Periodontal Ligament
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Periodontal ligament
Cell-rich, fiber-rich dense CT between root surface of tooth and alveolar bone proper
Binds cementum to alveolar bone
Continuous with the CT of gingiva at crest of the alveolar bone
Contains fiber bundles
Supportive function of PDL
Pain and pressure
Sensory function of PDL
Maintains width of 2 hard tissues
Homeostatic function of PDL
Fibroblasts
Cementoprogenitor cells
Osteoprogenitor cells
Epithelial cells
Undifferentiated mesenchymal cells
Macrophages
Leukocytes
Cells of the PDL
Fibroblasts
Prinicipal cells of the PDL
Densely packed, spindle or flat disk-shaped
Long ovoid nuclei
Numerous cytoplasmic processes of various length
The cytoplasm contains abundance of organelles associated with protein synthesis & secretion
satisfy functional demands required to change in shape & migrate
Cementoprogenitor and Osteoprogenitor cells
Found exclusively in those sections of the PDL adjacent to cementum and bone
Closely resemble inactive fibroblasts
Cementoblasts
Cementoclasts
Osteoblasts
Osteoclasts
Undifferentiated mesenchymal cells
Progenitor cells
Located within 5 μm of blood vessels
Source of new cells for the PDL
Apoptosis — physiologic cell death
Macrophages
Defense cells
Phagocytic activity
bacteria, dead cells, foreign bodies
Leukocytes
Special lymphocytes and plasma cells may appear in the PDL when stressed by disease
Alveolar crest group
Horizontal fiber group
Oblique fiber group
Apical fiber group
Interradicular fiber group
Principal collagen fibers of the PDL
Oxytalan fiber
Elaunin fiber
Immature elastin fibers of the PDL
Collagen fiber
Predominantly present in the fiber system
Basic component: collagen fibrils
Mix of type I & type III individual fibrils having an average diameter of 55 mm
Several fibrils become arranged parallel with one another to form a fibril bundle
