3.5.1 demand for labour
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:58 PM on 4/24/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
1
New cards
who demands labour?
firms and employers
2
New cards
what is the relationship (curve) between demand for labour + wage rate?
inverse relationship between demand for labour + the wage rate → lower wages makes it easier for employers to hire workers as labour becomes relatively cheaper than capital
a decrease in wage rate might create a substitution effect + lead to an expansion in labour demand
a decrease in wage rate might create a substitution effect + lead to an expansion in labour demand
3
New cards
what is marginal revenue?
marginal revenue is the addition to revenue of selling an additional unit of output:
=change in TR/change in Q
=change in TR/change in Q
4
New cards
what is marginal revenue product (MRP)?
the change in total revenue for the employment of an extra unit of labour (looks at production in terms of monetary units)
5
New cards
formula for MRP
MRP=MPP x MR
6
New cards
what is marginal \[physical\] product (MPP)?
the different between total output when an extra unit of the variable (labour) factor is added
=change in total output/change in variable input
as the number of workers increase so does output, however, due to diminishing marginal returns the MPP decreases
=change in total output/change in variable input
as the number of workers increase so does output, however, due to diminishing marginal returns the MPP decreases
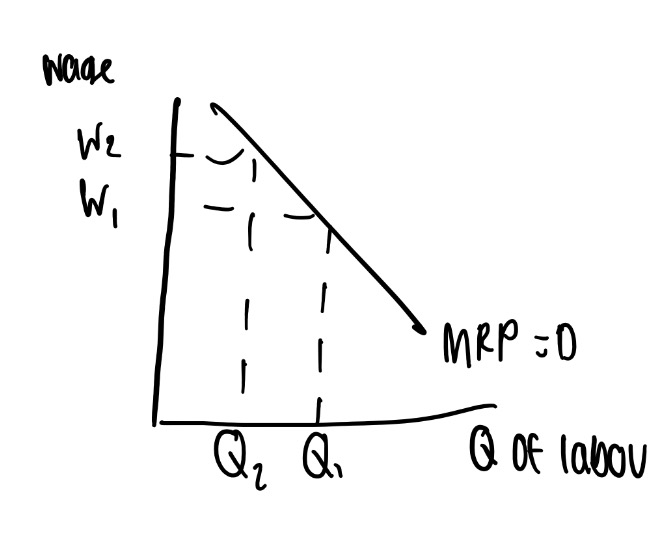
7
New cards
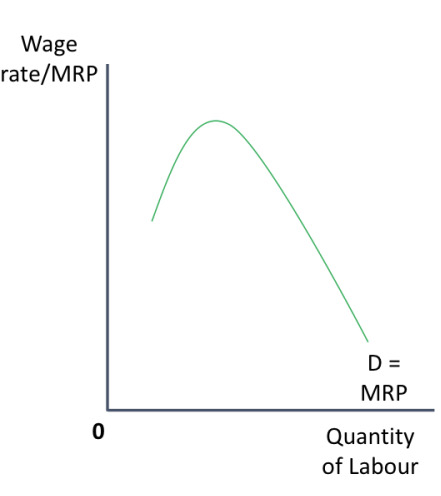
how can MRP be shown on a diagram?
