SB7: Animal Coordination, Control and Homeostasis
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/72
Last updated 4:05 PM on 5/30/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
1
New cards
What does the hormonal system do?
endocrine system has glands which secrete hormones as chemical messengers to cause long term change in body
2
New cards
What is a target organ
A target organ is a specific organ or tissue in the body that is affected by a particular hormone that has specific receptors to produce a response.
3
New cards
What hormone does the adrenal gland secrete and what is it used for?
* on kidneys
* secretes adrenaline for flight or fight response when “scared”
* increases heart rate
* increases blood pressure
* increases blood flow to muscles
* increases blood glucose levels by stimulating conversion from glycogen to glucose
* secretes adrenaline for flight or fight response when “scared”
* increases heart rate
* increases blood pressure
* increases blood flow to muscles
* increases blood glucose levels by stimulating conversion from glycogen to glucose
4
New cards
What hormone do the testes gland secrete and what is it used for?
* testosterone-controls puberty
* producing gametes (sperm)
* producing gametes (sperm)
5
New cards
What does oestrogen for? What gland is it produced in?
oestrogen- effects menstrual cycle and puberty
* holds gametes
* holds gametes
6
New cards
What is the pituitary gland?
“MASTER GLAND”-tells other glands what to do
7
New cards
What is the thyroid gland?
* neck
* secretes thyroxine
* regulate metabolic rate
* growth and development
* secretes thyroxine
* regulate metabolic rate
* growth and development
8
New cards
