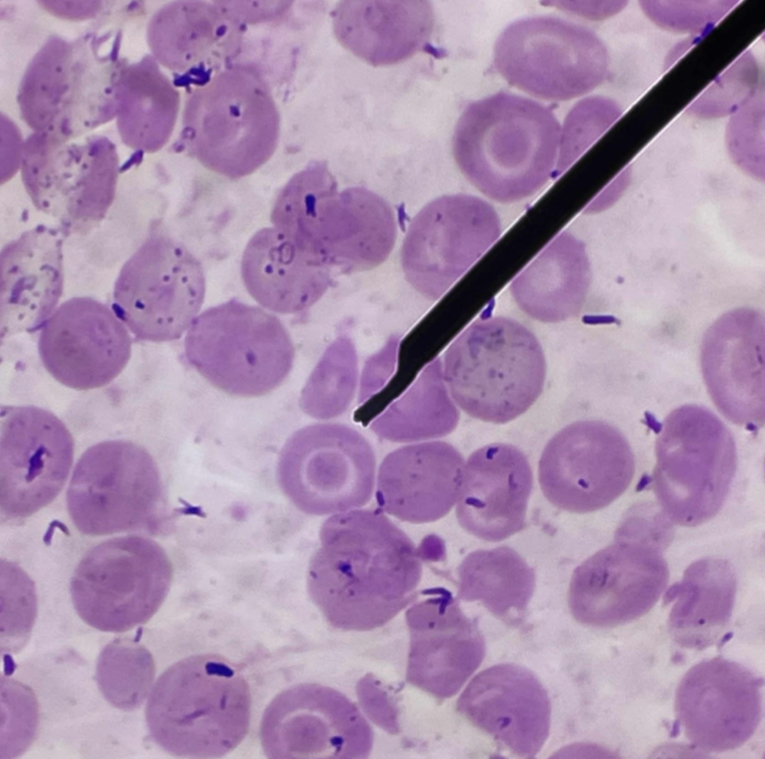
A. Red Blood Cell with Basophilic Stippling
B. dark blue to purple, fine or coarse granules
C. Lead poisoning
Others : Thalassemia, Alcoholism, Megaloblastic anemia, Arsenic intoxication
D. RNA
E. Pappenheimer bodies
F. Prussian blue stain
A. Identify the pointed cell
B. Describe the striking feature
C. Associated with what condition ?
D. What does the inclusion found on this cell represents ?
E. Is often confused with what other inclusion?
F. What stain is used to differentiate the inclusions?
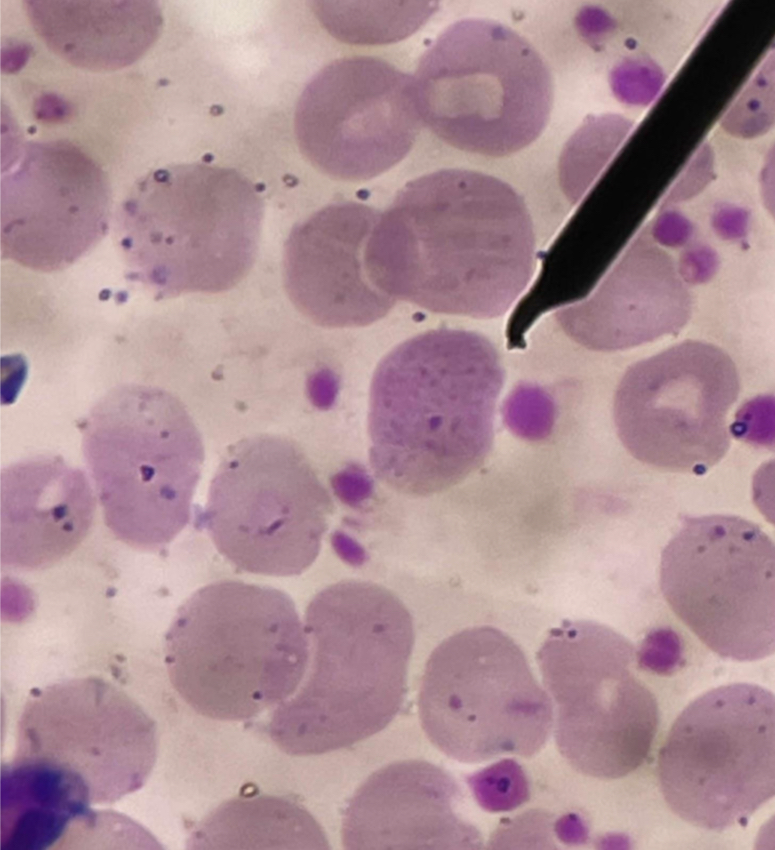
