Palmer- Spinal- Exam 2 LO/TQs
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
131 Terms
Which thoracic vertebrae are classified as typical and atypical thoracics
Typical: T2-T8
Atypical: T1, T9-T12
What is the height difference of thoracic vertebral bodies
posterior height of VB 1-2 mm greater than anterior height
T/F: thoracic vertebrae have a flat, leveled (planar) IVD
true
Explain the width between left and right superior and inferior articular processes between T2-T4.
What about T5-T8?
T2-T4: greater width between L/R superior articular process compared to inferior articular process.
T5-T8: are equal in distance
What degree do spinous processes slant posteriorly/inferiorly on T2-T4?
What about T5-T8?
T2-T4: 40 degree angle
T5-T8: 60 degree angle
what is the aortic impression and how is it formed?
flattened portion of vertebral bodies due to compression of sup/inf. epiphyseal rims by the aorta
ONLY on T5-T8
what are the two types of costovertebral joints associated with thoracic vertebrae?
- Costocentral joint (rib to VB)
- constotransverse joint (rib to TVP)
What is the level of the aortic impression? TQ
What side? TQ
T5-T8
left side
what is being compressed by the aorta, leaving the aortic impression
superior and inferior epiphyseal rims
What is the VB body shape of typical thoracic vertebrae (T2-T8)
triangular/ heart shaped
What is the vertebral foramen (spinal canal) shape of a typical vertebrae?
Oval/circular
What is responsible for the typical thoracic kyphotic curvature?
Does the IVD play a role?
The posterior part of the VB is greater than the height of the anterior part of VB
IVD does not contribute, it is FLAT
What is the location of the pars interarticularis
The region between the superior and inferior articular processes at the lamina
What is the location of the transverse tubercle and transverse costal facet
Transverse tubercle is on the end of the TVP
transverse costal facet is on the end of the transverse tubercle
The transverse costal facet of T2-T6 is _______________
The transverse costal facet of T7-T8 is ____________
TQ
concaved
Flat
where are superior and inferior demi-facets?
What parts of the ribs do they articular with?
between the head of the rib and the thoracic vertebral body
articulate with sup/inf. articular surfaces of the head of the rib
One typical thoracic vertebral body participates in how many costocentral joints?
4 (2 w/ superior demi-facets, 2 with inferior demi-facets)
The head of rib 7 with articulate with the _____________ costal demifacet of T6 and the _________________ costal demifacet of T7
TQ
inferior; superior
What are the supporting ligaments of the costotransverse joints, including joint classification and attachment sites
1) capsular ligament
2) superior costotransverse
3) inferior costotransverse
4) Lateral costotransverse
What is the classification of costovertebral (costocentral and costotransverse) joints?
synovial plane joints
describe the location of costotransverse joints
how many costotransverse joints does each vertebrae participate in?
One the transverse tubercles
2 joints (L/R transverse processes)
What are the supporting ligaments of the costocentral joints
1) Capsular ligament
2) Radiate/stellate ligaments
3) Intra-articular ligament
What structures do the radiate/stellate ligaments of the costocentral joint connect?
connects head of the rib to vertebral bodies and IVD in a vertebral couple
What 2 structures does the inter/intraarticular ligament connect?
interarticular crest on the head of the rib with associated IVD within a vertebral couple
What is the joint classification of a costocentral joint?
Synovial Plane diarthrosis joint
Understand and describe the location of costocentral joints
where the rib articulates with the vertebral BODY
What is the classification of the costotransverse ligaments?
fibrous syndesmosis
What two structures does the the inferior costotransverse ligament connect/attach?
lateral costrotransverse?
superior costrotransverse?
inferior: anterior border of TP to posterior neck of rib at SAME level
lateral: non-articular surface of rib tubercle to transverse tubercle at SAME level
superior: inferior border of TP above to neck of rib below. DIFFERENT levels.
