Animal and Plant Cells: Organelles, Functions, Labelling
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
17/9/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Cell Theory
All living things are made up of on or more cells and their products
Cells are the simplest unit that can carry out all life processes
All cells come from other cells
prokaryotes
pro rhymes with no: no nucleus
the simplest organism: a single-celled organism
archaea, bacteria
eukaryotes
eu rhymes with do: do have a nucellus
single-celled or multicellular organisms
protists, fungi, animal and plants
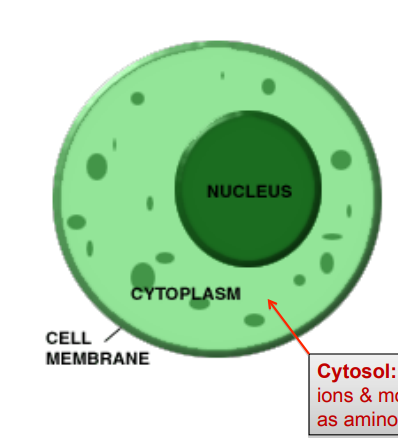
cytoplasm SFOCCRM
the fluid inside cell’s membrane and outside nucleus
all organelles suspended in cytoplasm
contains water and cytosol: fluid made of ions and molecules like amino acids, ATP
site of many chemical reactions
Give cell its structure
allow organelles to move around
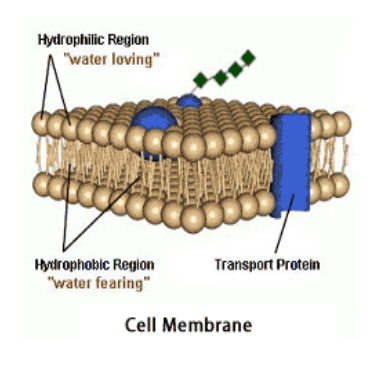
cell membrane
cell plasma membrane
Phospholipid bilayer containing proteins, cholesterol (lipids) and carbohydrates
has a hydrophilic and hydrophobic region
Separates cell contents from the environment; regulates movement of substances into and out of the cell
semi-permeable membrane: allows some substances in and keeps others out
nucleus NECM
Membrane bound spherical structure
Control centre: contains genetic information that controls all cell activities stored on chromosomes that contain DNA
has chromatin: DNA in a compact dense structure to fit inside nucleus