What are the differences between the nervous system and the endocrine system?
* endocrine system = hormones
* nervous systems = electrical impulses
* the nervous system is faster than the endocrine system
* endocrine system has long term effects
* nervous systems = electrical impulses
* the nervous system is faster than the endocrine system
* endocrine system has long term effects
9
New cards
What hormone do pancreas secrete and what is it used for?
secretes
10
New cards
What is puberty
adolescents develops secondary sexual characteristics like facial hair triggered by reproductive hormones (testosterone and estrogen)
11
New cards
What are the 4 stages of the menstrual cycle?
28 days!
12
New cards
Where are eggs kept?
From an ovary
13
New cards
What happens to an egg after ovulation if fertilised?
If this egg is fertilised and embeds itself in the thickened lining of the uterus, the lining is maintained and the woman becomes pregnant.
14
New cards
What happens to an egg after ovulation if not fertilised?
If the egg has not been fertilised, the corpus luteum dies and progesterone levels drop. This causes menstruation, where the uterus lining breaks down - this is known as having a period.
15
New cards
What happens to the uterus lining when an egg is fertilised
When an egg is fertilized, it implants into the thickened uterus lining, then the lining is maintained by progesterone to prevent it from shedding. This allows the fertilized egg to continue developing into an embryo and eventually a fetus.
16
New cards
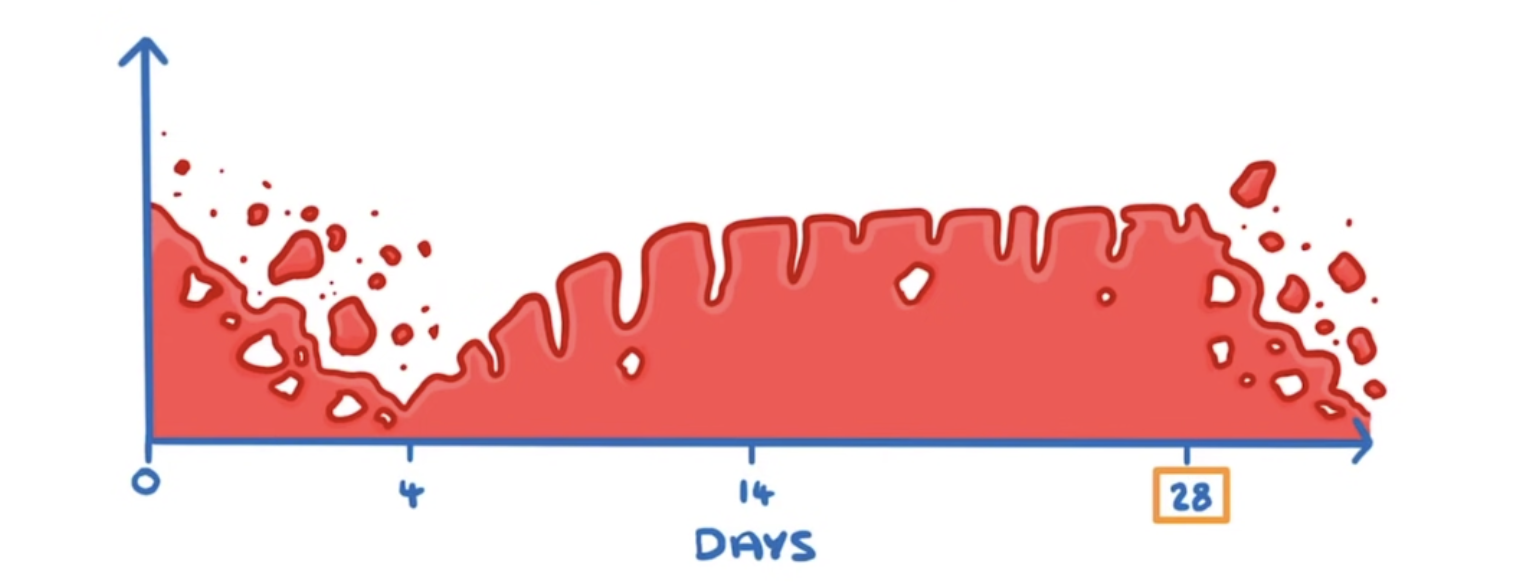
What is this a graph of?
Thickness of the uterus lining
17
New cards
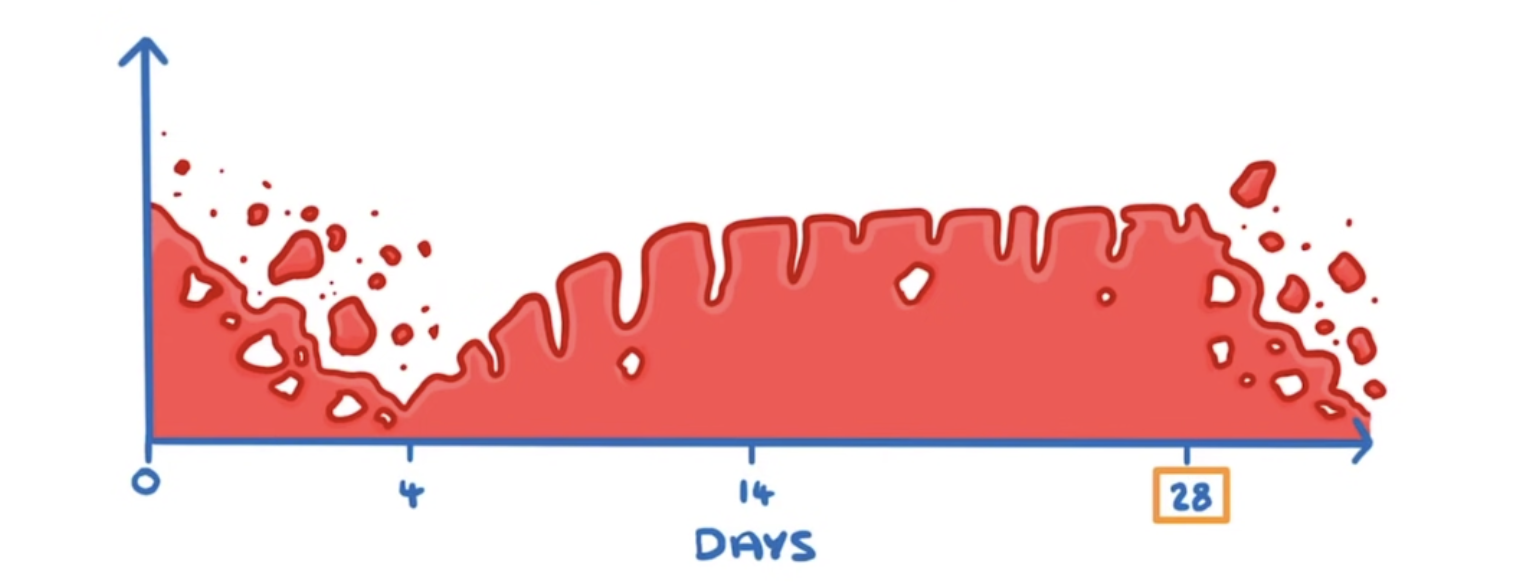
What is the first stage of the menstrual cycle (DAY 1-DAY 4)?