What are the muscles that attach at the spinous processes of thoracic vertebrae (13)
- Trapezius
- Lat. Dorsi
- Rhomboid Major
- Serratus posterior superior
- Splenius cervicis, capitus
- Spinalis thoracis, cervicis, capitus
- semispinalis thoracis
- multifidus
- rotators
-interspinalis
What are the ligaments that attach at spinous processes of thoracic vertebrae (2)
interspinous ligament
supraspinous ligament
What are the muscles that attach at the transverse processes of thoracic vertebrae (10)
- Longissimus thoracic, cervicis, capitis
- semispinalis thoracis, cervicis, capitis
- multifidus
- Rotator longus, brevis
- intertransversarii
What are the joint surfaces and classifications on associated surfaces with costovertebral joints (10)
-2 superior costal demi facets
-2 inferior costal demi facets
-2 transverse costal facets
-2 superior articular facets
-2 inferior articular facets
ALL SYNOVIAL PLANE
how many cartilaginous symphysis joint surfaces are on a typical thoracic
2 (IVD)
how many costocentral joint surfaces are located on a typical thoracic
4
what joint classification does the costotransverse ligament support? NBQ/TQ
*hint: there is superior, inferior and lateral costotransverse ligaments.
synovial plane joint
(since the joint is supporting the articulation between the rib and TVP, which forms a plane joint)
What joint classification do the costotransverse ligaments associate with? TQ
BE CAREFUL!! Associate does NOT mean support!! She will try to trick you.
fibrous syndesmosis joints
(If I asked which joint they supported, it would be synovial plane joints.)
If inferior costotransverse ligament is attaching at C7, where is its other attachment point? TQ
posterior neck of rib 7
How many total synovial joint surfaces are on typical thoracic vertebrae?
10 total
What is the only feature on T9 that is variable, making it an atypical vertebrae?
everything else on T9 is the same as the typical vertebrae!
T9 inferior costal demi-facet may be ABSENT if 10th rib articulates with IVD between T9/T10
Which muscle is absent at spinous processes of T9 and T10? TQ/NBQ
Spinalis
which muscle attachment is absent from all spinous processes below T6?
TQ/NBQ
semispinalis
How many total synovial joint surface are there on T9?
10 total (same as typical vertebrae)
T/F: T10 vertebral body has a complete costal facet, meaning there is no interarticular ligament/crest on rib 10
TRUE
what is the most common site/vertebra for a para-articular process (ossification of ligamentum flavum)
T10
T/F: T10 has a costotransverse facet and a costotransverse joint.
TRUE (in our book, it says t10 has this, but in real life it is variable. )
If t10 has a costotransverse joint, what ligament is also present?
costotransverse capsular ligament
what are the muscle attachments at T10 transverse process
Longissimus thoracis
semispinalis thoracis
multifidus
rotators
intertransversarii
levator costorum brevis and longus
What ligament(s) attach to the T10 transverse process?
intertransverse ligament
what muscle attach to the T10 spinous process
trapezius
latissimus dorsi
multifidus
rotators
interspinalis
what ligaments attach to t10 spinous process?
supraspinous
interspinous
What stabilizes the 12th rib? 100% TQ
Superior costotransverse ligament from T11
and Lumbocostal ligament from L1
How many total synovial plane joint surfaces are on T10? TQ
8 total
(4 Z joints, 2 Costocentral joints, 2 costotransverse joints)
what makes T11 unique?
-Transverse costal facet is ABSENT
-Complete costal facet on body is below superior epiphyseal rim, close to the pedicle
What is the classification of all the T10 synovial joints?
synovial plane (diarthrosis)
The spinous processes of T11 are ___________-like, and are short, thick and rectangular.
lumbar
how many synovial joint surfaces are present on T11?
6
(4 Z joint, 2 costocentral joints)
how many cartilaginous symphysis joints are on T11?
2
(VB and IVD superior and inferiorly)
how many synovial joint surfaces are on t11 vertebral body?
2 costocentral joints
The complete costal facet of T12 is located directly _________ the ___________
on; pedicles
how many tubercles are on T12 transverse process?
3
What are the three transverse tubercles on T12 and what are they each homologous for?
100% TQ
Superior tubercle- homologous for mammillary process
Inferior tubercle-homologous for accessory process
Lateral tubercle- homologous to transverse process
How is rib 12 stabilized? 100% TQ
stabilized by the superior costotransverse ligament from T11 and lumbocostal ligament from L1
T/F: T12 is the least commonly injured thoracic vertebra?
