Metamorphism and Earthquake Processes
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
Metamorphism
Process of rock transformation due to heat and pressure.
Metamorphic rock
Rock formed from existing rock through metamorphism.
Earthquake
Sudden release of energy in Earth's crust.
Impact craters
Depressions formed by meteorite impacts.
Shock metamorphism
Metamorphism caused by high-pressure shock waves.
Deformation
Change in shape due to applied forces.
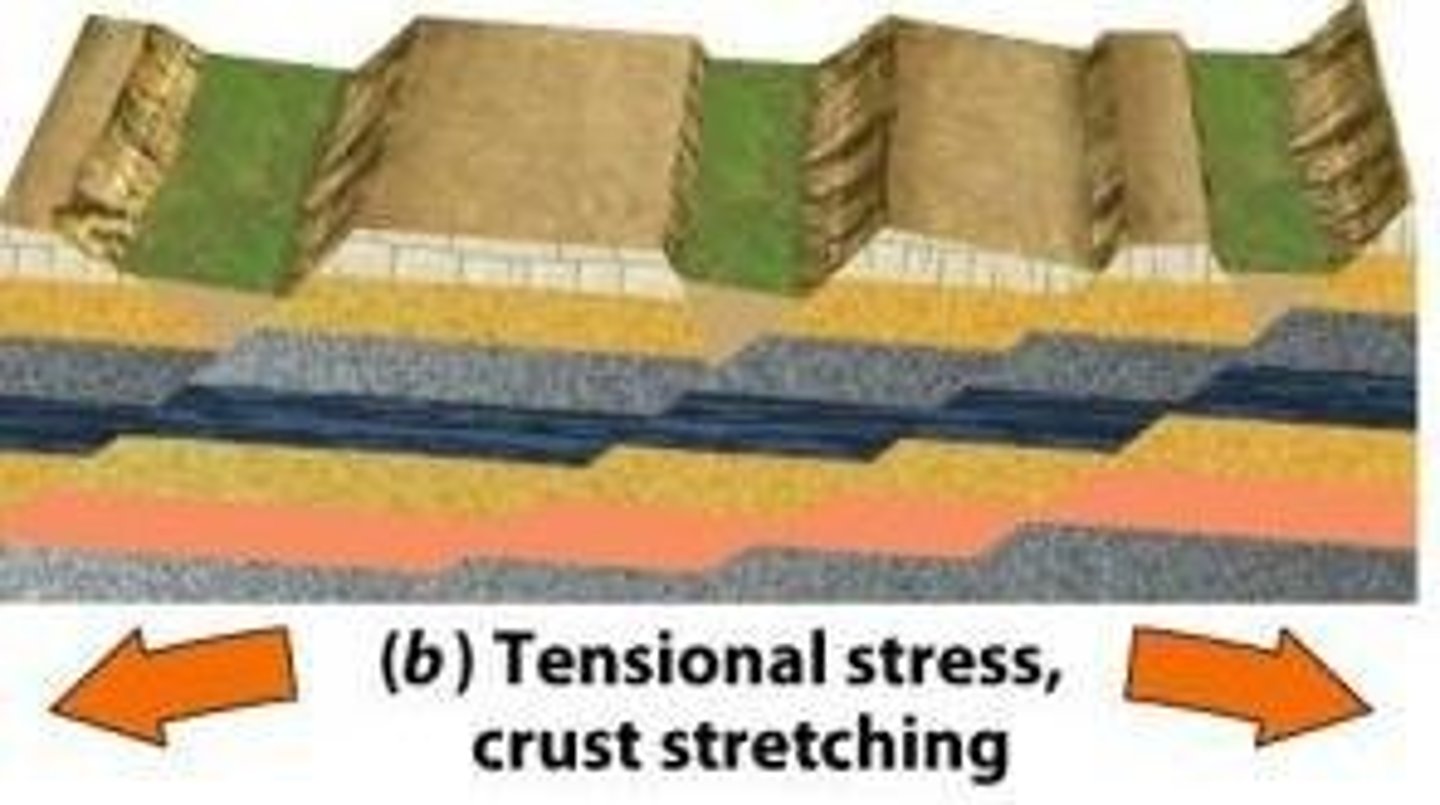
Stress
Force applied to rocks causing deformation.
Strain
Physical change resulting from stress on rocks.
Elastic deformation
Reversible change; rock returns to original shape.
Brittle deformation
Fracture occurs under stress; non-reversible.