This is menstruation. Usually when bleeding occurs and uterus lining breaks down.
18
New cards
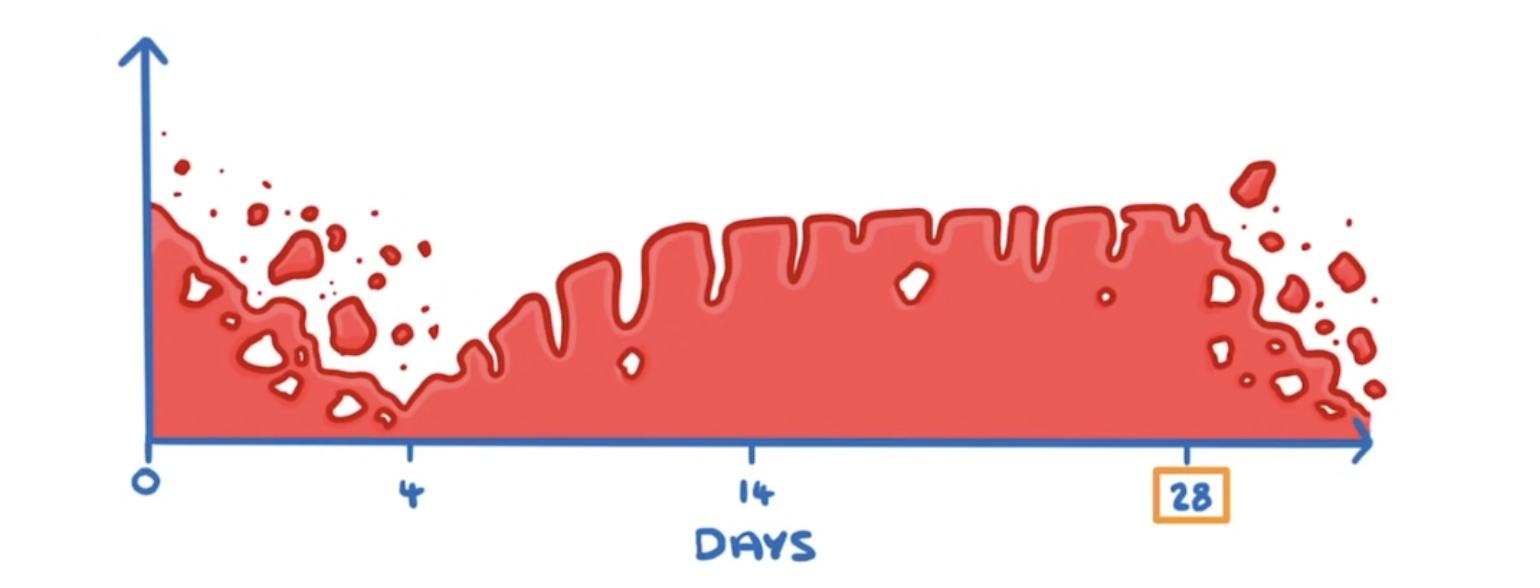
What is the secondstage of the menstrual cycle (DAY 4-14)?
This is when the lining builds up again. Uterus lining becomes a “thick spongy layer”. This prepares the uterus for a fertilised egg in stage 3.
