2.1.2 Biological molecules
5.0(1)Studied by 3 people
Card Sorting
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 11:55 PM on 8/31/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
1
New cards
what biological molecules are in carbohydrates?
C, H, O
2
New cards
what biological molecules are in lipids?
C, H, O
3
New cards
what biological molecules are in proteins?
C, H, O, N, S
4
New cards
what biological molecules are in nucleic acids?
C, H, O, N, P
5
New cards
what are the main cations used in biological processes?
Ca2+ - used for nerve impulses, muscle contractions
Na+ - used for nerve impulses, kidney function
K+ - used for nerve impulses, stomata
H+ - used for pH determination, catalysts
NH4+ - used for making nitrogen ions
Na+ - used for nerve impulses, kidney function
K+ - used for nerve impulses, stomata
H+ - used for pH determination, catalysts
NH4+ - used for making nitrogen ions
6
New cards
what are the main anions used in biological processes?
NO3- - used for amino acids
HCO3- - used for maintaining blood pH
Cl- - used for balancing sodium and potassium levels in cells
PO₄3- - used for cell membranes, nucleic acids and ATP formation, bone formation
OH- - used for pH determination, catalysts
HCO3- - used for maintaining blood pH
Cl- - used for balancing sodium and potassium levels in cells
PO₄3- - used for cell membranes, nucleic acids and ATP formation, bone formation
OH- - used for pH determination, catalysts
7
New cards
what is a hydrolysis reaction?
breaks molecules apart
requires/uses water
requires/uses water
8
New cards
what is a condensation reaction?
joins molecules together
forms water
forms water
9
New cards
what is a hydrogen bond?
covalent bond between hydrogen atoms
10
New cards
what is the structure of water?
oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen - electrons move around oxygen more
water is therefore polar - a molecule with an unequal share of electrons
water is therefore polar - a molecule with an unequal share of electrons
11
New cards
what are the properties of water?
cohesive - due to H bonds, creates surface tension, allows flow and transport of substances in organisms, e.g. xylem
solvent - good transport medium, can transport solutes
polar - can dissolve polar, non-polar and ionic molecules, good polar solvent, good reaction medium
metabolite - reactant or product in many important metabolic reactions
high specific heat capacity - due to H bonds, acts as a buffer against rapid temperature change
high latent heat of vaporisation - due to H bonds, lots of heat can be lost without losing lots of water
more dense than ice
solvent - good transport medium, can transport solutes
polar - can dissolve polar, non-polar and ionic molecules, good polar solvent, good reaction medium
metabolite - reactant or product in many important metabolic reactions
high specific heat capacity - due to H bonds, acts as a buffer against rapid temperature change
high latent heat of vaporisation - due to H bonds, lots of heat can be lost without losing lots of water
more dense than ice
12
New cards
what are carbohydrates?
used as energy sources
form hexoses or pentoses
form hexoses or pentoses
13
New cards
what is a monosaccharide?
a single sugar
e.g. glucose, fructose, ribose, galactose
soluble in water, insoluble in non-polar solvents, sweet reducing sugars
e.g. glucose, fructose, ribose, galactose
soluble in water, insoluble in non-polar solvents, sweet reducing sugars
14
New cards
what is a disaccharide?
two monosaccharides joined in a condensation reaction with glycosidic bonds
e.g. maltose = glucose + glucose, sucrose = glucose + fructose, lactose = glucose + galactose
soluble in water, sweet reducing sugars except sucrose
e.g. maltose = glucose + glucose, sucrose = glucose + fructose, lactose = glucose + galactose
soluble in water, sweet reducing sugars except sucrose
15
New cards
what is a polysaccharide?
many monosaccharides joined in condensation reactions by glycosidic bonds
e.g. glycogen, starch, cellulose
large, insoluble molecules, used as energy stores and storage molecules
e.g. glycogen, starch, cellulose
large, insoluble molecules, used as energy stores and storage molecules
16
New cards
what is a glycosidic bond?
