Continental drift and the theory of plate tectonics
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Who created the first modern atlas?
Abraham Ortelius

Which meteorologist proposed the theory of continental drift?
Alfred Wegener

In what year was the theory of continental drift proposed?
1912
What evidence is there to support the theory of continental drift?
the theory of plate tectonics
Mesosaurus fossils
geological columns
plant fossils
animal fossils
complimentary continent shapes
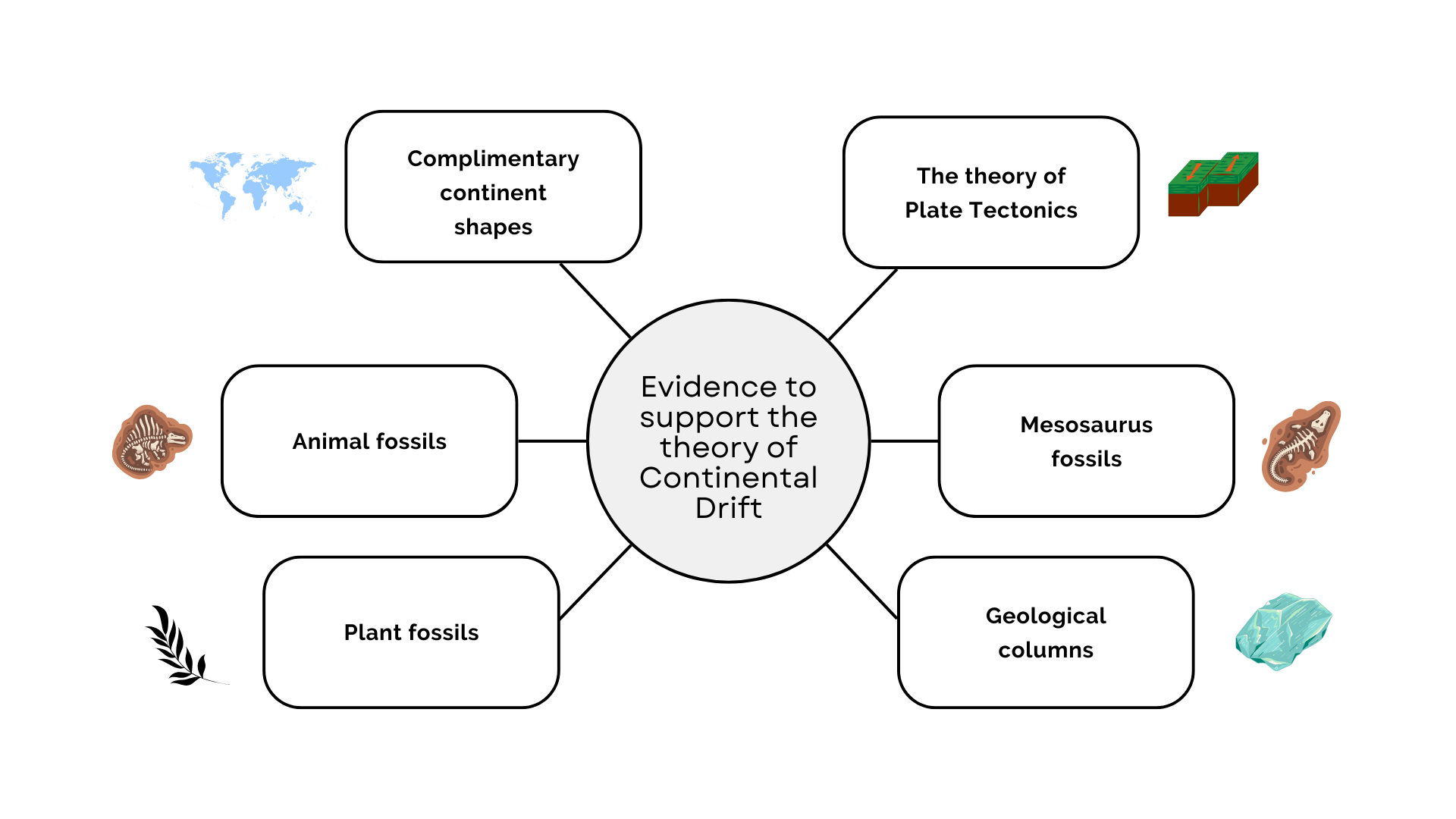
plate tectonics
the process whereby heated rock is moved within the Earth in vast convection currents, which drag along the underside of the Earth’s plates, forcing them to slowly drift across the planet
What is the thickness of conintental crust?
30-70km
What is the age of continental crust?
over 1,500 million years old
What is the density of continental crust?
2.6g/cm3
What is the composition of continental crust?
mainly granite
What is the thickness of oceanic crust?
6-10km
What is the age of oceanic crust?
less than 200 million years old
What is the density of oceanic crust?
3.0g/cm3
What is the composition of oceanic crust?
mainly basalt
convection currents
Heat from the core (hot spots) warms the mantle, causing it to rise up
This movement within the mantle moves the plates above it
The mantle nearer the surface cools and creates new crust
The mantle moves back down towards the core
ridge push
At a constructive plate boundary, plates are pulling apart
Magma rises to the surface and forms new crust
This heats the surrounding rocks, which expand and rise above the surface, creating a slope
New crust cools and becomes denser, sliding downslope away from the late margin
This puts pressure on the plates, causing them to pull apart
slab pull
At destructive plate margins, denser crust is forced under less dense crust
The sinking of the plate edge pulls the rest of the plate towards the boundary