Sem. 1 AP Bio: Final Exam Review
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
What types of chemical bonds are responsible for most of water’s special properties?
H+ bonds
How does the specific heat of water affect the environment?
Water’s high specific heat helps it absorb high temperatures which means it can lower the heat of its environment
What is special about the structure of carbon that makes it important for life?
Carbon can bond with four other elements which means it can create complex molecules essential for life.
What are chemical functional groups?
Chemical functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that determine the chemical properties.
What functional groups are found on amino acids?
Amino acids contain an amino group (-NH2), a carboxyl group (-COOH), and a variable side chain (R group) that determines the properties of each amino acid.
What is the important role of ATP in living systems?
ATP is an energy carrier that stores and provides energy for cellular processes and biochemical reactions.
What is the difference between dehydration (condensation) and dehydration reactions?
Dehydration refers to the loss of water and a dehydration reaection is the process in which two molecules join together by losing a water molecule, creating larger molecule as a result.
Why can humans digest starch but not cellulose?
We don’t have the enzyme cellulase to break down cellulose but can digest starch due to the presence of amylase, which breaks down starch into glucose.
What happens when lipids (and phospholipids) are mixed with water?
They create a bilayer due to lipids having a hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail which is key to the structure of a cell membrane.
What is the structural difference between saturated vs. unsaturated fats?
Unsaturated fats have one or more double bonds making them, oftentimes, liquid due to their structure. Whereas, saturated fats do not contain double bonds which makes them solids due to their tightly packed molecular structure.
What is the functional difference between saturated vs. unsaturated fats in the membrane of cells?
Saturated fats are less fluid and more stable, while unsaturated fats increase membrane fluidity due to their kinked structure.
What makes each of the 20 amino acids unique?
The unique side chains (R groups) attached to the central carbon atom determine the characteristics and functions of each amino acid.
What is the structural difference between the 5’ and 3’ ends of a nucleic acid?
The 5' end has a phosphate group attached to the fifth carbon of the sugar, while the 3' end has a hydroxyl group attached to the third carbon of the sugar.
What are the major differences between prokaryotic vs eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus or cell membrane-bound organelle. Whereas, eukaryotic cells possess a nucleus and various membrane-bound organelles, allowing for compartmentalization of cellular functions.
What structures do plants animal cells have in common?
They both share a cell membranes, a nucleus, and cell membrane-bound organelle.
What factor limits the maximum size of a cell?
The ratio between surface area and volume limits the maximum size because a lower ratio makes it harder for the cell to perform certain processes to the level of efficiency a cell with a high ratio can.
What is the parthway a protein destined to be secreted from a cell takes?
It goes through the secretory pathway: From the rough endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus, carried by vesicles, and out of the cell membrane into the cell exterior.
What types of molecules diffuse through the membrane the membrane the easiest?
Small nonpolar molecules, like oxygen (O2), diffuse through the membrane the easiest.
What is diffusion?
Diffusion is the process in which something of high concentration flows into something of lower concentration.
What is osmosis?
Osmosis is the process in which a solvent flows through a semi-permeable membrane from high concentration to low concentration in order to reach equilibrium.
How does solute concentration affect osmosis?
A solvent with low solute concentration will flow into a solvent with higher solute concentration. This is because solute takes up space in a solvent leading to a lower solvent concentration.
What is the difference between hypertonic vs hypotonic solutions?
Hypertonic: High solute concentration, water will flow into it
Hypotonic: low solute concentration, water will flow out of it
What circumstances require active transport using ATP hydrolysis?
Active transport using ATP hydrolysis is needed when transporting a molecule against the concentration gradient
What is the difference between anabolic vs. catabolic metabolic pathways
Anabolic metabolic pathways need energy to create a large molecule. Whereas, catabolic metabolic pathways release energy through the breakdown of molecules.
What is the function of enzymes in chemical reactions?
Enzymes can speed up a reaction by lowering the activation energy needed to catalyze the reaction.
What is feedback inhibition?
Feedback inhibition is when an enzyme is inhibited by the end-product of a reaction.
During aerobic cellular respiration which chemical compounds are oxidized and which become reduced?
Glucose is oxidized to create carbon dioxide, while oxygen is reduced to create water
What are the end products of glycolysis?
2 Pyruvate, 2 ATP, and 2 NADH are the end products of glycolysis
What are the end products of the Krebs cycle?