covalent bond between carbohydrates
17
New cards
how are disaccharides and polysaccharides formed?
condensation reaction
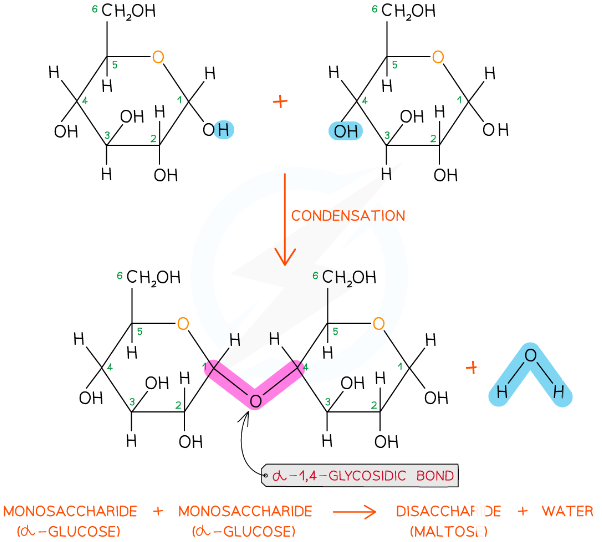
18
New cards
how are disaccharides and polysaccharides broken down?
hydrolysis reaction
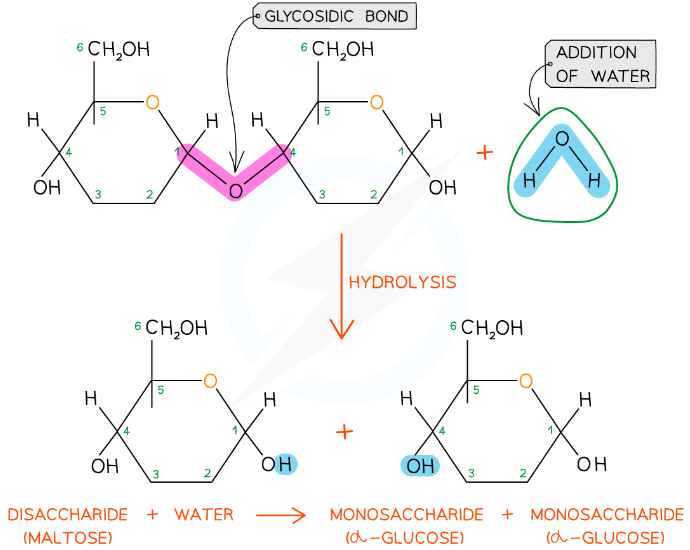
19
New cards
what are pentose and hexose sugars?
pentose sugars have 5 carbons - e.g. ribose, deoxyribose
hexose sugars have 6 carbons - e.g. glucose
hexose sugars have 6 carbons - e.g. glucose
20
New cards
what is glucose?
monosaccharide
hexose sugar
major energy source
highly soluble - main way carbohydrates are transported in animals
has 2 structural isomers - alpha glucose and beta glucose
hexose sugar
major energy source
highly soluble - main way carbohydrates are transported in animals
has 2 structural isomers - alpha glucose and beta glucose
21
New cards
what is alpha glucose?