A. Acanthocyte
B. Irregularly spaced, pointed spicules / thornlike projections that vary in width, length and number
C. Abetalipoproteinemia
D. change in the plasma lipids ratio (lecithin and sphingomyelin)
A. Identify the pointed cell
B. Describe the striking feature
C. Associated with what condition ?
D. What is the cause of the cell’s formation?
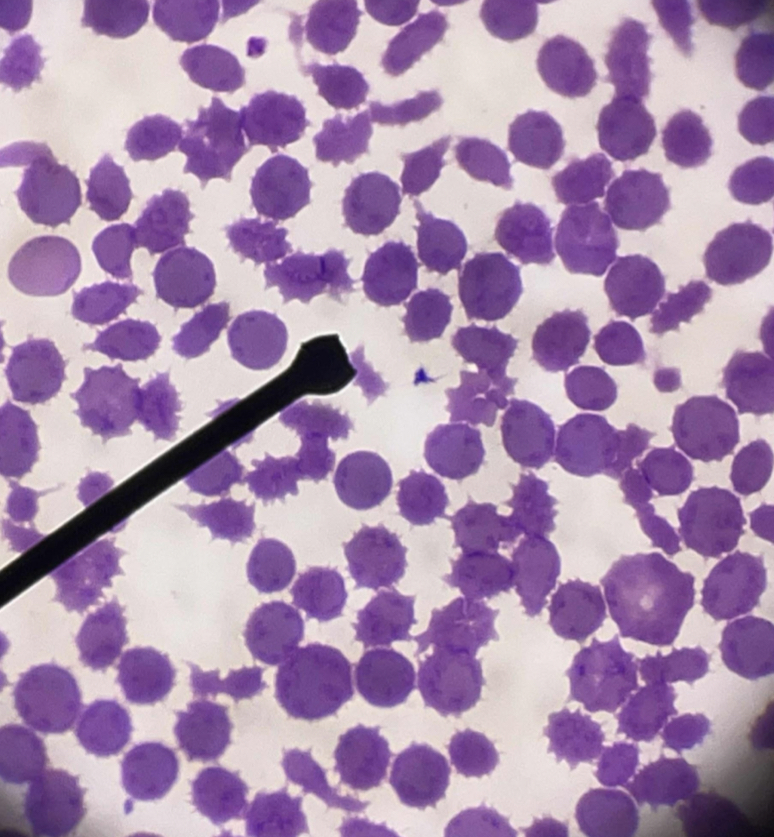
A. Teardrop cell ( codocyte)
B. Teardrop shaped
C. Myelofibrosis, B-thalassemia, Myelophthisic anemia
D. Heinz body
A. Identify the pointed cell