FALSE: most prone to injuries from stress
which two muscles insert to the vertebral body on T12 ? TQ
Psoas major, psoas minor
Give the Total synovial joints on each of the following vertebrae:
T1-9
T10
T11-12
T1-9: 10 total
T10: 8 total
T11-12: 6 total
What makes up the anterior, lateral and posterior walls of the thoracic cage?
Anterior wall: sternum and costal cartilage
Lateral walls: Ribs
Posterior wall: Thoracic Vertebrae
costal cartilage is made up of ______________ cartilage. TQ
hyaline cartilage
What makes up the costal margin?
Costal cartilage of ribs 7-10
What is the function of the costal margin? (inferior margin of anterior wall of thorax)
- Protects abdominal organs
- attachment point for diaphragm
What are the three osseous components of the sternum
1) Manubrium
2) corpus/body/gladiolus
3) xiphoid process
What are the two other names for the body of the sternum?
gladiolus and corpus sterni
what are the features of the manubrium? (3)
1) Jugular notch
2) Clavicular notches (sc joint)
3) Costal notch I-II (sternochondral joints)
The disc between the manubrium and sterni is made from ______________________ and forms the __________________________ symphysis.
fibrocartilage; manubriosternal
what is present in 4-7% of the population and is a result of failure of ossification centers between sternebrae?
Sternal foramen
What are the joints of the anterior thorax (4)
1) interchondral j.
2) costochondral j.
3) sternal j.
4) sternocostal j.
The xiphoid process is a _______________ _______________ from the inferior aspect of the corpus sterni (body). TQ
carilaginous extension
what is the ONLY part of the sternum that has a secondary ossification center?
Xiphoid process
The xiphoid process is the attachment site for the _____________ and the anchor for the ____________ ______________ muscle. 100% TQ
diaphragm; rectus abdominis
T/F: the xiphoid process ossifies by age 25
FALSE: variable ossification times throughout life
T/F: the caudal end of the xiphoid process remains a cartilage matrix into adult life.
TRUE
what is the joint classification of a costochondral joint?
