AP Bio Chapter 6 Cellular Energetics
1/59
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
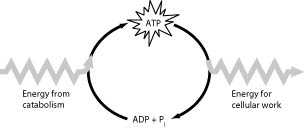
Which of the following is the most correct interpretation of the figure?
ATP is a molecule that acts as an intermediary to store energy for cellular work.
Energy from catabolism can be used directly for performing cellular work.
Pi acts as a shuttle molecule to move energy from ATP to ADP.
ADP + Pi are a set of molecules that store energy for catabolism.
ATP is a molecule that acts as an intermediary to store energy for cellular work.
When electrons move closer to a more electronegative atom, what happens? The more electronegative atom is _____.
reduced, and energy is released
oxidized, and energy is released
reduced, and energy is consumed
oxidized, and energy is consumed
reduced, and energy is released
Which of the listed statements describes the results of the following reaction?
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy
CO2 is reduced and O2 is oxidized.
O2 is oxidized and H2O is reduced.
O2 is reduced and CO2 is oxidized.
C6H12O6 is oxidized and O2 is reduced.
C6H12O6 is oxidized and O2 is reduced.
When a glucose molecule loses a hydrogen atom as the result of an oxidation-reduction reaction, the molecule becomes _____.
oxidizing agent
oxidized
reduced
hydrolyzed
oxidized
Which of the following statements about NAD+ is true?
NAD+ has more chemical energy than NADH.
NAD+ can donate electrons for use in oxidative phosphorylation.
In the absence of NAD+, glycolysis can still function.
NAD+ is reduced to NADH during glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, and the citric acid cycle.
NAD+ is reduced to NADH during glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, and the citric acid cycle
The oxygen consumed during cellular respiration is involved directly in which process or event?
accepting electrons at the end of the electron transport chain
glycolysis
the citric acid cycle
the oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA
accepting electrons at the end of the electron transport chain
Carbohydrates and fats are considered high-energy foods because they _____.
have a lot of oxygen atoms.
are easily reduced.
have a lot of electrons associated with hydrogen.
have no nitrogen in their makeup.
have a lot of electrons associated with hydrogen.
A cell has enough available ATP to meet its needs for about 30 seconds. What is likely to happen when an athlete exhausts his or her ATP supply?
Other cells take over, and the muscle cells that have used up their ATP cease to function.
Catabolic processes are activated that generate more ATP.
ATP is transported into the cell from the circulatory system.
He or she has to sit down and rest.
Catabolic processes are activated that generate more ATP.
The free energy for the oxidation of glucose to CO2 and water is -686 kcal/mol and the free energy for the reduction of NAD+ to NADH is +53 kcal/mol. Why are only two molecules of NADH formed during glycolysis when it appears that as many as a dozen could be formed?
Glycolysis is a very inefficient reaction, with much of the energy of glucose released as heat.
There is no CO2 or water produced as products of glycolysis.
Most of the free energy available from the oxidation of glucose is used in the production of ATP in glycolysis.
Most of the free energy available from the oxidation of glucose remains in pyruvate, one of the products of glycolysis.
Most of the free energy available from the oxidation of glucose remains in pyruvate, one of the products of glycolysis.
Which kind of metabolic poison would most directly interfere with glycolysis?
an agent that reacts with oxygen and depletes its concentration in the cell
an agent that closely mimics the structure of glucose but is not metabolized
an agent that reacts with NADH and oxidizes it to NAD+
an agent that binds to pyruvate and inactivates it
an agent that closely mimics the structure of glucose but is not metabolized
Most of the CO2 from the catabolism of glucose is released during _____.
chemiosmosis
electron transport
glycolysis
the citric acid cycle
the citric acid cycle
Which electron carrier(s) function in the citric acid cycle?
NADH and FADH2
NAD+ only
the electron transport chain
ADP and ATP
NADH and FADH2
If you were to add one of the eight citric acid cycle intermediates to the culture medium of yeast growing in the laboratory, what do you think would happen to the rates of ATP and carbon dioxide production?
There would be no change in ATP production, but we would observe an increased rate of carbon dioxide production.
