oral diagnosis and treatment planning (chapter 28)
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
To make an accurate dental diagnosis…
…. Review medical/ dental history and concerns, diagnostic procedures and thorough exams, treatment plan
Visual evaluation
examination of areas like the face, lymph nodes, TMJs , neck, lips, soft tissue within the mouth, tooth structure, restorations, and missing teeth.
Palpation
examination technique using your fingers and hands to feel texture, size, and consistency of the hard and soft tissue
What dental instruments are used to examine the teeth and surrounding tissues
Explorer, probe and dental mirror
Probe
Instrument used to detect periodontal disease
Explorer
Instrument used to detect imperfections in exposed surfaces of the tooth
Digital diagnostics
Used to identifying carious lesions, defective restorations, periodontal, pathologic and developmental conditions including other abnormalities
Dental photography
Used to provide the dentist and patient with a visuals of identifying and understanding specific problems
Describe anatomic tooth diagram
illustration that resembles the actual crown and root of the tooth
Describe geometric tooth diagram
Illustration where the circle represents each tooth and is divided to represent each tooth surface
What are the three types of tooth numbering systems
Universal, ISO and Palmer
What does the color code RED indicate in charting
treatment that needs to be completed
What does the color code BLUE/ BLACK indicate in paper charting
treatment that has been completed
What does the color code LIGHT BLUE indicate in digital charting
treatment that has been completed at another office
What does the color code DARK BLUE indicate in digital charting
treatment that has been completed at current office
Class 1 cavity
located in pits and fissures of the occlusal surfaces of premolars and molars
Class 2 cavity
located in interproximal surfaces of premolars and molars
Class 3 cavity
Located in interproximal surface and of incisors and canines
Class 4 cavity
Located in interproximal surface and incision edge of incisors and canines
Class 5 cavity
Located in gingival third
Class 6 cavity
Located in incisal edges and cusp tip of premolars and molars
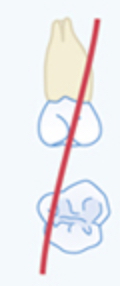
One Line crossed
To be extracted
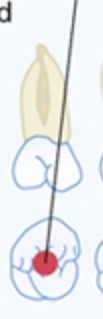
Shaded circle on occlusal surface
Class 1 cavity (chart)

Diagonal lines so all surfaces
Gold crown
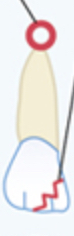
Zigzag line and circle near apical
Fracture and abscess
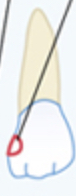
Circle on interproximal surface
Class 3 cavity (chart)

Shaded MOD cavity with outline
Amalgam restoration (MOD) with recurring caries

Circled tooth/ eeth
Impacted teeth
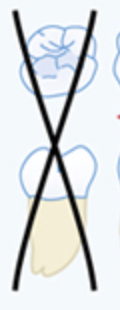
X on teeth/ tooth
Missing teeth

Arrow pointing
Drifting
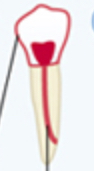
Outlined tooth with Shaded dot in crown and line in root
Post and core
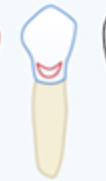
Circle on gingival third
Class 5 cavity (chart)
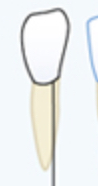
Outline of tooth
Veneer
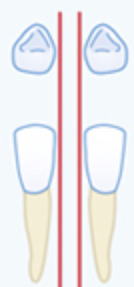
vertical lines between teeth
Diastema
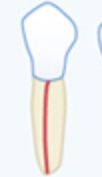
Line in root
Root canal
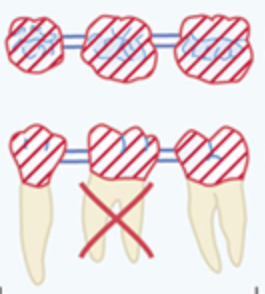
Diagonal likes in crown with in the middle tooth
Fixed bridge