ATP
1/18
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Which macromolecule is our main source of energy?
Carbohydrates
Where do we get carbohydrates?
Plants (either indirectly or directly)
Unlike proteins and lipids (which are also energy sources), carbohydrates give us more ________ and _______ energy.
Immediate, Efficient
Once carbohydrates are used up, then our cells look towards ________ and _________ to convert energy for work.
Proteins, Lipids
Cells store ATP so that it can be released/used SLOWLY rather than in large amounts at one time. True or False?
True
Which is the energy cells use: Glucose or ATP?
ATP
ATP is built from the stored chemical bond energy in ________.
Glucose
ATP is short for
adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine is a type of ________
nucleoside
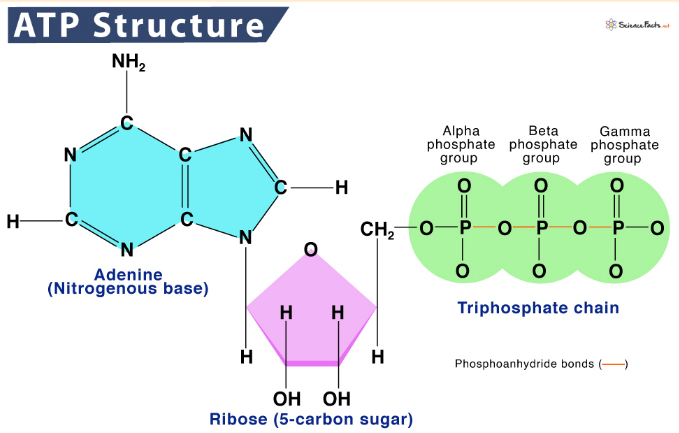
_______ is a sugar that is attached.
Ribose (a pentose sugar)
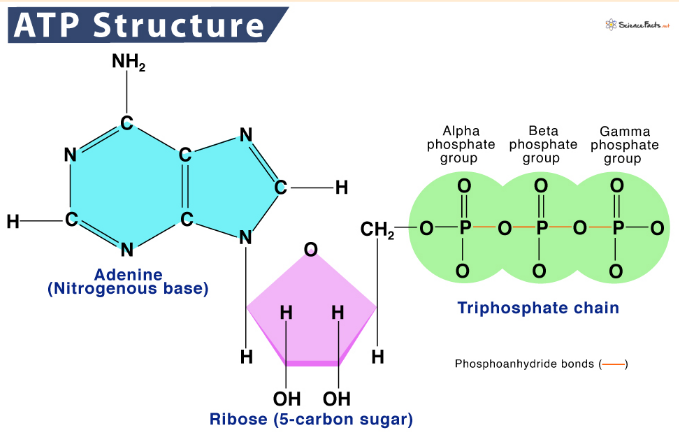
Triphosphate means there are __ ____________.
3 phosphates
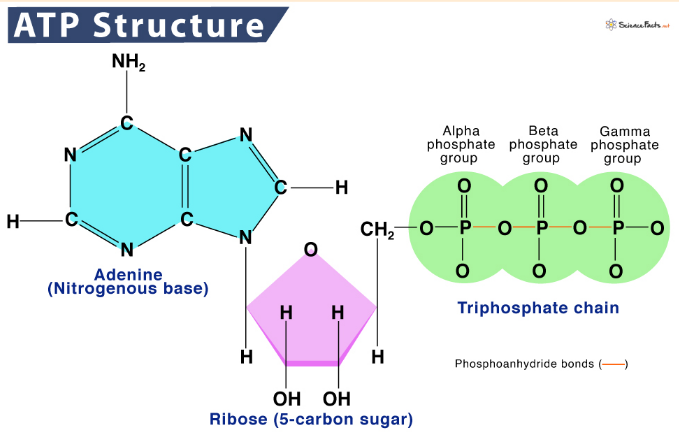
What holds the 3 phosphates in the triphosphate chain together?
