muscle physiology
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
muscle structure
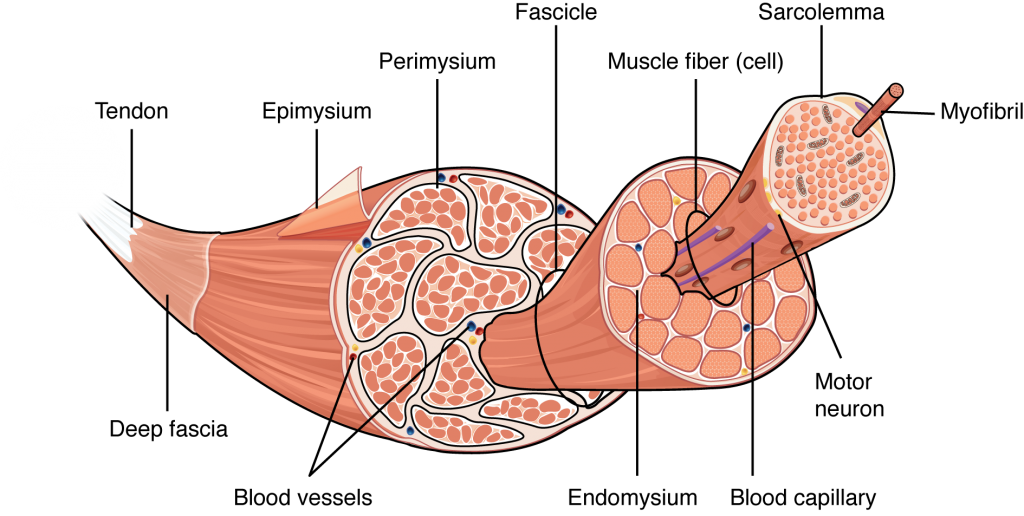
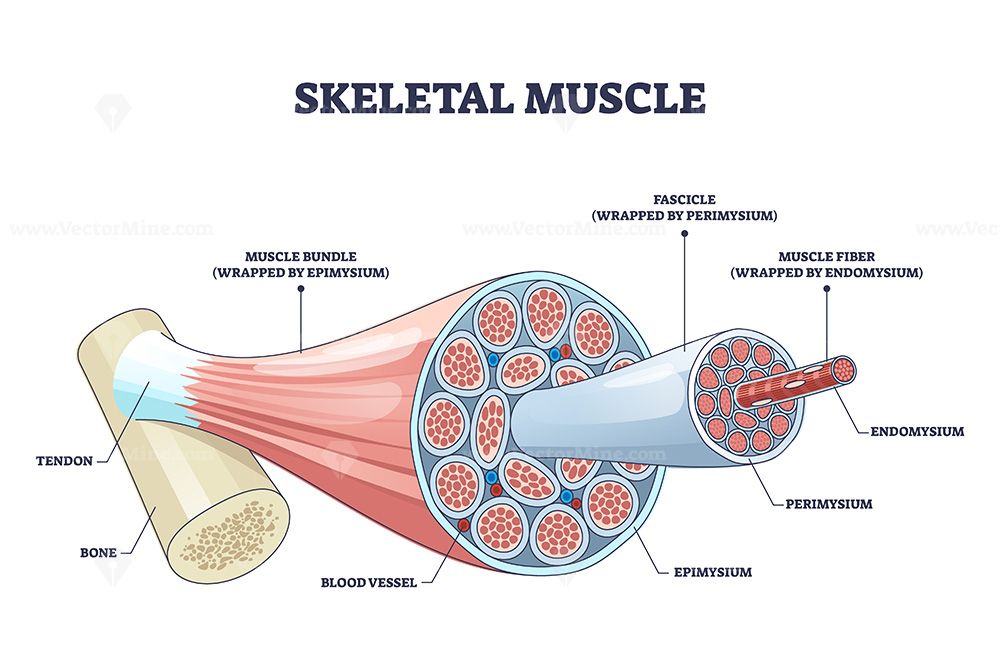
epimysium is a dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds the entire muscle.
It is the outermost layer of connective tissue, encircling the entire muscle and providing structural integrity.
It helps to separate the muscle from surrounding tissues and organs.
The epimysium is continuous with the tendons, which attach the muscle to bones, allowing for the transmission of force generated by the muscle.
perimysium
surrounds muscles fascicles in skeletal muscles
contains blood vessels, nerves, collagen
muscles fascicle
bundle of skeletal muscles surround by the perimysium
muscle fiber
wrapped by endomysium
made of myofibrils
contractile unit of skeletal muscles
blood capillaries
line muscle fibers and bring blood supply to the muscles