Fibers within fiber bundle are not parallel with each other but are interwoven
parallel
Several collagen fibers become arranged _____ to form a fibril bundle
interwoven
Arrangement of fibers within fiber bundle
Dento-alveolar group
Fiber apparatus that made up the principal fiber bundles
Arranged in orderly fashion running from cementum to alveolar bone
Alveolar crest group
Attached to the cementum just below the CEJ
Running downward & outward to insert into the rim of the alveolus
Function:
resist vertical and intrusive force
anchor the tooth to the alveolus
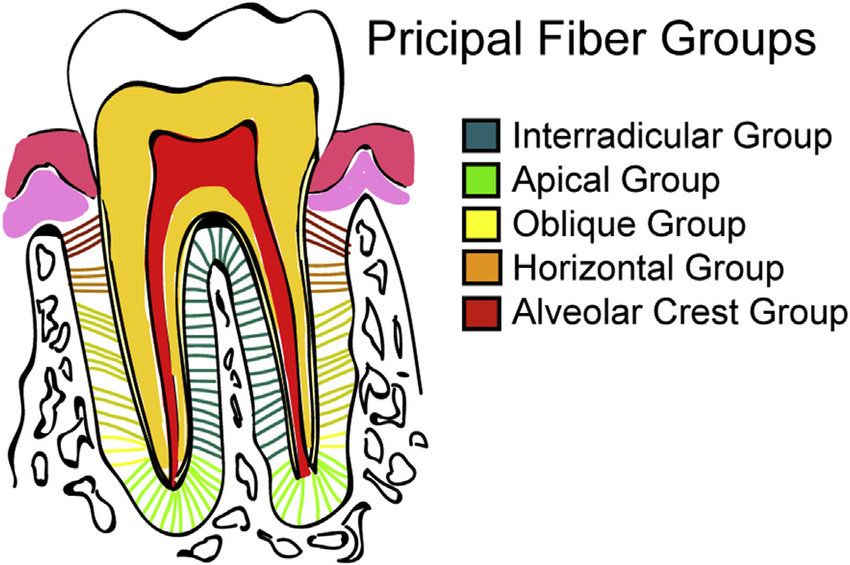
Resist vertical and intrusive force
Anchor the tooth to the alveolus
Function of alveolar crest group
Horizontal fiber group
Found immediately apical to alveolar crest at right angles to the long axis of the tooth
Run horizontally from cementum to bone
Function:
resist horizontal and lateral pressure applied to the tooth crown
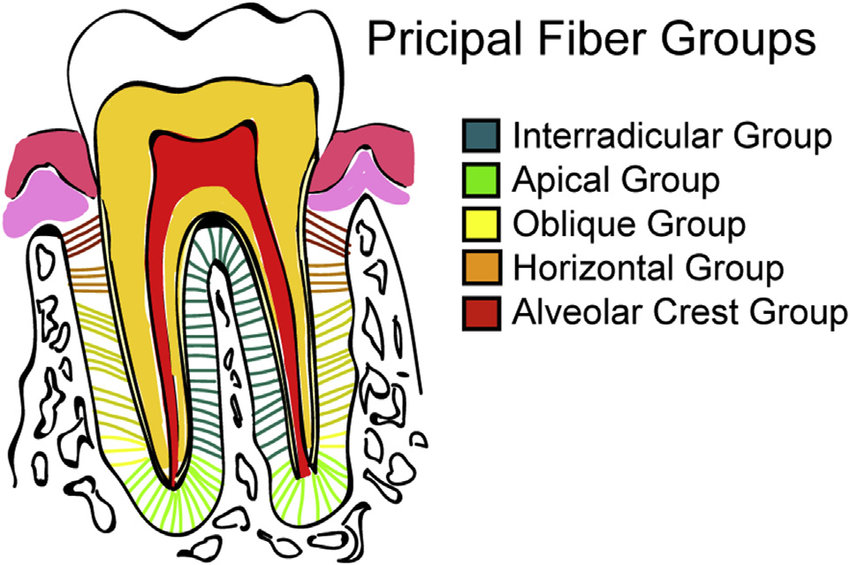
Resist horizontal and lateral pressure applied to the tooth crown
Function of horizontal fiber group
Oblique fiber group
Most numerous and largest fiber group
Run from cementum in an oblique direction to insert into bone coronally
Function:
Sustain occlusal forces
Resist intrusive masticatory forces (similar to ACG)
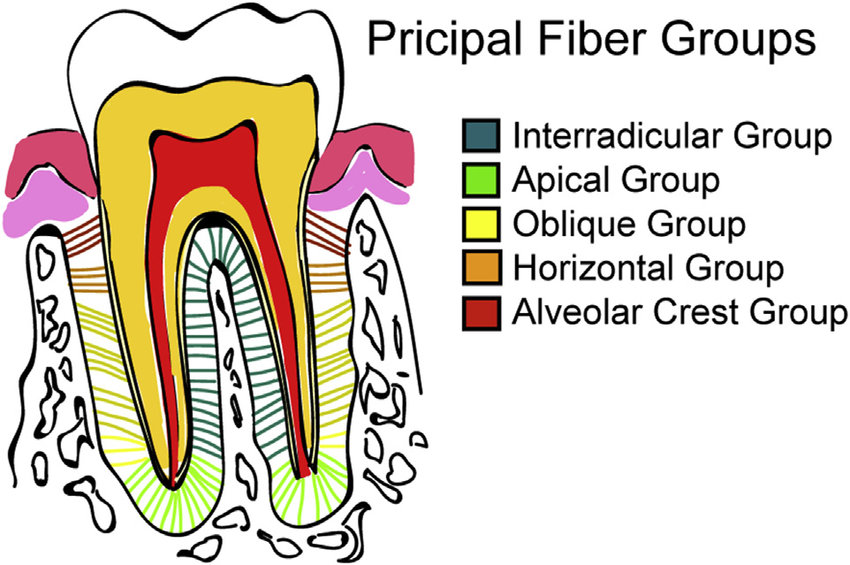
Sustain occlusal forces
Resist intrusive masticatory forces
Function of oblique fiber group
Apical fiber group
Radiating from cementum around the apex of the root of the bone
Found at the base of the socket
Function:
Prevents vestibulo-oral tipping
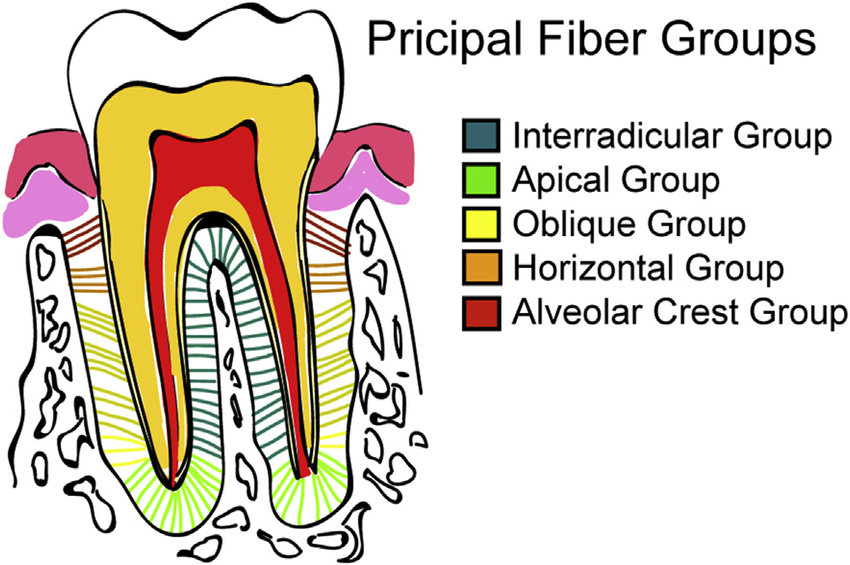
Prevents vestibulo-oral tipping
Function of apical fiber group
Alveolar bone proper
Tooth socket is aka _____
Interradicular fiber group
Found only between roots of multirooted tooth
Run from cementum into bone forming the crest of the interradicular septum
Function:
Resists tipping and torque (rotation)
