Behavioural Experiments
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Behavioural activation
Helping a person’s symptoms by having them engage in pleasant activities that reduce their depressive symptoms
How effective is behavioural activation?
It’s as effective as CBT, but more cost-effective. In more seriously depressed patients
A recent meta-analysis studied the change of dysfunctional thoughts and whether they are an attribute of cognitive behavioural therapy specifically
The results showed that they were actually not: dysfunctional thoughts is just an attribute that is changed over the course of all therapies - CBT just works specifically with those thoughts
How does the behavioural activation intervention work?
1) plan in advance the pleasant or satisfying activity of your choice
2) do the activity, independent from your mood state
How do you keep behavioural activation simple?
Make sure theActivity is feasable at a bad day
Plan activities you liked before the depression
Simple activities (drink your favorite tea, put on cosy clothes, listen to music you liked, go for a short walk)
As you go on, increase the frequency or duration or the type of activity
Go for a step by step approach
What avoidance behaviours are there in behavioural activation?
Social withdrawal: not answering telephone, avoiding friends
Non-social avoidance: not taking on challenging tasks, sitting around the house, spending excessive time in bed
Cognitive avoidance: not thinking about relationship problems, not making plans for future, not taking opportunities, not being serious about work or education, ruminating
Avoidance by distraction: watching rubbish on tv, playing computer games, gambling, comfort-eating, excessive exercise
Emotional avoidance: use of alcohol, drugs to numb feelings / emotions
Imaginary exposure therapy
A type of therapy where the client is asked to imagine a feared situation in intense detail (also useful for preparation for in-vivo exposure
What is the habituation model of exposure therapy
•Fear can also be reduced without avoidance •This is something the patient learns through exposure
•Fear must thus decrease during exposure •Therefore: prolonged exposure

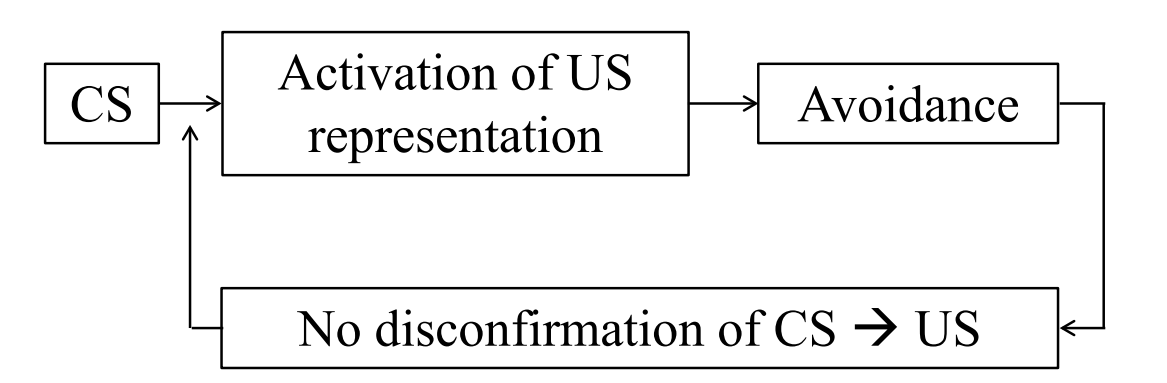
What is the extinction model of exposure therapy?
1) Learning that CS (= feared cue) does not lead to US (= catastrophe)
2) “Exposure as a behavioural experiment” : - Identify misinterpretations: if CS US
(if I blush, then I’ll look stupid; if my heart pounds, then I’ll have a heart attack; if there’s a dog, then I will be bitten) - Score the credibility of CS US relations - Work out which considerations are valid for and against the CS US rule - Use exposure as an experiment to test whether the CS US rule is empirically correct
What are some criticisms on the inhibitory learning model?
Empirical evidence for expectancy violation:
1) expectancy violation seems unrelated to exposure outcome
2) Exposure not more successful than before focusing on expectancy violation
3) Inconsistent definitions of expectancy violation 4) Currently rather learning rate than expectancy violation seems relevant
What is the self-efficacy explanation of exposure therapy?
The idea that through exposure, the client learns that they can manage stressful situations that come their way, therefore increasing their feelings of self-efficacy and reducing fear

What is the difference between inhibitory learning theory and extinction theory?
2) Extinction – behavior that is not reinforced will decrease over time
3) Inhibitory learning theory – disconfirm the CS -> US relationship
What is exposure with response prevention?
Conducting exposure therapy without allowing the client to engage in their usual safety behaviours
What is interoceptive exposure?
Exposure therapy where the focus is on an internal sensation (e.g. symptoms of a panic attack)
What do you need to do while planning a behavioural experiment?
Purpose: What belief is going to be tested? (Or which behavior you want to explore?)
Target: are the targets and outcomes clearly defined?
What does the experiment asks from you?
What, when, where, how often, with who? Alternative perspective identified?
Have you decided on type of experiment?
What is a potential obstacle of doing het experiment?
How will you deal with these problems?
What do you predict will happen?
What is the goal of a behavioral experiment?
Behavioral experiments are done to test a belief/expectancy (and disconfirm it). May have similar effects to exposure therapy
How can therapist avoidance make exposure therapy less effective?
If the therapist is actually avoiding the issue, the patient cannot be fully exposed and the anxiety will go down less