Amino Acids
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Amino acids
Are the building blocks of protiens
Monomer
Individual content of a patricular polymer
Amino acids, protiens
the monomer is the ________ and the polymer is the ________?
Biological activity
Each of the amino acids present in your protiens will determine the ________ ________ of your protien
General structure of amino acids

Amino group

Carboxyl group
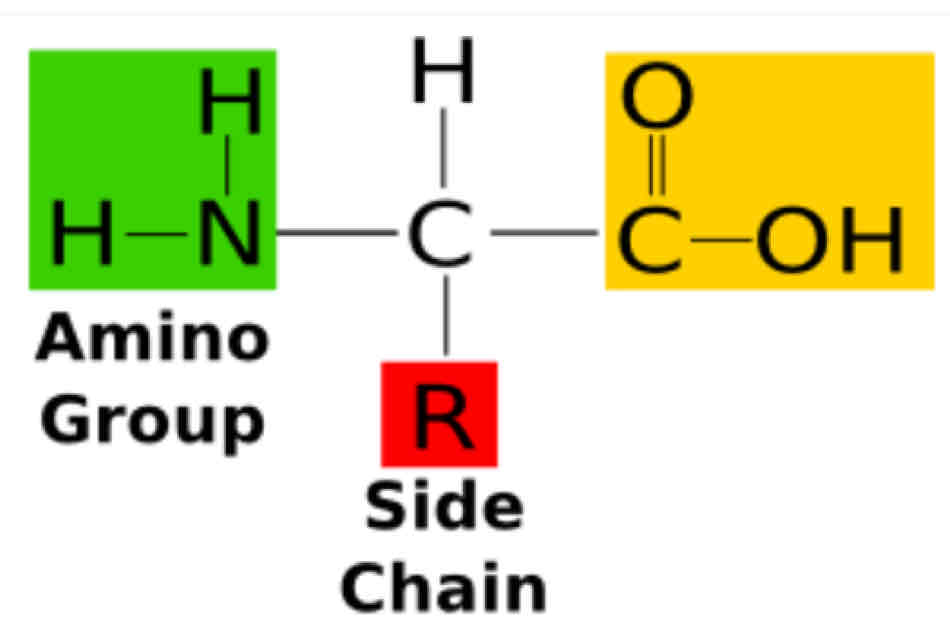
Side chain
This is the structure will make your amino acid unique from each other.
All of our amino acids contain the same amino group, the same carboxyl group, but different _________?
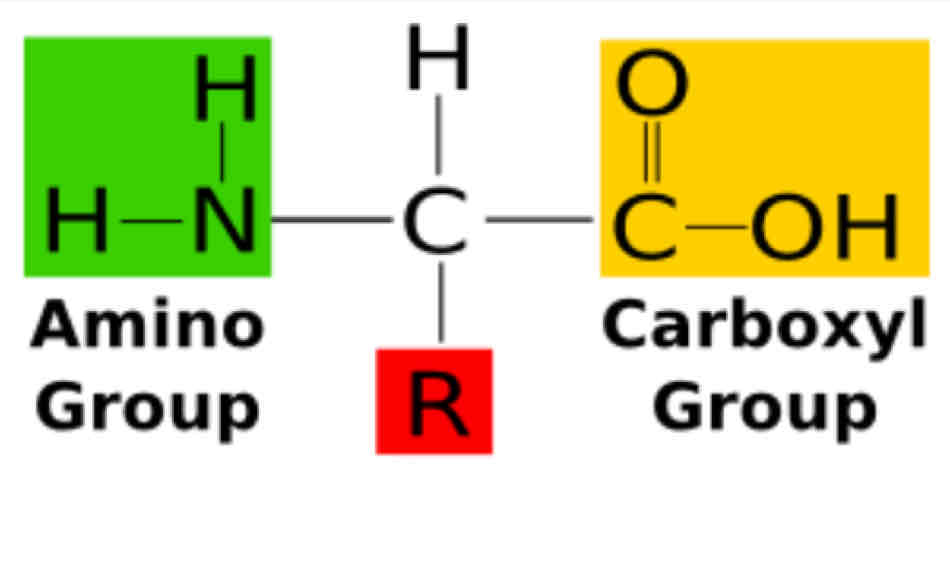
Side chain or R group
What specific structure that will make your amino acid unique to other amino acids?
This also determines the biological activity of a specific amino acid.