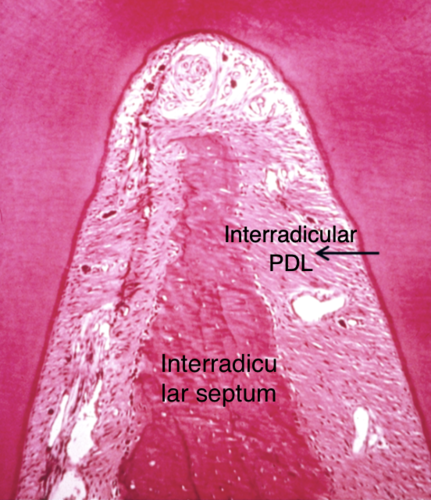
Resist tipping and torque
Function of interradicular fiber group
Circular fiber group
Part of gingival fibers
Encircle the tooth with free gingiva
Keeps free gingiva against tooth and keeps it from receding
Sharpey’s fiber
Embedded portion of PDL fibers in the cementum or bone
Periodontal ligament
Permit the individual tooth a certain degree of mobility
Periodontal space
PDL is located in the _____
middle root
PDL is narrower at the _____
0.10-0.38 mm
PDL width
Loss of function
Results to smaller PDL & its fiber bundles become thinner and atrophic
Attrition
As a person ages, the contact point becomes larger because of _____
Radiolucent
Appearance of PDL in x-ray
thickened
By function, PDL should be _____
Transseptal
Gingival fiber group
Cervical tooth to tooth mesial/distal to it
Resists tooth separation (mesial-distal)
Attached gingival
Gingival fiber group
Cervical tooth to attached gingiva
Resist gingival displacement
Free gingival
Gingival fiber group
Cervical tooth to free gingival
Resist gingival displacement
Circumferential
Gingival fiber group
Continuous around neck of tooth
Resist gingival displacement
Interstitial space
Found in between groups of fibers
Contain network of blood vessels, nerves, & lymphatics & loose CT cells
Interstitial indefinite tissue
Maintain the vitality of PDL
Also contains network of finer fibers interlaced and support the dense collagen bundles
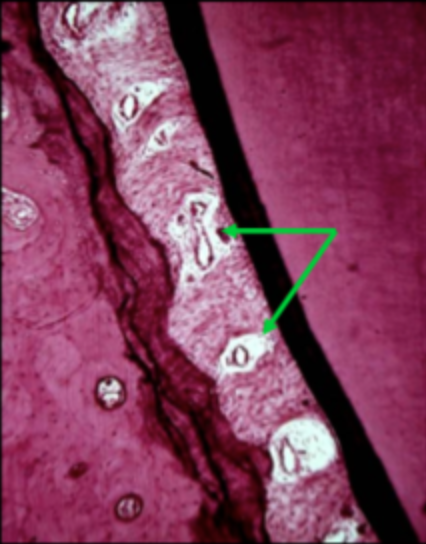
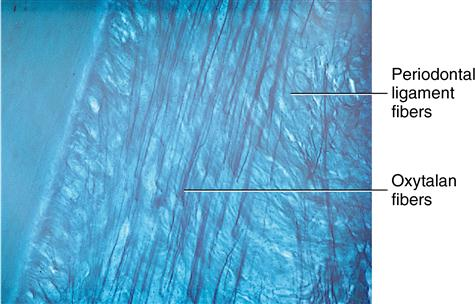
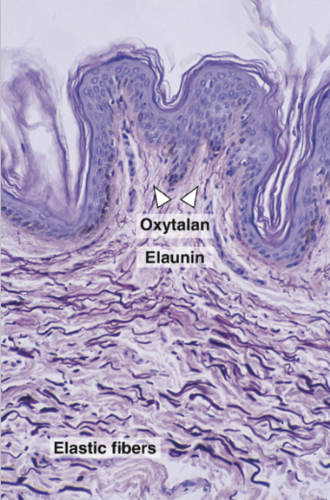
Oxytalan fibers
Bundles of microfibrils
Resemble elastic fibrils
Intertwined lengthwise to form fiber
Acid resistant
Insert into the cementum especially at the cervical region
Elaunin fibers
Embedded within a small quantity of elastin forming a network
Together with oxytalan fibers - form a meshwork extending from cementum to bone & sheathing the collagen fiber bundles