due to the law of diminishing marginal returns total product will rise at first and then start to decline → the MRP shows how many workers are demanded by a firm at each wage rate → therefore it is the demand curve for labour
8
New cards
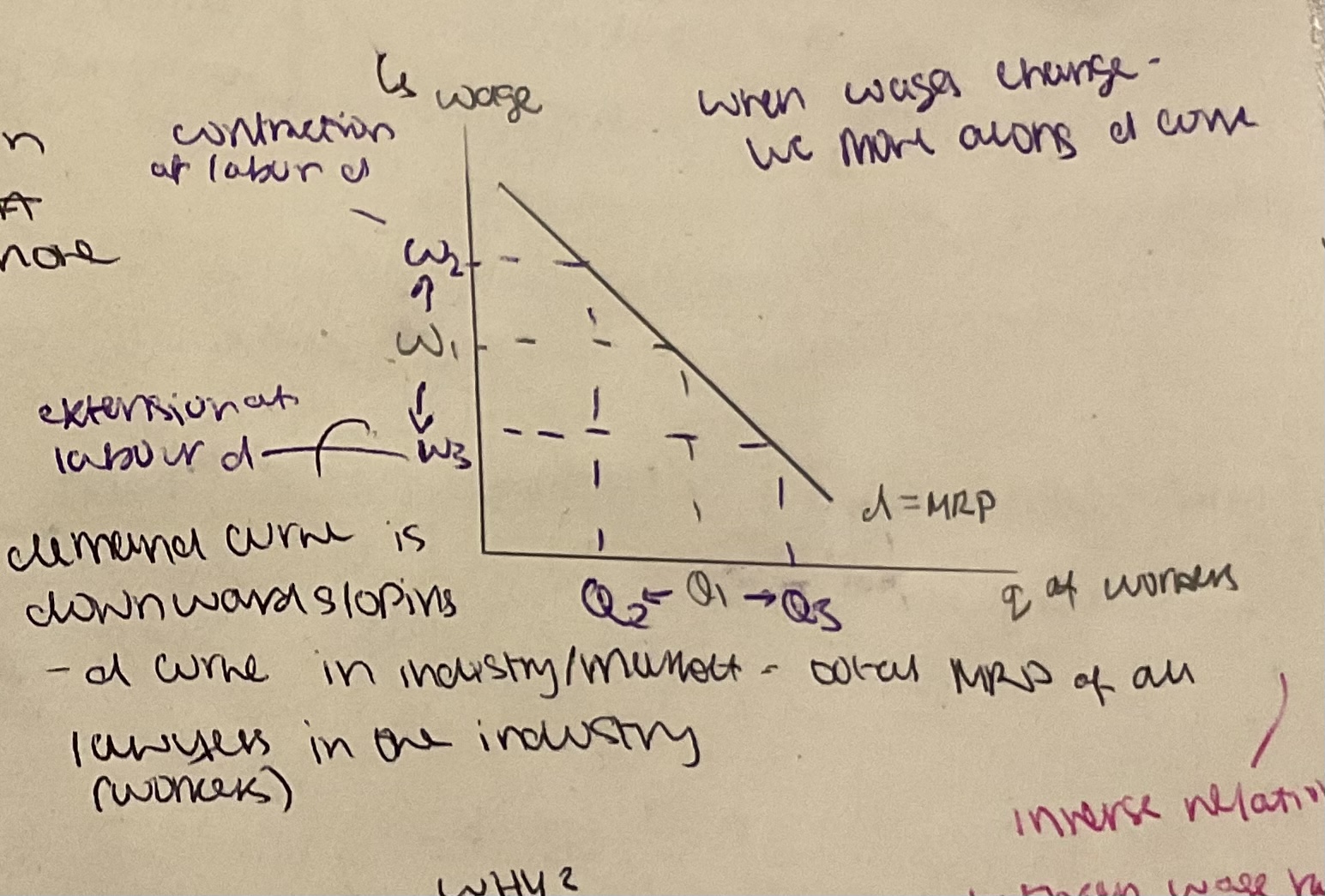
d curve for industry ( market)
inverse relationship between wage rate + q of workers
why?
**SR**- *law of diminishing returns*
**LR**- substitutability of L+C - ***all fop variable = capital can be employed to sub for labour***
- firms will think at __↑w__ %%labour x as cost effective as cheap capital = q of workers demanded ↓ at ↑w%%
\-↓w - workers become ↑ cost effective than capital - ↑q of workers likely to be employed
\
wage rate changes - movements along d curve
why?