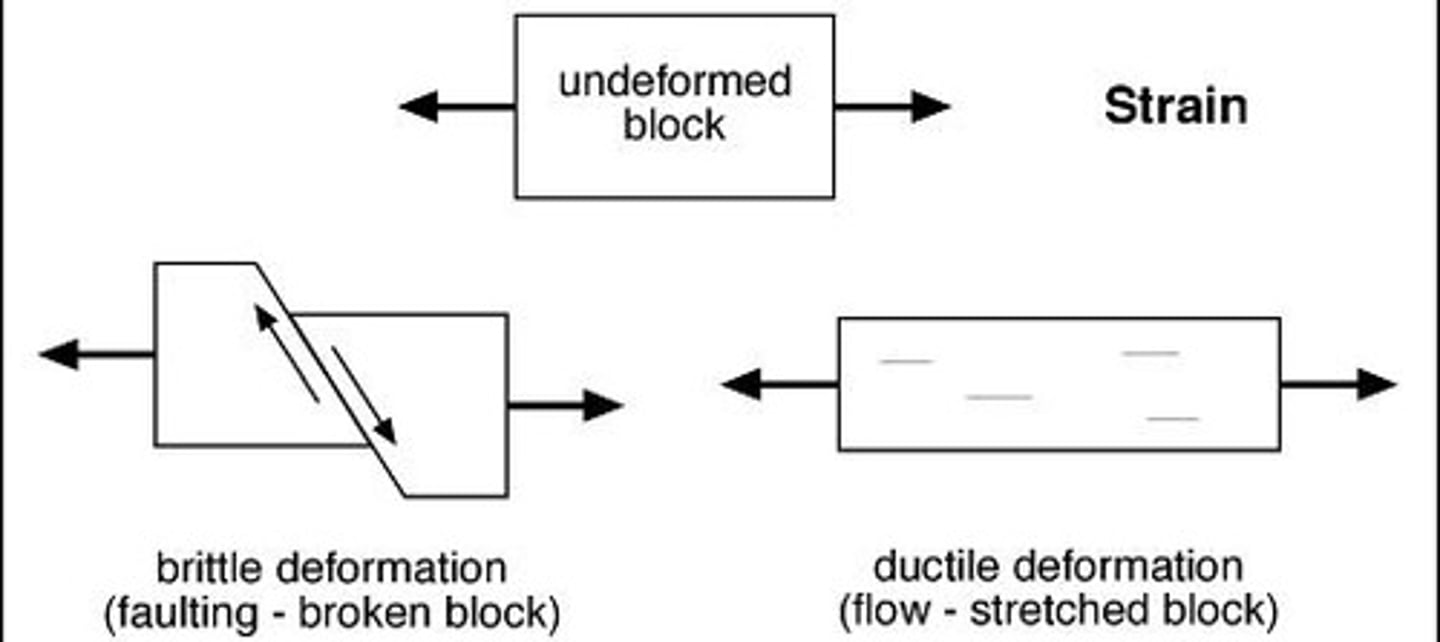
Ductile deformation
Irreversible change; rock does not return to shape.
Folds
Bends in rock layers from ductile deformation.
Faults
Fractures in rocks where displacement occurs.
Joints
Fractures without significant displacement.
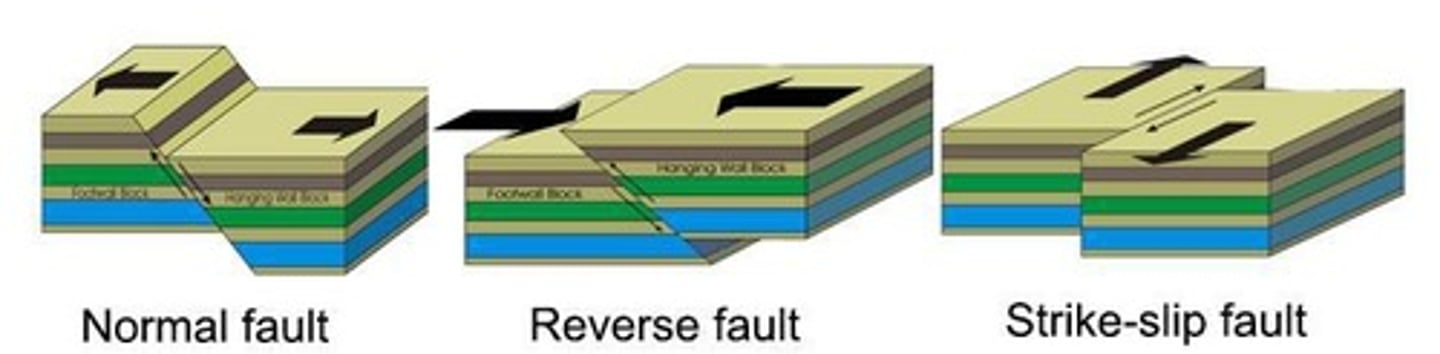
Normal fault
Occurs under tensional stress; rock stretches.
