Fundamentals Study Guide - Exam 1
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Week 1-3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
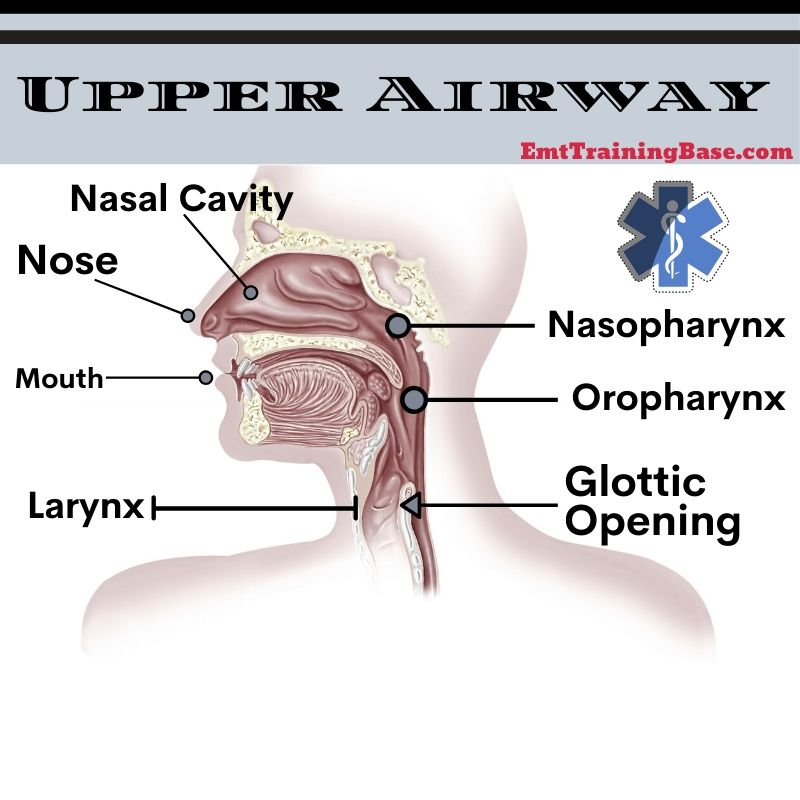
Identify the major structures of the upper respiratory tract.
Nasal cavity, Sinuses, Nose, Mouth, Pharynx, Larynx, Nasopharynx, Osopharynx, Glottic Opening.
How do airways move mucus?
cilia move the mucus through a wave like motion called mucociliary escalator.
Describe the blood-gas barriers (alveolar-capillary membrane) and how it functions normally.
the thin wall between alveoli and capillaries. It has three layers (alveolar epithelium, basement membrane, capillary endothelium). Its job is simple: oxygen in, carbon dioxide out.
(Think: “ABC → Air–Blood Connection”)
A = Alveolar epithelium
B = Basement membrane
C = Capillary endothelium
What is the primary function of the respiratory system?
Absorption of O2 and excretion of CO2
Differentiate between internal and external respiration.
Internal: Gas exchange between tissue cells and systemic capillary blood
External: Gas exchange between the gas of the atmosphere and blood
What is the primary function of the lymphatic system?
clear fluid from the interstitial and pleural spaces to help maintain the fluid balance in the lungs
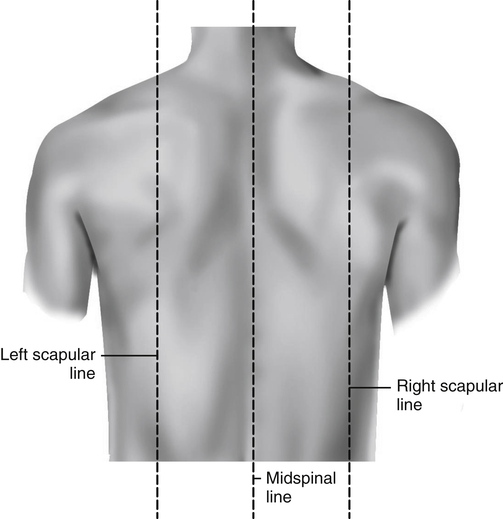
What are the plains (imaginary lines) of the anterior and posterior thorax?
Anterior: Right / left midclavicular line, midsternal line
Posterior: left/right scapular line, midspinal line
How many pairs of ribs are there in an adult?
12
What is the primary muscle of inspiration?
Diaphragm and intercostals
What are the accessory muscles of inspiration? When are they active?
scalene and sternocleidomastoids, Active only during increased demand
What nerve innervates the diaphragm?
The phrenic nerve
Differentiate between ventilation and respiration.