**SR**- *law of diminishing returns*
**LR**- substitutability of L+C - ***all fop variable = capital can be employed to sub for labour***
- firms will think at __↑w__ %%labour x as cost effective as cheap capital = q of workers demanded ↓ at ↑w%%
\-↓w - workers become ↑ cost effective than capital - ↑q of workers likely to be employed
\
wage rate changes - movements along d curve
9
New cards
marginal productivity theory
a theory which argues that the **demand for labour depends** upon @@balancing the revenue@@ that a @@firm gains from employing an additional unit of labour@@ *against the* ***marginal cost*** *of that unit of labour*
10
New cards
Criticisms of MRP theory
1. **measuring** productivity - can be **difficult** in some industries
\
2. **collaborative work** = *difficult to establish the* ==*productivity of individual workers*== - assume that each individuals productivity can b measured - irl ppl work + produce output as a team = output of each is difficult to measure
\
3. **self employed** - ==ability to set own pay== + x necessarily pay according to their MRP - __*distorts theory that workers are paid to their MRP*__
\
4. **imperfect labour markets (trade unions)** - what if labour x competitive - all of sudden ==↑wages tu's bargaining== for may __*x have to do w MRP at all*__ - maybe just want to ↑ pay even if ↑than MRP - against theory that workers are paid to their MRP
11
New cards
what causes a movement along the labour demand curve