can increase this through exercise
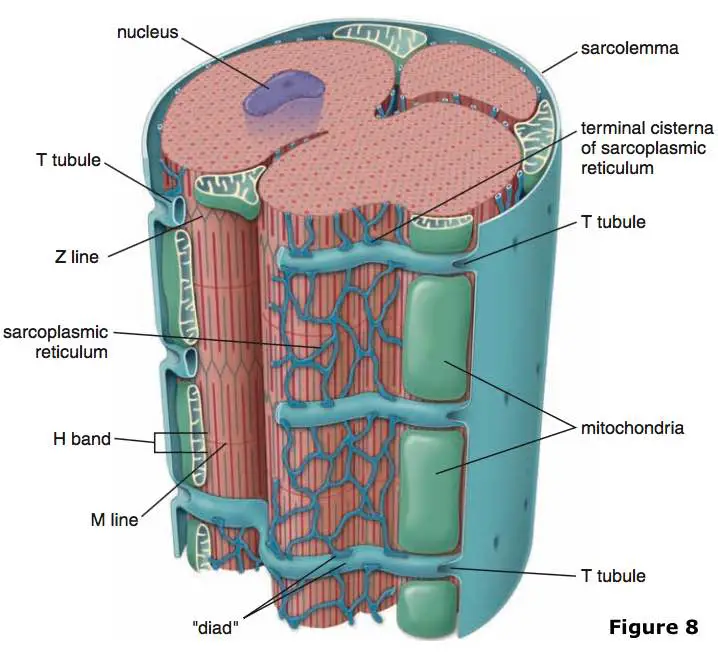
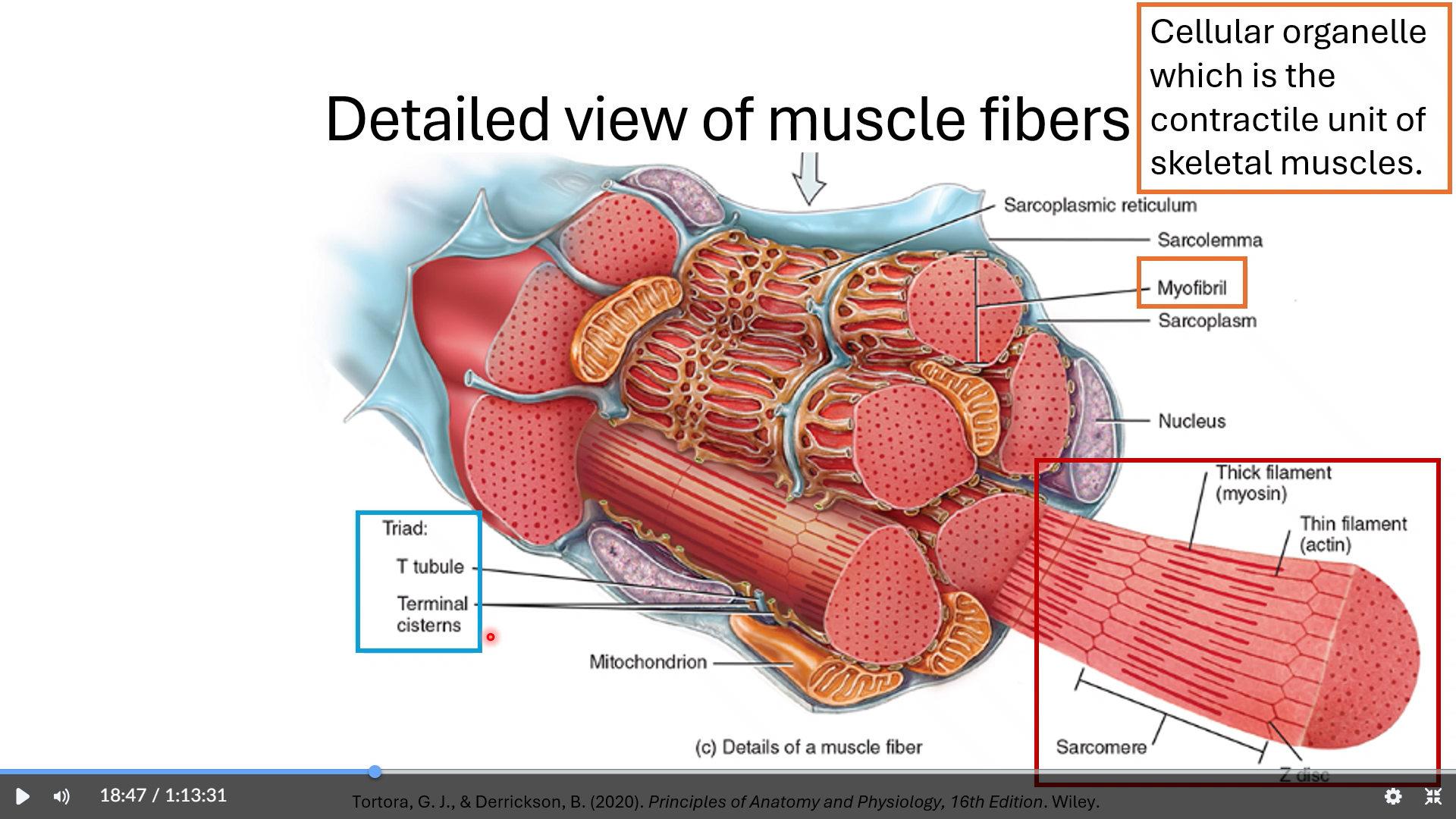
t tubules and terminal cisterns make up a triad
t tubules are projections of the sarcolemma which carry MAPs throughout the muscle fiber and terminal cisterns are part of the SR which releases Ca+2 to elicit muscle contraction
carry muscle action potentials (MAPs)
allow muscle action potentials to travel within the myofibrils in the muscle fibers (integration)
triggers calcium release
sarcoplasmic reticulum
orange “netting” in the third image
muscle organization
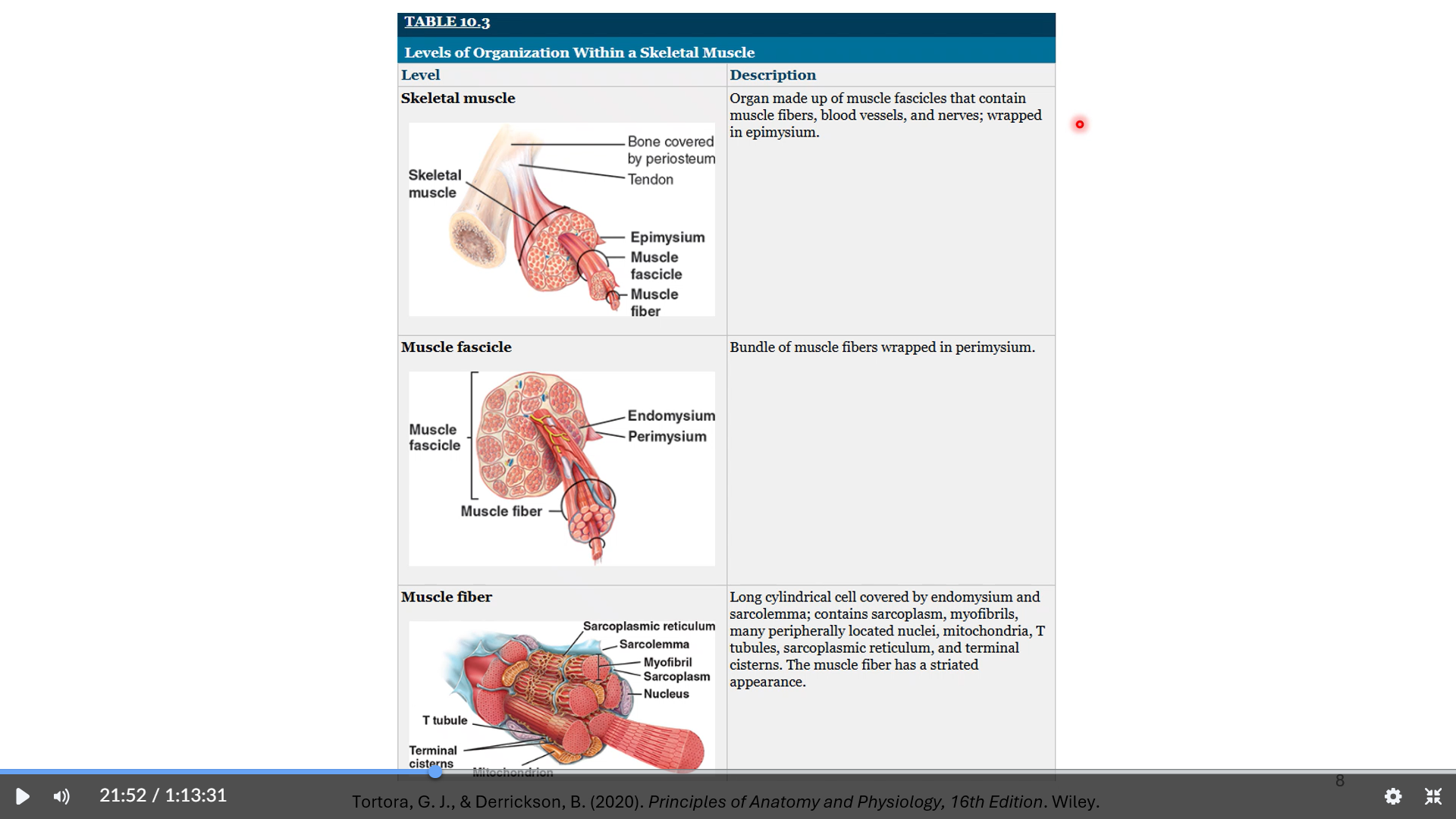
myofibril
sarcomere
includes thick and thin filaments
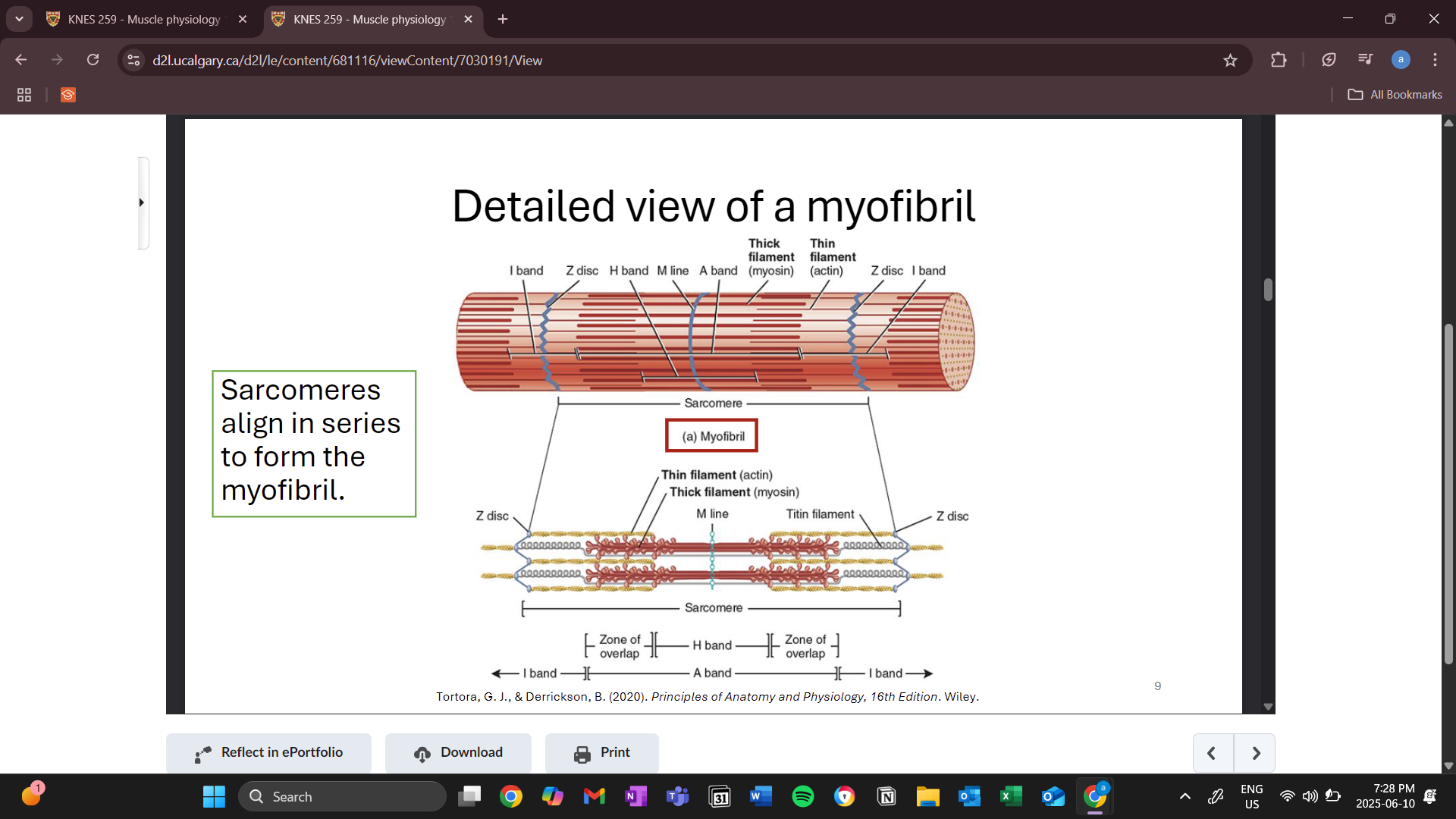
z disc
boundaries of the sarcomere (2 ends)
m line
middle of the sarcomere
titin filament
structural filament
a band
shows length of the thick filament
never changes
zones of overlap and h bands can change during contraction