Amino group
Particular structure of your amino acid that will participate in the formation of your peptide bond primarily?
Carboxyl group
is involved in the formation of esters, amides, and acid anhydrides.
Peptide bond
Is the bond or the force that will join your amino acids together to form a whole protien.
20
How many amino acids that are found in our protiens?
Essential and non essential
Two categories of amino acids
Essential amino acids
Are the one’s that we get externally from the food sources.
Non essential amino acids
Are naturally present in our body.
Asparagine 1806
The first amino acid that was first discovered? (Non essential amino acid)
Threonine 1938
The last amino acid discovered? (Essential amino acid)
Functions of amino acids
Components of peptides, proteins, and phospholipids
Neurotransmitters of glutamate, aspartate, and glycine
Precursors of keto acids, biogenic amines, glucose, nucleotides, heme, and creatinine. Amino Acids are precursors
Transport molecule for NH2 groups
These individual amono acids they do not just mearly exsist just for the synthesis of your protiens, but individually these amino acids have their own function, including there is that your amino acids can be precursors to certain metaboloc pathways, like for ex. Your lipid pathway, metaoxidation, your protien metabolisim, your amino acids are also there, even your glucose metabolisim, your amino acid is also there, not take note that excessive amino acid can harm your body. Ex. Keto diet, you replace your carbohydrates with fats, instead of consuming regular carbohydrates the person opt with fats like fatty foods. Now what is the danger of this? Although the keto diet is really effective, but in the state of starvation meaning that the body is always running out of carbohydrates, take note that the energy that we actually get is actually from carbohydrates. But what if your body is already out of carbohydrates, meaning that your body is in the state of starvation, your body will resort to other energy sources, and that includes your fats, if your body will consime fats for energy, ma memetabolize an fats, it will undergo metaoxidation, and when this happens, there will be a lot of keto acids, and a lot of amino acids produced by your body and take note, these keto acids, and these amino acids, in excessive amounts it can harm your kidneys and your liver.
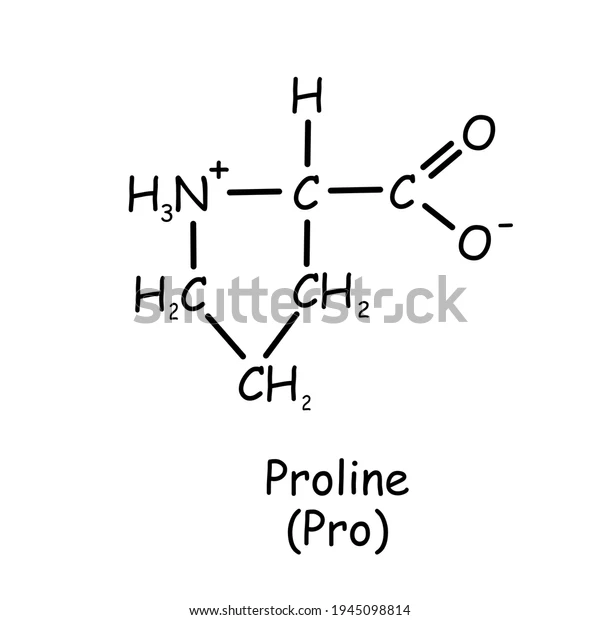
Proline
is the only amino acid that does not follow the general structure.
The R group (side chain) branches to the amino group, not on the alpha carbon.
It is a secondary amino acid because the amino group present in your proline is considered as a secondary amino group, or a secondary amide.
Aliphathic amino acid
A non polar, and hydrophobic amino acid
Lead acitate test
If there is a prescense of sulfur atoms or cystine and methionine, it will produce a black ppt, what test is this?
Carboxyglutamate
Found in the blood clotting protein prothrombin and in certain other proteins that bind calcium ion as part of their biological function.
Is a derivative of glutamic amino acid
High affinity to calcium
4 hydroxyproline
Derivative of proline
5 hydroxylysine
Derivative of lysine
Contains only one lysine residue
Usually found in cell walls
Desmosine
Derivative of four lysine/lys residues
Found in the fibrous protein elastin (Present in skin)
Selenocystine
21st amino acid
Contains selenium rather that the sulfur of cysteine
(sec) symbol
Pyrrolysine
22nd amino acid
(Pyl) symbol
Acidic, Basic
If the electrical charge of your amino acid is Positive meaning the amino acid is?