changes in wage rate
12
New cards
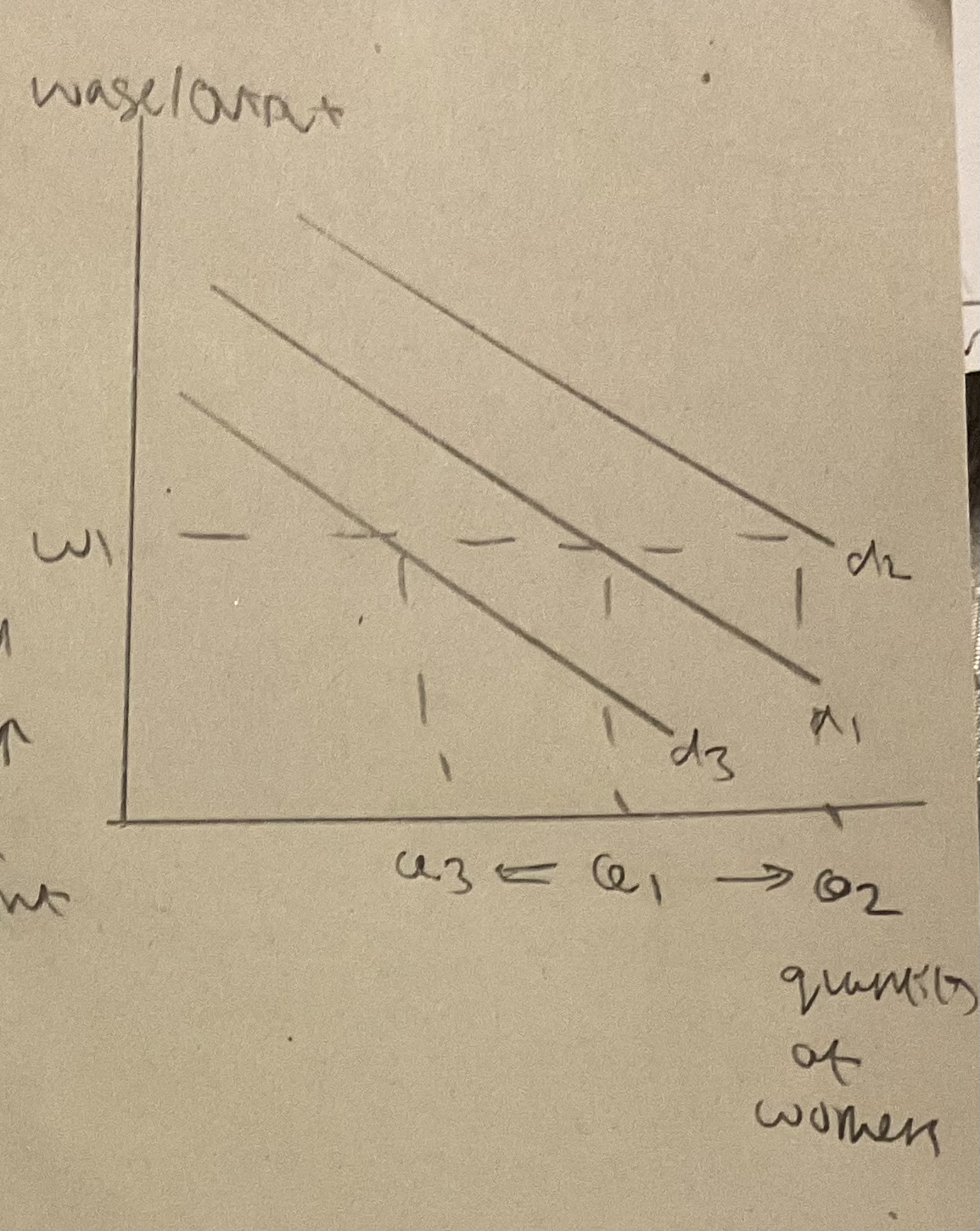
shifts in labour demand curve PDPCS
anything other than wage that affects labour = shift
\
1. **change in final** **price** of the **product labour is making**
\
2. **change in** **demand** **for the final product**
\
3. **changes in labour** **productivity**
\
4. **changes in the price of** **capital**
\
5. **govt employment** **subsidy**
\
1. **change in final** **price** of the **product labour is making**
\
2. **change in** **demand** **for the final product**
\
3. **changes in labour** **productivity**
\
4. **changes in the price of** **capital**
\
5. **govt employment** **subsidy**
13
New cards
govt subsidy S (shift labour demand curve)
**govt employment** **subsidy**- allows firm to employ ↑
14
New cards
changes in the price of capital C (shift labour demand curve)
**changes in the price of** **capital** - LR- firm decides wether to hire workers or capital - price of capital ↓ labour d↓ - substitutes
15
New cards
changes in labour productivity P (shift labour demand curve)
**changes in labour** **productivity** - ↑productivity = labour is ↑ cost efficient than capital - affects marginal product - ↑=↑MRP + shift right
16
New cards
change in demand D (shift labour demand curve)
**change in** **demand** **for the final product** - d↑ - d for labour↑ as derived demand
17
New cards
change in final price P (shift labour demand curve)