Rates of ATP and carbon dioxide production would probably both decrease.
The rate of ATP production would decrease, but the rate of carbon dioxide production would increase.
The rates of ATP production and carbon dioxide production would both increase.
The rates of ATP production and carbon dioxide production would both increase.
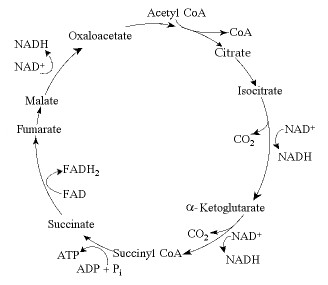
The citric acid cycle.
For each mole of glucose (C6H12O6) oxidized by cellular respiration, how many moles of CO2are released in the citric acid cycle (see the accompanying figure)?
4
2
32
6
4
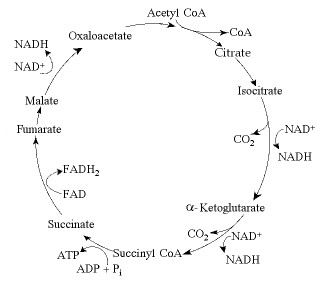
The citric acid cycle.
Starting with citrate, which of the following combinations of products would result from three acetyl CoA molecules entering the citric acid cycle (see the accompanying figure)?
3 ATP, 3 CO2, 3 NADH, and 3 FADH2
3 ATP, 6 CO2, 9 NADH, and 3 FADH2
38 ATP, 6 CO2, 3 NADH, and 12 FADH2
1 ATP, 2 CO2, 3 NADH, and 1 FADH2
3 ATP, 6 CO2, 9 NADH, and 3 FADH2
In the presence of oxygen, the three-carbon compound pyruvate can be catabolized in the citric acid cycle. First, however, the pyruvate (1) loses a carbon, which is given off as a molecule of CO2, (2) is oxidized to form a two-carbon compound called acetate, and (3) is bonded to coenzyme A.
The three listed steps result in the formation of _____.
acetyl CoA, NAD+, ATP, and CO2
acetyl CoA, FADH2, and CO2
acetyl CoA, O2, and ATP
acetyl CoA, NADH, and CO2
acetyl CoA, NADH, and CO2
Which one of the following is formed by the removal of a carbon (as CO2) from a molecule of pyruvate?
oxaloacetate
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
citrate
acetate
acetate
The electron transport chain _____.
is a series of redox reactions
is driven by ATP consumption
takes place in the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells
is a series of substitution reactions
is a series of redox reactions
Where are the proteins of the electron transport chain located?
mitochondrial matrix
mitochondrial intermembrane space
mitochondrial outer membrane
mitochondrial inner membrane
mitochondrial inner membrane
During aerobic respiration, which of the following directly donates electrons to the electron transport chain at the lowest energy level?
FADH2
ATP
ADP + Pi
NADH
FADH2
The primary role of oxygen in cellular respiration is to _____.
yield energy in the form of ATP as it is passed down the respiratory chain
combine with lactate, forming pyruvate
act as an acceptor for electrons and hydrogen, forming water
combine with carbon, forming CO2
combine with carbon, forming CO2
During aerobic respiration, H2O is formed. Where does the oxygen atom for the formation of the water come from?1
molecular oxygen (O2)
glucose (C6H12O6)
pyruvate (C3H3O3-)
carbon dioxide (CO2)
molecular oxygen (O2)
Energy released by the electron transport chain is used to pump H+ into which location in eukaryotic cells?
mitochondrial outer membrane
mitochondrial intermembrane space
mitochondrial inner membrane
mitochondrial matrix
mitochondrial intermembrane space
Which of the following normally occurs regardless of whether or not oxygen (O2) is present?
fermentation
citric acid cycle
glycolysis
oxidative phosphorylation (chemiosmosis)
glycolysis
In the absence of oxygen, yeast cells can obtain energy by fermentation, resulting in the production of _____.
