3.6 Predict, draw models (pictures), and explain why relative melting points and boiling points for substances that exist as molecules (like H2) differ from those that exist as continuous extended networks (like diamond or metals).
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
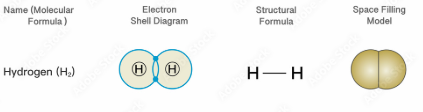
Why do molecular substances like H₂ have low melting and boiling points?
Molecular substances have weak intermolecular forces (like van der Waals forces), which require little energy to overcome.
What holds the molecules together in substances like H₂?
The weak intermolecular forces (van der Waals or dipole-dipole forces) hold the molecules together.
Why do extended network substances like diamond and metals have high melting and boiling points?
These substances have strong covalent bonds (diamond) or metallic bonds (metals) that require a lot of energy to break.
What kind of bonds hold the atoms together in diamond?
Strong covalent bonds form a continuous 3D network between carbon atoms.
What type of bonding occurs in metals?
Metallic bonding occurs, where electrons are delocalized and shared among metal atoms in a "sea of electrons."
What causes molecular substances to have lower melting and boiling points than extended network substances?
Molecular substances have weak intermolecular forces, while extended network substances have strong covalent or metallic bonds, requiring more energy to break.
Why is more energy needed to break bonds in diamond or metals?
In diamond, the covalent bonds between carbon atoms are very strong, and in metals, the metallic bonds are strong due to the delocalized electrons.
How are molecules in substances like H₂ arranged?
Molecules in H₂ are spaced apart and held together by weak van der Waals forces.
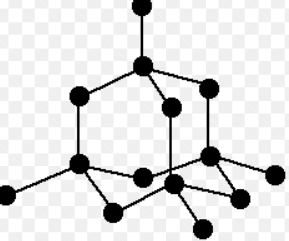
How are atoms arranged in diamond?
In diamond, carbon atoms form a continuous 3D network with strong covalent bonds.
How are atoms arranged in metals?
In metals, atoms are arranged in a regular pattern, with delocalized electrons flowing freely between them.