Reticular fibers
Aid in the support of blood and lymphatic vessels & nerves
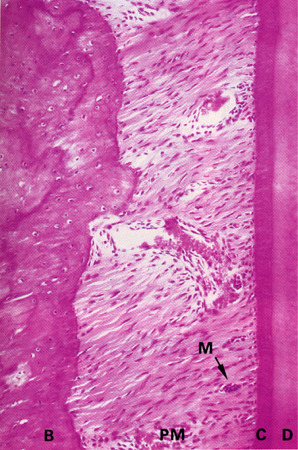
70% water
Glycosaminoglycans
Glycoproteins
Glycolipids
PDL ground substance
Glycosaminoglycans
Ligament dermatan sulfate (principal)
Plays an important role in ligament function
Superior and inferior alveolar arteries and veins
→ Dental artery
→ Interalveolar and interradicular arteries
→ Periosteal arteries
Vascular supply of PDL
Somatosensory
Superior & inferior dental plexus
Free nerve endings
Ruffini corpuscles
Coiled endings
Encapsulated spindle type ending
Autonomic system
Nerve supply of PDL
Alveolar bone proper
Where sharpey’s fibers are embedded in
Dental follicle
All periodontal tissue are derived from _____
Alveolar clade
Fibroblasts and osteoblasts
Cemental clade
Fibroblasts and cementoblasts
Closing the apical foramen to prevent infection of surrounding tissues (PDL)
What is apexification?
Calcium hydroxide
can help with apexification
can stop caries progression bc it can encourage dentin formation
recede because tertiary dentin develops
What will happen to pulp horns if calcium hydroxide is placed in a cavity without pulp exposure?
Canals of Zuckerkandl and Hirschfeld
Nutrient canals/perforating canals
Channels in the interdental and interradicular septa that house interdental and interradicular arteries, veins, lymph vessels, and nerves
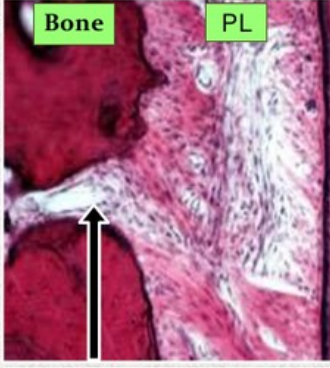
Canals of Zuckerkandl and Hirschfeld
What makes the vascular supply of PDL rich?
Mesial migration/physiologic mesial drifting
Periodontal space becomes narrower
Functional stresses → thicker periodontal fiber bundles & less interstitial tissue (loss of function)
PDL in permanent mandibular canine become thinner with age
Physiologic changes (PDL)
Cysts/tumors
Infections
Excessive orthodontic movements
Examples of pathologic conditions/changes