an isomer of glucose
\-OH group is below the carbon ring
forms polysaccharides e.g. amylose and amylopectin (starch), glycogen
\-OH group is below the carbon ring
forms polysaccharides e.g. amylose and amylopectin (starch), glycogen
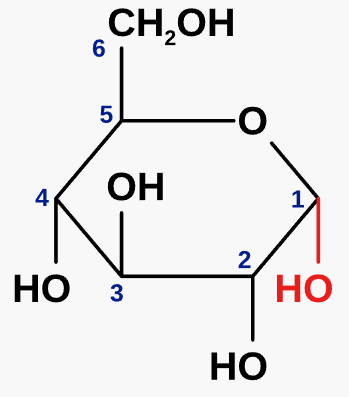
22
New cards
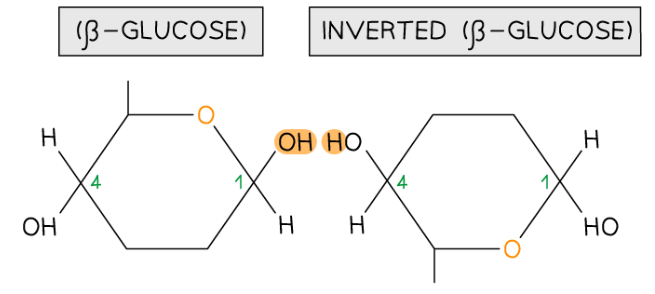
what is beta glucose?
an isomer of glucose
\-OH group is above the carbon ring
forms polysaccharides e.g. cellulose
\-OH group is above the carbon ring
forms polysaccharides e.g. cellulose
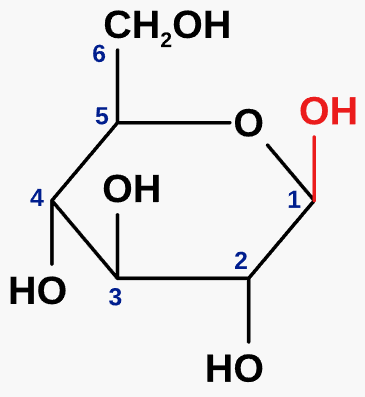
23
New cards
what is starch?
main carbohydrate storage in plants
made of amylose and amylopectin
produced from glucose made in photosynthesis
broken down during respiration to provide energy
made of amylose and amylopectin
produced from glucose made in photosynthesis
broken down during respiration to provide energy
24
New cards
what are amylose and amylopectin?
amylose - has 1-4 glycosidic bonds, helical, insoluble
amylopectin - has 1-4 and 1-6 glycosidic bonds, highly branched, insoluble
both made from alpha glucose
amylopectin - has 1-4 and 1-6 glycosidic bonds, highly branched, insoluble
both made from alpha glucose
25
New cards
what is glycogen?
storage molecule in animals
has alpha 1-6 glycosidic bonds
branched structure
found as small granules in the muscles and liver
less dense and more soluble than starch - broken down more quickly
has alpha 1-6 glycosidic bonds
branched structure
found as small granules in the muscles and liver
less dense and more soluble than starch - broken down more quickly
26
New cards
what is cellulose?
main component of plant cell walls - chains form microfibrils which are layered to form a network
has beta 1-4 glycosidic bonds
unbranched chains
most abundant organic polymer
has beta 1-4 glycosidic bonds
unbranched chains
most abundant organic polymer
27
New cards
what is the iodine test?
test for starch
dissolve the substance in water then add the iodine solution
a positive result is a colour change from red/brown to blue/black
dissolve the substance in water then add the iodine solution
a positive result is a colour change from red/brown to blue/black
28
New cards
what is a reducing sugar?
a sugar that can reduce (give electrons) to other molecules
29
New cards
what is the test for reducing sugars?
dissolve the substance in water then add benedict’s reagent
heat the solution in a water bath for 2 minutes
a positive result is a colour change from blue to green-brick red depending on the concentration of reducing sugars present
heat the solution in a water bath for 2 minutes
a positive result is a colour change from blue to green-brick red depending on the concentration of reducing sugars present
30
New cards
what is the test for non-reducing sugars?
perform the test for reducing sugars first
add hydrochloric acid and heat in a water bath for 2 minutes
neutralise the solution with sodium hydrogencarbonate
add benedict’s reagent and heat the solution in a water bath for 2 minutes
same positive results as reducing sugars test
add hydrochloric acid and heat in a water bath for 2 minutes
neutralise the solution with sodium hydrogencarbonate
add benedict’s reagent and heat the solution in a water bath for 2 minutes
same positive results as reducing sugars test
31
New cards
what are the three types of lipids?
