control of breathing
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
Ventilation (Alveolar)
Maintains blood gases and pH as well as brining gas and blood into contact
Alveolar ventilation = tidal volume - anatomic dead space x respiratory rate
Can also be alveolar ventilation of CO2 ie the amount of CO2 produced / partial pressure of CO2 in arterial blood

Control of respiration
under automatic control
Unconscious
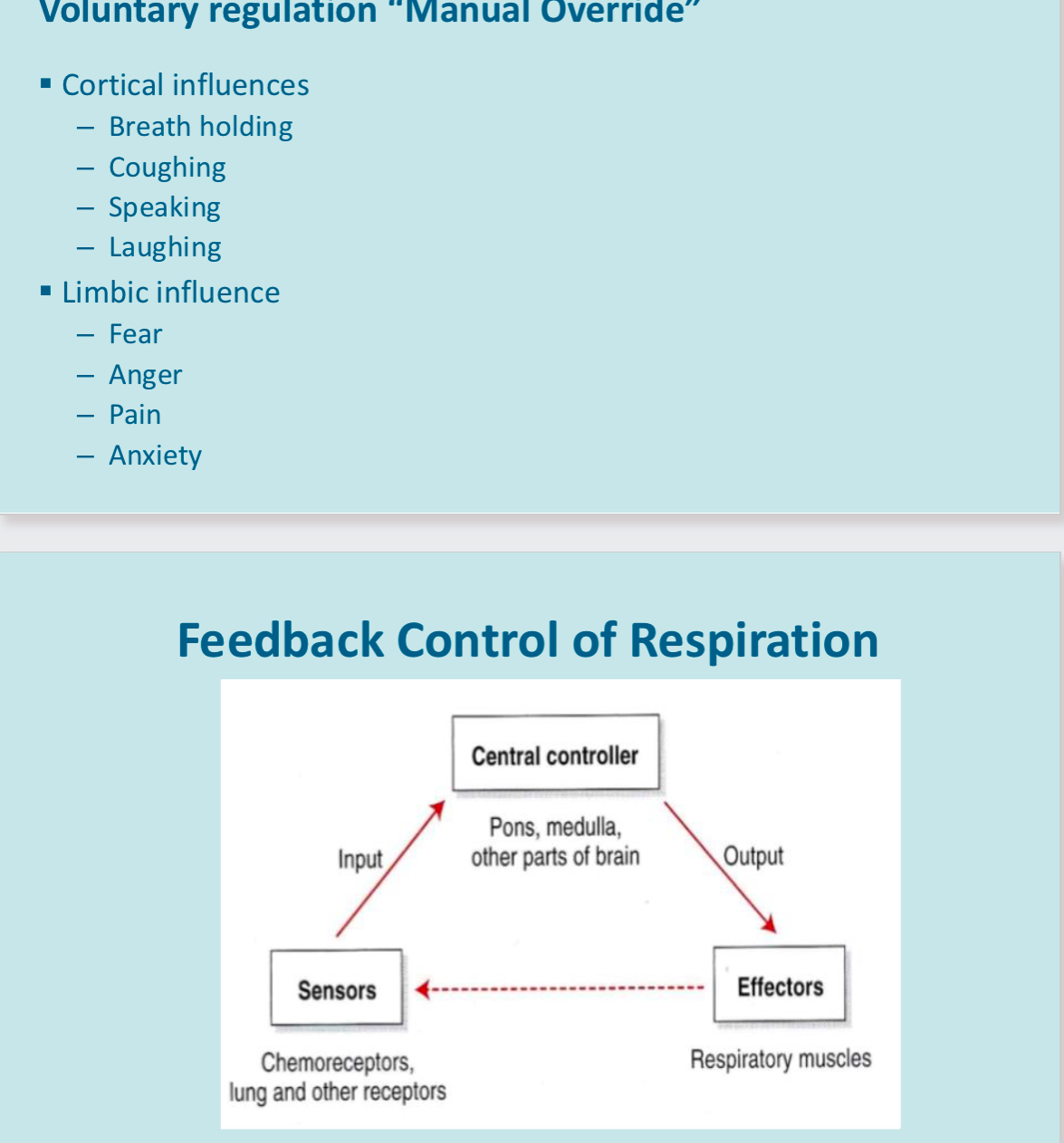
Negative feedback system to maintain blood gasses and acid base balance within normally ranges for optimal cellular function
Can be overridden manually
On Diane’s curse - congenital central hypo ventilation syndrome
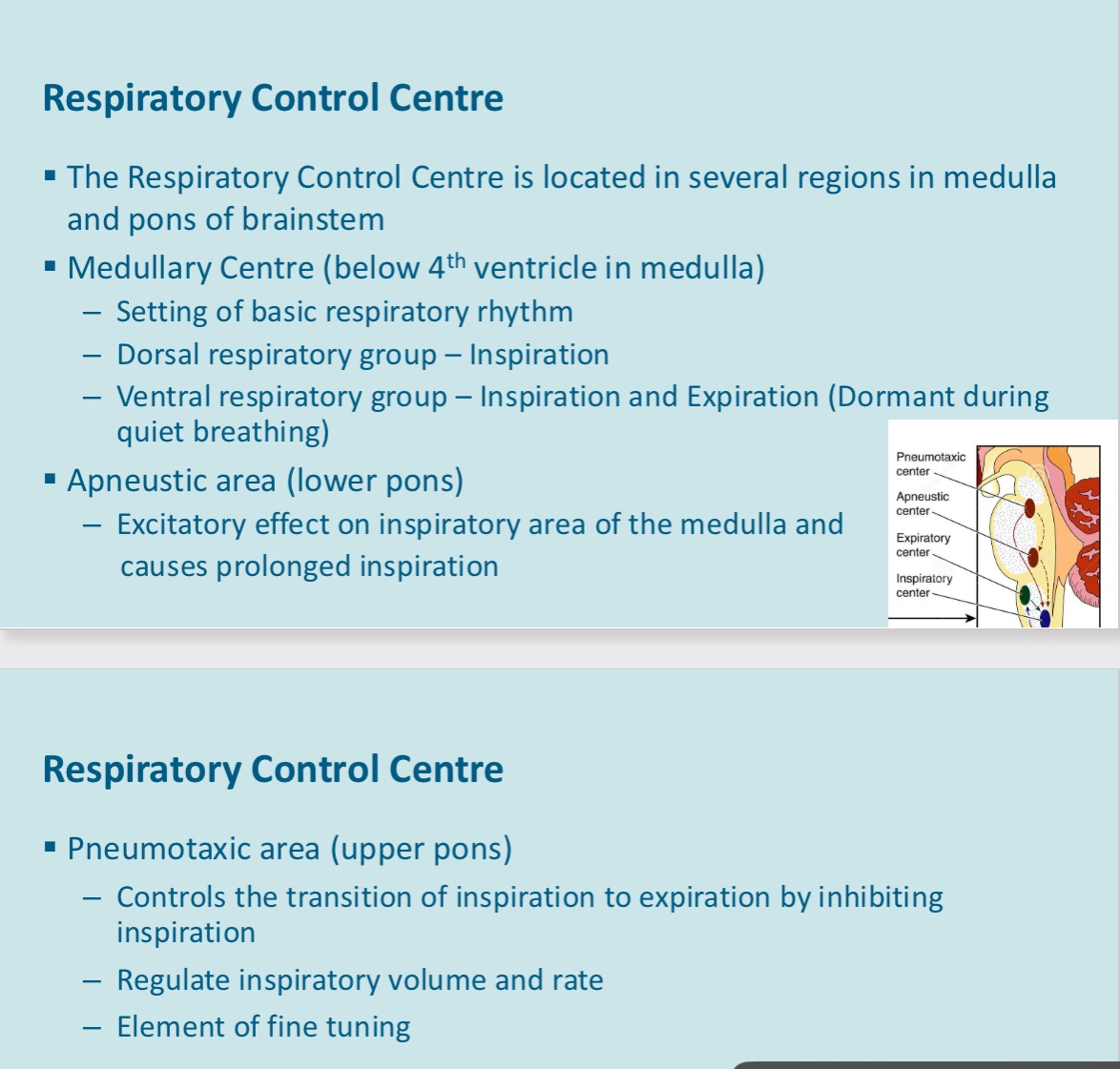
Respiratory centre
central controller
Located in several regions in the medulla and pons of brain stem
Generates respiratory rhythm
Control rate, depth and pattern of respiration
Dorsal respiratory group - this plays a fundamental role in the control of respiration, generating the basic rhythm of respiration. This is located in the dorsal medulla, which is close to the sensory termination of both vagaries and glossopharyngeal nerves which transmit sensory signals into the respiratory centre

Extra information
Receptors in muscles and joints
Central chemoreceptors - located on ventral surface of medulla in brainstem, carbon dioxide can diffuse across the blood brain barrier, this is an increase in co2 in csf will increase the hydrogen ion concentration and stimulate the central chemoreceptor, it is good to know that these are not sensitive to change


Peripheral chemoreceptors
Locations - carotid bodies at bifurcation of common carotid arteries, aortic bodies above ad below aortic arch and th carotid bodies are most important
Lung receptor and reflexes - stretch receptors and J receptors with irritant receptor and more

Summary
ventilation controlled automatically b negative feedback to maintain arterial blood gases and acid base balance
Central chemoreceptors respond to carbon dioxide levels only, whereas peripheral chemoreceptor respond to oxygen levels also
Carbon dioxide levels provide the main stimulus to ventilation, but low oxygen levels also contribute to an integrated response