h band is the area where there is only tick filament and shortens during a contraction( thin filament comes closer to the center)
i band
also decreases during contraction
zone of only thin filament
z disc passes through the center of each i band

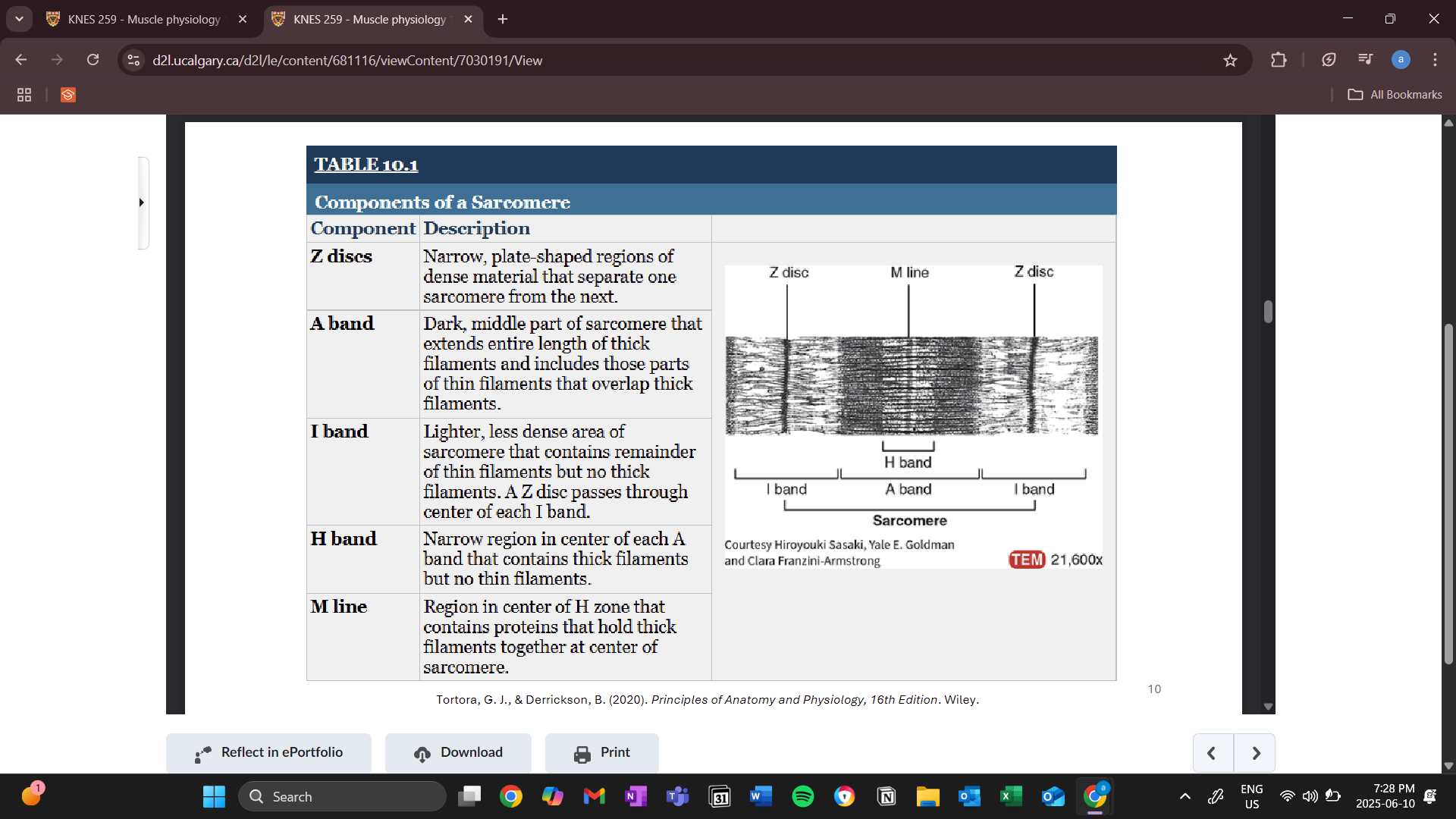
thick filament (myosin)
contains 2 myosin heads
contain actin binding sites and ATP binding sites
bind to actin binding sites on the thin filaments which allows for the pulling and contracting of muscle fibers
contains an ATPase enzyme that breaks down ATP
m lines attach the thick filaments
many myosin proteins join together to make up a thick filament

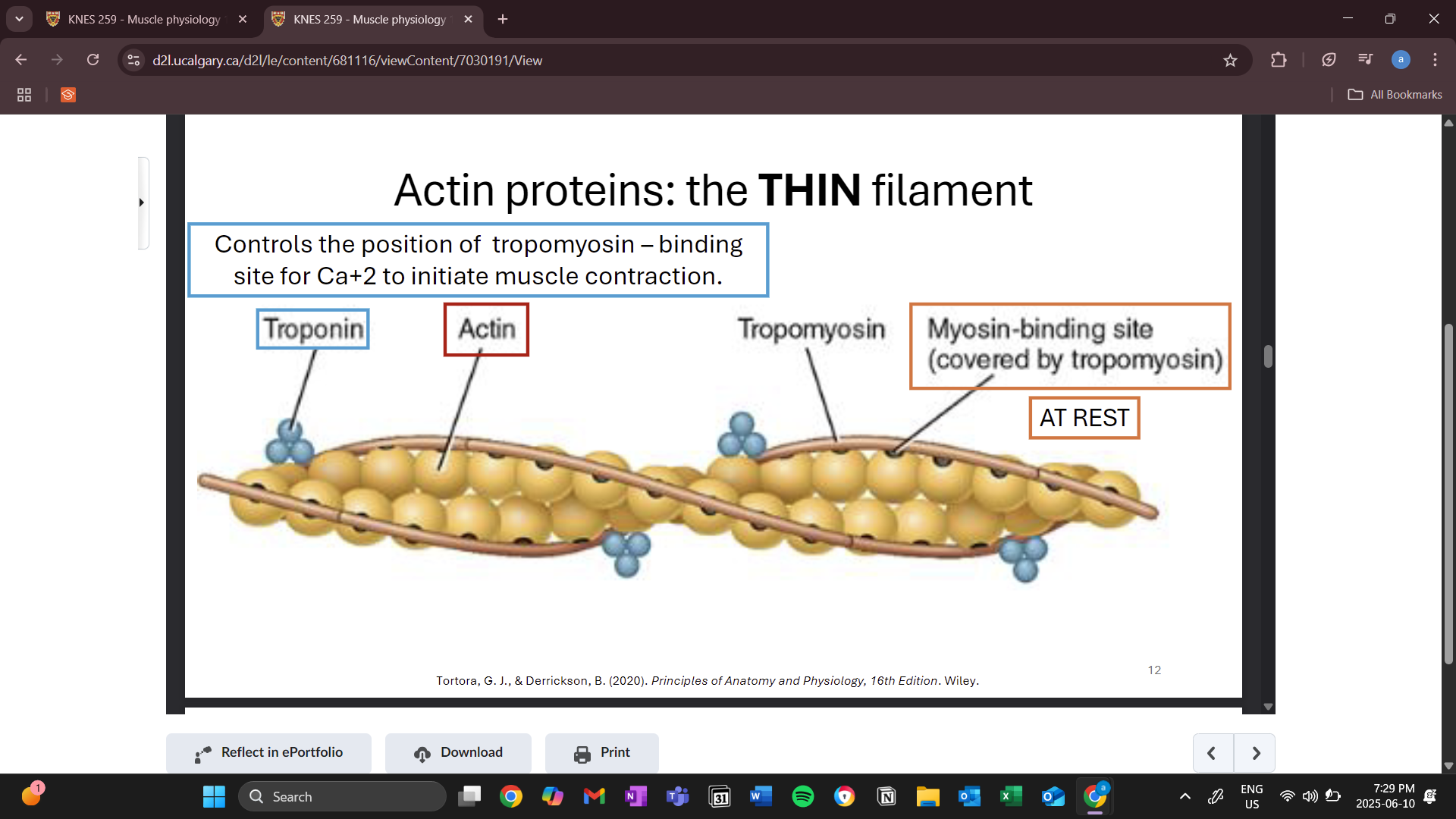
thin filaments (actin)
helix shape
myosin bind sites covered by tropomyosin during rest (stops contraction)
troponin
control whether tropomyosin covers binding sites or not
binding site for calcium to start an action potential (shortening of sarcomere)
