Biology 101: Intro to Biology Ch 3. Introduction to Organic Molecules & Heterotrophs
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
Organic Chemistry
the study of molecules from living things and formerly living things; the study of molecules that contain carbon
Organic molecules can contain:
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, & Sulfer
Functional Groups
Atoms or groups of atoms that have a predictable reactivity
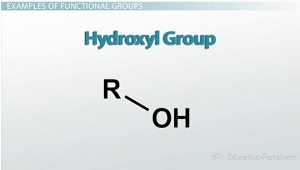
Hydroxyl Group
consists of an oxygen atom single-bonded to hydrogen and to a carbon group
Amine Group
a nitrogen atom that is single-bonded to three different groups that contain either hydrogen or carbon
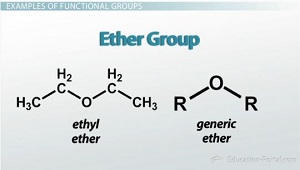
Ether Group
oxygen molecules that are single-bonded to two different carbon groups
Carbonyl Groups
a carbon that is double-bonded to oxygen
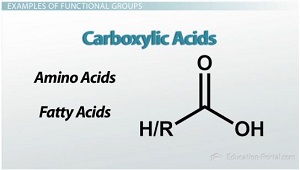
Carbonyl Acids
carbonyls that are bonded to hydroxyl groups
Ester Group
consists of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom that is single-bonded to an oxygen atom that is attached to a carbon atom
_____ hold fats together in biological systems and bond fatty acids to glycerol.
Esters
Amines
Ethers
Carbonyls
Hydroxyls
Esters
Which of the following is true about organic molecules?
None of the above
They can only be found in living organisms
They must contain carbon
They always have chains of carbon atoms
They contain only carbon
They must contain carbon
What is the shorthand for a carbon-containing substance in organic chemistry?
P
C
Ca
O
R
R
The _____ has an oxygen atom single-bonded to hydrogen and single-bonded to a carbon-containing group.
ether
hydroxyl
ester
amine
carbonyl
hydroxyl
Which of the following functional groups contains nitrogen?
Carboxylic Acid
Amine
Disulfide
Alcohol
Hydroxyl
Amine
Polymer
A long chain molecule formed by bonding together monomer units; can be made of the same monomer units; can be made out of different monomers
Monomer
the simplest unit from which a polymer can be formed
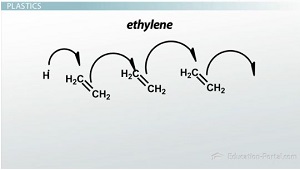
ethylene
is a gas that is polymerized to make milk jugs; reacts to form the polymer known as polyethylene
Dimer
polymer consisting of 2 monomer units
Trimer
polymer consisting of 3 monomer units
Nylon
is a combination of hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid
Kevlar
is a copolymer that is made of different types of monomers
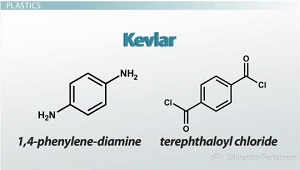
Cellulose
is a natural polymer that’s made up of repeating glucose monomers; a polymer that’s made of glucose
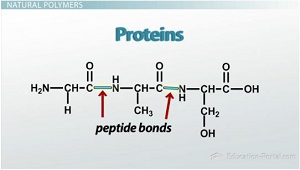
Proteins
are natural polymers; a polymer that’s made of amino acids
A single sugar is called a 'monosaccharide.'
'_____saccharide' refers to a three-sugar polymer.
Tri
Di
Penta
Hexa
Tri
A long chain molecule formed by many smaller units is called a
monomer
trimer
dimer
polymer
polymer
What holds high-density polyethylene together?