Carbon dioxide, 3 NADH, 1 FADH2, and 1 ATP are the end products of the Krebs cycle
What does the electron transport chain do?
The electron transport chain delivers electron through NADH and FADH2 (electron carriers) to create a proton gradient across the membrane in order to produce ATP. In other words, it is used in oxidative phosphorylation.
What is the sequential pathway electrons travel during aerobic respiration?
glucose → NADH → electron transport chain → oxygen
What energy-extracting step can still occur even if oxygen is absent?
Glycolysis can still occur even if oxygen is absent.
What is the function of the fermentation pathway?
It is meant to regenerate NAD+ from NADH for glycolysis without the use of oxygen.
What is the relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
They are opposite reactions, as their products and reactants are reversed. Photosynthesis created the glycolysis that cellular respiration needs.
What are the products of the light reactions of photosythesis?
ATP, NADPH, and oxygen are the products of the light reactions of photosynthesis
When is oxygen produced during photosynthesis?
Oxygen is byproduct of water when water molecules are split using light energy.
What is the sequential pathway electrons travel during photosynthesis?
H2O -> Photosystem II -> Electron Transport Chain -> Photosystem I -> NADPH
What must a target cell have to respond to a signaling molecule?
A target cell must have a specific receptor protein in order to respond to a signaling molecule.
What type of signal transduction proteins add phosphates to target molecules?
Protein kinases are a type of signal transduction protein that adds phosphates to target molecules.
What is a ligand-gated ion channel?
A ligand-gated ion channel is an ion channel that opens when a ligand binds to its signaling molecule binding site. When a ligand binds to it, the channels open allowing for ions to pass through. The walls of channels are hydrophillic which allows the ions to pass through the cell membrane without touching the hydrophobic layer of the membrane. Neurons and nerve cells have ligand-gated ion channels with neurotransmitters.
What is a G-protein receptor?
G-protein receptors have 7 transmembrane alpha helices (meaning one G-protein receptor crosses the cell membrane 7 times). They are coupled with G-proteins which are proteins that can bind to GTP and GDP. When G-protein receptors bind to a ligand, it sends signals into the cell using the g-protein. The g-protein will dehydrate GDP to GTP, and when this happens, the subunits can bind to other proteins to trigger a signalling pathway that will lead to a response. (I.e. cAMP). The process will relay when GTP hydrolyzes to GDP again.
What is are receptor tyrosine kinases?
Receptor tyrosine kinases are receptors that, when a ligand binds to 2 receptors’ binding sites, the 2 receptors dimerize and both transphosphorylate as the tyrosine-kinases are activated. Then, these tyrosines help other proteins phosphorylate, as other proteins bind to the phosphate.
How do steroid hormones differ from protein hormones in terms of their interaction with receptors?
Steroids are hydrophobic so their receptors are inside. Whereas, protein hormones are hydrophillic so their receptors are on their surface.
What are second messengers? What are examples?
Second messengers are small molecules or ions that rely signals from receptors on a cell surface to target molecules inside the cell. cAMP is a second messager, and it is ATP that's been synthesized by adenylyl cyclase from G-protein receptors. It can activate PKA to phosphorylate certain proteins.
Why are phosphorylation cascades useful in cellular signal transduction?
Phosphorylation cascades are useful in cellular signal transduction because it can amplify cellular response, as it will activate multiple protein kinases.
Why don’t all cells respond to all signal molecules?
Cells don’t respond to all signal molecules because they have specific receptors with binding sites that are specific to certain molecules.
What is an example of a pair of hormones that work antagonistically to maintain homeostasis
Insulin and glucagon are a pair of hormones that work antagonistically to maintain homeostasis, as insulin lowers blood sugar and glucagon raises blood sugar.
How do Helper T Cells become activated?
They become activated when they encounter an antigen, and they differentiate into a specific type of Helper T Cell based on the cytokines that are released by said antigen.
How do B cells and cytotoxic T cells respond differently to pathogens.
Cytotoxic T cells can directly kill an infected cell. Whereas, B cells secrete antibodies that can neutralize pathogens and stop them from entering a cell.
Why is your second exposure to a pathogen less likely to create symptoms of beng sick?
Our second exposure to a pathogen is less likely to create symptoms of being sick because, in the first exposure, the body created memory cells that know how to fight this pathogen.
What immune cell type interacts with both B cells and cytotoxic T cells?
Helper T cells interact with both B cells and cytotoxic T cells
What happens during G1, S, and G2 of the cell cycle?
