Hematology Exam 1 (chapter 4)
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Self-renewal and pluripotential differentiation potential are characteristics of:
A. mature cells
B. stem cells
C. progenitor cells
D. maturing cells
B. stem cells
Precursor cells that are morphologically recognizable are found in the:
A. stem cell compartment
B. progenitor cell compartment
C. maturing cell compartment
D. differentiating cell compartment
C. maturing cell compartment
The MEP gives rise to:
A. eosinophils and megakaryocytes
B. erythrocytes and monocytes
C. eosinophils and megakaryocytes
D. erythrocytes and megakaryocytes
D. erythrocytes and megakaryocytes
All hematopoietic cells are derived from the CFU-GEMM except:
A. lymphocytes
B. platelets
C. eosinophils
D. erythrocytes
A. lymphocytes
The following cell that is most sensitive to erythropoietin is:
A. reticulocyte
B. CFU-GEMM
C. BFU-E
D. CFU-E
D. CFU-E
All of the following are considered "early acting, multilineage" cytokines except:
A. IL-5
B. GM-CSF
C. SCF
D.IL-3
A. IL-5
Pleiotrophy refers to:
A. multiple different cells that can produce the same cytokine
B. a cytokine with multiple biologic activities
C. multiple cytokines that can induce the same cellular effect
D. a cytokine that can be produced by multiple different tissues
B. a cytokine with multiple biologic activities
Cytokine regulation in which the cytokine is not secreted by the producing cell but remains membrane bound, necessitating direct cell-cell contact to achieve the desired effect is:
A. paracrine
B. endocrine
C. juxtacrine
D. autocrine
C. juxtacrine
All of the following are thought to be negative regulators of hematopoiesis except:
A. TGF-beta
B. SCF
C. TNF
D. MIP-1alpha
B. SCF
The hematopoietic microenvironment is composed of:
A. hepatocytes and extrahepatic matrix
B. osteoblasts and osteoclasts
C. marrow stromal cells and extracellular matrix
D. hepatocytes and splenic macrophages
C. marrow stromal cells and extracellular matrix
Hematopoietic stem cells are characterized by all of the following markers except:
A. CD34+
B. Lin-
C. HLA-DR+
D. Rhodamine 123LO
C. HLA-DR+
The major molecule marker that differentiates CLP from CMP is:
A. IL7-R
B. FcRy
C. CD33
D. CD13
A. IL7-R
All of the following are important regulators of granulopoiesis except:
A. GM-CSF
B. FL
C. IL-2
D. IL-3
C. IL-2
The major cytokine important for eosinophil differentiation is:
A. IL-3
B. IL-5
C. IL-7
D. IL-11
B. IL-5
Which of the following growth factor receptors share a common β chain?
A. IL-3 and GM-CSF
B. TPO and EPO
C. IL-2 and IL-3
D. G-CSF and GM-CSF
A. IL-3 and GM-CSF
Cytokine receptors that lack an intrinsic kinase domain generally signal:
A. through an intrinsic phosphatase domain
B. by recruiting membrane-embedded kinases
C. through an intrinsic protease domain
D. by recruiting cytoplasmic kinases
D. by recruiting cytoplasmic kinases
The function of the JAK-STAT pathway in hematopoiesis is to:
A. localize cytokines in the hematopoietic microenvironment
B. generate homing receptors for stem and progenitor cells
C. produce cytoadhesion molecules to retain precursor cells in the marrow
D. function as a signal transduction pathway for cytokine activated receptors
D. function as a signal transduction pathway for cytokine activated receptors
The stromal elements of the hematopoietic microenvironment include all of the following except:
A. B lymphocytes
B. adipocytes
C. fibroblasts
D. osteoblasts
A. B lymphocytes
Which of the following cytoadhesion molecules plays an important role in retaining erythroid-developing cells in the bone marrow microenvironment?
A. hemonectin
B. fibronectin
C. thrombospondin
D. glycosaminoglycans
B. fibronectin
The role of the osteoblastic stem cell "niche" in the bone marrow is thought to be to:
A. protect hematopoietic precursor cells from the lytic action of osteoclasts
B. provide nourishment (oxygen, nutrients) to developing precursor cells.
C. regulate the quiescent state of stem cells blocking differentiation-inducing signals
D. produce cytoadhesion molecules important for homing to the marrow
C. regulate the quiescent state of stem cells blocking differentiation-inducing signals
Which of the following cells gives rise to the lymphoid and myeloid cells?
A. Committed lymphoid progenitor cell
B. Multipotential progenitor cell
C. Committed myeloid progenitor cell
D. CFU-GEMM
B. Multipotential progenitor cell
Which of the following molecules (synthetically generated) is administered to patients with renal disease to stimulate red cell production?
A. GM-CSF
B. Interleukin-2
C. EPO
D. G-CSF
C. EPO
Which of the following cytokines inhibits stem cell proliferation?
A. Interferon
B. MIP-1α
C. Lactoferrin
D. TNF-a
B. MIP-1α
Which term is used to describe the point when two cells from the same precursor take a separate route of development?
A. Maturation
B. Differentiation
C. Commitment
D. Specialization
B. Differentiation
Which of the following classes of hematopoietic cells is committed to becoming an erythrocyte?
A. Hematopoietic stem cell
B. Multipotential progenitor cell
C. Committed lymphoid progenitor
D. BFU-E
D. BFU-E
All of the following are key components of hematopoietic differentiation except:
A. The formation of mature blood components with a finite life span
B. The differentiation of blood components when exposed to different cytokines
C. The commitment to produce blood cells only
D. The activation of programmed cell death
D. The activation of programmed cell death
Which of the following classes of hematopoietic cells has the ability to self-renew?