B. Describe the striking feature
C. Associated with what condition ?
D. What rigid inclusion does this cell contain?
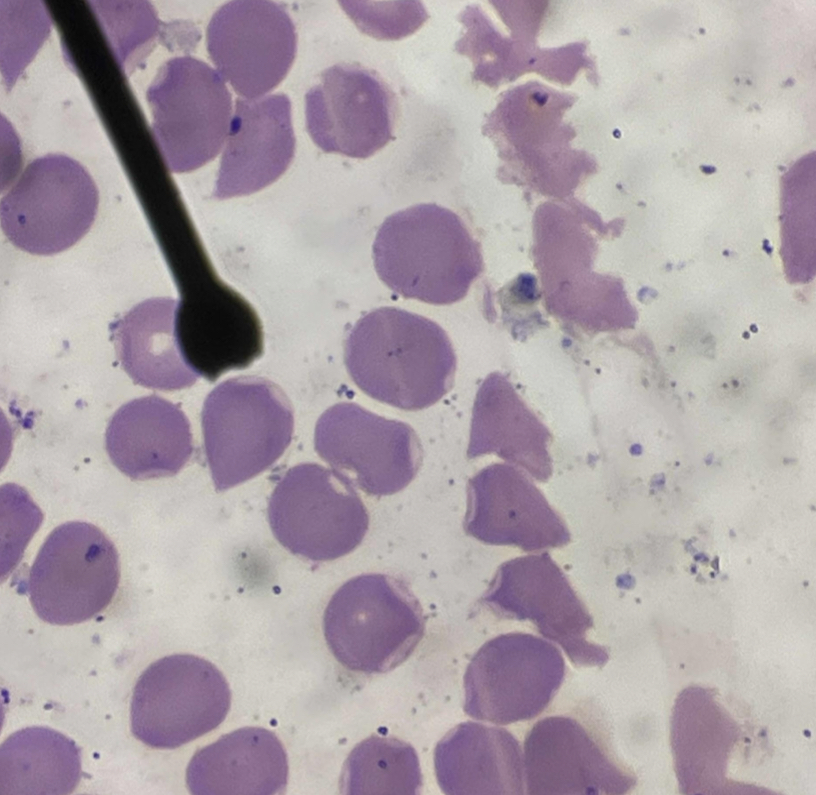
A. Ovalocyte
B. Oval in shape / egg-shaped
C. Megaloblastic anemia
D. Protein band 4.2 and ankyrin - 3
A. Identify the pointed cell
B. Describe the striking feature
C. Associated with what condition ?
D. Main membrane defect?
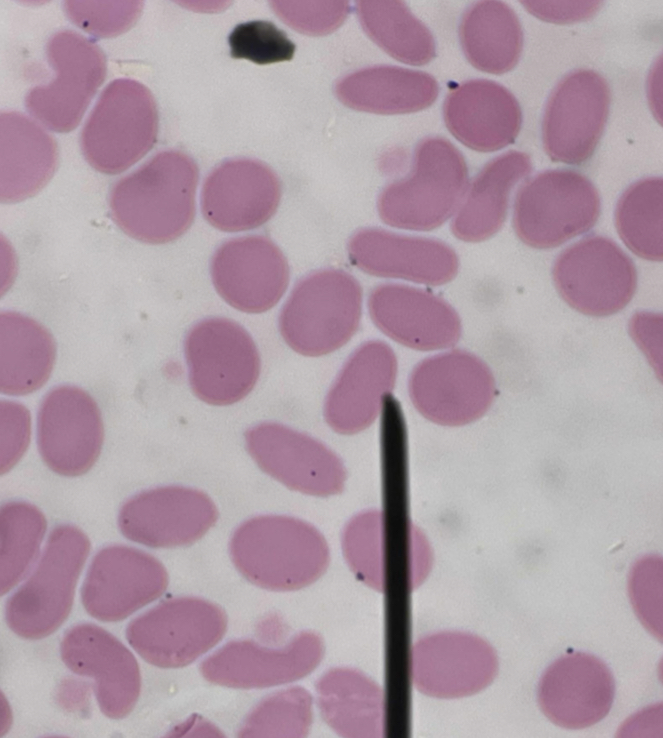
A. Spherocyte
B. Do not contain central area of pallor
C. Hereditary spherocytosis
D. Splenomegaly, Mild jaundice, Pigmented gallstones
E. Osmotic Fragility Test