19
New cards
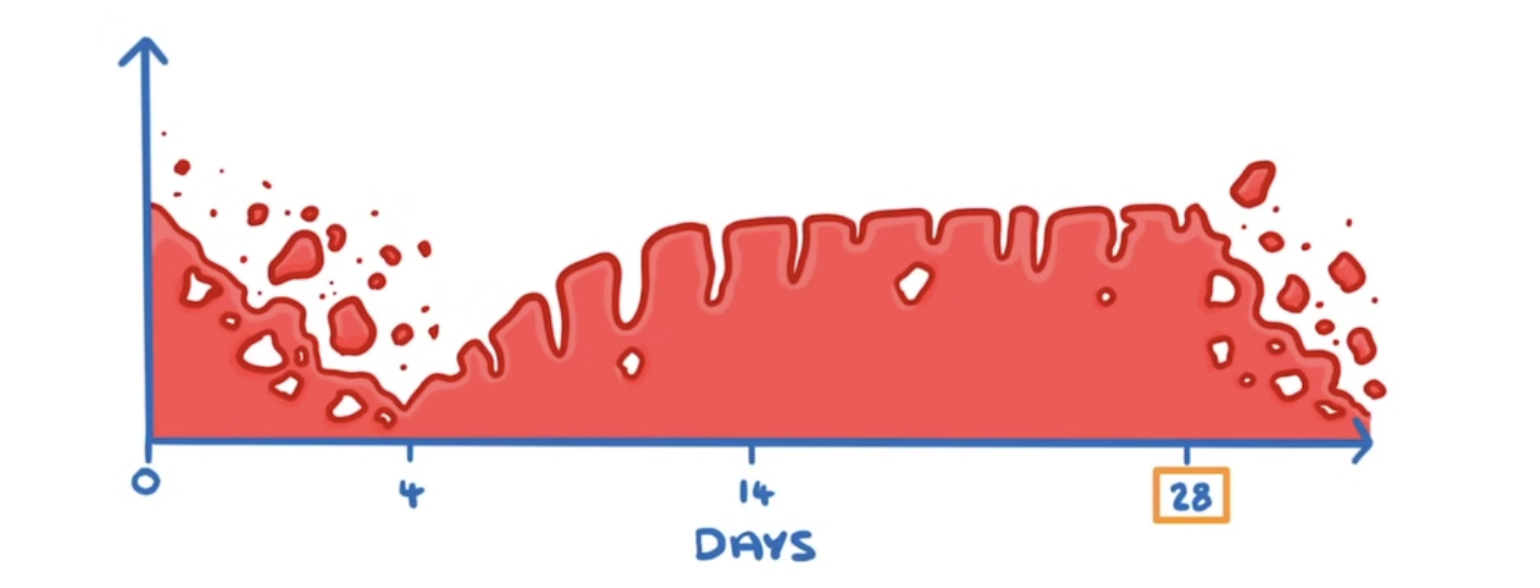
What is the third stage of the menstrual cycle? (day 14)
This is ovulation. This happens in one single day and an egg is released from the ovaries.
20
New cards
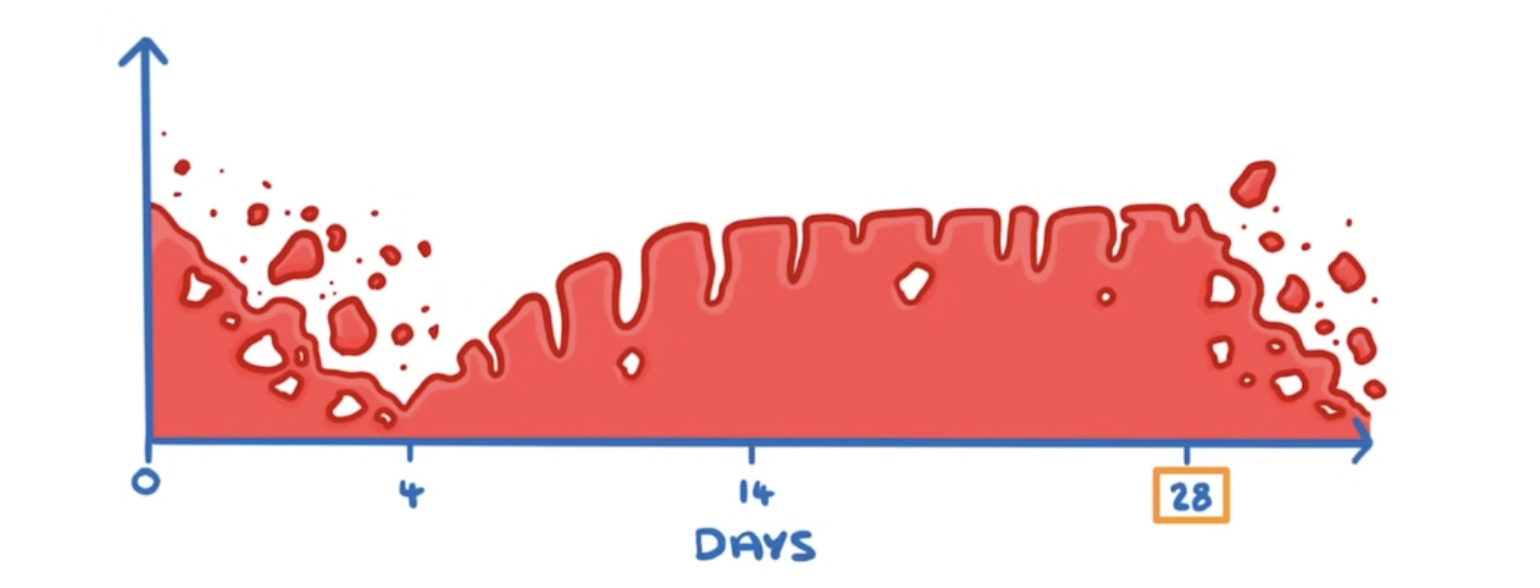
What is the fourth stage of the menstrual cycle? (day 15-28)
This involves maintaining the uterus lining. If no egg is fertilised, the uterus lining will break down within the cycle that repeats. If the egg is fertilised, the egg will implant into the uterus lining. The cycle won’t start again if it is fertilised.
