Chapter 1 Content
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Plasma Membrane
The periphery of the cell, separating its contents from the surroundings
composed of lipid and protein molecules that form a thin, tough, pliable hydrophobic bilayer.
barrier to the free passage of inorganic ions and most other charged or polar compounds
Transport Proteins
allow the passage of certain ions and molecules
Receptor proteins
transmit signals into the cell
Membrane Proteins
participate in some reaction pathways
All cells have
a nucleoid/nucleus that replicates cells
Eukaryotes
Double membrane
bigger
membrane-enclosed organelles: mitochondria, chloroplasts, lysosomes
The compartmental segregation of energy-yielding and energy-consuming reactions helps cells to maintain homeostasis and stay away from equilibrium
Prokaryotes
no nuclear membrane
Aerobic Environment
plentiful supply of oxygen
some resident organisms derive energy from the trasnfer of electrons from fuel molecules to oxygen within the cell
Anaerobic Environment
devoid of oxygen
microorganisms adapted to these environments get energy by transferring electrons to nitrate (makes N2), sulfate (makes H2S), or CO2 (makes CH4)
many die when exposed to oxygen: obligate _____
Facultative Anaerobe
can live with or without oxygen
Phototroph
trap and use sunlight as an energy source
Chemotroph
get energy from the oxidation of chemical fuel
some oxidize organic fuels: HS to S^0 (elemental sulfur), S^0 to SO4-, NO2-, NO3-, or Fe2+ Fe 3+
Autotrophs
can make all of their biomolecules from CO2
Heterotrophs
need organic nutrients from other organisms
Cyanobacteria
photoautotrophs
Chemoheterotrophs
Humans
Gram-Positive Bacteria
colored by Gram’s stain
thick layer of peptidoglycan outside plasma membrane
lack other membrane
Gram-Negative Bacteria
have an outer membrane made of a lipid bilayer - inserted lipopolysaccharides and proteins called porins that provide channels for diffusion of low molecular weight compounds and ions across this outer membrane
Nucleoid
contains single smaller, circular molecule of DNA
Endoplasmic Reticulum and Golgi Complex
play central roles in the synthesis and processing of lipids and membrane proteins
Peroxisomes
where very-long chain fatty acids are oxidized
Lysosomes
filled with digestive enzymes to degrade unneeded cellular debris
Three Types of Cytoplasmic FIlaments
actin filaments
microtubules
intermediate filaments
Endomembrane System
segregates specific metabolic processes and provides surfaces in which certain enzyme-catalyzed reactions occur
Four Most Abundant Elements in Living Organisms
Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, and Carbon
Macromolecule
polymers with molecular weights above ~5000 made from relatively simple precursors
Proteome
The sum of all the proteins functioning in a given cell
Genome
the entire sequence of a cell’s DNA
Glycome
its entire complement of carbohydrate-containing molecules
stereoisomers
diff physical properties
Geometric Isomers (cis-trans isomers)
differ in the arrangement of their substituent groups with respect to the nonrotating double bond
different physical and chemical properties
Enantiomers
have identical physical properties (except with regard to polarized light) and react identically with achiral reagents
Diastereoisomers
different physical and chemical properties
Number of Stereoisomers
2^n
(n = chiral centers)
Optically Active
Molecule:
one chiral center
doesn’t have an internal plane of symmetry
Mixture:
pure - need to be all R or S
NOT RACEMIC; majority one configuration
Oxidation of Glucose
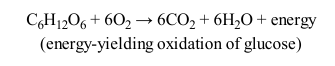
Change in Gibbs Free Energy
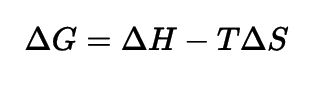
Hexokinase Reaction
First step of Glycolysis
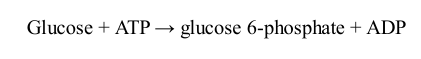
Standard Free Energy Change Equation
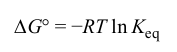
Reaction 1 of Glycolysis
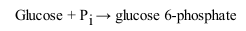
Reaction 2 of Glycolysis
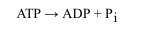
Reaction 3 of Glycolysis

Increasing
The entropy of the world is constantly ____
Glucose Reaction