F. Spectrin deficiency
A. Identify the pointed cell
B. Describe the striking feature
C. Associated with what condition?
D. Manifestations of the condition?
E. What Laboratory test detects the presence or absence of this cell in the blood?
F. Main membrane defect of the cell?
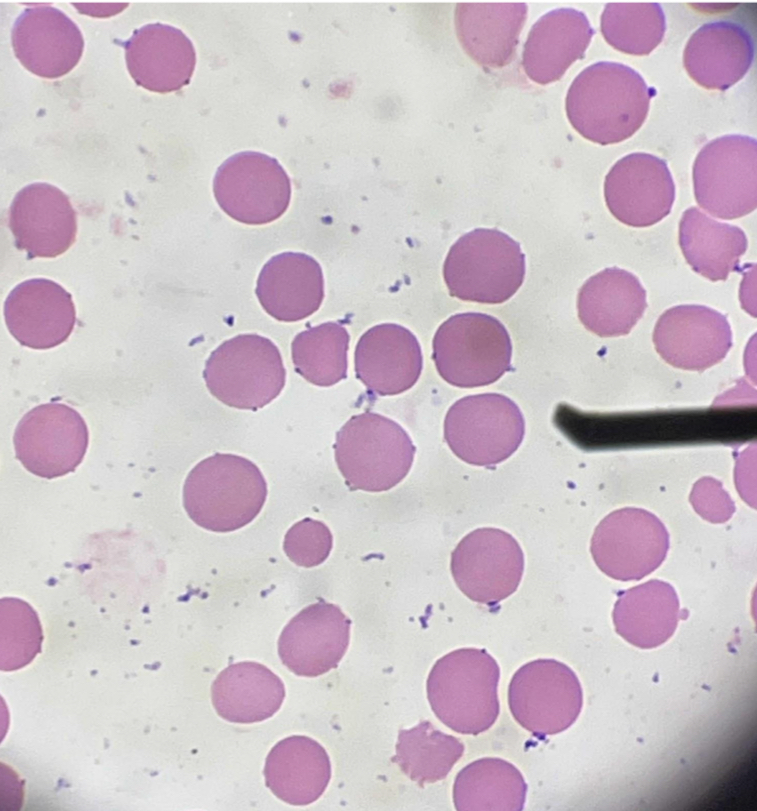
A. Microcyte
B. Smaller than normocyte
C. Iron deficiency anemia
A. Identify the pointed cell
B. Describe the striking feature
C. Associated with what condition?
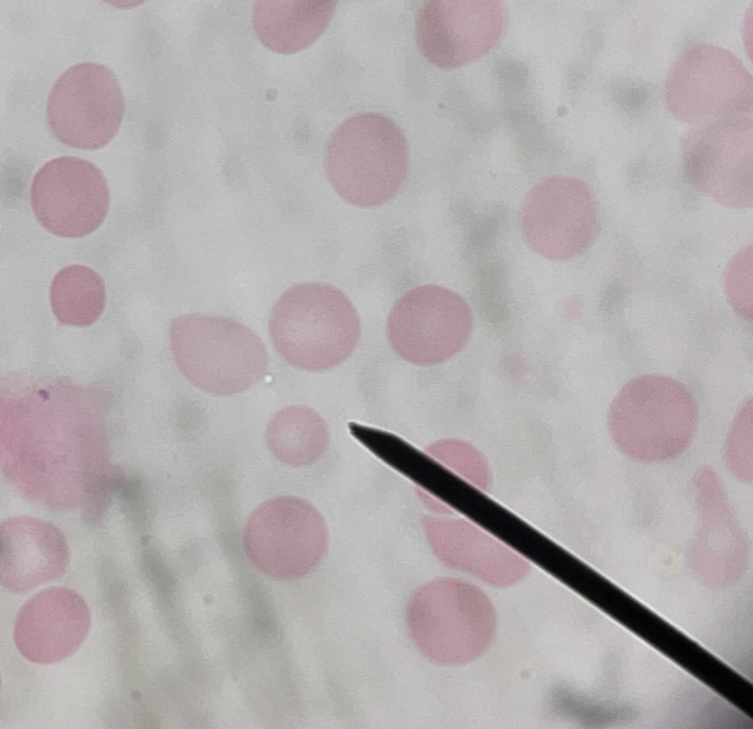
A. Elliptocyte
B. Pencil-shaped / cigar - shaped