DNA is copied when cell divides to ensure each cell has a full set of chromosomes
surrounded by nuclear envelope/membrane: acts as a physical barrier between nucleus and cytoplasm and allows molecular processes like transport and cell division
mitochondria (singular: mitochondrion)
Membrane bound, bean shaped
mostly protein, but also contain lipids, DNA and RNA
Mitochondrial DNA is passed down from the mother only
Site of Aerobic Metabolism: breaking down substrate into ATP using oxygen
Releases energy from food in the form of ATP
main power source of cell that makes energy available to cell
active cells, like muscle cells, require more cellular respiration so they have more mitochondria
less active cells, like fat storage cells, don’t need to respire as quickly so they have less mitochondria
cellular respiration
mitochondria enzymes convert stored energy (glucose) into usable energy, requiring oxygen and creating waste product of carbon dioxide and water
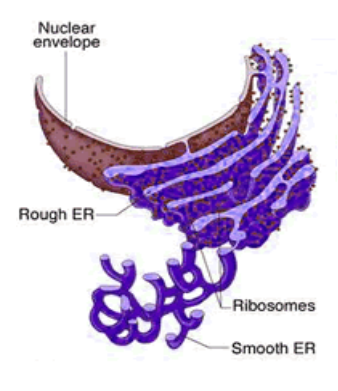
endoplasmic reticulum CHMTM
membrane bound channels of tubes and pockets that extend from cytoplasm to nuclear membrane to cell membrane
transports materials, like proteins, through cells
assists with production and release of hormones in brain
involved with muscle contraction in muscles
composed of rough ER and smooth ER
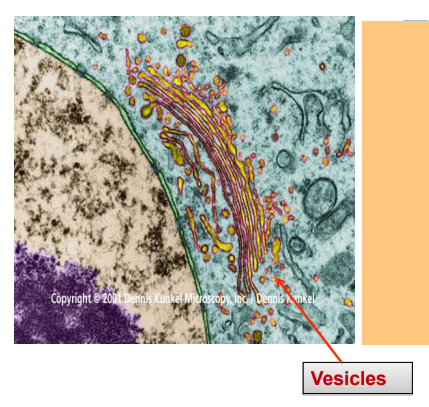
Golgi body PRVMFMF
also called golgi apparatus and golgi complex
Flattened, membrane bound, fluid filled disks, with associated vesicles surrounding the disks
