Unit 1 section A
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Water. DNA. RNA. Origins of Life.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
Hydrogen Bonds
A weak bond of attraction between a hydrogen atom and another atom
Polar covalent bond
when atoms with different electronegativities share electrons unequally in a covalent bond
Cohesion
Attraction between molecules of the same substance
Adhesion
An attraction between molecules of different substances
Solvent
A liquid substance capable of dissolving other substances
Metabolism
The combination of chemical reactions through which an organism builds up or breaks down materials
Xylem
Nonliving vascular tissue that carries water and dissolved minerals from the roots of a plant to its leaves
Surface tension
The force that acts on the surface of a liquid to minimize the area of the surface
Capillary action
The ascension of liquids through a slim tube due to adhesive and cohesive forces interacting between the liquid and the surface
Hydrophobic
Having an aversion to water; tending to coalesce and form droplets in water.
Hydrophilic
A molecule that is able to interact with water
Buoyancy
The ability of a fluid to exert an upward force on an object placed in it
Viscosity
A liquid's resistance to flowing
Thermal conductivity
The rate at which a substance transfers heat
Specific heat capacity
The amount of heat one gram of a substance must absorb or lose to change its temperature by one degree Celsius
Apoplast pathway
A route that water takes through a plant root to the xylem through cell walls.
Extraplanetary
Situated or originating outside the region of the planetary orbits
Goldilocks zone
habitable zone able to sustain life (has the necessities for organisms to live, grow, and reproduce)
Extraterrestrial
out of this world; above and beyond what is found on planet Earth
Asteroid
any of numerous small celestial bodies composed of rock and metal that move around the sun
Exoplanet
a planet-like body that orbits a star other than the sun outside of our solar system
Comet
A loose collection of ice and dust that orbits the sun, typically in a long, narrow orbit.
Frost line
the boundary in the solar nebula beyond which ices could condense; only metals and rocks could condense within the frost line
Genetics
the study of how genes and how traits are passed down
DNA
A complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes
RNA
A single-stranded nucleic acid that passes along genetic messages
Nucleotide
Basic units of DNA molecule, composed of a sugar, a phosphate, and one of 4 DNA bases
Phosphate Group
A functional group consisting of a phosphorus atom covalently bonded to four oxygen atoms
Deoxyribose
A five-carbon sugar that is a component of DNA nucleotides
Ribose
A five-carbon sugar found in RNA
Nitrogen base
carbon ring structure found in DNA or RNA that contains one or more atoms of nitrogen
What consists of a nitrogen base?
adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine, and uracil
Genetic code
the ordering of nucleotides in DNA molecules that carries the genetic information in living cells
Polymer
A long molecule consisting of many similar or identical monomers linked together.
Monomer
a molecule that can be bonded to other identical molecules to form a polymer.
Condensation reaction
monomers join to form polymers and water molecules are formed as a result
Complementary base pairs
Hydrogen bonding between particular pyrimidines and purines. Adenine & Thymine. Cytosine & Guanine.
What is the complementary base pair of Adenine?
Thymine
What is the complementary base pair of guanine?
Cytosine
What is the complementary base pair of thymine?
Adenine
What is the complementary base pair of cytosine?
Guanine
Polynucleotides
A polymer consisting of many nucleotide monomers in a chain; nucleotides can be those of DNA or RNA.
Endotherm
A polymer consisting of many nucleotide monomers in a chain; nucleotides can be those of DNA or RNA.
Antiparallel
The opposite arrangement of the sugar-phosphate backbones in a DNA double helix.
DNA replication
The process in which DNA makes a duplicate copy of itself.
Gene expression
The process by which a gene produces its product and the product carries out its function
Virus
A tiny, nonliving particle that invades and then reproduces inside a living cell.
Homeostasis
relatively constant internal physical and chemical conditions that organisms maintain
Metabolism
the combination of chemical reactions through which an organism builds up or breaks down materials
Purine definition
a nitrogenous base that has a double-ring structure; one of the two general categories of nitrogenous bases found in DNA and RNA
What nucleotide bases are purine?
Adenine and Guanine
Pyrimidines
The nucleotide bases present in DNA and RNA
What nucleotide bases are pyrimidine?
Cytosine, Uracil, and Thymine
What are the pyrimidines in RNA?
cytosine and uracil
What pyrimidine is only found in DNA?
Thymine
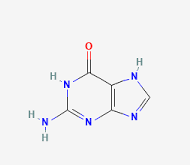
Guanine
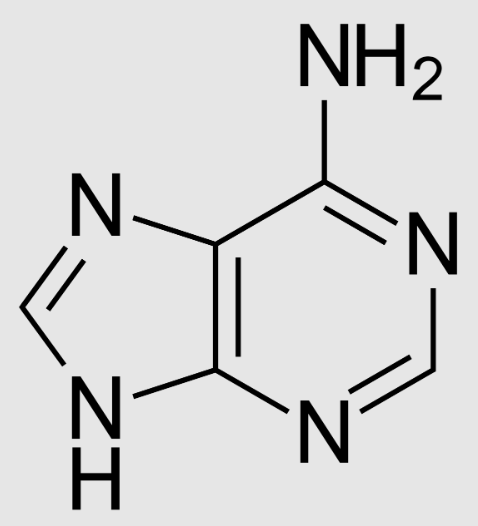
Adenine
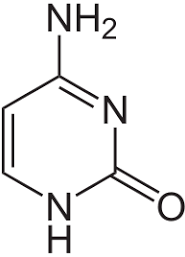
Cytosine
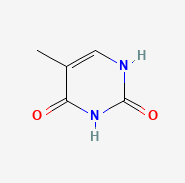
Thymine