MSK - Disorders of Pigmentation
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
LOs - (1) Describe the clinical characteristics of the hyperpigmentation disorders acanthosis nigricans, lentigo, melasma, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. (2) Describe the clinical characteristics and pathophysiology of the hypopigmentation disorders albinism and vitiligo. (3) Describe the synthesis of melanin.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Melanin
Determines the color of skin and hair
pigment produced by melanocytes to show color of skin and hair
People can have too much melanin (hyperpigmentation) or too little melanin (hypopigmentation)
genetic variations will produce melanin which cause difference in skin color and hair from person to person
UV radiation can also stimulate melanocytes to produce more melanin, which can cause “tanning”
Two major types of melanin in the skin
Eumelanin - responsible to produce brown or black color
Pheomelanin - responsible for a yellow or red color
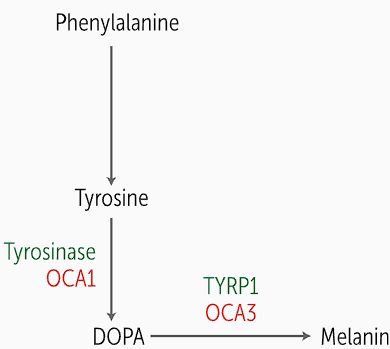
Melanin is produced by melanocytes located in ; melanin pathway
the basal layer of the epidermis, created from phenylalanine (Phe) which is converted in tyrosine
Phe is converted into tyrosine and then tyrosinase oxidase turns tyrosine into DOPA, which is the rate limiting step
DOPA will be converted to melanin through multiple steps including tyrosinase-related protein 1 (TYRP1)
In albinism, tyrosinase is mutated in one form of melanin and TYRP1 is also mutated
Once formed, melanin gets packaged into specialized lysosomes called melanosomes
Melanosomes are responsible for
Defects in this pathway result in
transferring melanosomes into the epidermal keratinocytes
excess or deficient pigment
Two common disorders that lead to absent or reduce pigment
albinism and vitiligo
albinism is a ______ disorder leading to
diffuse hypopigmentation of the skin, hair and eyes
vitiligo leads to __ areas of ; vitiligo is secondary to
hypopigmentation; abnormal immune regulation, leading to autoimmune attack on melanocytes
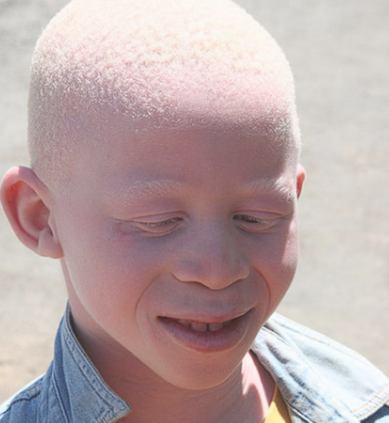
Albinism refers to defect in normal synthesis of ____, leading to
albinism; white hair, pale skin, eyes and poor eyesight
Oculocutaneous albinism (OCA) is what most patients have, invoving
hair, skin and eyes — this is different from ocular albinism which is an X linked hypopigmentation disorder restricted to the eyes
Almost all types of albinism are inherited in
an AR pattern. Different gene defects can cause oculocutaneous albinism (OCA)
Enzymes relating to OCA1, OCA2, OCA3, OCA4
OCA1 — tyrosinase
OCA2 — P protein
OCA3 — TYRP1
OCA4 — membrane associated transport protein
Albinism is associated with another AR syndrome known as and explain pathophys
Chediak-Higashi syndrome, which is an immunodeficiency disorder that causes frequent infections in children, neutropenia (reduced PMNs), recurrent infections, neuro abnormalities, peripheral neuropathy, coagulation defects and lymphohistiocytosis — abnormal immune activation or infiltration or macrophages and lymphocytes
Due to mutation in CHS1/LYST gene, which causes defective lysosomal trafficking regulation; melanosomes and lysosomes are dysfunction, which leads to albinism
Characteristics of Chediak-Higashi - PLAIN
Progressive neurodegeneration
Lymphohistiocytosis (abnormal infiltration of macrophages and leukocytes)
Albinism (partial)
Recurrent pyogenic Infections (due to neutropenia)
Peripheral Neuropathy
Vitiligo is an autoimmune skin disorder that causes destruction of
melanocytes in the epidermis, causing depigmented macules and patches

Vitiligo is an acquired condition, unlike albinism, and it due to
destruction of innate immune response, which causes an autoimmune destruction of melanocytes
Vitiligo is associated with other ___ disorders like
autoimmune ; endocrine disorders like hypothyroidism and type 1 diabetes