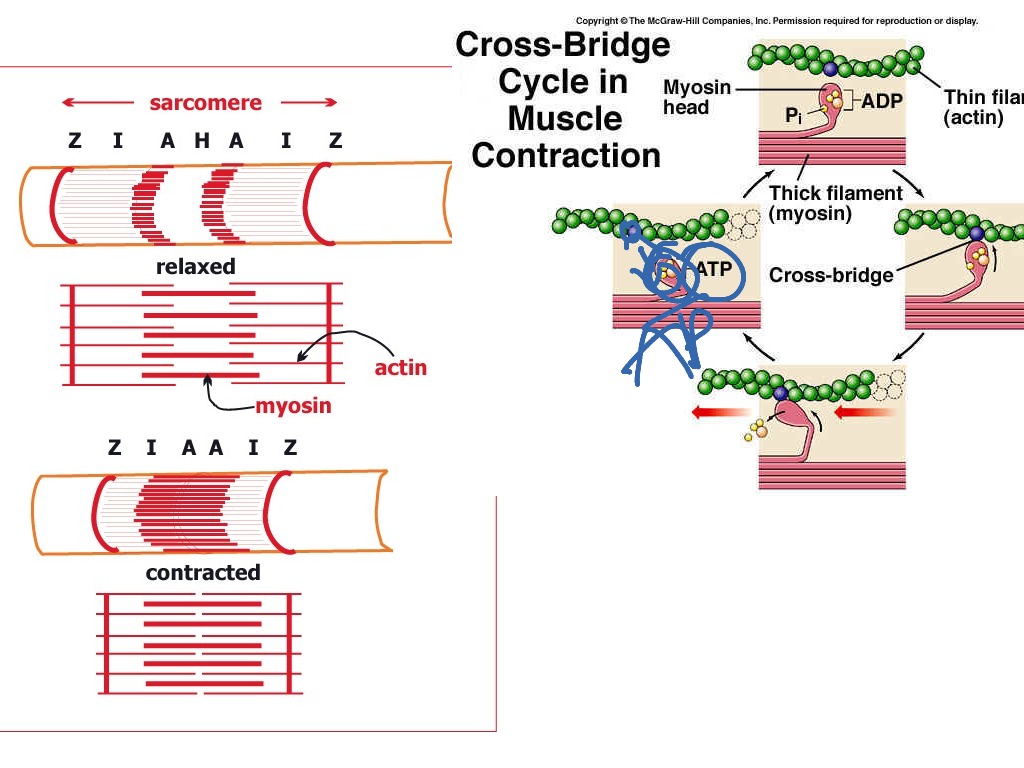
sliding filament theory
binding of myosin heads to the actin to shorten the sarcomere and bring the z discs closer together
contracted until h and i bands are no longer present
THICK (a band) AND THIN FILAMENTS NEVER CHANGE IN LENGTH
muscle contraction cycle
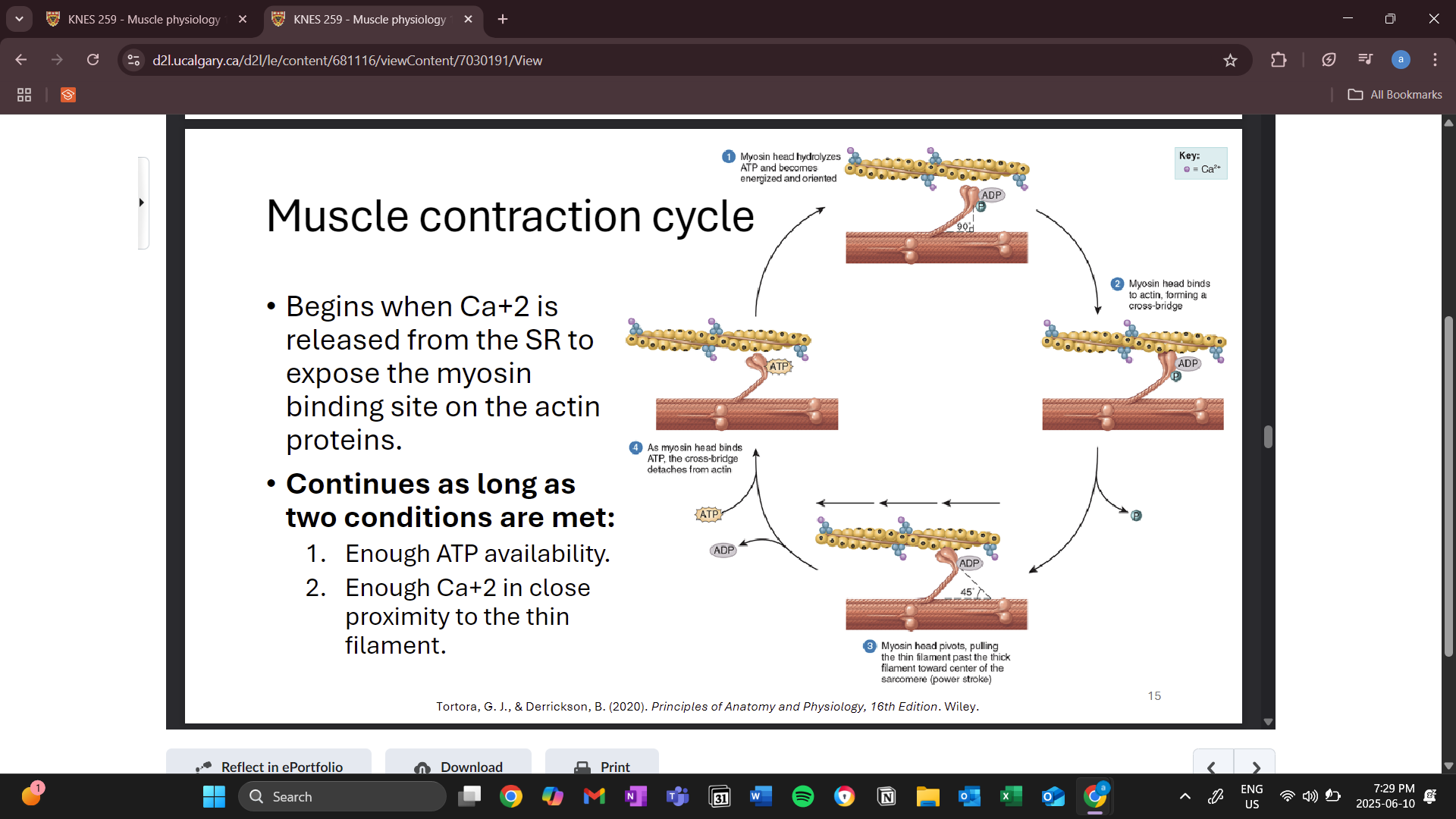
binding between thick and thin is called a cross bridge
many cross bridges are formed
pull thin and thick filaments past each other (power stroke)
release is caused by ATP binding to the myosin head

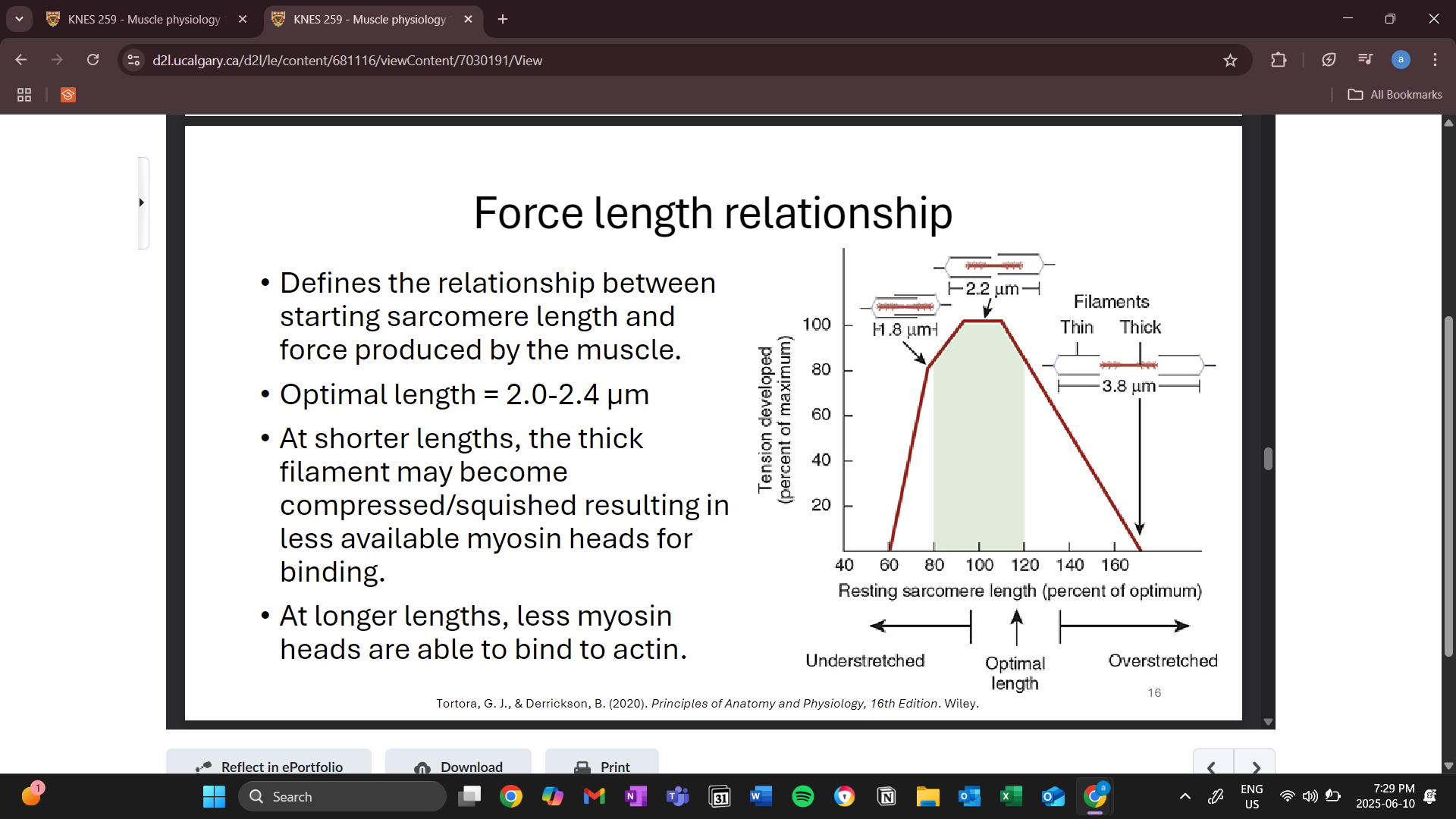
force length relationship
sarcomere length and force produced by the muscle during a contraction
optimal length is the maximal force that can be produced
less myosin binding heads available during non optimal lengths

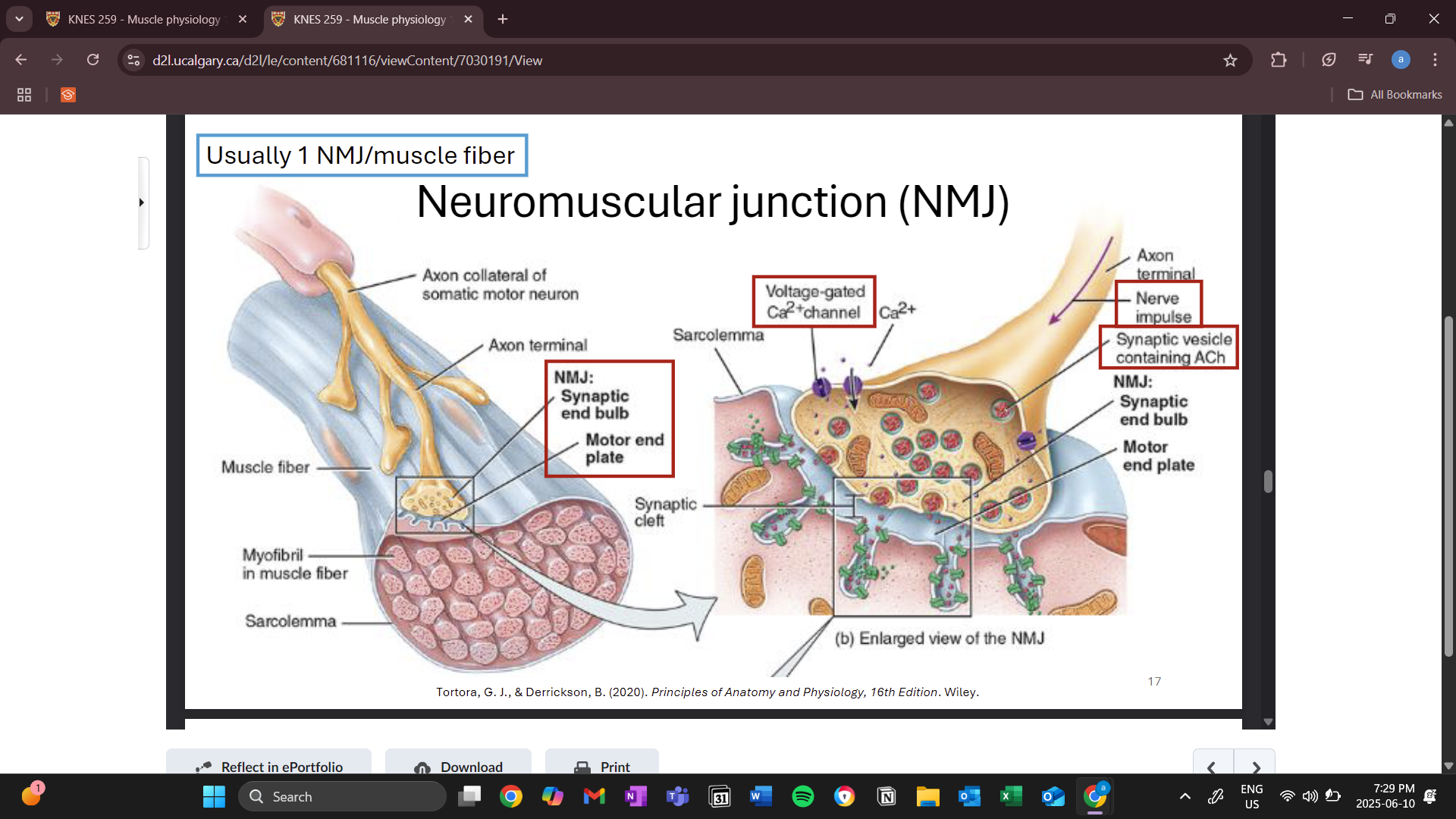
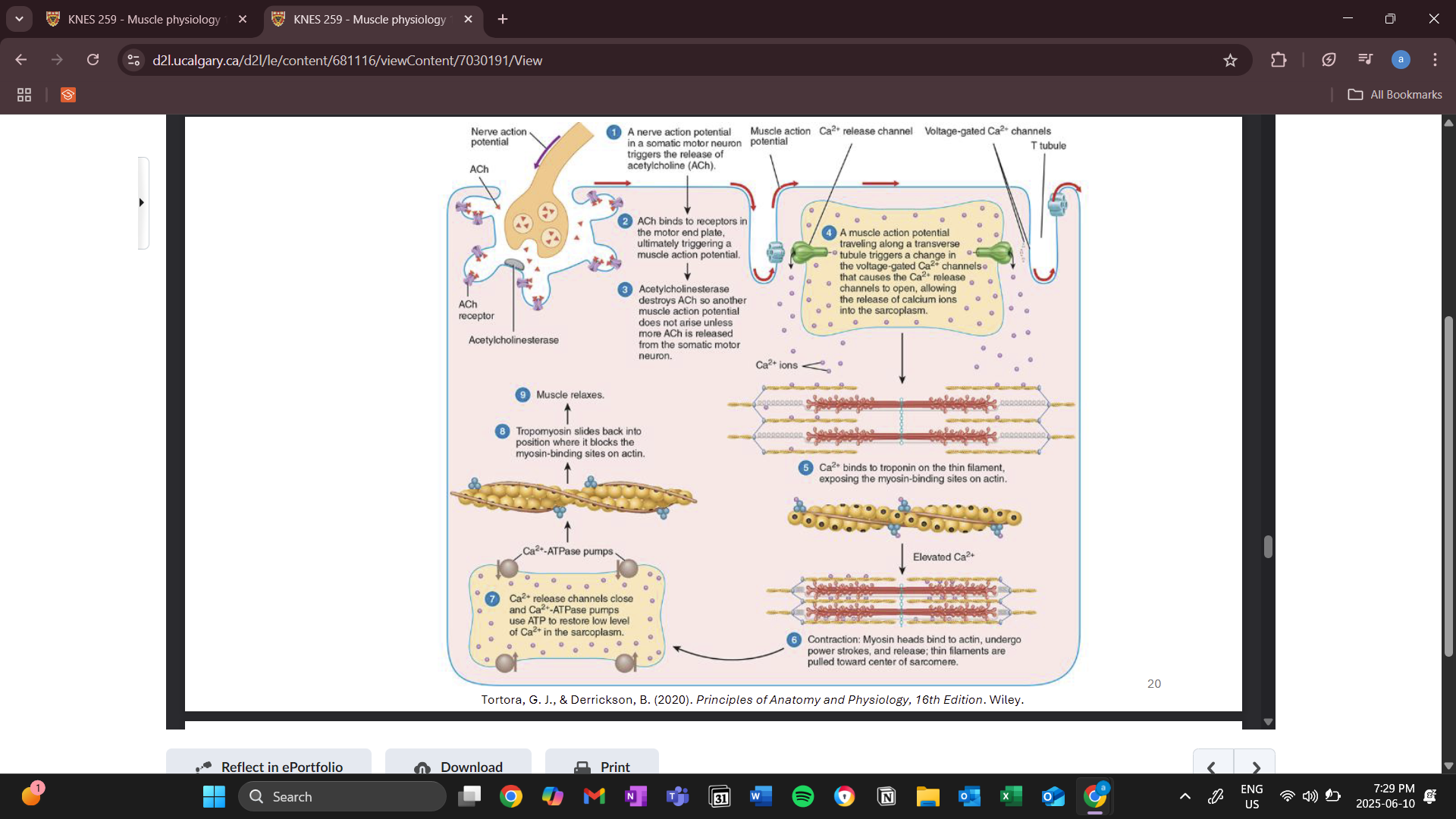
neuromuscular junction (NMJ)
where the nervous system meets the muscle