**change in final** **price** of the **product labour is making** - price↑ = MRP↑+ d shift right
18
New cards
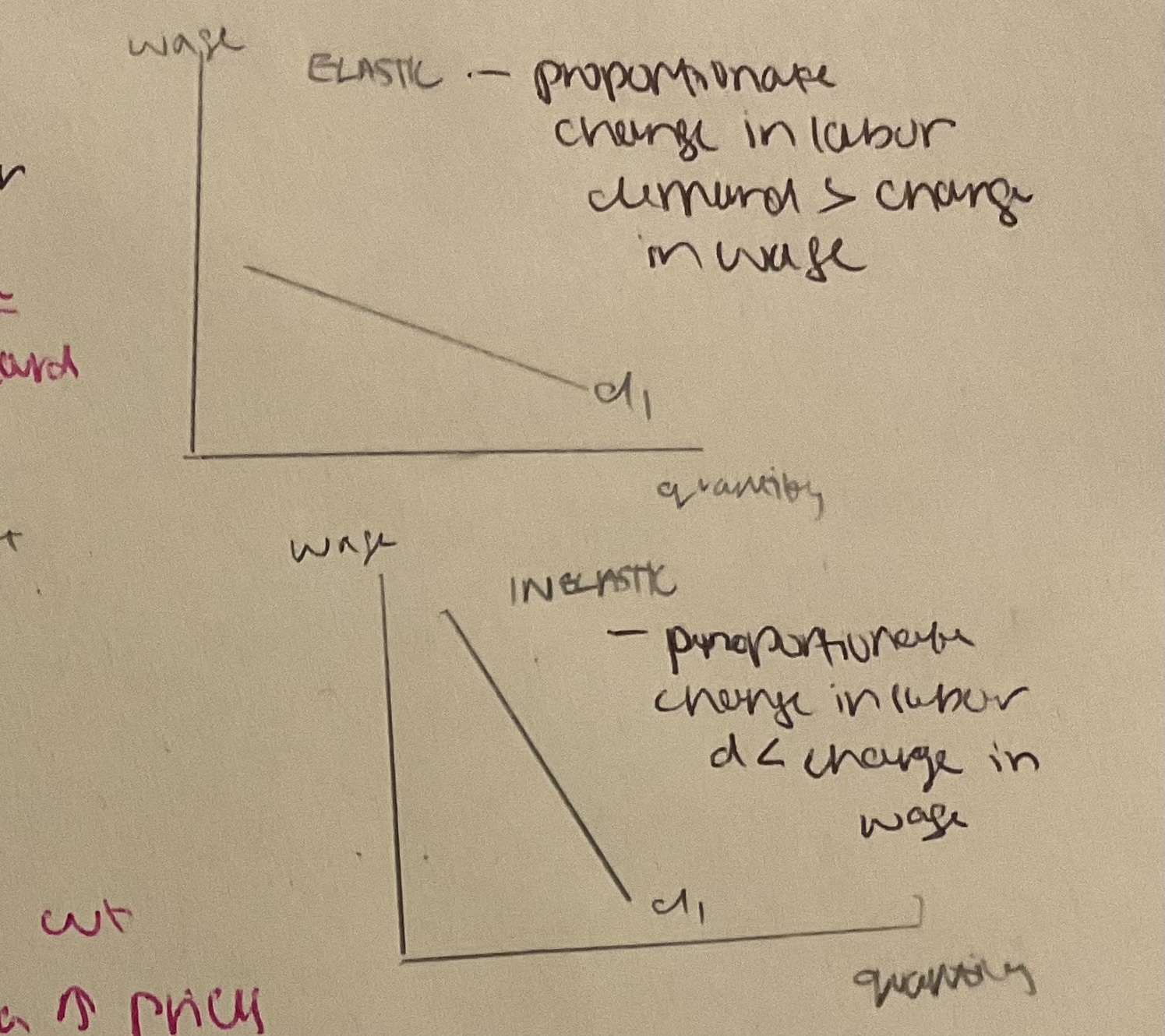
factors influencing wage elasticity of demand SECT
%%**Substitutability of capital for labour**%%
\
%%**Elasticity of demand for product**%%
\
%%**Cost of labour as a % of total costs**%%
\
%%**Time period**%%
\
%%**Elasticity of demand for product**%%
\
%%**Cost of labour as a % of total costs**%%
\
%%**Time period**%%
19
New cards
time period T (WED)
*LR*- all fop variable = ↑ easier to bring in capital for a time = *labour demand ↑ wage elastic* *SR*- v difficult to ↑ capital = *↑ inelastic*
20
New cards
cost of labour as a % of total costs C (WED)
↑labour costs are as % of tc = ↑ wage elastic labour demand wages ↑ firms tc shoot up massively = need to cut workforce - labour demand ↓ proprtinal more than ↑ in wages
*↑ insignificant l.c. are as % of tc = ↑ wage inelastic ld*
*↑ insignificant l.c. are as % of tc = ↑ wage inelastic ld*
21
New cards
elasticity of demand for product E (WED)
if inelastic + wages go↑ - firms x cut workers - will pass on ↑ wages via ↑ prices *↑ inelastic d for product = ↑ inelastic d for labour*
22
New cards
substitutability of capital for labour S (WED)
*↑substitutable capital is for labour = ↑ wage elastic labour demand* wages ↑= firms x need to hire as many workers - can sack workers + bring in substitute capital
23
New cards
what is wage elasticity of demand (WED)?