triglycerides (fats and oils)
phospholipids
cholesterol
phospholipids
cholesterol
32
New cards
what is adipose tissue?
fatty connective tissue that surrounds the organs
good thermal insulator
protects the organs from injury
good thermal insulator
protects the organs from injury
33
New cards
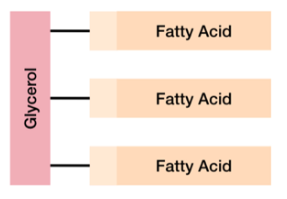
what is a triglyceride?
one glycerol and three fatty acid chains
non-polar molecule
hydrophobic
contain a lot of energy
non-polar molecule
hydrophobic
contain a lot of energy
34
New cards
what are the functions of triglycerides?
major source of energy - provide 2x as much energy as carbohydrates
source of water for metabolic reactions
used to store energy
source of water for metabolic reactions
used to store energy
35
New cards
how are triglycerides formed?
esterification - condensation reaction
ester bonds formed between glycerol and fatty acids
phospholipids are formed the same way
ester bonds formed between glycerol and fatty acids
phospholipids are formed the same way
36
New cards
how are triglycerides broken down?
broken down by lipase
hydrolysis reaction
hydrolysis reaction
37
New cards
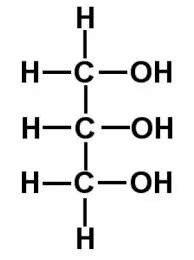
what is glycerol?
C₃H₈O₃
has three hydroxyl groups
has three hydroxyl groups
38
New cards
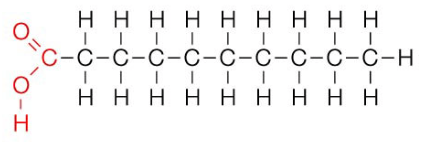
what is a saturated fatty acid?
contains only single covalent bonds between carbon atoms
solid at room temperature
fat
solid at room temperature
fat
39
New cards
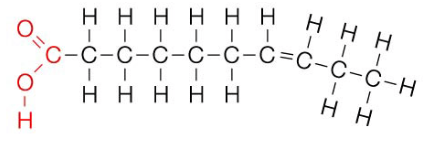
what is an unsaturated fatty acid?
monosaturated fatty acid - contains only one double covalent bond between carbon atoms
polysaturated fatty acid - contains many double covalent bonds between carbon atoms
liquid at room temperature
oil
polysaturated fatty acid - contains many double covalent bonds between carbon atoms
liquid at room temperature
oil
40
New cards
what is the difference between fats and oils?
fats are solid at room temperature and oils are liquid - due to the double bond in the hydrocarbon tail of unsaturated fatty acids in oil, they move further away from each other than saturated fatty acids do, and this weakens intermolecular forces
41
New cards
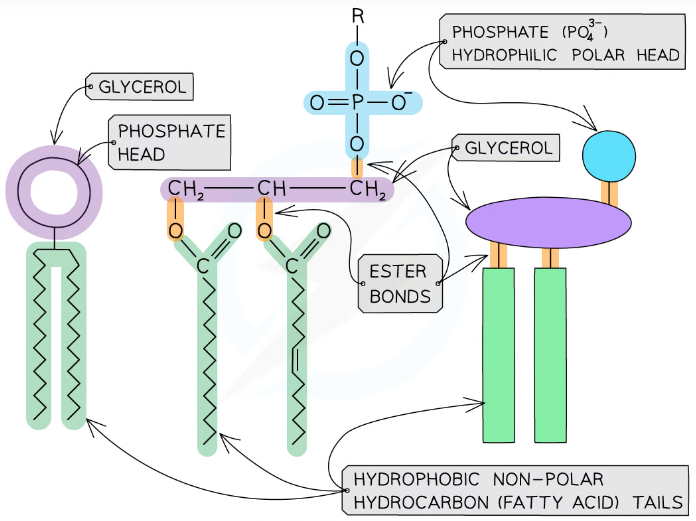
what is a phospholipid?