Vitiligo lesions are asymptomatic ____ and ____ type lesions
macule and patch with irregular borders
Vitiligo can impact mental health as it often presents on the
face, hands and genitals, leading to anxiety, especially in Black + Brown populations
Clinical course of vitiligo is unpredictable, patients can undergo periods of
progression, stabilization and re-pigmentation
First line treatment for vitiligo and severe cases
Topical glucocorticoids and phototherapy; immunosuppressive agents
The deadliest hyperpigmented lesion is
malignant melanoma, a form of skin cancer
Acanthosis Nigricans, pigmentation disorder
Hyperpigmentation with velvety plaques, usually in the axilla and posterior neck. Has regular borders
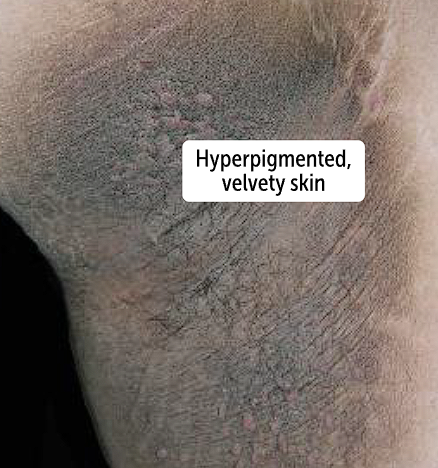
Acanthosis nigricans can be present due to an underlying disease such as the following 3 causes
metabolic syndrome —> Acanthosis nigricans is associated with obesity and type 2 DM due to insulin resistance, which could be due to high levels of insulin causing skin findings like velvety, hyperpigmented plaques in axilla and posterior neck
Paraneoplastic syndrome and gastric adenocarcinomas are highly associated
Medications can cause acanthosis which are sometimes used for diabetes treatment such as insulin and glucocorticoids
Acanthosis can be genetic but
secondary causes should be ruled out before making diagnosis
Lentigo will lead to darkened
skin lesions which are macules, that are hyperpigmented, flat, and <1 cm wide
resemble lentils and looks like big freckles
The hyperpigmented macules are known as lentigines, with a circular sharp border
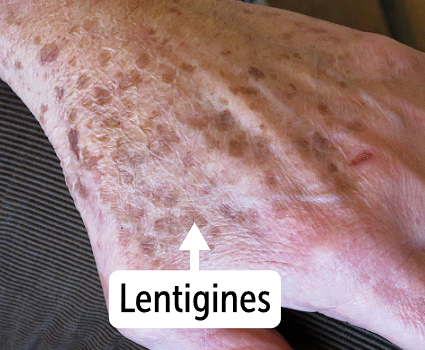
Lentigines are the hyperpigmented macules that are flat and less than 1 cm, caused in Lentigo
Simple vs solar types
Simple lentigines are small, benign, <5mm, tan to brown macules that are often seen in children and can form on mucosal surfaces
Solar lentigines are found on sun-exposed regions of the body, which means solar lentigines can cause a multitude of solar lentigines and are called liver spots sometimes
More common in older patients
Melasma, hyperpigmentation
benign disorder of hyperpigmentation that results in brown or tan macules and patches, primarily on the face.
major concern is cosmetic disfigurement
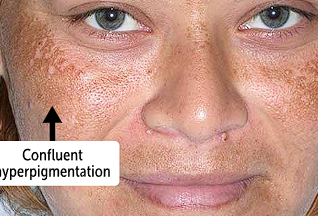
Sun exposure and melasma
Sun exposure worsens melasma because it stimulates production of melanin from melanocytes, which can cause progressive darkening of the skin
More common in women and starts occurring after puberty
Melasma is called the mask of pregnancy
50% of melasma patients are due to pregnancy or hormonal contraception, and women tend to have their melasma worsen
Both of these situations cause increase levels of female hormones
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation
benign syndrome of pigmentation that often leads to cosmetic concerns. It occurs after an episode of inflammation such as acne, psoriasis, burns, or trauma
The inflammation is due to release of cytokines which force development of the lesions seen
Lesions will have deposits of excess melanin in the epidermis
Excess melanin gets deposited in macrophages of dermis, called pigment incontinence
Those with darker skin are at an increased rate of getting this due to higher melanin content in skin
A 31-year old woman presents to her primary care physician with complaints of skin darkening over the cheeks of her face. Detailed history taking elicits that the patient also has been experiencing amenorrhea, nausea, and breast tenderness over the past 2 months. Physical examination shows nontender, 4- to 6-cm brown macules on the face. Which of the following diagnoses is most likely?
Which of the following pigmentation disorders most likely has an autoimmune component involved in its pathogenesis?
Which pigmentation disorder would be best described as a velvety plaque?