Package proteins, lipids and carbohydrates
collects and processes materials to be removed from cells
makes and secretes mucus
cells that secrete a lot of mucus have a lot of Golgi bodies, like cells in intestine lining
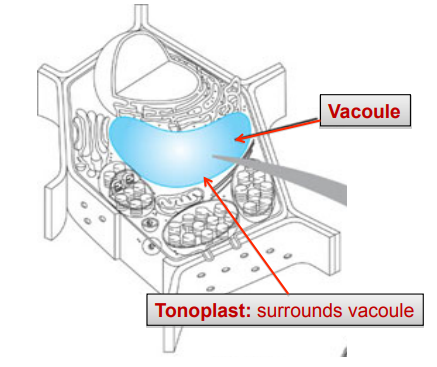
vacoule SWFTSMT
single layer, Membrane bound, fluid-filled sacs
vacuole surrounded by tonoplast
Stores starch & water
supports cell
In plants, involved in turgor pressure
animal cells may have many invisible vacuoles
plant cells usually have a large central vacuole
turgor pressure
pressure exerted by fluid in a cell that presses the cell membrane against the cell wall. A loss of pressure in plant cells causes a loss of water, causing plants to wilt
organelles in plant cells only
cell wall
vacuole (singular)
chloroplasts
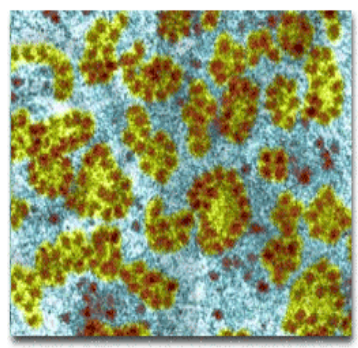
ribosomes
Small spherical bodies free floating in the cytoplasm or attached to ER
made of RNA and protein
Site of protein synthesis
DNA goes from nucleus to ribosome to form protein
lysosomes MEDBDP5
Membrane bound spherical sacs, containing enzymes
pH of approx. 5
Site of digestion and storage of digestive enzymes
Can destroy harmful invaders to the cells
engulfs and breaks down material (recycling and waste material)
stores proteins until they are needed inside/outside the cell
in animal cells
golgi apparatus
process and package protiens and fat molecules
cell wall
Made of cellulose
Freely permeable to water and most solutes
Only in Plant cells
Maintains cell turgidity
Provide mechanical support