contains a phosphate group, glycerol and two fatty acid tails
has a negative polar hydrophilic head (phosphate group and glycerol) and non-polar hydrophobic tails (two fatty acids)
phosphate ester bond forms when phosphoric acid joins to glycerol - condensation reaction
in water they position themselves with the hydrophilic head outwards and the hydrophobic tails cluster together away from the water - forms droplets
has a negative polar hydrophilic head (phosphate group and glycerol) and non-polar hydrophobic tails (two fatty acids)
phosphate ester bond forms when phosphoric acid joins to glycerol - condensation reaction
in water they position themselves with the hydrophilic head outwards and the hydrophobic tails cluster together away from the water - forms droplets
42
New cards
what are the functions of phospholipids?
form phospholipid bilayers in cell membranes
43
New cards
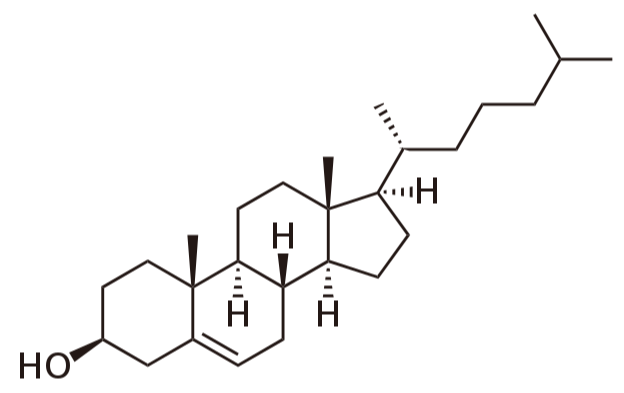
what is cholesterol?
part of the lipid family called sterols
the hydroxyl group is hydrophilic and the rest is hydrophobic
can insert into cell membranes - hydrophilic hydroxyl group interacts with the polar head of phospholipids and the rest interacts with the hydrophobic tails
the hydroxyl group is hydrophilic and the rest is hydrophobic
can insert into cell membranes - hydrophilic hydroxyl group interacts with the polar head of phospholipids and the rest interacts with the hydrophobic tails
44
New cards
what are the functions of cholesterol?
controls the fluidity of cell membranes
starting point of many hormones - e.g. oestrogen, progesterone
used to make vitamin D
used in the liver to make bile - emulsifies lipids, increases the digestion of lipids
starting point of many hormones - e.g. oestrogen, progesterone
used to make vitamin D
used in the liver to make bile - emulsifies lipids, increases the digestion of lipids
45
New cards
what is the emulsion test?
test for lipids
dissolve the substance in water and add ethanol
a positive result is a white emulsion/precipitate
can be difficult to see if the initial substance is cloudy
dissolve the substance in water and add ethanol
a positive result is a white emulsion/precipitate
can be difficult to see if the initial substance is cloudy
46
New cards
what is an amino acid?
monomer of protein
47
New cards
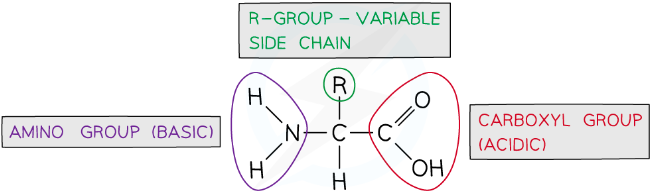
what is the structure of amino acids?
