2-HELLP syndrome -
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
pg 23-
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
HELLP syndrome →
acute fatty liver of pregnancy (AFLP) →
haemolysis, elevated liver enzyme, low platelet
no haemolysis, low glucose ± high ammonia, vomit ± DIC, prolonged PT and PTT
acute fatty liver of pregnancy
risk factors → ___________, ___________, ___________
SX → (7)
occurs after _____________ typically / ________________.
it may lead to ________ and _______ →_______ → ______
DX → __________
pre-eclampsia, first pregnancy, multiple pregnancy
nausea, vomit, abdominal pain, fever, jaundice, headache, itch (pruritus)
30 weeks after gestation…right after delivery
severe hyperglycemia…abnormal clotting factor…stoke…death
liver biopsy
presentation of acute cholecystitis
pain (right upper quadrant/epigastric) radiates to flank, back, R shoulder
MURPHY SIGN - pain or inspiration arrest when pressed at R costal margin of midclav line
± pain precipitated by meals
± nausea, vomit, fever
± deranged LFT (hight alk. phosphatase → biliary obstruction)
± inflammatory elements : WBC and fever
*jaundice - if stone in common bile duct.
*in AC, cystic duct is blocked, so mild or no jaundice
acute cholecystitis
risk factors →
DX →
TX →
5F syndrome (fat, forty, female, fertile, fair) / men, thin, < 40
high WBC, abdomen U/S → thick wall, shrunken gallbladder
IV analgesic, IV fluids, IV AB
early laparoscopic cholecystectomy < 1 week
incidental finding during CT or U/S of
gallstone + asymptomatic patient →
CBD stone ± asymptomatic →
reassurance (no interventions needed)
ERCP or laparoscopic cholecystectomy
*Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
features of plummer vinson syndrome
→
→
→
TX → ___________ + ___________
oesophageal web, dysphagia, iron def anemia
iron supplement…web dilatation
alderonate biphosphonate used in _________ and NSAIDS can worsen ___________ and ___________.
leading to _____________ → ______________.
this condition is characterised by _____________ without ____________
osteoporosis…oesophagitis...gerd
scarring of oesophagus…benign oesophageal stricture
persistent dysphagia…regurgitation
*HX of taking H2 blockers (ranitidine) for retrosternal discomfort (GERD) for long period → benign oesophageal/peptic stricture
barret’s oesophagus is similar to benign oesophageal stricture except
the dysphagia is occasional, not persisted like the latter
persistent dysphagia + alendronate for osteoporosis + no regurgitation
benign oesophageal stricture
acute pancreatitis
HX of _________, _________, _________, _________.
SX → _________, ___________
± _________, _________, _________, _________, ________
DX → ___________ (______>______) and ____________
TX → _________, ________, ________. then _________ (eg _________). ___________ is done only if there is __________ using minimally invasive procedures such as _______________ and _________________
gallstone, alcoholism, trauma, ercp
nausea, vomit
tenderness, shock, tachycardia, cullen’s sign, jaundice
lipase > amylase serum (X3 norm), CT w contrast of pancreas
IV fluid, analgesics, nutritional support → IV AB (IV imipenem)
surgical debridement…necrosis…transgastric endoscopy…VATRN(video assisted translumbar retroperitoneal necrosectomy)
*cullen’s sign is periumbilical bleeding(within or behind the peritoneum)
acute cholangitis “ascending cholangitis” is _______________.
main feature is _______ which includes _____,_____, _____
± _______ and _______
DX → _________ and ________
TX → ________, _________, _________, __________
inflammation of the bile duct
charcot’s triad → fever, R upper quadrant pain, jaundice
HL - hypotension and leucocytosis
U/S, blood culture
IV fluid, IV AB broad, correct coagulopathy, early ERCP
organisms causing diarrhea
e.coli → ________, _________, _________
giardia → ______, ______, ______, ______, _______
campylobacter jejuni → ______, ______, ______ then ________
bloody diarrhea organisms → ________, ________, ________
(traveller’s diarrhea) short period,self limiting, hx of travel to africa
watery, weight loss(chronic), abd pain, bloating (symptoms >10d)
fever, headache, myalgia (muscle pain) → bloody diarrhea
campylobacter, shigella, salmonella
bloody diarrhea → (2)
traveller’s diarrhea →
diarrhea in paeds →
diarrhea + weakness + areflexia →
diarrhea + renal impairment + hemolysis →
diarrhea + RUQ pain →
watery diarrhea + long camp/travel in EU →
diarrhea after long term AB → (+TX)
diarrhea after eating eggs/chicken →
diarrhea just hours after meal →
diarrhea in bedridden-patient + stony hard stool →
campylobacter(more common), shigella
e.coli
rotavirus
guillain-barre syndrome
haemolytic uremic syndrome
amoeba
giardia
clostridium difficile (1st line - vancomycin / 2nd - metronidazole)
salmonella
staph toxins
fecal impaction
young + diarrhea, sometimes bloody + chronic abdominal pain, tenesmus → ____________
why not diverticulosis?