21
New cards
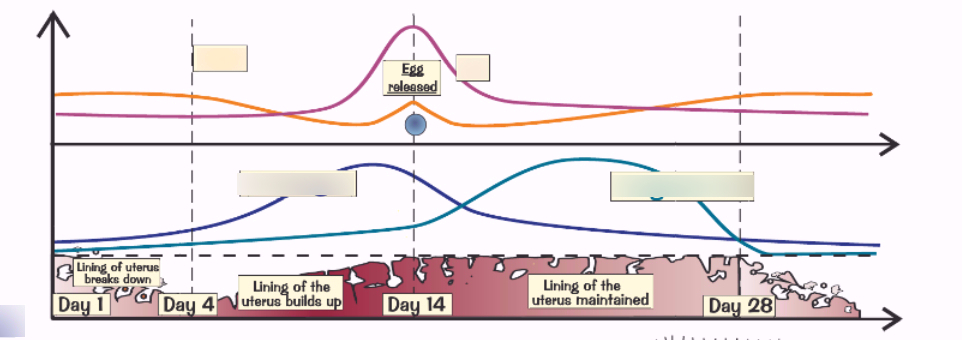
What is the dark blue line?
Oestrogen- stimulates the uterus lining to grow. The line rises in stage 2 as the uterus develops and falls when the lining grows
22
New cards
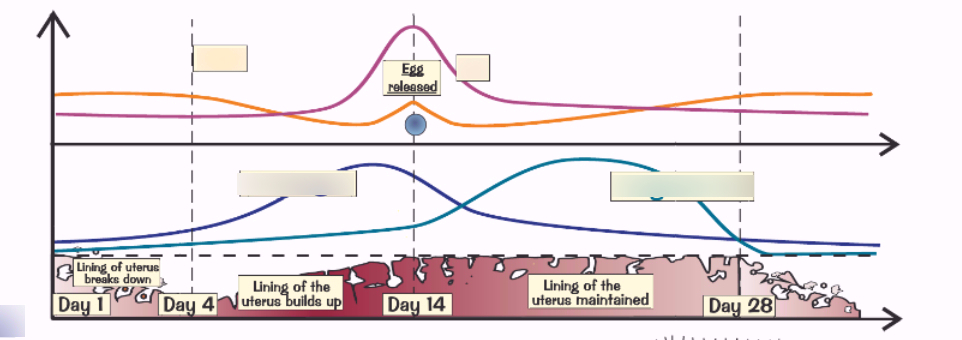
What is the light blue line?
Progestorne- increases in stage 4 and maintains lining of uterus. If lining breaks down progestorne decreases
23
New cards
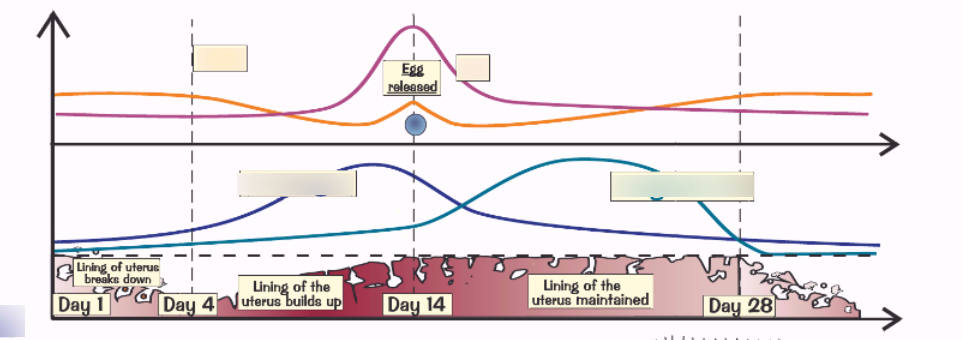
What is the orange line?