Cartilaginous (amphiarthrosis) synchondrosis
What is the classification of the sternoclavicular joint?
synovial saddle (diarthrosis sellar) joint
the sternoclavicular joint is shaped like a _____________ joint, classifies as a __________________ joint, and acts like a _______________ joint. NBQ/TQ
synovial plane; synovial saddle; ball and socket
What separates the articular surfaces of the sternum and clavicle, forming two synovial joints? (100% TQ)
interarticular disc of sc joint
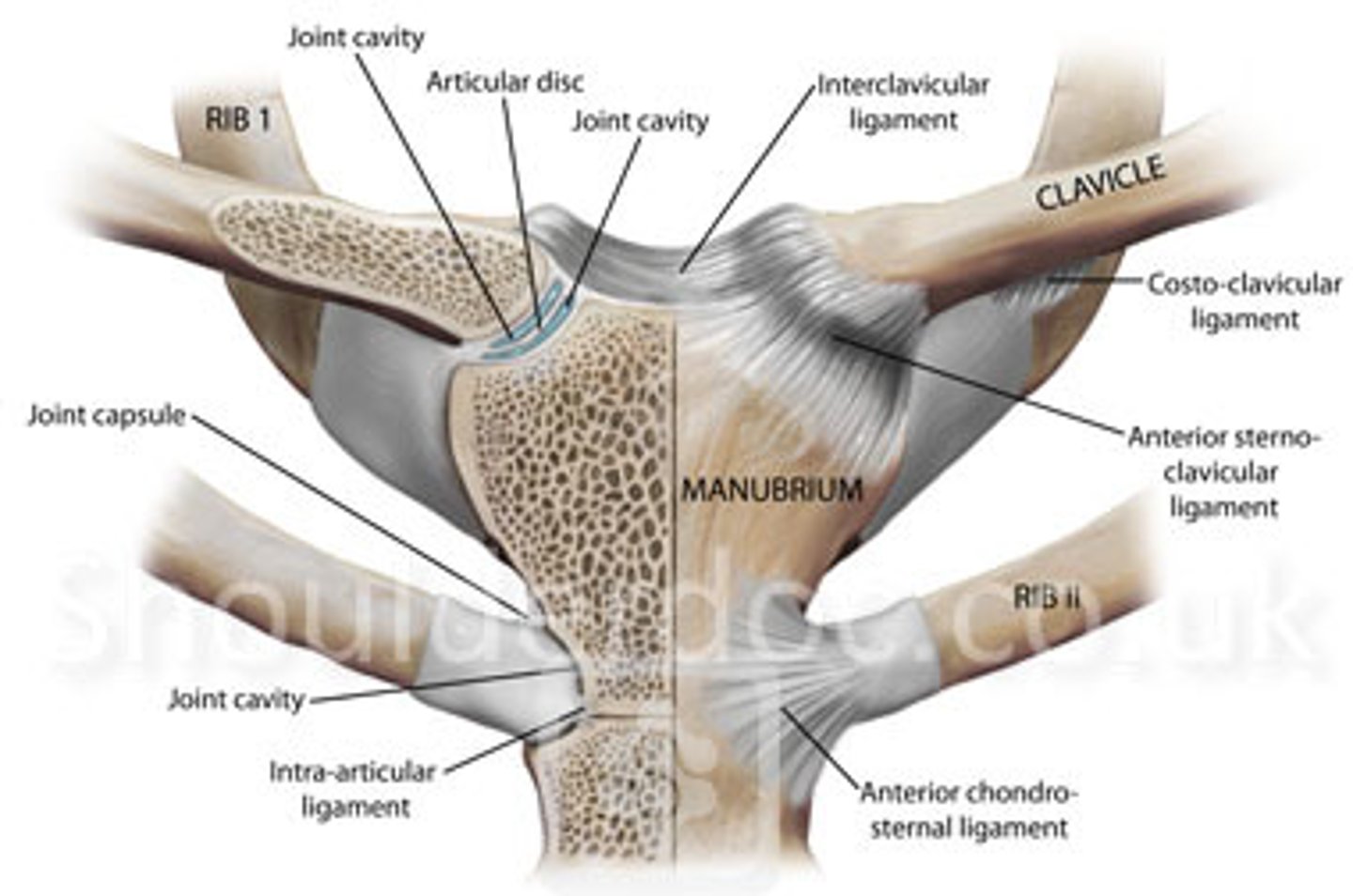
What are the supporting ligaments of the Sternoclavicular joint?
TQ- asked as "all of the following support the SC joint except...)
- anterior sternoclavicular
- posterior sternoclavicular
- interclavicular
- costoclavicular ligaments
the first sternochondral joint is classifies as ___________________?
What are the supporting ligaments
- cartilaginous synchondrosis joint
- anterior/posterior radiate sternocostal ligaments
What is the only rib-sternum articulation that is not synovial, but is separated by hyaline cartilage? (cartilaginous synchondrosis joint)
first sternochondral joint
What is the difference between true and false ribs
true; attch directly to sternum
False: attach indirectly to sternum
which rib articulating joint has 2 synovial cavities? (100% TQ- watch for tricky wording)
Second sternochondral joint
which joint has 2 synovial cavities and does NOT articulate with the ribs?
sternoclavicular joint
the ____________________ ligament attaches fibrous capsule to the manubrium symphysis in the second sternochondral joint, forming 2 synovial cavities. TQ
interarticular ligament
what is the classification and supporting ligaments of the second sternochondral joint
- synovial plane joint
- anterior/posterior radiate sternocostal ligaments
What is the classification of the sternochondral joints for Ribs 3-7?
What are the supporting ligaments?
synovial plane joints
anterior/posterior radiate sternocostal ligamentsw
what is the classification of the interchondral joint? What are the supporting ligaments?