Ventilation is the act of breathing air in and out of the lungs, while respiration is the actual exchange of gases.
Ventilation = Vent (airflow), Respiration = Resp (swap gases).
What is the only point of attachment for the lungs?
hilum
Differentiate between visceral and parietal pleurae.
visceral pleura: Serous membrane that covers the lungs
parietal pleura: Inner layer lined with serous membrane. (diaphragm)
Visceral = on the lung, Parietal = on the wall.
What is the primary function of each of the following: AARC
American Association for Respiratory
Care - advocates for profession
What is the primary function of each of the following: NBRC
National Board for Respiratory Care: offers certification and registry examination
What is the primary function of each of the following: CoARC
Committee on Accreditation for Respiratory Care: accreditation body for respiratory care education programs
What is the primary function of each of the following: OSRC
Ohio Society for Respiratory Care: promotes the education, licensing, and safety of respiratory care services and issues in Ohio
What is the primary function of each of the following?: KBRC
Kentucky Board of Respiratory Care: regulates respiratory care practitioners within Kentucky
What two factors affect normal volume of ventilation?
Tidal volume (vt) and respiratory rate
Describe the importance of surfactant.
Reduces surface tension and alveolar tendency to collapse
Differentiate between compliance and airway resistance.
Compliance = how easily the lungs and chest expand when filled with air. (High compliance = easy to expand, low compliance = stiff lungs).
Airway resistance = how much the airways resist airflow. (High resistance = harder for air to move, like in asthma or obstruction).
Compliance = stretch
Resistance = push air
Is normal exhalation active or passive? Explain.
Passive as the lungs/chest wall naturaly recoil. Muscles are only needed for forced exhalation.
What is work of breathing?
WOB: how hard and much energy your body has to work just to breathe.
Describe how oxygen and CO2 move between the atmosphere and tissues.
Simple Diffusion: Oxygen moves from high partial pressure to low partial pressure in the tissues.
Carbon Dioxide moves in the opposite direct from high Partial Pressure in tissues to low Partial Pressure in atmosphere.
Define diffusion.
movement of gases.
Describe each of the following: Hyperventilation
breathing faster/deeper then normal
Describe each of the following: Hypoventilation
too slow/too shallow (low o2)
Describe each of the following: Tachypnea
fast breathing rate (faster than 20 bpm)
Describe each of the following: Bradypnea
abnormally slow breathing rate (slowler than 12 bpm)
Describe each of the following: Tachycardia
fast heart rate of more than 100 beats per minute when at rest
Describe each of the following: Bradycardia
slow heart rate, defined as fewer than 60 beats per minute (BPM) at rest
How do you estimate anatomical deadspace in an adult (nonintubated)?
Vdanat = 1 ml/ lb IBW
What is the costophrenic angle?
the sharp corner where the diaphragm meets the ribs (chest wall) on each side of the lungs.
How do you calculate IBW for a male or female?
Male: 106 + 6(height in inches – 60)/2.2
Female: 105 + 5(height in inches – 60)/2.2
Name the cartilaginous structures in the adult larynx.
Unpaired:
Thyroid cartilage
Cricoid cartilage
Epiglottis
Paired (two of each):
Arytenoid cartilages
Corniculate cartilages
Cuneiform cartilages
Differentiate between the right and left main stem bronchi.
Right: Wider, Shorter, branches at 20- 30-degree angle
Left: Narrower, Longer, branches at 45- 55-degree angle
Describe the structure and function of the mucociliary escalator.
Structure: Mucociliary escalator is formed by the lining of the airway, the two main parts are cilia and mucus layer.
Function: Lungs self cleaning system
Trace the normal flow of blood through the adult heart.
Body → RA → RV → Lungs → LA → LV
What causes gas to flow from the mouth to the alveoli?
pressure gradient created by breathing muscles
How do you calculate PAO2? (Alveolar Gas Equation)
PAO2 = (Pb – 47) x FIO2) – (PaCO2/0.8)
How do you calculate A-a gradient?
PAO2 – PaO2
How do you calculate minute ventilation?
VE = Vt x f
How do you calculate minute alveolar ventilation?
VA = (Vt – Vd) x
What is the function of the epiglottis?
Closes laryngeal opening during swallowing, to prevent liquids and food from entering respiratory tract
What is the largest cartilage in the larynx?
thyroid cartilage
What is the Valsalva maneuver?
takes a deep breath and forcefully exhales against a closed airway (like closing the mouth and pinching the nose while trying to blow out).
can be used to decrease heart rate
Name the parts of the sternum.
manubrium, body, and xiphoid process
What are the general functions of the Upper Airways?
Passageway for gas flow
Filter
Humidification