FSH-Produced in the pituitary gland. FSH makes egg mature in ovaries
24
New cards
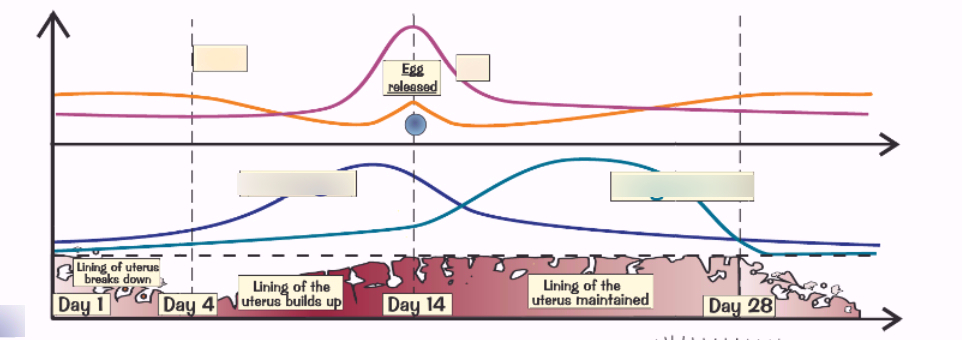
What is the pink line?
LH-Produced in the pituitary gland. LH causes the egg to be released
25
New cards
How are FSH and Oestrogen related?
* when FSH causes a follicle to mature the levels of FSH increases causing an increase in oestrogen to build up the lining fo the uterus.
* When oestrogen increases it will inhibit FSH
* When oestrogen increases it will inhibit FSH
26
New cards
What is the FSH and oestrogen relationship an example of?
Negative feedback
27
New cards
What does increases oestrogen trigger?
* oestrogen increasing causes a spike in LH
* LH increase results in ovulation
* this causes an increase in progesterone
* LH increase results in ovulation
* this causes an increase in progesterone
28
New cards
What relationship does progesterone have with FSH and LH
When progesterone increases it will inhibit FSH and LH.
29
New cards
What is contraception?
A method to prevent pregnancy
* hormonal methods
* barrier method
* hormonal methods
* barrier method
30
New cards
What does the combined oral contraceptive pill do?
Releasing Oestrogen- This inhibits FSH. FSH is required to stimulate egg development so eggs won't mature or be released.
Releasing Progesterone- This inhibits LH and FSH. So an egg cannot be released and ovulation is stopped.
Progesterone also releases a thick mucus preventing sperm from fertilizing the egg
Releasing Progesterone- This inhibits LH and FSH. So an egg cannot be released and ovulation is stopped.
Progesterone also releases a thick mucus preventing sperm from fertilizing the egg
31
New cards
What are other hormonal methods?
* contraceptive patch
* contraceptive implant-most permanent
* contraceptive injection
* IUD-placed in the uterus and releases progesterone (plastic) or prevents sperm fertilising eggs (copper)
* contraceptive implant-most permanent
* contraceptive injection
* IUD-placed in the uterus and releases progesterone (plastic) or prevents sperm fertilising eggs (copper)
32
New cards
Define the purpose of a non homronal contraceptive methods
Prevent sperm from meeting egg. Acts as a physical barrier
33
New cards
Why are non-hormonal contraceptives important?
The physical barrier can be used to prevent STI/STD.
34
New cards
What are other non-hormonal contraceptives methods?
* diaghram
* femdom
* sterilization
* femdom
* sterilization
35
New cards
What pills are administered to increase fertility?
FSH hormone in pill
LH hormone in pill
LH hormone in pill
36
New cards
IVF (In-vitro fertilisation)
* Women are given FSH and LH to mature eggs and increase ovulation
* Eggs are collected from women’s ovaries and then fertilised by sperm from a man.
* They will then develop ot embryos
* Then inserted into mothers uterus
* external to the human body
* Eggs are collected from women’s ovaries and then fertilised by sperm from a man.