If the electrical charge of your amino acid is Negative meaning the amino acid is?
Equal
Net charge will become zero if there is an ______ number of positive and negative charges
Optimum pH
If a amino acid reaches a zero net charge it simply means that this amino acid has reached is ?
Example, if we put aspartic acid in a particular solution, mag zero ngani an iya net charge, it means that this is an _________ of aspartic acid.
Zwitter ion
If that particular amino acid reaches a zero net charge we call this amino acid as? (40 min timestamp)
Aspartic acid, the platonic equilibria or the state in which the positive and negative charges are equal for your amino acid is at pH 3.0. (Neutral)
If you place your aspartic acid in a solution with a pH of 3.0, its net charge will become 0.
The question there is, what if we place your aspartic acid in a lower pH? Meaning a pH less than 3, what will happen to the net charge of your aspartic acid?
If ig butang mo hiya ha mas acidic meaning there are more positive charges, so the net charge of your aspartic acid will become positive, so thats why there, you put your aspartic acid in a pH 1, or in a solution with a pH of 1, the net charge of your aspartic acid became +1, naging positive, which is initially naging zero ha pH 3.
Now what if you place your aspartic acid in a higher pH, so kun higher it pH its more on the negative, the net charge will become negative or -1
—
ZI Can either be a proton donor or a proton acceptor. What will your Zwitter ion do?
Example, you have excess proton, meaning too acidic an imo solution, so anot trabaho ni zwitter ion? You add your zwitter ion, what will your zwitter ion do? Will it contribute more proton or will it get more proton? It will “recieve” “accept” “get” the excess proton.
If the solution is too basic, meaning there is less proton, what will your zwitter ion do? It will donate proton, so in such way the pH will be buffered out, or it will be maintained because you have your zwitter ion which can function as a proton donor or a proton acceptor.
Negative
When amino acids are placed in a basic solution, net charge becomes?
Positive
When placed in acidic solution, net charge is ?
Histidine
Which amino acid has the best buffering capacity?
Takw note that all of our amono acids contain two ionizable groups which is your carboxylic group and your amino group. But in the case of _________ its R group is a imidazole group which is an adittional ionizable group, which makes it a good buffe rbecause its optimum pH is 7.5 which is neutral.
Solubility & Melting point
soluble in polar solvents such as water and ethanol
insoluble in nonpolar solvents such as benzene, hexane, or ether
The high amount of energy required to disrupt the ionic forces that stabilize the crystal lattice account for the high melting points of amino acids (>200°C).
We have mentioned ago that amino acids, it iya polarity will depend on its side chain, but take note that amino acids in general is considered as POLAR so meaning if it is polar it would be soluble also in polar solvents, and that includes water and ethanol.
In contradiction, it is insoluble in non polar solvents, includes benzene hexane and ether.
It fats naman kabaliktaran la ..
Melting point is high (200) degrees celcius, why is that so? Its because of a very strong ionic forces, a very strong lattice ionic force that binds your amino acids together, thats why mataas ang melting point niya.
Peptide
2-10 amino acids joined together are called?
polypeptide
Example lets say 88 amino acids that are joined together, what is it called? It is a chain of many but less that 100 AA.
Protien chain
More than 100 amino acids will form a
Peptide bond formation
Dehydration or removal water.
Removal of an oxygen and hydrogen from carboxylic group and hydrogen from amino group of the other amino acid forming water.
Peptide bond can be hydrolyzed by strong acids and base at high temperature.
How do we form peptide bond? So basically the principle of it is Dehydration or the removal of water, where do we remove water?
Ex. Forming a di peptide or two amino acids, you remove water where? In the amino group because asya it primary in bond formation but it is also your carboxyl group, because you remove 1 water from your nitrogen from your amino group, and then you remove 1 oxygen, and 1 hydrogen from the carboxyl group, so that makes 2 hydrogen and 1 oxygen, that makes water.
And if you remove this branch here, ano it mananabo kan imo carbon ngan nitrogen? It will now form your peptide bond.
Insulin
Particular protien that we consider a protien despite of it having less than a hundred amino acids?
We consider it as a protien because the structure of your insulin is the same or almost the same with the structure of a whole protien macro molecule, in additin to that it contains diverse functions, anot function it aton insulin, regulates sugar.
It is the first protien to be fully sequenced.
51
How many amino acid residues does insulin have?