Short Run Aggregate Supply
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
Short Run definition
At least one factor of production is fixed (usually capital), meaning that we can't easily increase or decrease the amount of that specific input in our economy or move it between different uses
Short Run Aggregate Supply
SRAS is the relationship between real GDP and the price level.
There is a positive relationship between the price level and real GDP in the short-run.
To produce more in the short-run, firms are unable to hire more capital, so they have to hire any extra workers, or ask the existing workforce to work more intensively (e.g. through overtime).
This is costly as existing workers require extra overtime pay, and new workers require higher wages to encourage them to join the labour force. This will result in firms raising prices.
Factors affecting the SRAS
Any change that will affect the costs of production for all firms in an economy will affect SRAS. These include:
Price of raw materials, e.g. oil, food, metals
Cost of labour, (wages, taxes, regulation)
Levels of tax and subsidies
Exchange rates
SRAS curve definition
The SRAS curve graphs the relationship between actual real GDP and the price level.
SRAS curve diagram
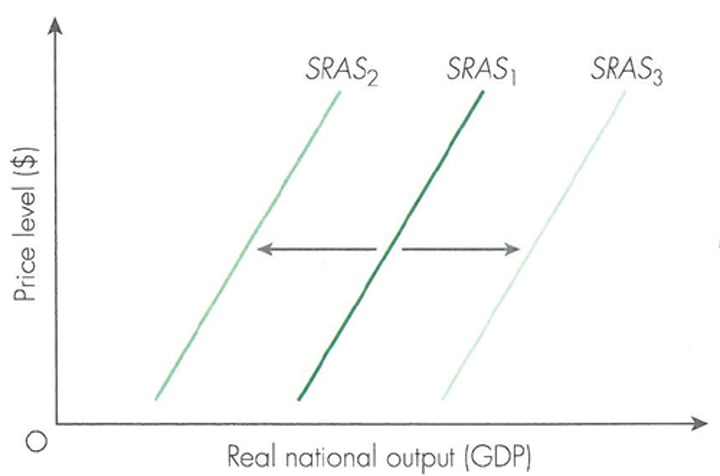
Why is the SRAS Curve upward sloping?
As output rises, free labour becomes more scarce, driving up wages. Firms must charge higher prices as a result, to pay for the increasing wages.
Movements Along the SRAS Curve
Correspond to changes in price level
A fall in the price level leads to a contraction in SRAS
A rise in the price level leads to an expansion in SRAS
Shifts of the SRAS curve
Correspond to shocks that directly or indirectly affect the level of the costs of production
Changes in costs of raw materials and energy
Changes in (indirect) tax rates
Changes in exchange rates