* They will then develop ot embryos
* Then inserted into mothers uterus
* external to the human body
37
New cards
Homeostasis
the regulation of conditions within the body to maintain a stable internal environment to respond to external and internal changes.
38
New cards
Automatic control systems (Loop of negative feedback)
Comprised of receptors, coordination centres and effectors (muscles that contract or glands for hormones). Since these may be in different parts of the body electrical impulses can be used to transport signals between them(quick). Endocrine system releases chemicals into bloodstream (slow but longterm)
39
New cards
Negative Feedback
Whenever the level of something is too high, negative feedback will “inhibit” the production of this so it will be higher. (It does the opposite of whatever the change is)
40
New cards
Blood glucose concentration
* sugar within blood
* important so that glucose can always be used by cells for respiration
* if it is too high it can damage tissues
* important so that glucose can always be used by cells for respiration
* if it is too high it can damage tissues
41
New cards
glycogen
Long term storage glucose
42
New cards
glucagon
Secreted by the pancreas when glucose levels are too low to convert glycogen to glucose
43
New cards
insulin
Secreted by the pancreas when glucose levels are too high to convert glucose to glycogen.
44
New cards
How does the body combat a spike in glucose levels?
1. Pancreas detect increased glucose
2. Secrete insulin in response and this binds to receptors on the cells (in liver).
3. The insulin causes the cells to take up the glucose and convert this to glycogen.
4. Glucose levels will decrease
45
New cards
How does the body combat a decresae in glucose levels?
1. Pancreas detect decreased glucose
2. Secretes glucagon and this binds to receptors in liver cells
3. The insulin would take the glycogen and convert it back to glucose
4. This increases glucose concentration in the blood so more cells have glucose for respiration
46
New cards
What problem does diabetes cause?
People with diabetes won’t be able to regulate their blood glucose levels as the pancreas produce low levels or no insulin.
47
New cards
Type 1 Diabetes
* occurs early in life
* Pancreas stops producing insulin or low levels of insulin
* This means blood glucose can become extremely high
\
MAIN SOLUTION: inject glucose into abdomen based on exercise done and amount of carbohydrates eaten
* Pancreas stops producing insulin or low levels of insulin
* This means blood glucose can become extremely high
\
MAIN SOLUTION: inject glucose into abdomen based on exercise done and amount of carbohydrates eaten
48
New cards
Type 2 Diabetes
* occurs to older people with unhealthy diets
* cells grow resistant to insulin
* No longer respond to insulin so cells dont take in glucose from bloodstream
* this means insulin as a treatment wont help
\
MAIN SOLUTION: healthy low sugar diet and regular excercise
* cells grow resistant to insulin
* No longer respond to insulin so cells dont take in glucose from bloodstream
* this means insulin as a treatment wont help
\
MAIN SOLUTION: healthy low sugar diet and regular excercise
49
New cards
Thermoregulation
Regulation of the internal body temperature (achieves homeostasis)
37 degrees
37 degrees
50
New cards
Why does the body need to be kept at 37 degrees?
this is the optimum temperature for our body’s enzymes to function and react
BELOW THIS TEMP: react much slower
ABOVE THIS TEMP: may denature and no longer collide successfully
BELOW THIS TEMP: react much slower
ABOVE THIS TEMP: may denature and no longer collide successfully
51
New cards
What does hypothalymus do?
“body thermostat”
* paired with effectors in skin to detect change
* the brain can detect wether we are too warm or cold overall
* signals are sent out to reverse whatever the external condition is
* paired with effectors in skin to detect change
* the brain can detect wether we are too warm or cold overall
* signals are sent out to reverse whatever the external condition is
52
New cards
TOO WARM UP
1. vasoconstriction
2. shivering
53
New cards
Vasoconstriction
* constrict blood vessels near surface of skin
* this causes less blood to flow near surface and less heat energy is lost towards the surroundings
* this causes less blood to flow near surface and less heat energy is lost towards the surroundings
54
New cards
What do erector muscles do to warm up body?
* contract erector muscles to make hairs stand up
* this creates an insulating layer of air so less heat energy is lost
* this creates an insulating layer of air so less heat energy is lost
55
New cards
How does shivering warm up the body?
