Amines and Amides
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
how are amines prepared from halogenoalkanes?
nucleophilic substitution with ammonia
amine functional group?
R-NH2
conditions required for halogenoalkane + ammonia -> amine?
ethanolic, heat, high pressure, excess ammonia
how are amides formed from amines?
additional-elimination reaction by adding acid anhydride or acyl chloride
5 classifications of amines?
primary, secondary, tertiary, aliphatic, aromatic
primary amine?
1 carbon bonded to nitrogen
secondary amine?
2 carbons bonded to nitrogen
tertiary amine?
3 carbons bonded to nitrogen on amine group
aliphatic amine?
doesn't contain a benzene ring
benzene ring is present but not directly bonded to nitrogen
aromatic amine?
has a benzene ring directly bonded to nitrogen
suffix for simple amines?
-yl amine
how to name amines if the amine group isn't at the end?
use longest carbon chain for root
use longest carbon chain for root
add -an after root
use -amine
position number
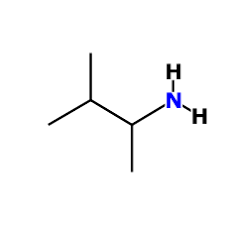
draw 3-methylbutan-2-amine
prefix used if amine group isn't the highest priority?
amino-
suffix used if amine group is the highest priority?
-amine
what multiplier is used when naming secondary amines if groups attached to the nitrogen are identical?
di, e.g. dimethylamine
what multiplier is used when naming tertiary amines if 3 groups attached to nitrogen are identical?
tri, e.g. trimethylamine
order of functional group priority?
1 carboxylic acid
2 amide
3 nitrile
4 aldehyde
5 ketone
6 alcohol
7 amine
8 alkene
9 benzene
10 halogenoalkane
11 alkane
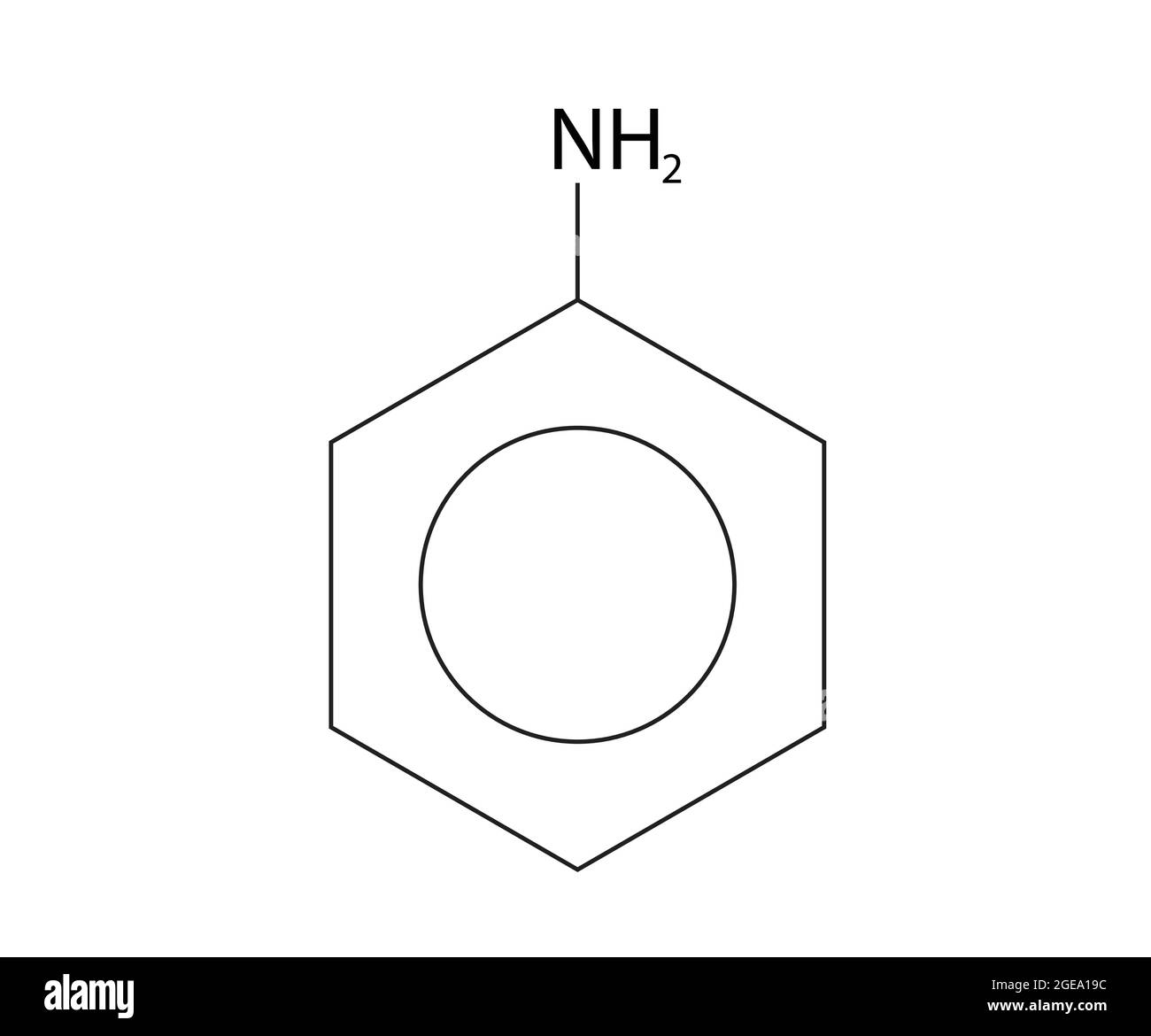
draw phenylamine
practice naming on uplearn pls
amide functional group?
O=C-NH2
3 classifications for amides?
primary, secondary, tertiary
primary amide?
nitrogen is bonded to 1 carbon
secondary amide?
nitrogen bonded to 2 carbons
tertiary amide?
nitrogen bonded to 3 carbons
suffix for naming amides?
- amide, e.g. propanamide
how to name secondary amides?
N- before prefix
group with the carbonyl group = main chain
group without = substituent