synovial plane (diarthrosis arthrodial ) joint
anterior/posterior interchondral ligaments
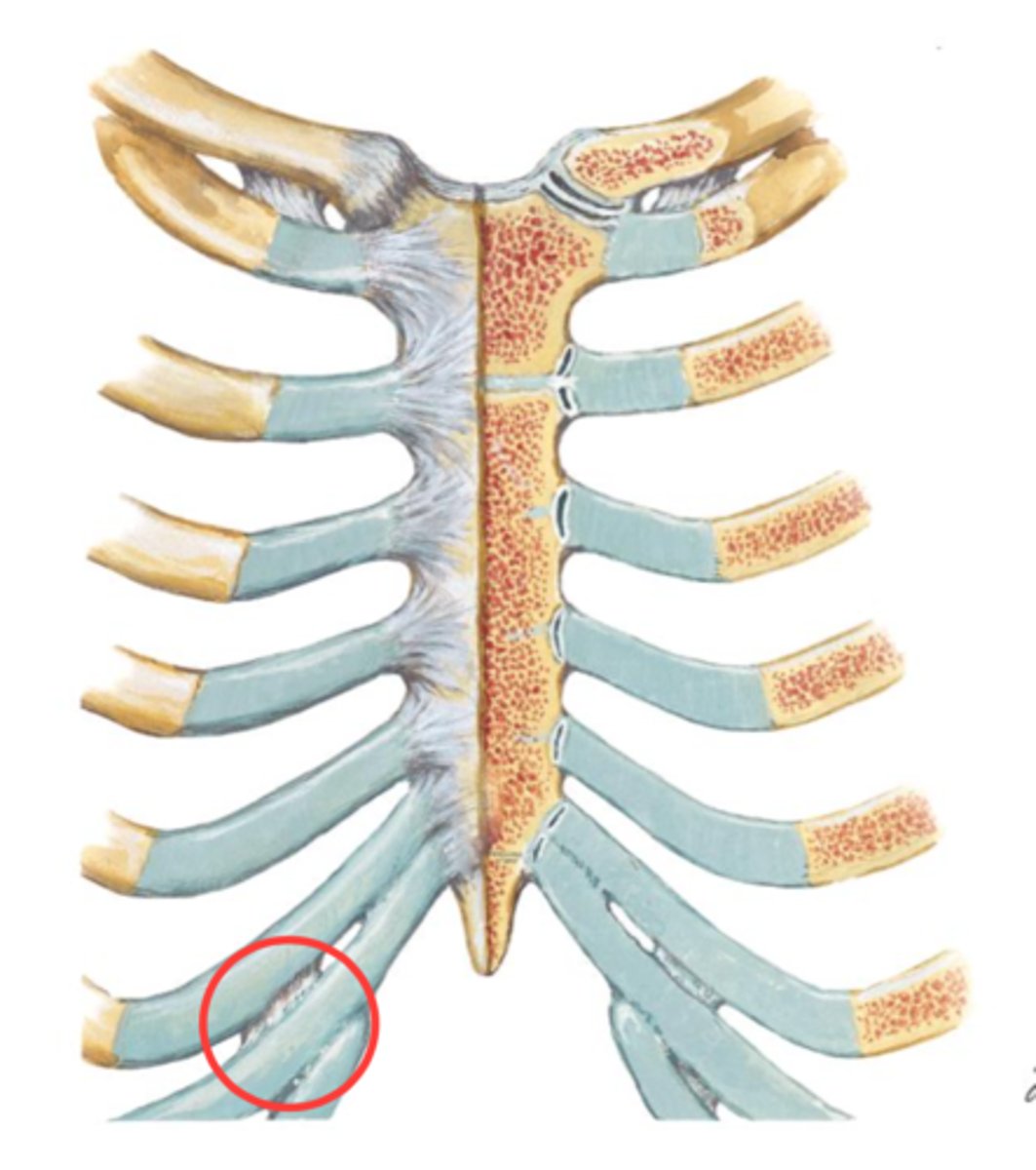
where are interchondral joints located (TQ)
between 5th-7th costal cartilages
the manubriosternal joint forms the ____________ of ___________
angle of Louis
which ribs participate in the sternocostal joint?
only ribs 1-7
what is the joint classification of the costochondral joint?
cartilaginous (amphiarthrosis) synchondrosis
(remember, hyaline cartilage= synchondrosis)
what is the classification of the interarticular ligament at the second sternocostal joint?
Fibrous (amphiarthrosis) syndesmosis
What are the true and false ribs?
True: Ribs 1-7, connect directly to sternum
False: ribs 8-12, do not connect directly to sternumw