ATP, pyruvate, and acetyl CoA
ATP, NADH, and pyruvate
ATP, CO2, and lactate
ATP, CO2, and ethanol (ethyl alcohol)
ATP, CO2, and ethanol (ethyl alcohol)
One function of both alcohol fermentation and lactic acid fermentation is to _____
reduce NAD+ to NADH
oxidize NADH to NAD+
reduce FADH2 to FAD+
reduce FAD+ to FADH2
oxidize NADH to NAD+
Canine phosphofructokinase (PFK) deficiency afflicts Springer spaniels, affecting an estimated 10% of the breed. Given its critical role in glycolysis, one implication of the genetic defect resulting in PFK deficiency in dogs is _____.
a reduced life span
an intolerance for exercise
early embryonic mortality
elevated blood-glucose levels in the dog's blood
an intolerance for exercise
Which of the following statements accurately describes the function of a metabolic pathway involved in cellular respiration?
The function of the citric acid cycle is the transfer of electrons from pyruvate to NADH to O2.
The function of glycolysis is to begin catabolism by breaking glucose into two molecules of pyruvate, with a net yield of two ATP.
The function of the bonding of acetic acid to the carrier molecule CoA to form acetyl CoA is the reduction of glucose to acetyl CoA.
The function of glycolysis is to begin catabolism by breaking glucose into two molecules of pyruvate, with a net yield of two ATP.
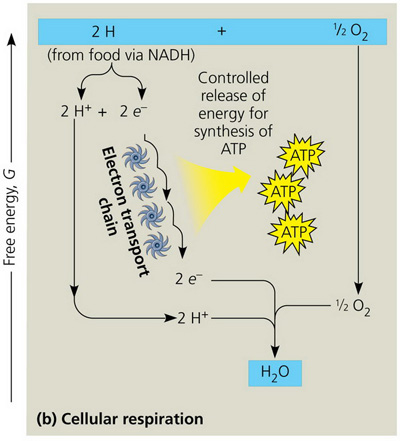
In cellular respiration, a series of molecules forming an electron transport chain alternately accepts and then donates electrons. What is the advantage of such an electron transport chain?
The advantage of the respiratory electron transport chain is that oxygen is the final electron acceptor.
The advantage of an electron transport chain is that a small amount of energy is released with the transfer of an electron between each pair of intermediates.
The advantage of an electron transport chain is the production of a large number of reduced, high-energy intermediates.
The advantage of an electron transport chain is that a small amount of energy is released with the transfer of an electron between each pair of intermediates.
How will a healthy individual’s ATP production change during an eight-hour fast?
The individual’s ATP production will decrease significantly.
The individual’s ATP production will increase significantly.
The individual’s ATP production will not change significantly.
The individual’s ATP production will not change significantly.
Identify all correct statements about the basic function of fermentation.
Select all that apply.
The basic function of fermentation is the regeneration of NAD+, which allows continued ATP production by glycolysis.
The basic function of fermentation is the production of additional ATP by further oxidation of the products of glycolysis.
The basic function of fermentation is the production of ethyl alcohol or lactic acid.
The basic function of fermentation is the regeneration of NAD+, which allows continued ATP production by glycolysis.
Select the correct statement about cellular respiration.
Cellular respiration and breathing differ in that cellular respiration is at the cellular level, whereas breathing is at the organismal level.
Plants carry out cellular respiration only in organs such as roots that cannot carry out photosynthesis.
Animals carry out cellular respiration whereas plants carry out photosynthesis.
Cellular respiration and breathing differ in that cellular respiration is at the cellular level, whereas breathing is at the organismal level.
Plants photosynthesize _____.
only in the light but respire in light and dark
only in the light but respire only in the dark
and respire only in the light
only in the dark but respire only in the ligh
only in the light but respire in light and dark
Early investigators thought the oxygen produced by photosynthetic plants came from carbon dioxide. In fact, it comes from _____.
air
water
electrons from NADPH
glucose
water
Every ecosystem must have _____.
photosynthesizers
autotrophs and heterotrophs
autotrophs
producers and primary consumers
autotrophs
When oxygen is released as a result of photosynthesis, it is a direct by-product of _____.
the electron transfer system of photosystem I
splitting water molecules
the electron transfer system of photosystem II
chemiosmosis
splitting water molecules
Which of the following statements is a correct distinction between autotrophs and heterotrophs?