all have the same general structure - central carbon atom bonded to a carboxyl group (-COOH) and an amino group (-NH₄), a hydrogen atom and an R group
an R group is a carbon chain which is different in each amino acid
they differ in size, polarity and charge
an R group is a carbon chain which is different in each amino acid
they differ in size, polarity and charge
48
New cards
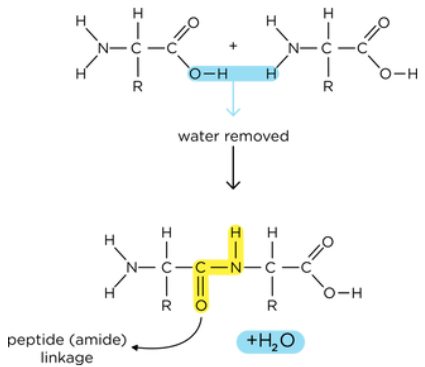
how are peptide bonds formed?
condensation reaction
takes place in the ribosomes
takes place in the ribosomes
49
New cards
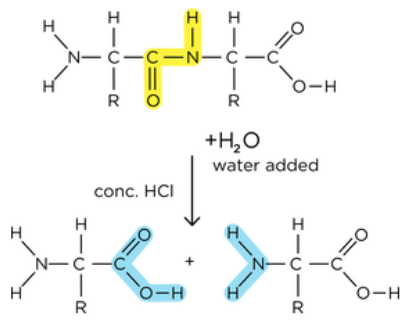
how are peptide bonds broken down?
hydrolysis reaction
catalysed by protease
catalysed by protease
50
New cards
what is a dipeptide?
two amino acids joined by a peptide bond - condensation reaction
51
New cards
what is the difference between polypeptides and proteins?
a protein is a polypeptide folded into a complex 3D shape - once a polypeptide is folded it can carry out its function
many proteins have multiple polypeptide chains
proteins often contain other molecules (prosthetic groups) which help them carry out their functions - e.g. haemoglobin
many proteins have multiple polypeptide chains
proteins often contain other molecules (prosthetic groups) which help them carry out their functions - e.g. haemoglobin
52
New cards
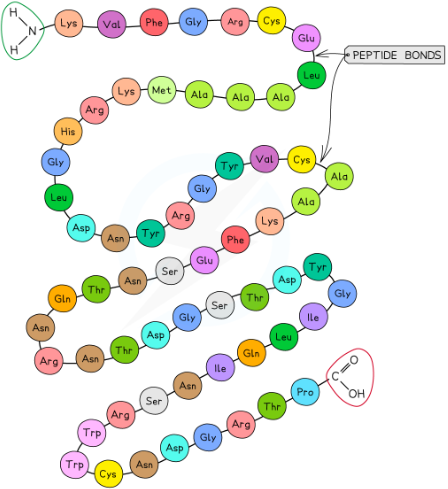
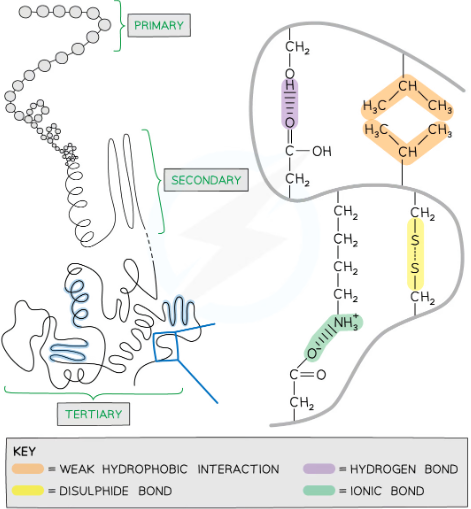
what is the primary structure of proteins?