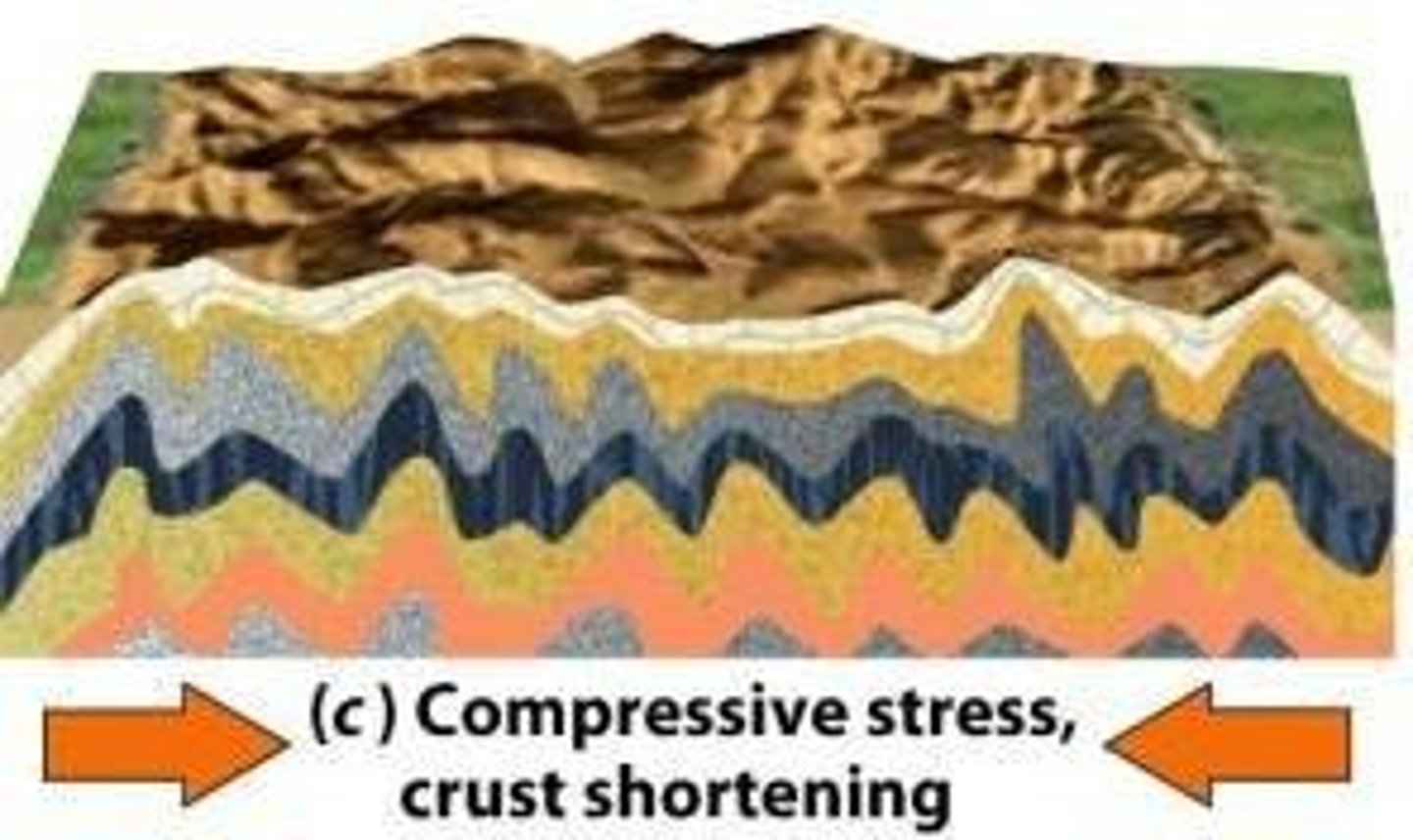
Reverse fault
Occurs under compressional stress; rock shortens.
Strike-slip fault
Lateral movement along the fault plane.
Dip-slip fault
Movement along the dip of the fault.

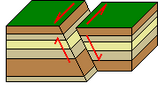
Oblique-slip fault
Combination of dip-slip and strike-slip movements.

Elastic rebound theory
Energy release during rock breakage causes earthquakes.