Protect from mechanical damage
found just outside of cell membrane
can hold together long after plant dies
used in materials, i.e. textbook paper
singular vacuole
plant cells usually have one main central vacuole
takes up most space in cell
contains water and dissolved solutes that help with turgor pressure
turgor pressure helps keeps plants plump when full of water
cells become soft when turgor pressure drops and leaves and stems becomes limp and droopy until water is replaced
chloroplasts
in plants and cyanobacteria
Used for absorption of light
Site of photosynthesis: a series of chemical reactions resulting in the production of glucose (converted into ATP) and oxygen from sunlight, water and carbon dioxide
has chlorophyll that gives it green colour
rough endoplasmic reticulum PRCT
apart of ER
series of canals that carry material throughout the cell
ribosomes attached to outside
involved in protein synthesis and folding
involved in transportation of lipids and proteins to golgi apparatus
protein → hydrophilic
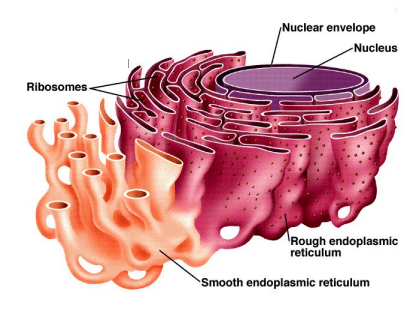
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Ribosomes NOT attached to outside
Transports molecules in the cell
Makes lipids (lipid synthesis)
Stores and releases calcium ions, important for cell function
detoxification: breaks down harmful substances
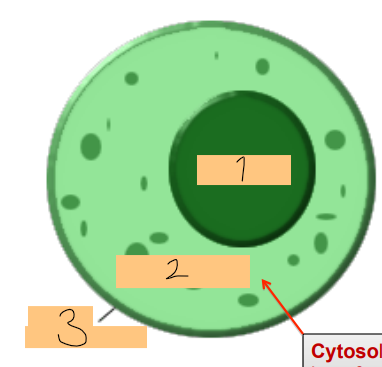
label
1 - nucleus
2 - cytoplasm
3 - cell membrane
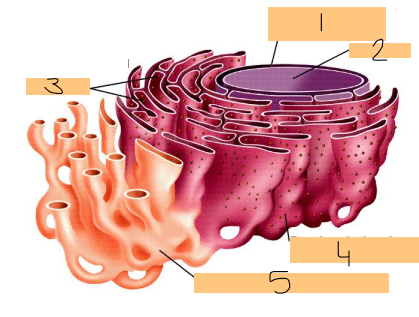
label
1 = nucear envelope
2 - nucelus
3 = ribosomes
4 = rough ER
5= smooth ER