the order of amino acids in a polypeptide
determined by the DNA sequence of the gene that encodes the polypeptide
determines the final 3D shape of the protein
determined by the DNA sequence of the gene that encodes the polypeptide
determines the final 3D shape of the protein
53
New cards
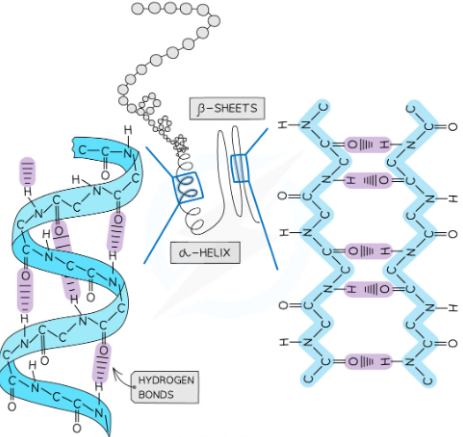
what is the secondary structure of proteins?
the shape that the chain of amino acids takes - alpha helix and beta pleated sheets
shape is determined by weak hydrogen bonds
shape is determined by weak hydrogen bonds
54
New cards
what is the tertiary structure of proteins?
the overall 3D shape of the polypeptide
held together by: hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, disulphide bonds, and hydrophilic and hydrophobic interactions
held together by: hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, disulphide bonds, and hydrophilic and hydrophobic interactions
55
New cards
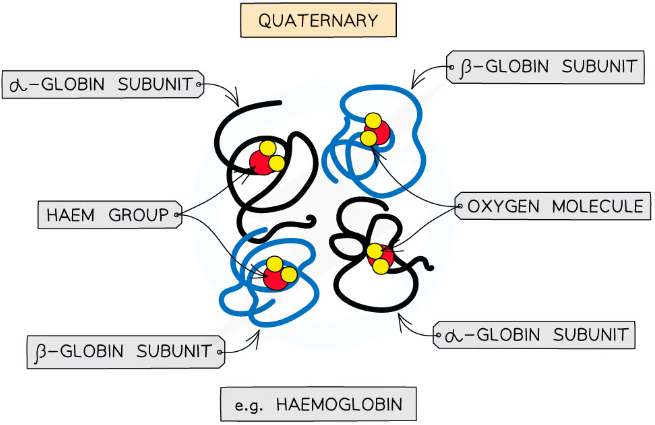
what is the quaternary structure of proteins?
only applies to proteins with at least 2 polypeptide chains (subunits)
may also contain a prosthetic (non-protein) group - proteins with these are called conjugated proteins
may also contain a prosthetic (non-protein) group - proteins with these are called conjugated proteins
56
New cards
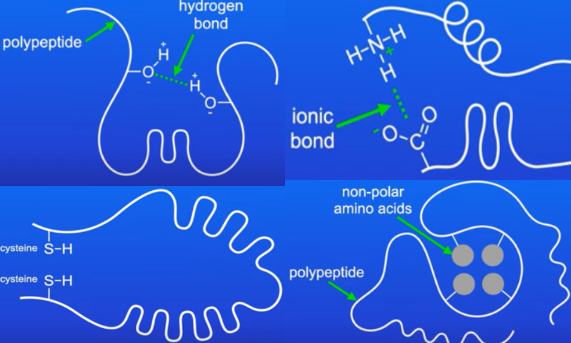
what are the bonds in the tertiary and quaternary structures of proteins?
form between the R groups of amino acids in polypeptide chains
type of bonding depends on the amino acids present and contributes to the final 3D shape
1) hydrogen bonding - between the slightly negative oxygen atom of a hydroxyl group of one amino acid and the slightly positive hydrogen atom of another, weak bonds, can be broken by high temperatures or pH changes
2) ionic bonding - between amino acids with oppositely charged R groups, can be broken by changes in pH
3) disulphide bonds - between the R groups of cysteines, strong, not broken by temperature or pH changes
4) hydrophilic and hydrophobic interactions - weak bonds
type of bonding depends on the amino acids present and contributes to the final 3D shape
1) hydrogen bonding - between the slightly negative oxygen atom of a hydroxyl group of one amino acid and the slightly positive hydrogen atom of another, weak bonds, can be broken by high temperatures or pH changes
2) ionic bonding - between amino acids with oppositely charged R groups, can be broken by changes in pH
3) disulphide bonds - between the R groups of cysteines, strong, not broken by temperature or pH changes
4) hydrophilic and hydrophobic interactions - weak bonds
57
New cards
what are the 2 types of proteins?