* muscles contract automatically
* muscle contraction requires lots of energy from respiration
* results in lots of heat energy being released as waste to warm body
* muscle contraction requires lots of energy from respiration
* results in lots of heat energy being released as waste to warm body
56
New cards
Vasodilation
* widens blood vessels near surface of skin
* this causes more blood to flow near surface and more heat energy is lost towards the surroundings
* this causes more blood to flow near surface and more heat energy is lost towards the surroundings
57
New cards
How does sweating cool body?
When sweat evaporates heat energy is taken with our body so that heat is lost and we are left cooler
58
New cards
What happens to erector muscles to cool down body?
The hair erector muscles in the skin **contract**, causing hairs to **stand on end.** This forms an insulating layer over the skin's surface by trapping air between the hairs and stops heat from being lost by **radiation**
59
New cards
Define Urea
excess amino acids that are no longer needed by the body are converted to fats and carbohydrates
60
New cards
How are some ions and water molecules lost?
sweating-ions and water
respiration-water
respiration-water
61
New cards
Why is water regulation important?
Cells can gain or lose water based on osmosis.
62
New cards
How does thyroxine control the metabolic rate?
LOW LEVELS OF THYROXINE:
* this stimulates production of TRH in the hypothalymus
* TRH causes the release of TSH from the pituitary gland
* TSH acts on thyroid to produce thyroxine
\
Normal levels of thyroxine will inhibit the production of TSH. This is negative feedback as limiting production of TSH makes level of thyroxines fall.
* this stimulates production of TRH in the hypothalymus
* TRH causes the release of TSH from the pituitary gland
* TSH acts on thyroid to produce thyroxine
\
Normal levels of thyroxine will inhibit the production of TSH. This is negative feedback as limiting production of TSH makes level of thyroxines fall.
63
New cards
What is clomifene therapy?
Artificial hormones are used when the female is not producing enough eggs, or they are not producing them on regular basis. This is usually as a result of the pituitary gland not producing sufficient FSH to cause egg maturation. This clomifene drug produces more FSH and LH
64
New cards
What is the importance of homeostasis? (thermoregulation and osmoregulation)
THERMOREGULATION: if the body gets to above 37 degrees, this will cause enzymes to be less effective as they denature
OSMOREGULATION: if too much water enters cells they will burst as they swell. if blood is too concentrated then the cells will shrink.
OSMOREGULATION: if too much water enters cells they will burst as they swell. if blood is too concentrated then the cells will shrink.
65
New cards
BMI equation
BMI = mass (kg) (height (m))2
66
New cards
Explain how thermoregulation takes place, with reference to the function of the skin (the role of the dermis)
**Sweat glands** in the dermis release more sweat onto the surface of the epidermis. The sweat evaporates, transferring heat energy from the skin to the environment
67
New cards
Explain how thermoregulation takes place, with reference to the function of the skin (the role of the hypothalymus)
This has receptors that receive impulses from EPIDERMIS + DERMIS skin receptors that provide information about the external temperature.If the hypothalamus detects temperature change, a response occurs.
68
New cards
What is the purpose of the kidneys?
To filter the blood and remove all waste products, the main one is urea.
The kidney also regulates the level of useful substances (ions)
The kidney also regulates the level of useful substances (ions)
69
New cards
What do tubules in the nephrone do?
when blood passes through kidneys tubules absorb all smaller particles.
70
New cards
Describe the structure of the urinary system?
Regions of the kidney:
**Cortex** - the outermost region
**Medulla** - the inner section of the kidney
**Renal pelvis** - the tube linking the kidney to the ureter
* Nephrons start in the **cortex** of the kidney, loop down into the **medulla** and back up to the cortex
* The contents of the nephrons drain into the **renal pelvis** and the **urine collects** there
**Cortex** - the outermost region
**Medulla** - the inner section of the kidney
**Renal pelvis** - the tube linking the kidney to the ureter
* Nephrons start in the **cortex** of the kidney, loop down into the **medulla** and back up to the cortex
* The contents of the nephrons drain into the **renal pelvis** and the **urine collects** there
71
New cards
What is absorbed in filtration and what is not?
absorbed: water, glucose, amino acids, urea
not absorbed: cells and proteins
not absorbed: cells and proteins
72
New cards
73
New cards
What occurs in selective reabsorption?
Glucose is always reabsorbed, some water is reabsorbed and no urea is absorbed back into the bloodstream