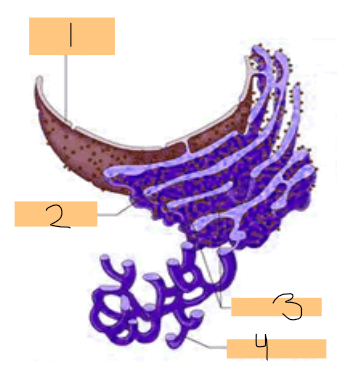
label
1 = nucelar envelope
2 = rough er
3 = ribosomes
4 = smooth er
vesicles
membrane bounds sacs
transport materials between or within cells
“mail”
secretory vesicle: store and transport hormones, neurotransmitters and digestive enzymes
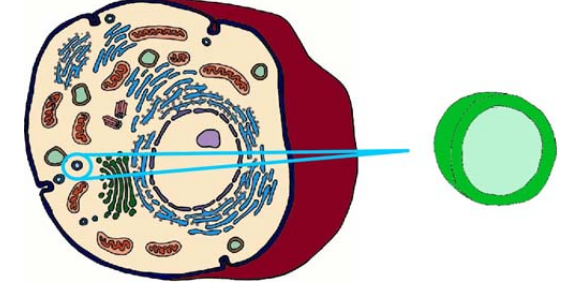
microtubule and microfilament
protein rich rods
microtubules: provide internal support
microfilaments: responsible for contraction of cells for movement of vesicles, granules and cytoplasmic organelles
centrosome: organizes microtubule into cytoskeleton and spindle fibres for cell division
centriole CFSP
Paired cylindrical structures, made of protein
Assist in cell reproduction by producing spindle fibres (a type of microfilament)
Assists in the formation of cilia and flagella

cilia and flagella
Used for movement
Cilia are tiny hair-like projections
Flagella are long tail-like projection
composed of arranged of microtubules
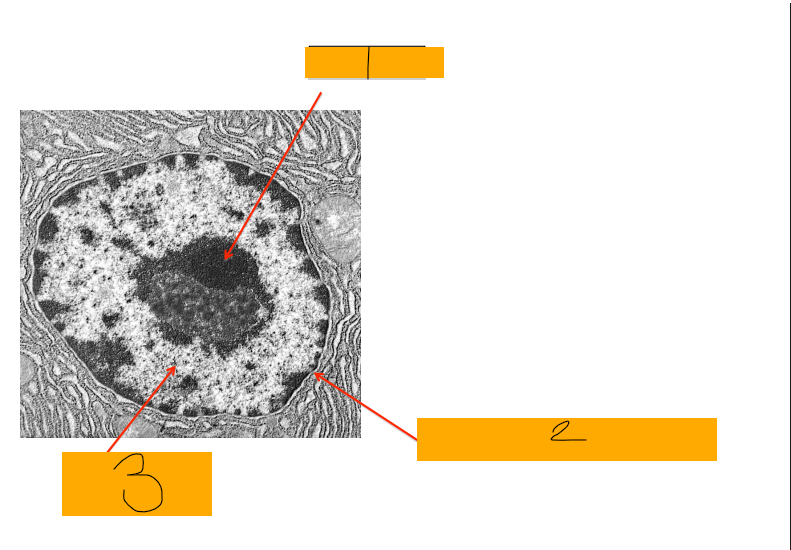
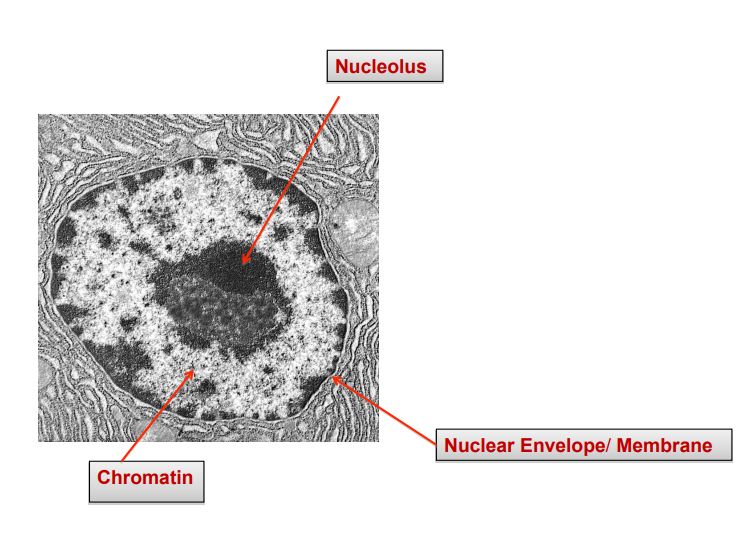
label
the nucleus
1 = nucleolus
2 = nuclear envelope/membrane
3 = chromatin
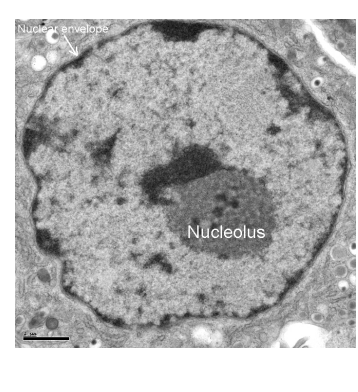
nucleolus RPS
Dense, spherical structure in nucleus
composed of DNA, RNA and protein
Site of ribosome synthesis
nuclear membrane
phospholipid protein bilayer
contains nuclear pores: transport between nucleus and cytoplasm and selective passage (small molecules can diffuse more easily than larger ones)
controls what enters and leaves nucleus
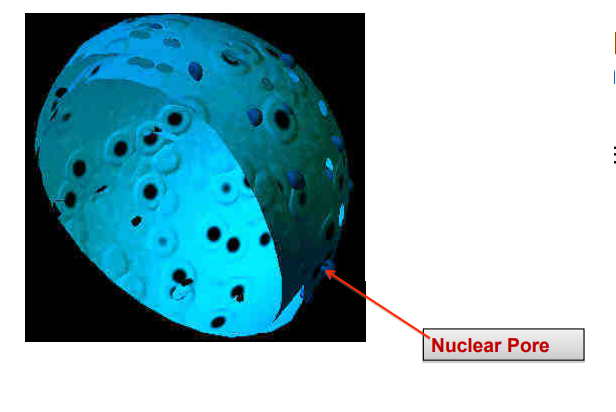