Only heterotrophs have mitochondria.
Only heterotrophs require oxygen.
Cellular respiration is unique to heterotrophs.
Autotrophs, but not heterotrophs, can nourish themselves beginning with CO2 and other nutrients that are inorganic
Autotrophs, but not heterotrophs, can nourish themselves beginning with CO2 and other nutrients that are inorganic
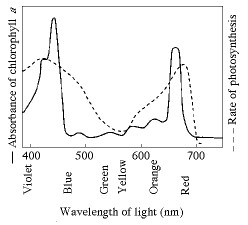
What wavelength of light in the figure is most effective in driving photosynthesis?
420 mm
730 mm
575 mm
625 mm
420 mm
Theodor W. Engelmann illuminated a filament of algae with light that passed through a prism, thus exposing different segments of algae to different wavelengths of light. He added aerobic bacteria and then noted in which areas the bacteria congregated. He noted that the largest groups were found in the areas illuminated by the red and blue light.
An outcome of Engelmann's experiment was to help determine the relationship between _____.
wavelengths of light and the amount of heat released
the concentration of carbon dioxide and the rate of photosynthesis
wavelengths of light and the rate of photosynthesis
wavelengths of light and the rate of aerobic respiration
wavelengths of light and the rate of photosynthesis
A spaceship is designed to support animal life for a multiyear voyage to the outer planets of the solar system. Plants will be grown to provide oxygen and to recycle carbon dioxide. Since the spaceship will be too far from the sun for photosynthesis, an artificial light source will be needed.
What wavelengths of light should be used to maximize plant growth with a minimum of energy expenditure?
green light
full-spectrum white light
a mixture of blue and red light
UV light
a mixture of blue and red light
Suppose a plant has a unique photosynthetic pigment and the leaves of this plant appear to be reddish yellow. What wavelengths of visible light are absorbed by this pigment?
red and yellow
blue, green, and red
green and yellow
blue and violet
blue and violet
In autumn, the leaves of deciduous trees change colors. This is because chlorophyll is degraded and _____.
water supply to the leaves has been reduced
the degraded chlorophyll changes into many other colors
sugars are sent to most of the cells of the leaves
carotenoids and other pigments are still present in the leaves
carotenoids and other pigments are still present in the leaves
What event accompanies energy absorption by chlorophyll (or other pigment molecules of the antenna complex)?
Electrons are stripped from NADPH.
An electron is excited.
A carboxylation reaction of the Calvin cycle occurs.
ATP is synthesized from the energy absorbed.
An electron is excited.
The final electron acceptor associated with photosystem I is _____.
water
oxygen
NADPH
NADP
NADP
The electrons of photosystem II are excited and transferred to electron carriers. From which molecule or structure do the photosystem II replacement electrons come?
water
the electron carrier, plastocyanin
photosystem I
oxygen
water
What are the products of linear electron flow?
heat and fluorescence
ADP and NADP+
ATP and NADPH
ATP and P700
ATP and NADPH
Which of the following statements best describes the relationship between photosynthesis and respiration?
Respiration runs the biochemical pathways of photosynthesis in reverse.
Photosynthesis is catabolic; respiration is anabolic.
Photosynthesis occurs only in plants; respiration occurs only in animals.
Photosynthesis stores energy in complex organic molecules; respiration releases energy from complex organic molecules
Photosynthesis stores energy in complex organic molecules; respiration releases energy from complex organic molecules
In photosynthetic cells, synthesis of ATP by the chemiosmotic mechanism occurs during _____.
respiration only
photosynthesis only
photosynthesis and respiration
neither photosynthesis nor respiration
photosynthesis and respiration
What is the relationship between the wavelength of light and the quantity of energy per photon?
They are separate phenomena.
They have a direct, linear relationship.
They are inversely related.
They are logarithmically related.
They are inversely related.
Carotenoids are often found in foods that are considered to have antioxidant properties in human nutrition. What related function do they have in plants?
They protect against oxidative damage from excessive light energy.
They serve as accessory pigments to increase light absorption.
They shield the sensitive chromosomes of the plant from harmful ultraviolet radiation.
