WK4-Adrenergic Synapse
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
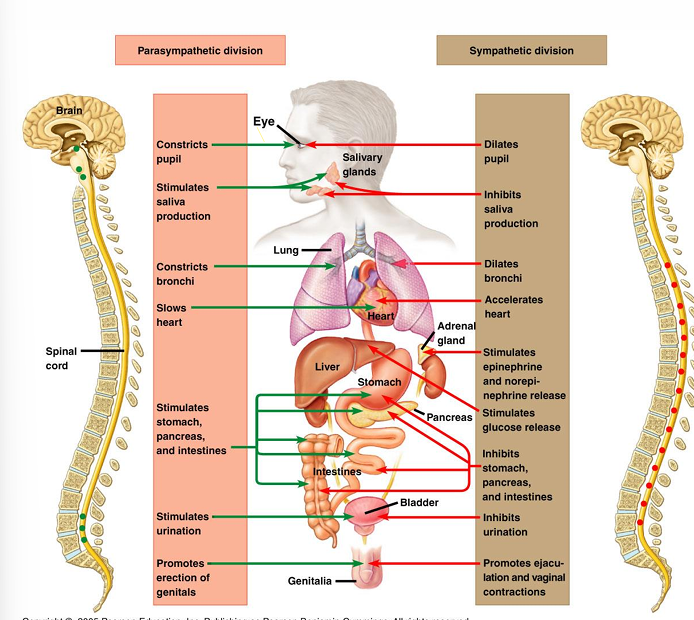
what are the 2 branches of the autonomic system
rest & digest system (PSNS)
Fight or flight system (SNS)
what is the synapse
where 2 neurons communicate in one direction
it is the cleft between the preganglionic & post ganglionic
what is the main neurotransmitter for sympathetic nervous system
Noradrenaline , which is also known as norepinephrine
it is fight or flight which increase heart rate
how is noradrenaline regulated
synthesis of norepinephrine takes place
dopamine enters the vesicle which is converted to norepinephrine
neurotransmitter is released so a influx of calcium causes fusion of the vesicle with the cell known as exocytosis - release is then blocked by guanethidine
the postsynaptic receptor is then activated by the binding of the neurotransmitter
norepinephrine is then released & rapidly taken into the neuron
NA is finally metabolised & broken down by COMT & oxidised by MA O
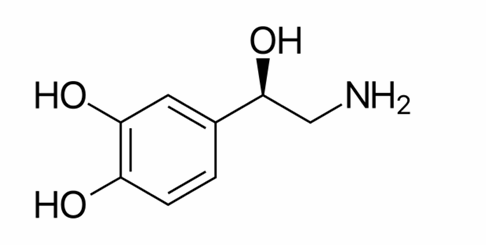
how is noradrenaline synthesised
phenylalanine hydroxylase converts phenylalanine to tyrosine by adding on a -OH group
Tyrosine Hydroxylase then convert tyrosine to L-dopa by adding another -OH group
DOPA Decarboxylase then covert L-DOPA to dopamine by removing -COOH (activating the dopamine)
Dopamine B-hydroxylase is then used to convert dopamine to Noradrenaline by adding -OH to the side chain
what happens when a vesicle contain VMAT (vesicular monoamine transporter)
it is powered by a proton gradient , so when monoamine OR NA is pumped in, a proton is pumped out
what triggers the release of NA
action potential , as it travels across the presynaptic neurons to depolarise & repolarise
what is noradrenaline metabolism
it allows termination of a signal
NA is metabolised by the 2 intracellular enzymes MONOAMINE OXIDE (MAO) & Catechol-o-methyl transferase (COMT)
what is GDP & GTP bound
GDP is inactive whereas GTP is active
what are the 5 subtypes for adrenergic receptors
Alpha 1
alpha 2
beta 1
beta 2
beta 3
they used G proteins & activate second messengers
describe the location, type of GPCR & basic pathway of Alpha 1
it is located in the sooth muscle
it is a Gq gpcr which activates
it increase in PLC, IP3, intracellular calcium
describe the location, type of GPCR & basic pathway of Alpha 2
it is found in the presynaptic nerves
it is a Gi(inhibition) GPCR
it decreases the activation of Adenylate cyclase
decrease in cAMP
describe the location, type of GPCR & basic pathway Beta 1,2,3
it is found in the heart, smooth muscle & fatty tissue
it is a Gs(stimulation) GPCR
it increases activation of Adenylate cyclase
increase cAMP
increases intracellular signalling pathway
describe alpha 1 adrenergic receptor signalling
it is found in smooth muscle cell which causes contraction
it uses the Gq protein, so NA brings the leads of activating PLC
it then catalyses PIP2 to break down to DAG and IP3. This cause IP3 to open up calcium channels on the endoplasmic reticulum which increases the cytoplasmic calcium conc.
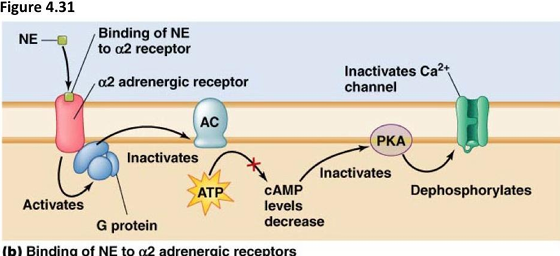
describe alpha 2 adrenergic receptor signalling
Alpha 2 receptors inhibit the release of from the presynaptic nerve
binding of NA causes the release of the inhibitory Gi protein
this become active & inactivates the adenylate cyclase by inhibiting it
this causes a decrease in cAMP & inactivate PKA & voltage gated calcium channels
describe beta 1 adrenergic receptor signalling
it is found in cardiac muscle which stimulates contraction
NA binding activates adenylate cyclase
this increases cAMP levels & activates PKA
it then opens plasma membranes & SR calcium channel which increase cytoplasmic calcium concentration
describe beta 2 adrenergic receptor signalling
it is found in the lung of smooth muscle cells which stimulates bronchodilation
NA then binds & stimulates adenylates cyclase
this increase cAMP levels which PKA
and inactivates myosin light chain kinase (MLCK)
describe beta 3 adrenergic receptor signalling
it is located mainly in the adipose tissue (fatty ) which regulates lipolysis
NA binds & stimulates the adenylate cyclase which increase cAMP level
this activates PKA which stimulates the breakdown of lipids