A. Hematopoietic stem cell
B. Multipotential progenitor cell
C. Committed myeloid progenitor
D. Maturing cell
A. Hematopoietic stem cell
Several cytokines are used for clinical purposes. Which three cell lines are primarily increased by the injection of EPO, TPO, and CFU-GM?
A. Lymphocytes, monocytes, and platelets
B. Erythrocytes, platelets, and granulocytes
C. Monocytes, platelets, and stem cells
D. Stem cells, precursor cells, and maturing cells
B. Erythrocytes, platelets, and granulocytes
Erythropoietin is produced by the:
A. Kidneys
B. Liver
C. Spleen
D. Thymus gland
A. Kidneys
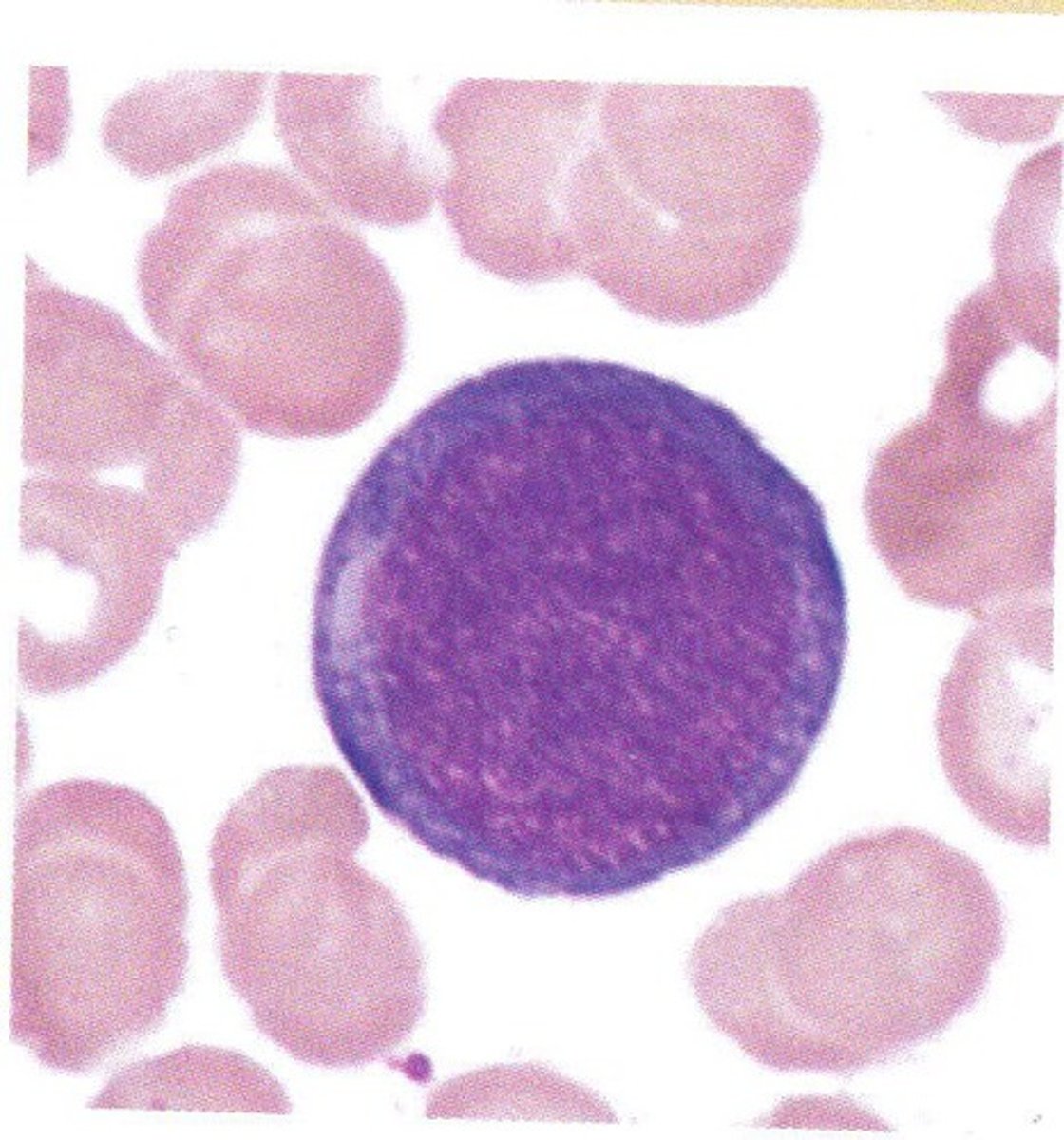
From the answer choices below:
Identify the following cell.
Please note: more than one answer may apply.
A. Erythrocyte
B. Pronormoblast
C. Orthochromic normoblast
D. Pronormocyte
E. Rubriblast
B. Pronormoblast
E. Rubriblast
MCV (fL) is calculated by dividing hematocrit by RBC count x 10.
just remember
The CBC parameter that gives insight as to the amount of anisocytosis present in a specimen is:
A. RDW
B. MCHC
C. MCV
D. Hgb
A. RDW
The ______ is one of the most stable parameters in a CBC.
A. MCV
B. Hct
C. MCHC
D. MCH
A. MCV
The hormone responsible for red blood cell development in the bone marrow is:
A. Thyroxin
B. Insulin
C. Leukopoietin
D. Erythropoietin
D. Erythropoietin
The key organs involved in extramedullary hematopoiesis include the:
A. Kidney and thymus
B. Lymph nodes and heart
C. Liver and spleen
D. Kidney and liver
C. Liver and spleen