Phosphoanhydride bonds
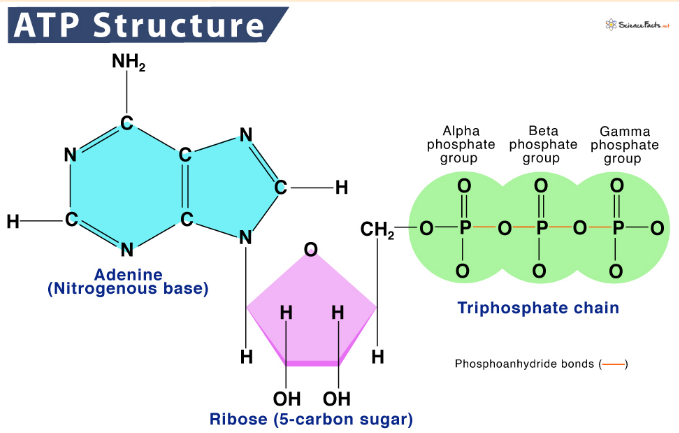
Energy is released when a ______________ (P) breaks off through ___________. This new molecule is called ____ aka ____________________.
Phosphate group, hydrolysis, ADP, adenosine diphosphate.
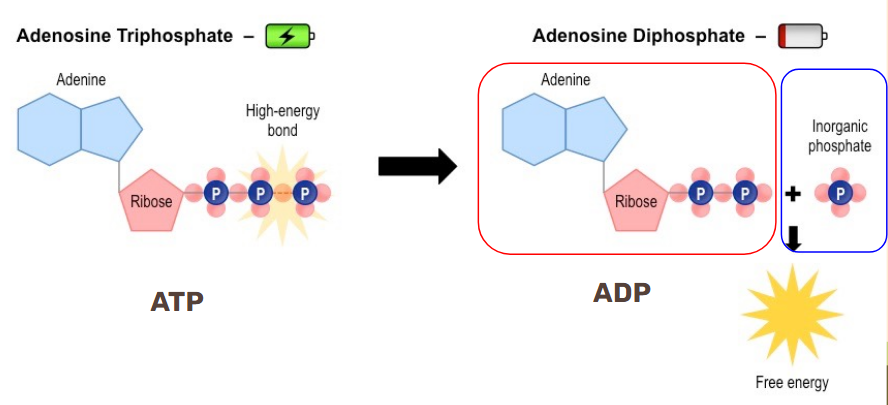
Cells use energy from/break down ________ to put _________ and ADP to make _____ again which is called ___________.
Glucose, phosphate, ATP, phosphorylation
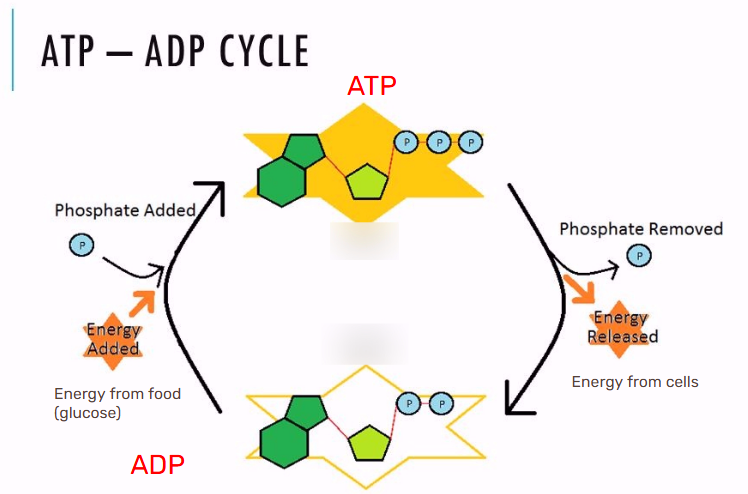
Cells will ________ have ______ of ATP, single P’s, and ADP in the cell.
Always, lots
Why don’t cells use glucose for energy?
Glucose is too big to store but ATP is small and easier to store.
Describe the computer and charger analogy with the ATP-ADP reaction.

Where does the ATP-ADP reaction occur?
The chloroplast and mitochondria
Cells use the energy in ATP to maintain __________.
Homeostasis