Addition of other atoms to the plastic
Carbon-carbon double bonds
Intermolecular forces between polymer chains
Branching of carbon chains
Intermolecular forces between polymer chains
Cellulose & proteins are types of
monomers
man-made polymers
dimers
natural polymers
natural polymers
A two-unit molecule is a
dimer
none of these answers
trimer
monomer
dimer
Carbohydrates (a.k.a sugars)
comes from the atom carbon and hydrate, or water
Polysaccharide
big sugar; sugar molecules consisting of more than three sugar units
Glucose
the sugar that serves as fuel for our bodies
Fructose
the sugar found in high-fructose corn syrup
Ribose
plays an important role in holding together our genetic material
Deoxyribose
similar to ribose except that it lacks an oxygen or hydroxyl group on one of its carbons; this is also an important sugar that helps hold our genetic material together
Monosaccharide
single sugar molecule
Disaccharide
sugar molecule containing two monosaccharides
Dehydration
The loss of a water molecule
Trisaccharides
sugar molecules containing three monosaccharides
Which set of functional groups is always found in sugars?
Amines and alcohols.
Ethers and amines.
Ethers and carboxylic acids.
Hydroxyl groups
Hydroxyl groups
Carlos just finished an exhausting workout. Which of the following carbohydrates can be readily used by his body as a source of fuel?
Any kind of polysaccharide.
Dietary fiber
Glucose
Cellulose
Glucose
What type of reaction causes the formation of sugar molecules larger than monosaccharides?
Decarboxylation
Dehydration
Deamination
Hydration
Dehydration
All of the following statements are true, EXCEPT _____.
mammals store carbohydrates in the form of glycogen
pasta and cereals are good sources of carbohydrates
starch is composed of amylopectin and amylose
sugars are found only in plants
sugars are found only in plants
Lactose is composed of a glucose molecule and a galactose molecule, therefore, lactose is classified as a _____.
monosaccharide
disaccharide
trisaccharide
polysaccharide
disaccharide
amino acids
the building blocks of proteins
a central carbon atom
a hydrogen atom
an amino group
a carboxyl group
an R-group or side chain
essential amino acids
amino acids that our body cannot make on its own
L-methionine (Met, M)
L-threonine (Thr, T)
L-valine (Val, V)
L-leucine (Leu, L)
L-isoleucine (Ile, I)
L-arginine (Arg, R)
L-histidine (His, H)
L-phenylalanine (Phe, F)
L-tyrosine (Tyr, Y)
L-lysine (Lys, K)
nonessential amino acids
amino acids that our bodies can synthesize
glycine (Gly, G)
L-alanine (Ala, A)
L-glutamic acid (Glu, E)
L-glutamine (Gln, Q)
L-proline (Pro, P)
L-serine (Ser, S)
L-asparagine (Asn, N)
L-cysteine (Cys, C)
L-tyrosine (Tyr, Y)
L-aspartic acid (Asp, D)
Amino acids are the building blocks of which of the following?
Amino groups
None of the answers are correct.
Nucleic acids
Proteins
DNA
Proteins
Which of the following is true about essential amino acids?
They typically include serine.
None of the answers are correct.
They must be obtained through foods.
All of the answers are correct.
They can be synthesized by your body.
They must be obtained through foods.
An amino group consists of
A carbon and two nitrogen atoms
A nitrogen and one carbon atom
A carbon and two hydrogen atoms
An oxygen and two hydrogen atoms
A nitrogen and two hydrogen atoms
A nitrogen and two hydrogen atoms
All amino acids contain which of the following?
An amino group
An R group
A central carbon
A carboxyl group
All of the answers are correct.
All of the answers are correct.
The group that is unique in each of the 20 amino acids is
All of the answers are correct.
Carboxyl group
Amino group
R-group
None of the answers are correct.
R-group
Lipids
biological molecules that are insoluble in water, but are soluble in nonpolar solvents
Unsaturated and Saturated Fats
found in nature
Trans Fats
synthetic
Saturated Fats
triglycerides that have no double bonds in their carboxylic acid chains
Unsaturated Fats
triglycerides that have double bonds in their carboxylic acid chains
Trans Fats
triglycerides that have trans double bonds in their carboxylic acid chains
Steroids
contain a particular system of carbon rings
Lawrence wants to eat food that is high in energy before he starts training for his tennis competition. Which of the following types of food will give him the most energy per pound?