what does the 'N-' mean when naming secondary and tertiary amides?
acts as a position number, tells you that the substituent is bonded to the nitrogen
when naming tertiary amides, if 2 substituent are identical, what multiplier is used?
di, e.g. N,N-Dimethylpropanamide
how do we name tertiary amides if the 2 substituents aren't identical?
name both with N- in front, then add in alphabetical order, e.g. N-ethyl-N-methylpropanamide
what intermolecular forces to amines and amides have?
van der waals
primary and secondary experience hydrogen bonding
why don't tertiary amides experience hydrogen bonding?
they don't have an N-H bond
melting and boiling point properties for amines and amides?
primary and secondary have higher melting and boiling points than tertiary
why do primary and secondary amines/amides have higher melting and boiling points than tertiary?
primary and secondary have hydrogen bonding
solubility properties of amines and amides?
all small amines and amides are highly soluble in water
as size of molecule increases, solubility decreases
why does solubility of amines/amides decrease as the size of molecule increases?
a greater region of the molecule is non-polar, non-polar molecules are highly soluble in water
why can amines act as bases when forming a bond with water or nucleophilic when reacting with electrophiles?
- nitrogen has 5 electrons in outer shell, so when they form 3 covalent bonds, it still has a lone pair
base properties: what is gas sweetening?
natural gas contains harmful gases, amines convert CO2 gas and hydrogen sulfate gas into less harmful products by acting as a base
base properties: issues with CO2 and hydrogen sulfide in natural gas?
can corrode pipes, hydrogen sulfide causes instant death at high concentrations
How is base strength measured?
pH
Order aliphatic, ammonia and aromatic in base strength?
Aliphatic > ammonia > aromatic
What determines base strength?
if lone pair more or less available
more available = stronger base
lone pair better at accepting a proton = more available = stronger base
Why are aliphatic amines stronger bases than ammonia?