synaptic end bulb
end of the nerve
motor end plate
when the electrical impulse from a somatic motor neuron reaches the synaptic end bulb, it triggers the voltage gated calcium channels to open
synaptic vesicles move toward the synapse and through exocytosis releases acyltocholine
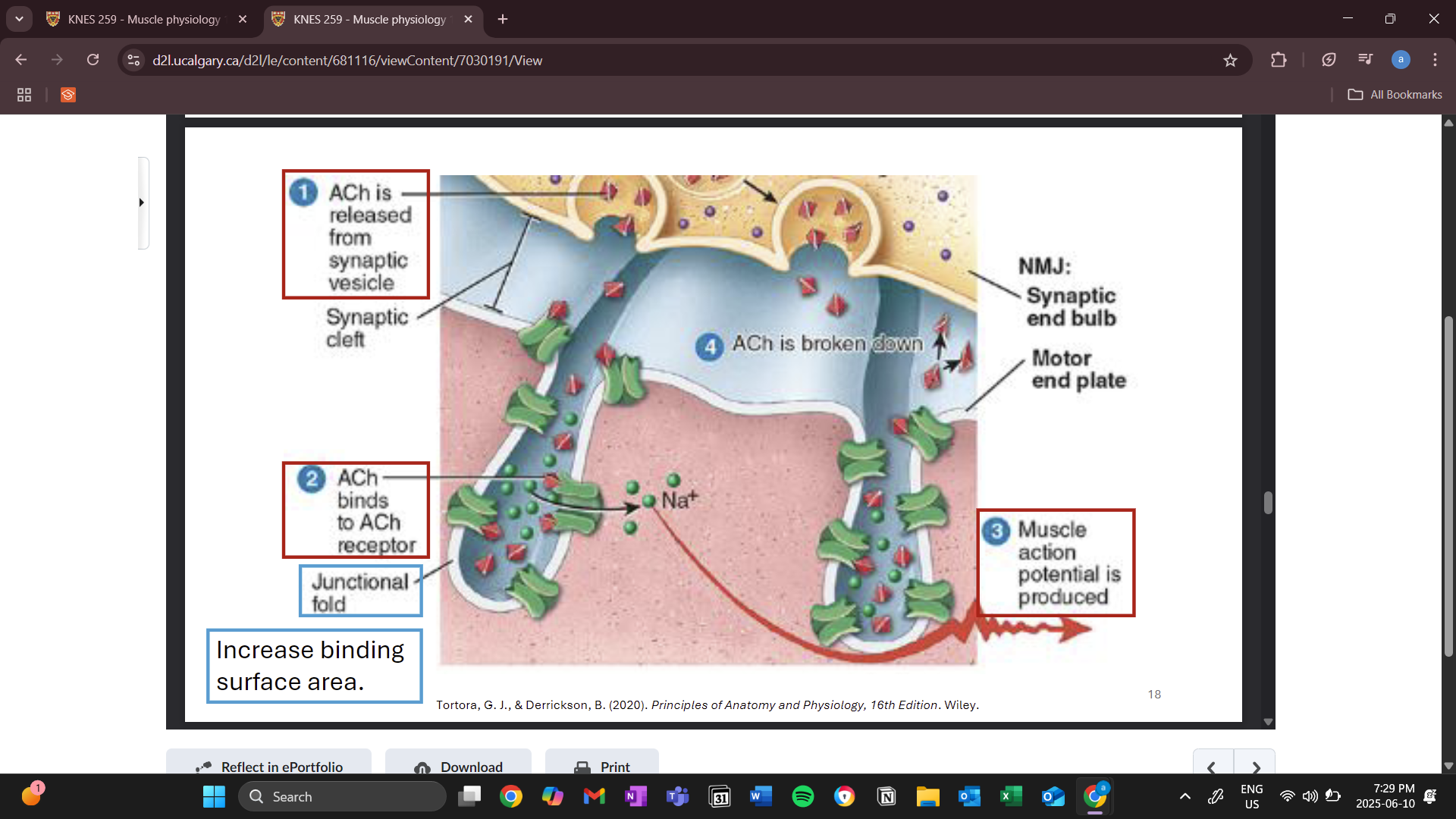
movement of ions causes action potential

muscle in resting state vs contracting state
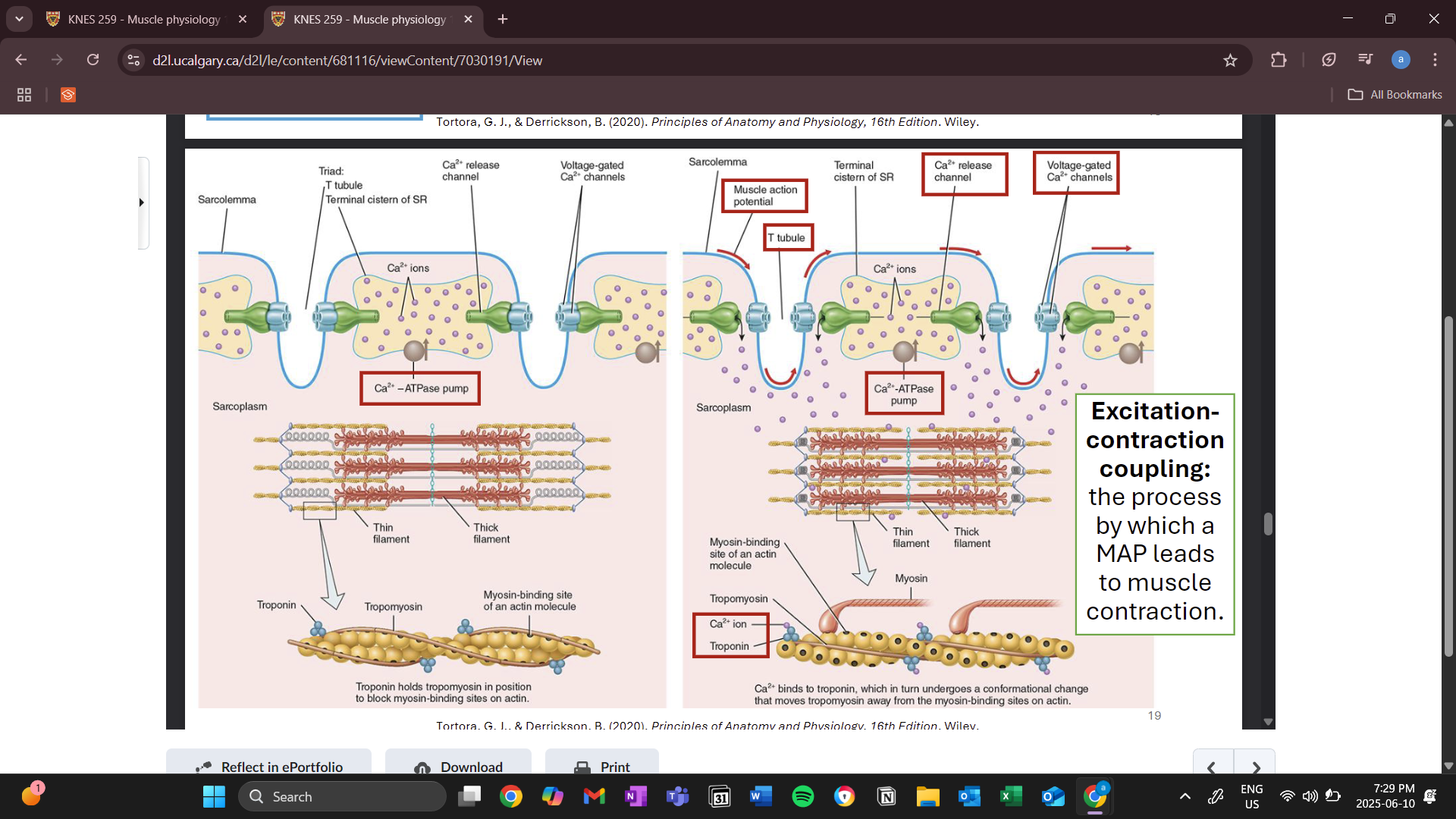
red arrows show action potential travelling down the sarcolemma
calcium release channels and voltage gated channels change shape allowing calcium to be released from the sarcoplasmic articulum into the cytoplasm
calcium is the purple circles
calcium then triggers troponin to cause an action potential
ATPase pump is constantly pumping calcium into the sarcoplasmic articulum from the cytosol/ sarcoplasm

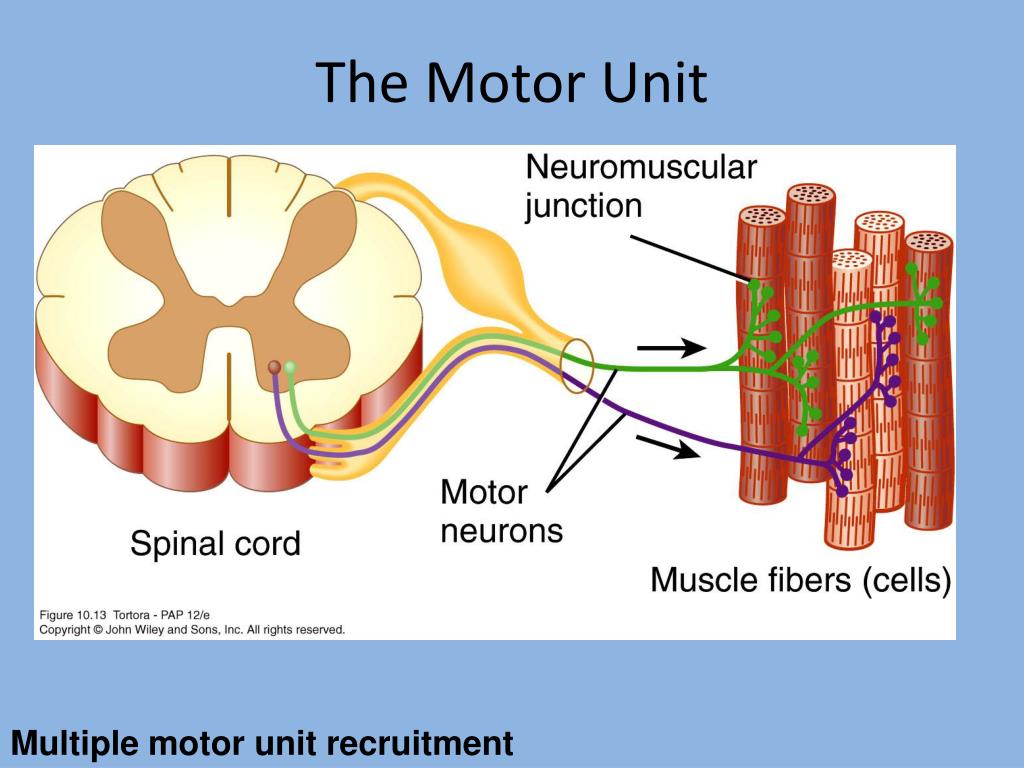
motor unit (MU)