In G1, the cell grows in preparation for mitosis. In the S phase, a copy of the cell’s DNA is synthesized. In G2, the cell continues to grow, and the DNA is checked for errors before dividing.
What happens during each step of mitosis
Prophase- cell membrane breaks down and chromosomes become visible
Metaphase- the chromosomes line up along the equator of the cell, and spindles attach to the centromeres of the chromosomes
Anaphase- Sister chromatids of each chromosome are pulled apart to opposite poles of the cell
Telophase- A new membrane forms around the separated chromosomes at both poles, and chromosomes decondense.
Cytokinesis- The cells divide
How does the amount of DNA in a cell change as it goes through the different stages and steps of the cell cycle?
In G2, the amount of DNA doubles in preparation for metaphase. After metaphase and after cytokinesis, the DNA is back to the amount it was before division for each daughter cell (G1: 2x; G2: 4x; Metaphase: 4x; After cytokinesis: 2x)
What is the diffference between chromosomes and sister chromatids?
A chromosome is made up of sister chromatid and a chromosome is not identical to another. Whereas, chromosomes are comprised of sister chromatids, and those sister chromatids are identical to each other.
What are cyclins and cdks and what is their functional role?
Cyclins are proteins, and they can activate CDKs (cyclin-dependent kinases) which are enzymes that will then modify target proteins.
What is the role of mitotic spindle?
The mitotic spindles pulls apart the chromosomes by attaching to a their centromere.
What factors lead to the development of cancer cells?
Environmental factors, genetic mutations in DNA, and viruses can lead to the development of cancer cells.
What features do cancer cells exhibit?
They can uncontrollably duplicate due to their G1 and G2 phases becoming unable to check errors in the DNA and inhibit the cell from entering metaphase. They have many irregularities and mutations.
What experiment did Hershey and Chase do and how did it help us understand the nature of the material of genetics?
They used bateriophages to prove that DNA is the genetic material of a cell and not protein.
What experiment did Frederick Griffith do and how did it help us understand the nature of the material of genetics?
He found that DNA is the genetic material responsible for inheritable traits when he infected mice with a combination of two bacteria which ended up killing the mice.
What experiment did Meselson and Stahl do and how did it help us understand how DNA is replicated?
They found that DNA replication is semi-conservative when they used a heavy and light isotope of nitrogen in DNA and found that the DNA kept the old DNA strand and created a new DNA strand with the light isotope of nitrogen.
How do the proportions of each type of base in a DNA molecule relate to each other?
Adenine and thymine are equal in amount, and guanine and cytosine are also equal in amount.
During DNA polymerization, what is the 3’ vs 5’ orientation of the nucleotides as they are added?
Nucleotides are added to the 3’ end of the growing strand.
What does it mean that DNA strands are antiparallel?
DNA strands are antiparallel because they run in opposite directions of each other.
What is the difference between leading vs lagging strands during DNA replication?
The leading strand is longer and is being synthesized continuously in the same direction of the replication fork. Whereas, the lagging strand is shorter and is being synthesized in okazaki fragments away from the replication fork. Both need RNA primer, but the leading strand only needs it once, and the lagging strand needs a new one for each okazaki fragment.