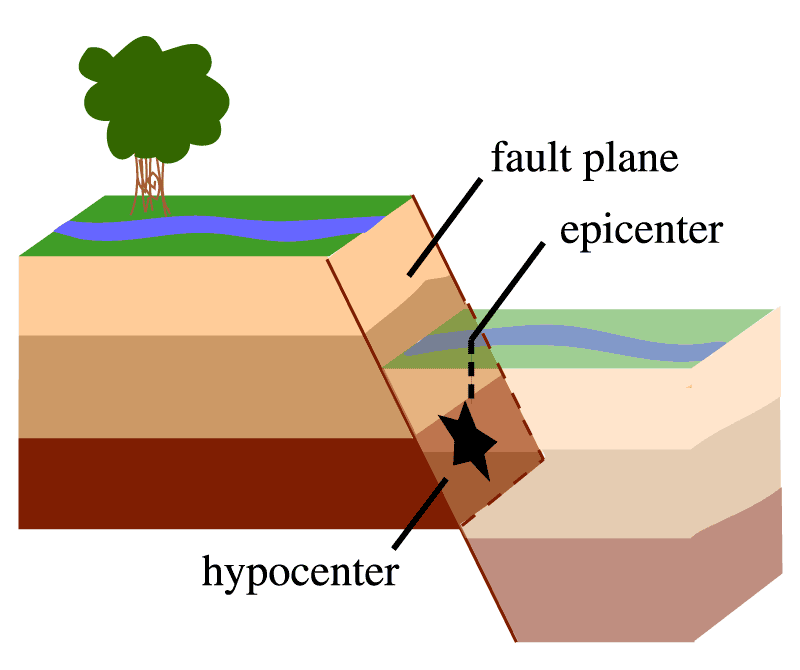
Focus (hypocenter)
Point within Earth where seismic waves originate.
Epicenter
Point on surface directly above earthquake focus.
Seismic waves
Energy waves released during an earthquake.
Body waves
Seismic waves traveling through Earth's interior.
P wave
Fastest seismic wave; compressional motion.
S wave
Slower seismic wave; transverse motion.
P waves
Primary waves that travel through solids and fluids.
S waves
Secondary waves that only travel through solids.
Surface waves
Slowest seismic waves causing most damage.
Love waves
Side-to-side motion with no vertical displacement.
Rayleigh waves
Rolling motion causing significant ground movement.
Seismometer
Internal component of a seismograph recording ground motion.
Seismograph
Instrument for recording earthquake ground motion.
P-S interval
Time difference between P and S wave arrivals.
Travel-time curve
Graph plotting seismic wave arrival time versus distance.
Moment Magnitude (MW)
Magnitude scale based on seismic moment measurements.
Seismic moment
Force needed to generate recorded seismic waves.
Tectonic earthquakes
Earthquakes caused by tectonic plate movements.
Volcanism
Earthquakes resulting from volcanic activity.
Artificial induction
Earthquakes caused by human activities or interventions.
Reservoir induction
Seismicity increase after water impounding behind dams.
Divergent boundaries
Plates move apart, creating new lithosphere.
Convergent boundaries
Plates collide, leading to mountain formation.
Transform-fault boundaries
Plates slide past each other horizontally.
Normal faults
Faults where one side slips down.
Thrust faults
Faults where one plate is pushed over another.
Reverse faults
Similar to thrust faults, but steeper.
East African Rift
Example of continental plate separation.
Ocean-ocean convergence
Forms oceanic trench and volcanic island arcs.
Ocean-continent convergence
Creates volcanic mountain chains and deep earthquakes.
Continent-continent convergence
Results in crustal thickening and folded mountains.
Subduction zone
Where one plate moves under another, causing earthquakes.
Nazca Plate
Oceanic plate subducting under South American Plate.
Peru-Chile Trench
Trench formed by Nazca Plate subduction.
Megathrust earthquakes
Largest earthquakes at convergent boundaries.
Wadati-Benioff Zone
Seismicity zone along subducting plate's plane.
Depth of focus
Distance between earthquake focus and epicenter.
Shallow focus earthquakes
0-70 km deep, 85% of occurrences.
Intermediate focus earthquakes
70-350 km deep, 12% of occurrences.
Deep focus earthquakes
350-670 km deep, 3% of occurrences.
Ductile manner
Deep rocks flow under stress, limiting energy release.
Transform boundaries
Plates slide past each other horizontally.
Strike-slip fault
Fault where plates move laterally against each other.
San Andreas Fault
Major transform fault in California.
Secondary hazards
Additional risks caused by primary earthquake hazards.
Liquefaction
Soil behaves like liquid during shaking.
Tsunamis
Waves caused by underwater earthquakes or landslides.
Ring of Fire
Area with high earthquake and tsunami risk.
Cascadia Subduction Zone
Location of potential megathrust earthquakes in Canada.
Creepmeters
Devices measuring fault movement over time.
Tiltmeters
Instruments monitoring land slope changes.