They reflect orange light and enhance red light absorption by chlorophyll.
They protect against oxidative damage from excessive light energy.
Which of the following are products of the light reactions of photosynthesis that are utilized in the Calvin cycle?
ADP, Pi, and NADP+
ATP and NADPH
CO2 and glucose
H2O and O2
ATP and NADPH
Where does the Calvin cycle take place?
thylakoid membrane
outer membrane of the chloroplast
interior of the thylakoid (thylakoid space)
stroma of the chloroplast
stroma of the chloroplast
CAM plants keep stomata closed in the daytime, thus reducing loss of water. They can do this because they _____.
fix CO2 into organic acids during the night
fix CO2 into sugars in the bundle-sheath cells
fix CO2 into pyruvate in the mesophyll cells
use photosystem I and photosystem II at night
fix CO2 into organic acids during the night
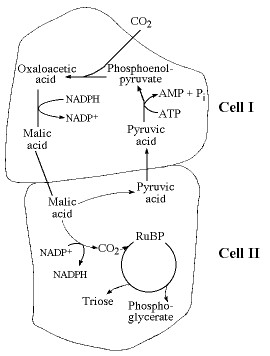
Which of the following statements is true concerning the accompanying figure?
It represents a CAM photosynthetic system.
It represents an adaptation that maximizes photorespiration.
It represents a C4 photosynthetic system.
It represents a C3 photosynthetic system.
It represents a C4 photosynthetic system.
Photorespiration _____.
generates ATP and sugars and consumes oxygen and carbon dioxide
generates oxygen and consumes ATP, carbon dioxide, and sugars
consumes carbon dioxide and generates ATP, sugars, and oxygen
generates carbon dioxide and consumes ATP and oxygen
generates carbon dioxide and consumes ATP and oxygen
Select the correct molecule that is the main product of the Calvin cycle.
Glucose
NADPH
G3P
G3P
What is the basic role of CO2 in photosynthesis?
CO2is a source of electrons in the formation of organic molecules.
CO2 is taken in by plants as a form of inverse respiration, in which carbon dioxide is “breathed in” and oxygen is “breathed out.”
CO2 is fixed or incorporated into organic molecules.
CO2 is fixed or incorporated into organic molecules.
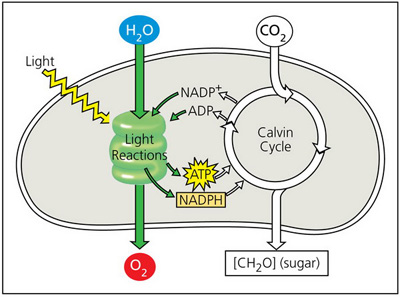
Select the most accurate statement describing the basic function of the light reactions of photosynthesis.
The basic function of the light reactions of photosynthesis is the trapping of light energy.
The basic function of the light reactions of photosynthesis is the production of glucose.
The basic function of the light reactions of photosynthesis is the conversion of solar energy to chemical energy.
The basic function of the light reactions of photosynthesis is the conversion of solar energy to chemical energy.
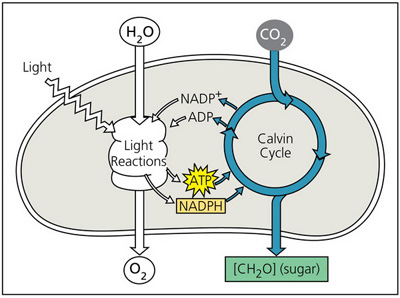
Select the correct statement about the Calvin cycle.
The Calvin cycle takes place primarily in the dark.
The basic function of the Calvin cycle is the conversion of solar energy to chemical energy.
The Calvin cycle has three phases: carbon fixation, reduction, and regeneration of RuBP.
The Calvin cycle has three phases: carbon fixation, reduction, and regeneration of RuBP.
Why are plants classified as producers?
Plants are classified as producers because they fix inorganic carbon into organic molecules.
Plants are classified as producers because they produce oxygen.
Plants are classified as producers because they are at the bottom of the food chain.
Plants are classified as producers because they fix inorganic carbon into organic molecules.