1 motor neuron and its muscle fibers it supplies (about 150)
1 motor neuron action potential = 1 MAP occurs all muscle fibers in that MU simultaneously
muscles involved in fine motor movements have less fibers per MU
how is force controlled and produced
the rate of incoming motor neuron action potentials to each MU
faster = more force
number of motor units recruited
weaker MU enlisted first and stronger ones involved if we need more force for a certain task
example: milk carton taking more strength to lift than expected
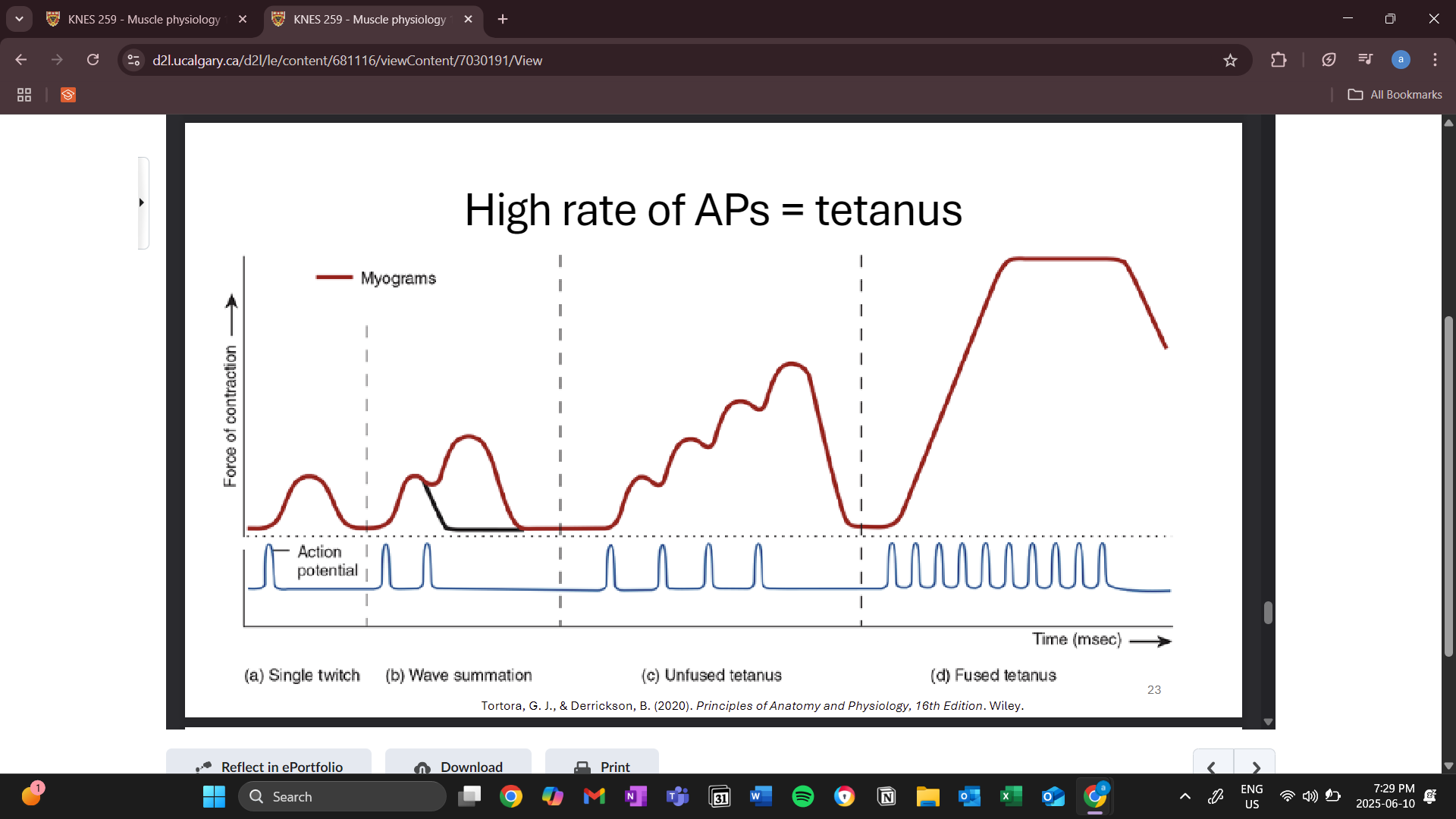
wave summation
summation occurs when the second action potential comes before the first finishes
fused tetanus
no relaxation between action potential

types of muscle fibers
slow oxidative fibers
high myoglobin (binds oxygen)
dark red
capillarization
high mitochondrial size/ amount
favour oxidative metabolism (aerobic) to be more fatigue resistant
generate force more slowly