globular protein
fibrous protein
fibrous protein
58
New cards
what are globular proteins?
soluble in water - hydrophilic R groups on their surface
spherical
have more functional roles - e.g. metabolic
e.g. haemoglobin, insulin, lysozyme
spherical
have more functional roles - e.g. metabolic
e.g. haemoglobin, insulin, lysozyme
59
New cards
what is haemoglobin?
has 4 polypeptide subunits - 2 alpha, 2 beta
found in red blood cells
conjugated protein with the prosthetic group haem - contains Fe2+ ions which bind to the oxygen
each molecule can bind to 4 oxygens - when they bind, the molecule conforms to make it easier for others to bind
found in red blood cells
conjugated protein with the prosthetic group haem - contains Fe2+ ions which bind to the oxygen
each molecule can bind to 4 oxygens - when they bind, the molecule conforms to make it easier for others to bind
60
New cards
what is insulin?
has 2 polypeptide subunits - linked by disulphide bonds
hormone transported in the blood
plays a role in blood glucose regulation
binds to specific receptors on the cell membranes of target cells - shape fits perfectly into the receptor
hormone transported in the blood
plays a role in blood glucose regulation
binds to specific receptors on the cell membranes of target cells - shape fits perfectly into the receptor
61
New cards
what is lysozyme?
has a single polypeptide chain
enzyme found in tears and saliva
catalyses the breakdown of a molecule in bacterial cell walls
enzyme found in tears and saliva
catalyses the breakdown of a molecule in bacterial cell walls
62
New cards
what are fibrous proteins?
insoluble in water - hydrophobic R groups on its surface
long strands
have more structural roles
e.g. collagen, keratin, elastin
long strands
have more structural roles
e.g. collagen, keratin, elastin
63
New cards
what is collagen?
has 3 polypeptide chains that form a triple helix - many hydrogen bonds join them together
found in tendons (connect muscle to bone) and ligaments (connect bones to each other)
insoluble in water - every third amino acid is glycine (smallest R group), so chains can wrap very tightly
many of the triple helical molecules join to make fibrils and microfibrils - molecules are staggered to avoid weak spots
found in tendons (connect muscle to bone) and ligaments (connect bones to each other)
insoluble in water - every third amino acid is glycine (smallest R group), so chains can wrap very tightly
many of the triple helical molecules join to make fibrils and microfibrils - molecules are staggered to avoid weak spots
64
New cards
what is keratin?
found in hair, fingernails, the outer layer of the skin, etc.
insoluble
strong - due to many disulphide bonds
insoluble
strong - due to many disulphide bonds
65
New cards
what is elastin?
has 2 polypeptide chains - contain hydrophobic regions, cross linked
found in arteries, skin, lungs, bladder, blood vessels
allows structures to stretch
when they are stretched, the hydrophobic regions on different strands (usually associated) move apart but remain attached at the crosslinks - after stretching, the molecules reassociate and spring back together
found in arteries, skin, lungs, bladder, blood vessels
allows structures to stretch
when they are stretched, the hydrophobic regions on different strands (usually associated) move apart but remain attached at the crosslinks - after stretching, the molecules reassociate and spring back together
66
New cards
what is the biurets test?
test for proteins
dissolve substance in water then add biuret’s solution (or sodium hydroxide and copper sulphate)
colour change is due to a complex forming between nitrogen atoms in peptide chains and Cu2+ ions
a positive result is a colour change from blue to purple
dissolve substance in water then add biuret’s solution (or sodium hydroxide and copper sulphate)
colour change is due to a complex forming between nitrogen atoms in peptide chains and Cu2+ ions
a positive result is a colour change from blue to purple