Protein
Carbohydrates
Fat
Sugar
Fat
Why does soap remove grease from pans when we wash dishes?
Part of the soap molecule is polar and dissolves in water, while part is non-polar and dissolves in the lipids.
Soap molecules react with fats to break up fat blobs.
Soap sends a chemical message to fats to break up fat blobs in the pan.
The whole soap molecule is non-polar, so it breaks apart fat blobs.
Part of the soap molecule is polar and dissolves in water, while part is non-polar and dissolves in the lipids.
What is the functional group that is formed when glycerol reacts with carboxylic acids to form triglycerides?
Carboxylic acid
Ether
Ester
Carbohydrate
Ester
Which of the following roles do lipids NOT play in our bodies?
Make up part of our cell membranes
Generate heat
Act as hormones
Store energy
Generate heat
All of the following statements are true about lipids, EXCEPT that _____.
steroid hormones like testosterone are lipids
all lipids are fats
lipids are good at storing energy
lipids are biological molecules that are insoluble in water
all lipids are fats
Peptide Bond
the covalent bond that holds amino acids together
Keratin
found in hair, skin, and nails; is hydrophobic
Collagen
main component of connective tissue
important for structure of body
Enzymes
Proteins that enable chemical reactions in our bodies; decrease activation barrier
Lactaid
The enzyme lactase splits apart lactose sugars
Hemoglobin
A protein that carries oxygen from lungs to tissues throughout the body
Lipoprotein
A protein that can transport multiple fat molecules throughout blood
insulin
A protein that is able to lower blood sugar
Human Growth Hormone
A protein that sends a message of growth to cells
Protein Functions
store energy
provide structure
act as enzymes
allow for movement
transport things
act as messengers
protect from invaders
regulate genes/proteins
Which of the following is a function performed by proteins?
Transportation
Regulation
Muscle contraction
All of the answers are correct.
All of the answers are correct.
Proteins are biological molecules made of _____.
nucleotides
sugars
amino acids
glycerol
amino acids
When a protein makes it easier for a biological reaction to happen, it is acting as _____.
a structural protein
a messenger
an enzyme
a transporter
an enzyme
Proteins in our skin, hair, and nails are called what?
Storage proteins
Regulatory proteins
Structural proteins
Transport proteins
Structural proteins
What atoms are connected by a peptide bond?
Carbonyl carbon and amino group nitrogen
Amine nitrogen and another amine nitrogen
Carbonyl carbon and carbonyl oxygen
Side chain groups
Carbonyl carbon and amino group nitrogen
Heterotroph
need to eat other organisms to get energy
Autotrophs
able to survive by making their own food
Detritivores
break down dead and decaying organisms
Herbivores
eat only producers
Carnivores
eat only other consumers
Omnivores
eat both producers and consumers
Which of the following are heterotrophs?
All of the answers are correct.
Fungi
Bacteria
Carnivorous and parasitic plants
All of the answers are correct.
What is a detritivore?
An organism that consumes living producers.
An organism that consumes dead and decaying material.
An organism that consumes both living producers and consumers.
An organism that consumes other living consumers.
An organism that consumes dead and decaying material.
What are autotrophs?
Organisms that produce their own food.
All other organisms besides plants and some algae.
All other organisms besides humans and some animals.
Organisms that consume other organisms.
Organisms that produce their own food.
What is another name for a heterotroph?
Autotrophs
A producer
A self-feeder
An 'other feeder'
An 'other feeder'
Which of the following is true about heterotrophs?
They all rely on only one type of food source.
They may be carnivores, herbivores, or omnivores.
They all eat both consumers and producers.
They all rely on the same types of food sources.
They may be carnivores, herbivores, or omnivores.