fast oxidative-glycolytic fibers
biggest fiber type
high myoglobin
dark red
high capillarization
high glycogen
participate in both aerobic and anaerobic metabolism
(intermediate between slow and fast glycolytic)
fast glycolytic fibers
low myoglobin
less capillarization and mitochondria
white
high glycogen
quick and strong movements
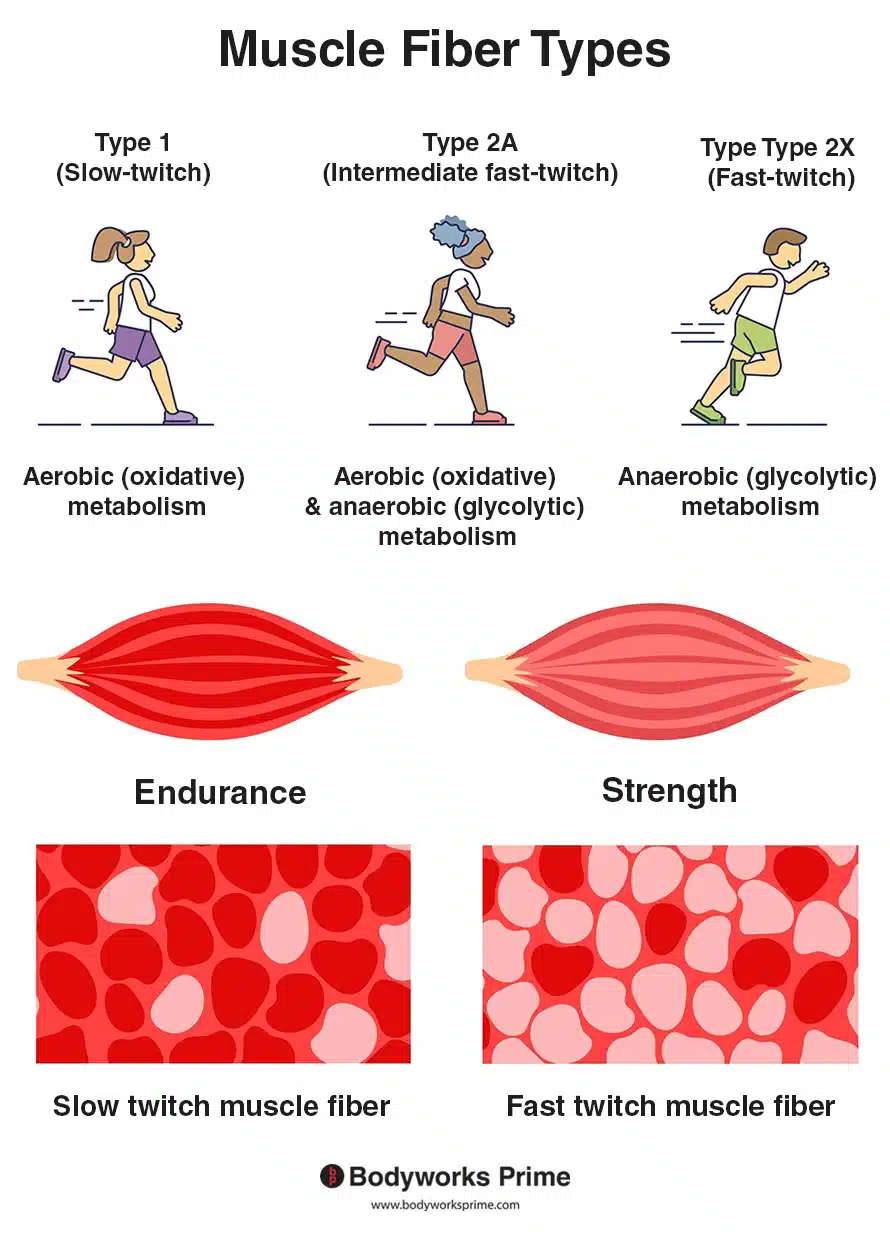
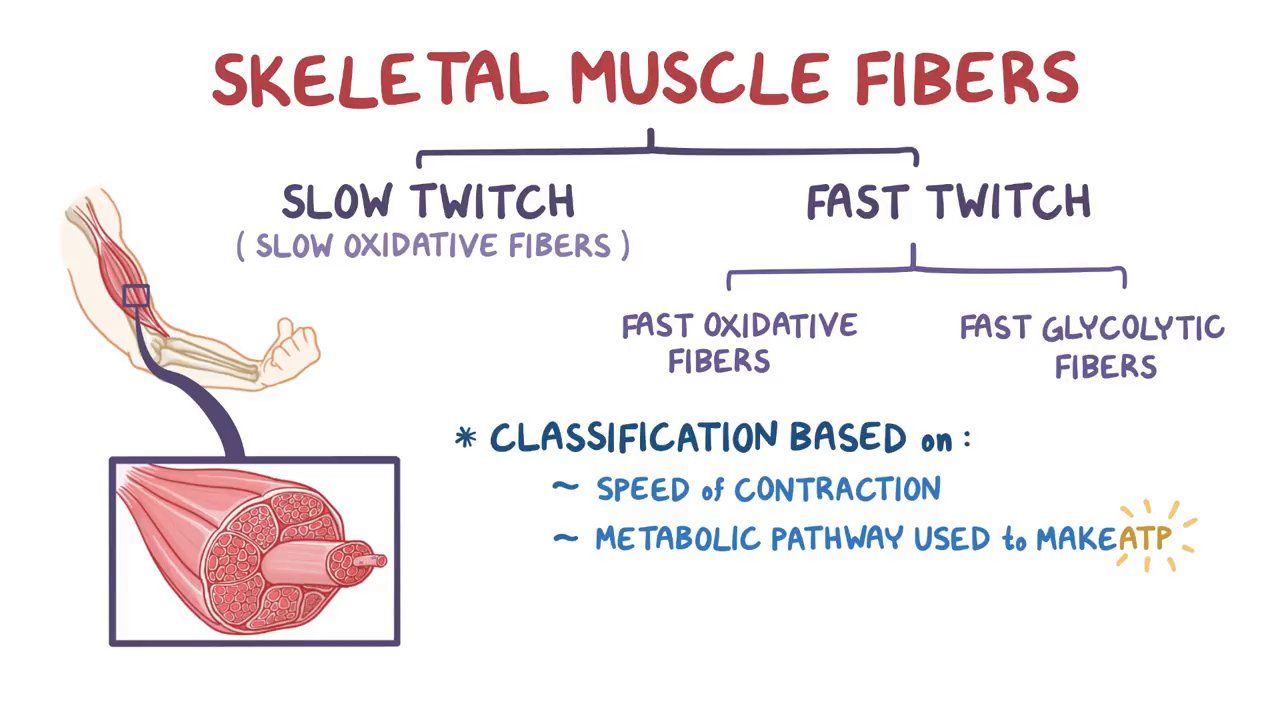
relationship between MU and fiber type
all muscle fibers within a motor unit will be the same type
with progressive MU for bigger tasks, MU are recruited in order of slow oxidative, fast oxidative-glycolytic, fast glycolytic
maximal contractile activities require all fiber types
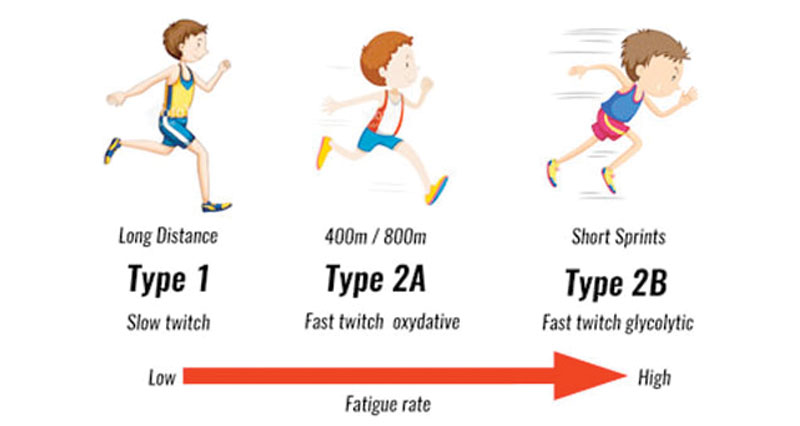
main types of muscle contractions
concentric (shortening)
eccentric (lengthening)
isometric (no movement)
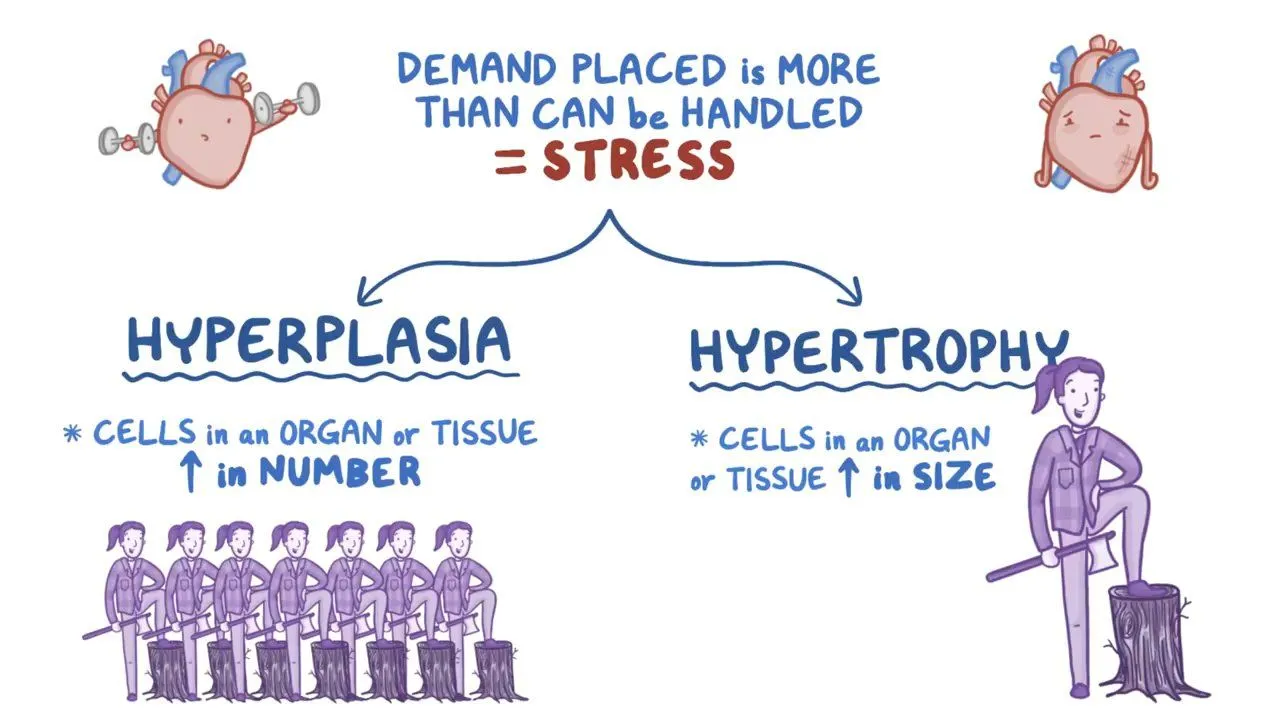
types of muscle growth
hypertrophy
muscles increase in size