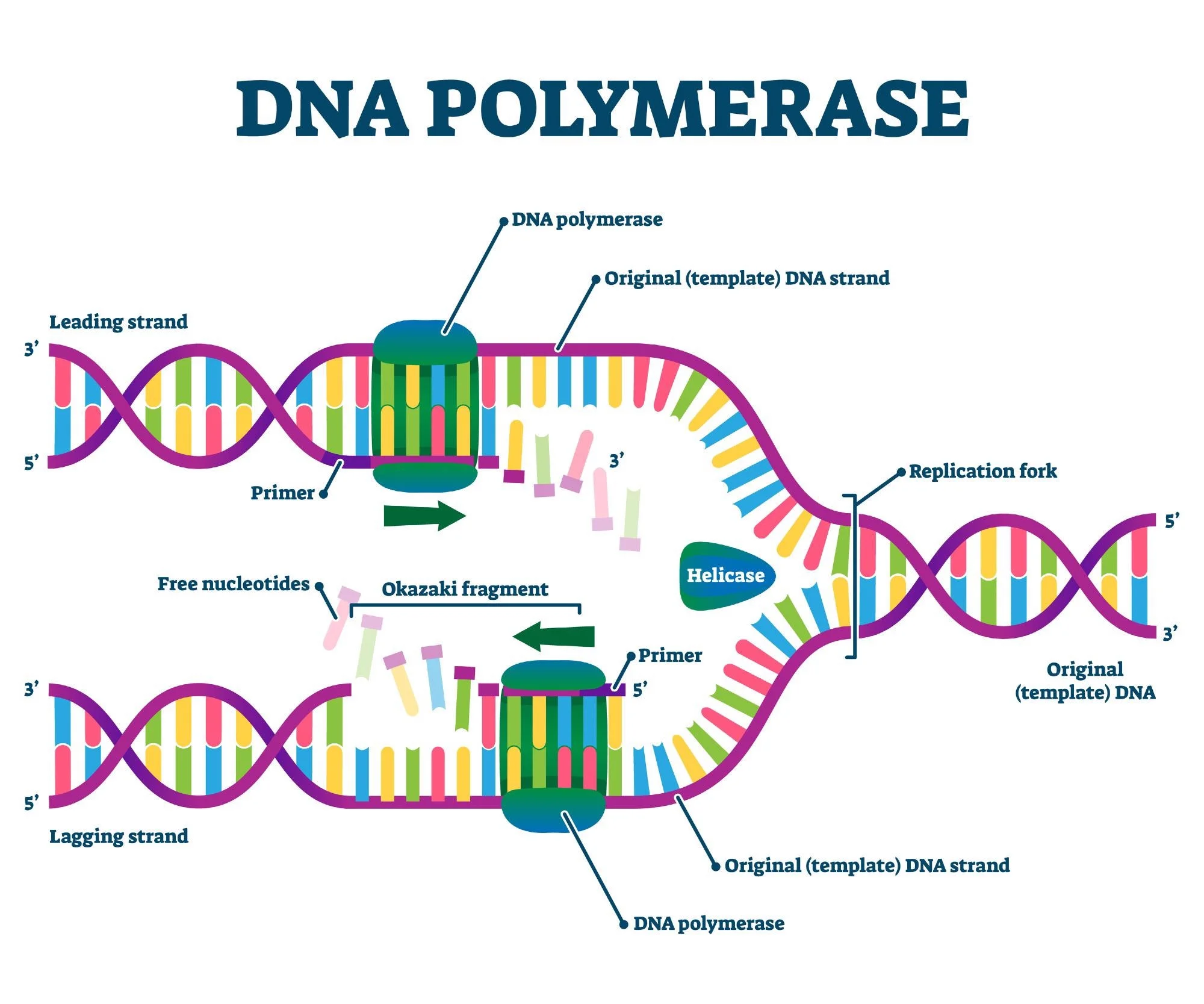
What is the role of DNA polymerase?
It adds nucleotides to the expanding DNA chain and ensures an accurate replication of the original DNA.
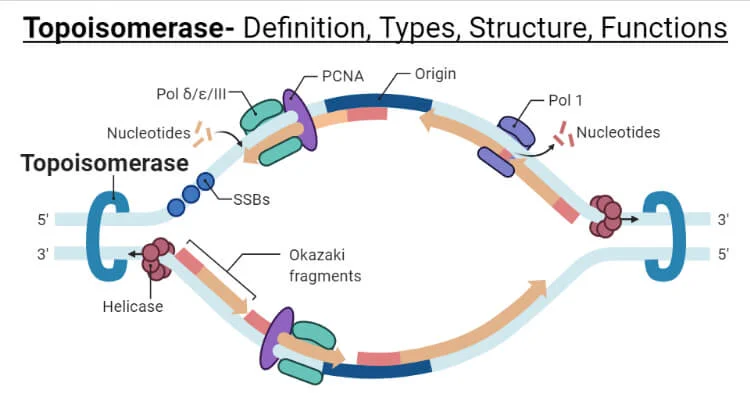
What is the role of Topoisomerase?
It prevents the DNA from become over or undercoiled by cutting and rejoining DNA strands.
What happens during the lytic cycle of a virus?
In the lytic cycle, a virus introduces its genome into a cell, and the starts to replicate until the cell explodes and dies.
What happens during the lysogenic cycle of a virus?
The lysogenic cycle of a virus is when a virus introduces its genome into a cell and then remains dormant until the cell is triggered again to enter the lytic cycle.
Why do RNA viruses have a high rate of mutation?
RNA viruses have a high rate of mutation because they are signle stranded and do not have any proofreeding mechanisms to check for errors in replication.