why not irritable bowel syndrome?
inflammatory bowel disease (UC/CD)
diverticulosis - usually asymptomatic
irritable bowel syndrome - no bloody diarrhea
*tenesmus - the feeling that you need to pass stools, even though your bowels are already empty
oesophageal cancer + liver metastasis
TX →
to relieve the symptoms of severe dysphagia →
no surgery, stage 4 cancer is inoperable
‘endoluminal stenting’
left supraclavicular mass →
indicates →
SX →
sign →
right supraclavicular mass
indicates →
pancoast tumour →
virchow’s node
gastric carcinoma (anorexia, dyspepsia, weight loss, old age)
troisier’s sign
oesophageal cancer, lung cancer, hodgkin’s lymphoma
tumour at the apex of the lung (L/R), spreads to ribs & vertebrae
Virchow’s Node = The physical finding (enlarged left supraclavicular node)
Troisier’s Sign = The clinical significance (strong suspicion of metastatic cancer due to this finding)
priMary biliary cirrhosis features
3M →
others →
TX →
common association → _______________ syndrome
anti Mitochondrial antibodies, Middle age, igM
pruritus, jaundice, high ALP (alkaline phosphatase)
ursodeoxycholic acid, cholestyramine
sjogren’s
primary sclerosing cholangitis
diagnosed by →
common association →
features →
TX →
ercp
IBD - ulcerative colitis
pruritus, jaundice, high ALP
ursodeoxycholic acid, cholestyramine
mid age female + abnormal LFT + 2ry amenorrhea + presence of autoimmune disease (e.g. hyperthyroidism) →
*ALP is norm or mildly increased
autoimmune hepatitis
hx of heavy alcohol consumption + signs of liver disease (ascites, hepatomegaly, jaundice, spider naevi, hematemesis) →
alcoholic liver disease
+ increased AST : ALT ratio (e.g. AST:150, ALT:70)
+ increased GGT
albumin infusion → increases ___________ → shift of _________ from ______________ → reduces _______and________ → good perfusion to ____________→ thus restoration of ____________
oncotic pressure
fluids…extracellular to intracellular
ascites…edema
kidneys
norm urine output
haloperidol can be used in small doses as __________.
it can cause __________
anti-emetic
hyponatremia
in ascites secondary to cirrhosis, we give _______ and _______
spironolactone…albumin infusion
50 y/o male + celiac disease since childhood + diarrhea + weight loss, complication of celiac →
intestinal lymphoma
conditions that may develop due to celiac disease (7)
iron def anemia (**)
folic acid def
vitamin b12 def
osteoporosis
t-cell lymphoma
dermatitis herpetiformis
DM 1
TX of acute cholecystitis
-stable patient →
-unstable patient (temperature, tenderness, low bp) →
laparoscopic cholecystectomy
emergency laparotomy
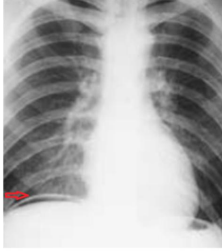
perforated peptic ulcer
features →
X-ray →
TX →
sudden severe abdominal pain
ill looking (motionless, diaphoretic, shallow rapid breathing)
abdominal tenderness and guarding
FREE AIR under diaphragm
NBM : IV fluids, antiemetics, analgesics, AB → urgent surgery
nil by mouth
you are not allowed to have any form of food, drink or medications by mouth
triple therapy for eradication of h.pylori →
(7-14 days)
PPI - omeprazole, esomeprazole 20mg BID
amoxicillin 1g BID
clarithromycin 500mg BID
PPI should be stopped 14d before h.pylori test, AB 28d
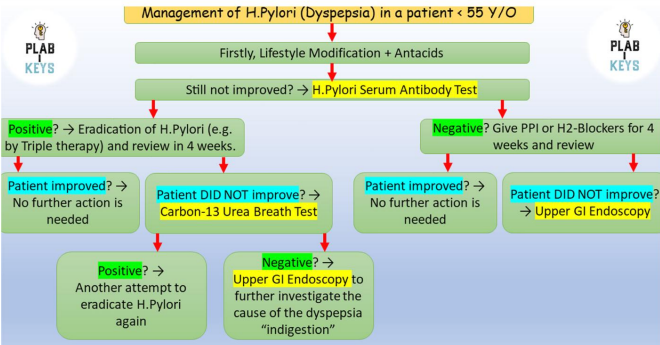
in treated patient of h.pylori + symptoms persistence, we do
carbon13 urea breath test
if N/A then stool antigen test
SX of H.pylori infection (10)
abdominal pain (burning)
pain worse on empty stomach or night
poor appetite
weight loss
heart burn
indigestion (dyspepsia)
belching/burping
nausea
vomit
blood in stool
≥ 55y/o + dyspepsia +weight loss →
urgent upper GI endoscopy to exclude oesophageal/gastric cancer