hyperplasia
more muscle fibers
main functions of muscles
movement
stability and posture
substance transport and storage
sphincters, stomach, bladder, heart, blood vessels, skeletal muscles
thermogenesis
generating heat via muscle contraction
main properties of muscles
1. Electrical excitability
• Autorhythmic electrical signals (i.e., digestive tract, heart) or chemical
stimuli (i.e., neurotransmitters, hormones) can stimulate a muscle
action potential which produces muscle contraction
2. Contractility
• Muscle shorten for movement to occur
3. Extensibility
• The ability for muscle tissue to stretch (i.e., stomach, heart)
4. Elasticity
• Bounce back to original shape and length
appearance of types of muscular tissue
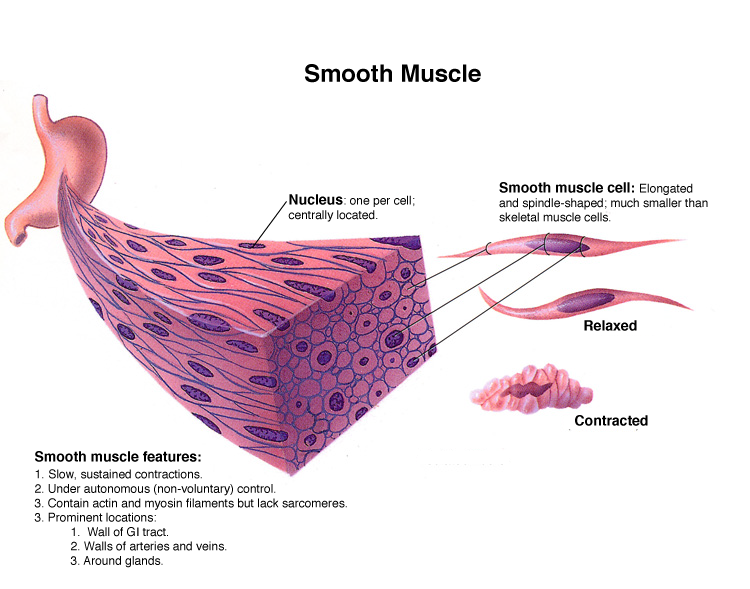
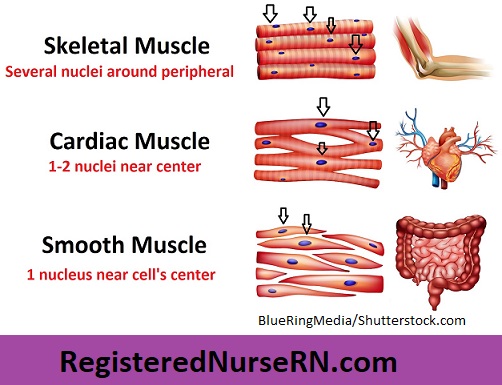
skeletal is somatic
cardiac and smooth are autonomic
cardiac muscles have intercalated discs joining neighbouring fibers