C. Hereditary elliptocytosis
D. Protein band 4.1 and ankyrin - 3
A. Identify the pointed cell
B. Describe the striking feature
C. Associated with what condition ?
D. Main membrane defect?
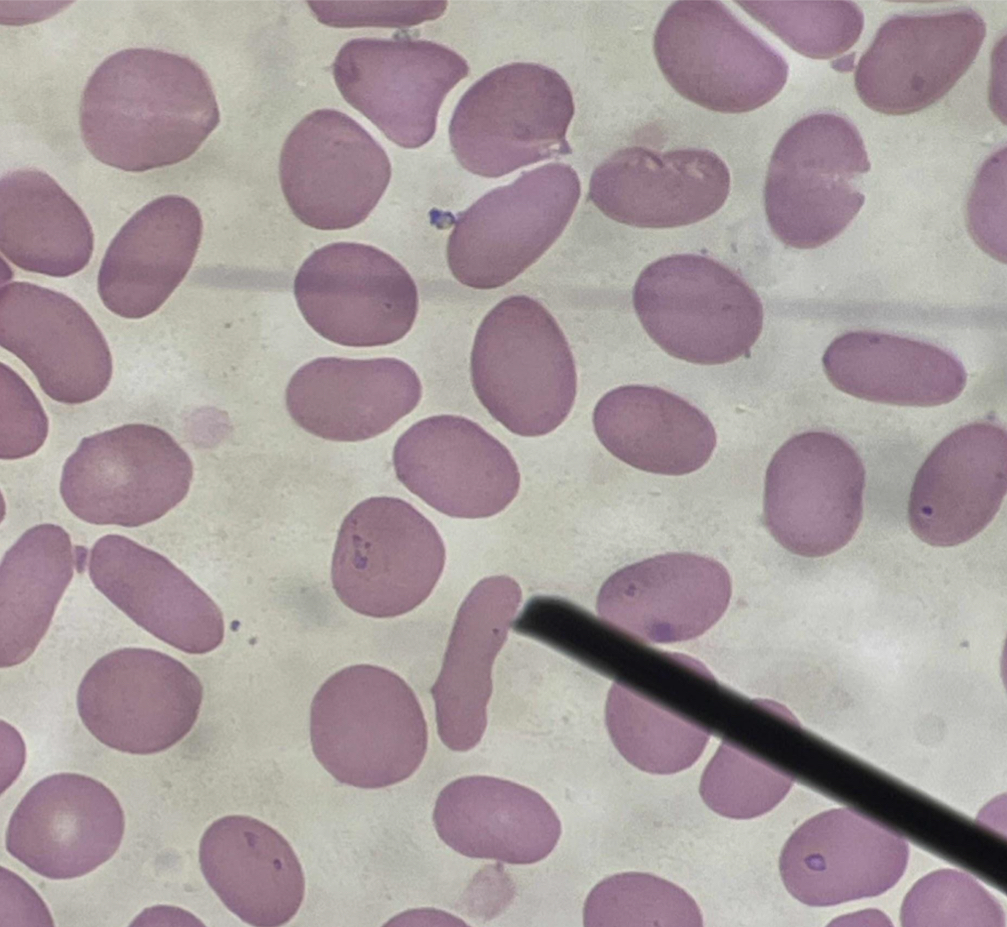
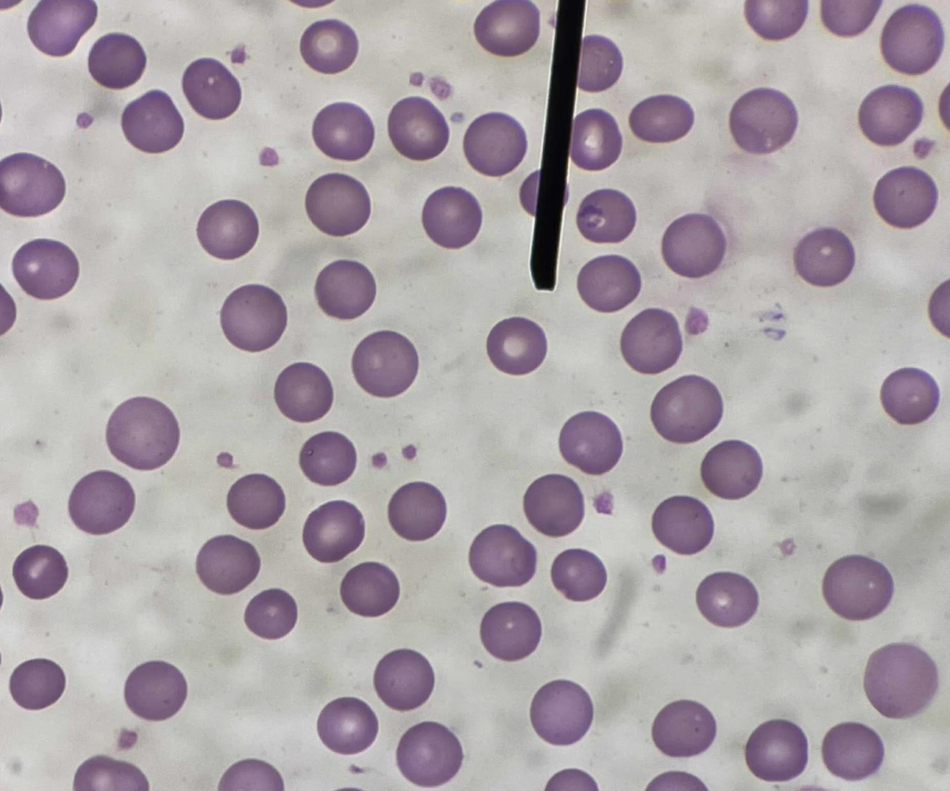
A. Normocyte (Erythrocyte)
B. Round, or slightly oval without nucleus
C. Biconcave disc shape
D. Discocyte
A. Identify the pointed cell
B. Describe the striking feature
C. What characteristic shape of the cell is responsible for its deformability and flexibility ?
D. Other term for this cell?