measures the responsive of labour demanded given a change in the wage rate
responsiveness of the quantity demanded of labour to the wage rate
responsiveness of the quantity demanded of labour to the wage rate
24
New cards
what is derived demand?
demand for labour is directly linked to demand for the product being made → demand for labour is therefore dependent on demand for the final goods and services they produce
25
New cards
what influences demand for labour
* wage rates
* demand for the product
* productivity of labour
* profitability of the firm - the higher the profits of the firm, the more labour they can afford to employ
* number of firms in the market
* prices of factors of production - if machinery and equipment becomes cheap, people will switch machinery for labour and therefore the demand for labour will fall
* wages in other countries
* technology
* regulation
* demand for the product
* productivity of labour
* profitability of the firm - the higher the profits of the firm, the more labour they can afford to employ
* number of firms in the market
* prices of factors of production - if machinery and equipment becomes cheap, people will switch machinery for labour and therefore the demand for labour will fall
* wages in other countries
* technology
* regulation
26
New cards
explain the influence of productivity of labour on labour demand
o The more productive workers are, the higher the demand for them.
o This can be increased with education and training, and by using technology.
* (Ev) Demands on the capital available - more advanced technology/machinery over training labour
* (Ev) If labour is becoming more productive and increasing output per worker - less workers needed in the future so demand will decrease
o This can be increased with education and training, and by using technology.
* (Ev) Demands on the capital available - more advanced technology/machinery over training labour
* (Ev) If labour is becoming more productive and increasing output per worker - less workers needed in the future so demand will decrease
27
New cards
explain the influence of the number of firms on labour demand
o This determines how many buyers of labour there is. If there is only one employer, for example the NHS, the demand for labour is lower than if there are many employers, such as in the supermarket industry.
o The lower demand for labour can mean wages are lower, so trade unions try to encourage higher wages.
Wage rates:
* A wage is the price of labour and so has the same influence on demand for labour as price has on the demand for a product. As wage rates increase, demand for labour contracts since the MRP of labour must be higher for it to be worthwhile employing more people, so less people are employed.
o The lower demand for labour can mean wages are lower, so trade unions try to encourage higher wages.
Wage rates:
* A wage is the price of labour and so has the same influence on demand for labour as price has on the demand for a product. As wage rates increase, demand for labour contracts since the MRP of labour must be higher for it to be worthwhile employing more people, so less people are employed.
28
New cards
explain the influence of wages in other countries on labour demand
if wages are lower in other countries and therefore wages in the UK are relatively high, people will be employed in other countries as it represents a lower cost for businesses. This means that demand in the UK is low
29
New cards
explain the influence of technology on labour demand
improvements in computers and technology means that many jobs have been lost with the work being done by machines. This means that there is less demand for labour, but demand for labour in technological based industries is increasing - by 2040, about 47% of jobs could be lost to technology
30
New cards
explain the influence of regulation on labour demand
as laws are passed some jobs disappear, such conductors, whilst other jobs are made → high regulation within the labour market is likely to discourage firms from hiring since it can be very costly and time-consuming so this will reduce demand for labour in these areas.
* France is a country that used to have high levels of labour regulation and this is something the new president, Emmanuel Macron, is trying to change - while the US lacks labour regulation as firms can easily hire and fire workers
* France is a country that used to have high levels of labour regulation and this is something the new president, Emmanuel Macron, is trying to change - while the US lacks labour regulation as firms can easily hire and fire workers
31
New cards
/ what is the suplly of labour
ability and willingness of people to make themselves available to work at different wage rates.
32
New cards
/ what influences supply of labour
Wages Population and distribution of age Non-monetary benefits(non financial benefits of the job/satisfaction)Education/training/qualification Trade unions and barriers to entry Wages and conditions of other jobs Legislation
33
New cards
/ how are wages decided in perfect competition\`\`
wages are determined purely by demand and supply and all workers are paid the same