Lone pair of electrons on N atom more AVAILABLE to accept protons
why are aliphatic amines' lone pairs more available?
alkyl groups donate electron density to nitrogen via inductive effect = nitrogen is better at accepting a proton = increases availability of the lone pair = stronger base
How do alkyl groups stabilize carbocations?
by donating electron density to the carbon via inductive effect
trend in number of alkyl groups and base strength?
as number of alkyl groups bonded to the nitrogen increases
Why are aromatic amines weak bases?
p orbital containing lone pair on nitrogen becomes apart of the pi system on benzene ring, so becomes delocalised = lone pair is less available = weaker
nucleophilic properties of amines?
nucleophilic addition-elimination reaction with acyl chlorides/acid anhydrides to form primary amides
primary, secondary, tertiary, NH3 all undergo nucleophilic substitution with halogenoalkanes
why can primary, secondary, tertiary amines and ammonia all undergo nucleophilic substitution with halogenoalkanes?
they all have a lone pair on the nitrogen
when reacting halogenoalkanes with NH3, why is excess ammonia used?
to decrease chances of the amine (nucleophile) reacting with the halogenoalkane
if the concentration of halogenoalkane is increased, what happens?
chances of halogenoalkane and amine reacting increases
primary amine + halogenoalkane -> ?
secondary amine via nucleophilic substitution
secondary amine + halogenoalkane -> ?
tertiary amine via nucleophilic substitution
tertiary amine + halogenoalkane -> ?
quaternary ammonium ion
what is a quaternary ammonium ion?
4 carbons are directly bonded to the nitrogen atom, giving it a positive charge (NH4+)
how are quaternary ammonium SALTS formed?
quaternary ammonium ions always have a positive charge, so can form lattices with anions, e.g. Cl-
use of quaternary ammonium salts?
Cationic Surfactants (fabric softeners)
structure of cationic surfactants?
polar end (NH4+) that's highly soluble in water,
non-polar chain high insoluble in water
how to surfactants act when dissolved in water?
they move to the surface, polar head in the water, non-polar poke out of the surface
2 ways primary aliphatic amines are produced?
1) halogenoalkane + ammonia -> primary aliphatic amine via nucleophilic substitution
2) reduction of nitriles
conditions for nucleophilic substitution of halogenoalkanes with ammonia? why?
ethanolic, to ensure ammonia reacts with halogenoalkane and not water
heated to increase rate, NH3 has a low boiling point, so high pressure is used to keep it dissolved in ethanol
excess ammonia to prevent further reaction of primary amine to secondary
how are primary aliphatic amines produced from nitriles?
nitriles in solution, metal catalyst added (Ni), bubble in H2
H2 (g) is the reducing agent
in each reduction of nitrile reaction, how many hydrogens are added to the nitrile?
4, C-N triple bond breaks -> CH2-NH2 single bond
general equation for reduction of a nitrile?
RCN + 2H2 -> RCH2NH2
why are nitriles preferred to halogenoalkanes when producing primary aliphatic amines?
efficient due to 100% atom economy (only 1 product produced, using halogenoalkane produces a salt too)
no chance of any further reactions = 100% atom economy + efficient
why is using halogenoalkanes less efficient?
atom economy isn't 100% as a salt is also produced
although we use excess ammonia to decrease chance of amine + halogenoalkane it still happens, producing secondary and tertiary = decreases atom economy more
how are aromatic amines produced?
By reducing an aromatic nitro compound, like nitrobenzene,
nitro groups are reduced to NH2
what is an aromatic nitro compound?
aromatic compounds containing a nitro group (NO2)
conditions required for reduction of aromatic nitro compounds to produce aromatic amines?
concentrated HCl and Sn (tin) mixture
general equation for reduction of aromatic nitro compounds?
C6H5NO2 + 6[H] -> C6H5NH2 + 2H2O
what does the [H] represent in the equation?
reducing agent
use of aromatic amines?
manufacturing dyes