label
nucelar pore
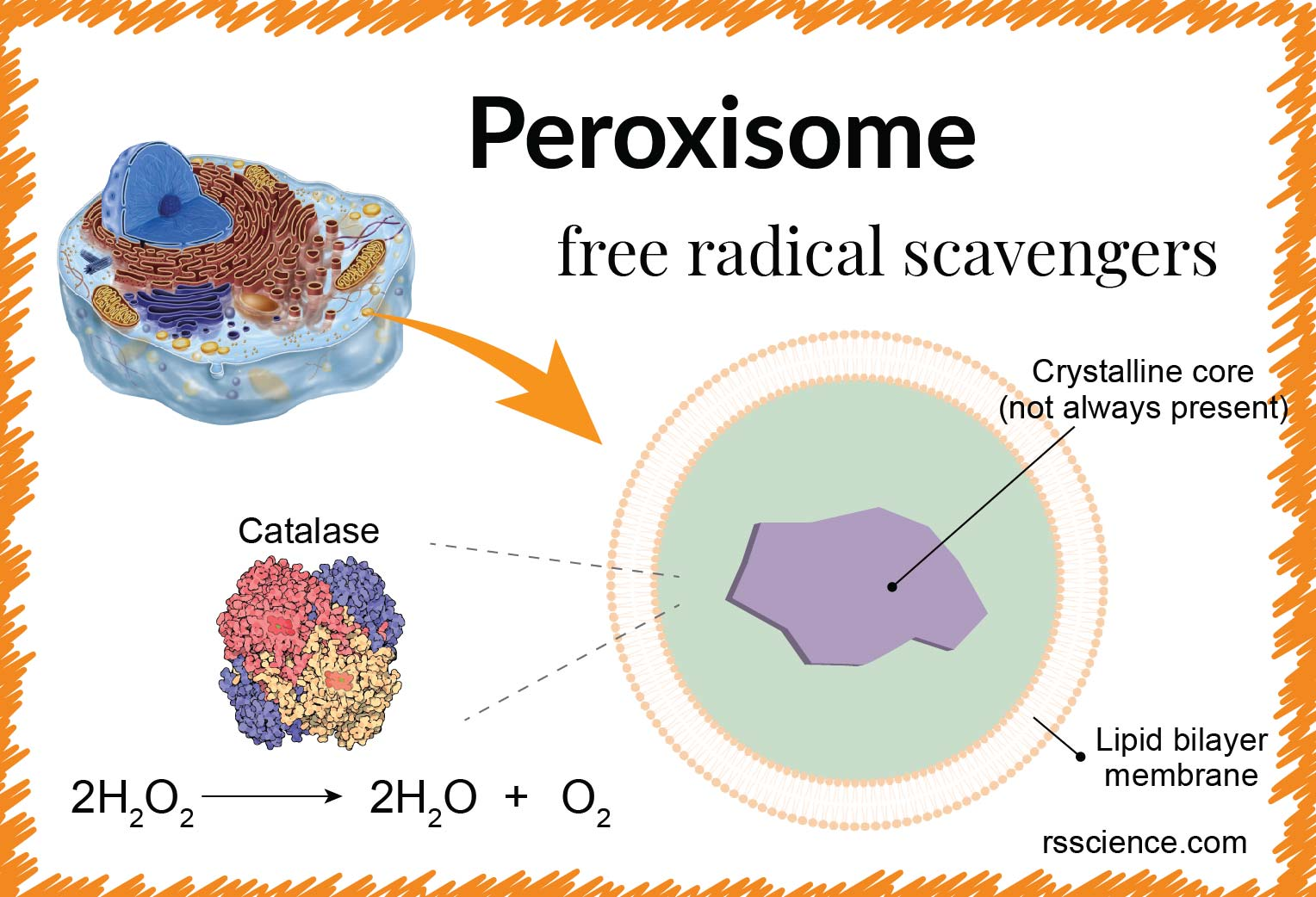
peroxisome
break down long fatty acid chains and other lipids
can also participate in synthesis of lilpids
catalyze oxidation reactions and produce hydrogen peroxide
then quickly break down H2O2 as they contain catalase
cytoskeleton SPAMT
network of protein filaments
provides structural support
maintains cell shape
anchors organelles
facilitates intracellular transport
drives cell movement
plasmodesmata
channels in cell walls of plant cells
allow for molecules and substances to move back and forth as needed
differences between plant and animal cells: cell wall, chloroplast, vacoule size, centrosomes, atp
plant cells: have cell wall, have chloroplast, larger vacuole, no centrosomes, atp produced by chloroplast and mitochondria
animal cells: no cell wall, no chloroplast, small vacoule or absent in some cells, has centrosomes, atp produced only by mitochondria
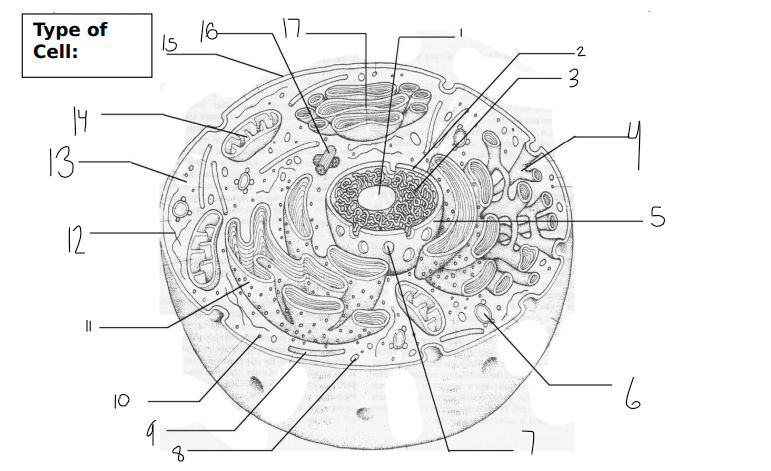
label
animal cell
1 = nucleolus
2= nucleus
3= chromatin
4= smooth er
5= nuclear envelope
6= vacuole
7= nuclear pore
8= lysosome
9= microtubule
10 = ribosome
11= rough er
12= microfilament
13= cytoplasm
14= mitochondria
15= cell membrane
16= centriole
17 = golgi body
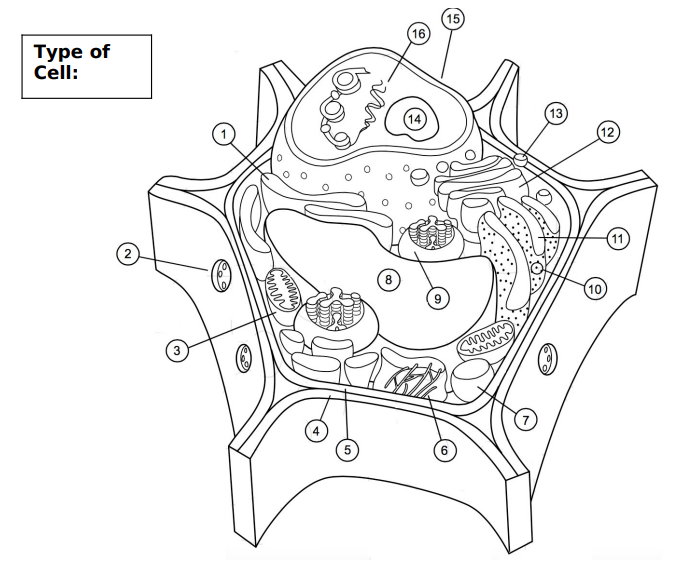
label
plant cell
1 = smooth er
2= plasmodesmata
3= mitochondria
4= cell wall
5= cell membrane
6= cytoskeleton
7= peroxisome
8= vacuole
9= chloroplast
10 = ribosome
11= rough er
12= golgi body/apparatus
13= vesicles
14= nucleolus
15= nucleus
16= DNA