A&P Unit 2: Layers of the Skin and Integumentary System
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What are the six functions of the skin?
protection from disease
protection from UV radiation
Protection from desiccation—drying out!
Non-verbal communication
Vitamin D Synthesis
Temperature Regulation
What are the layers of the skin?
Epidermis
Dermis
Hypodermis
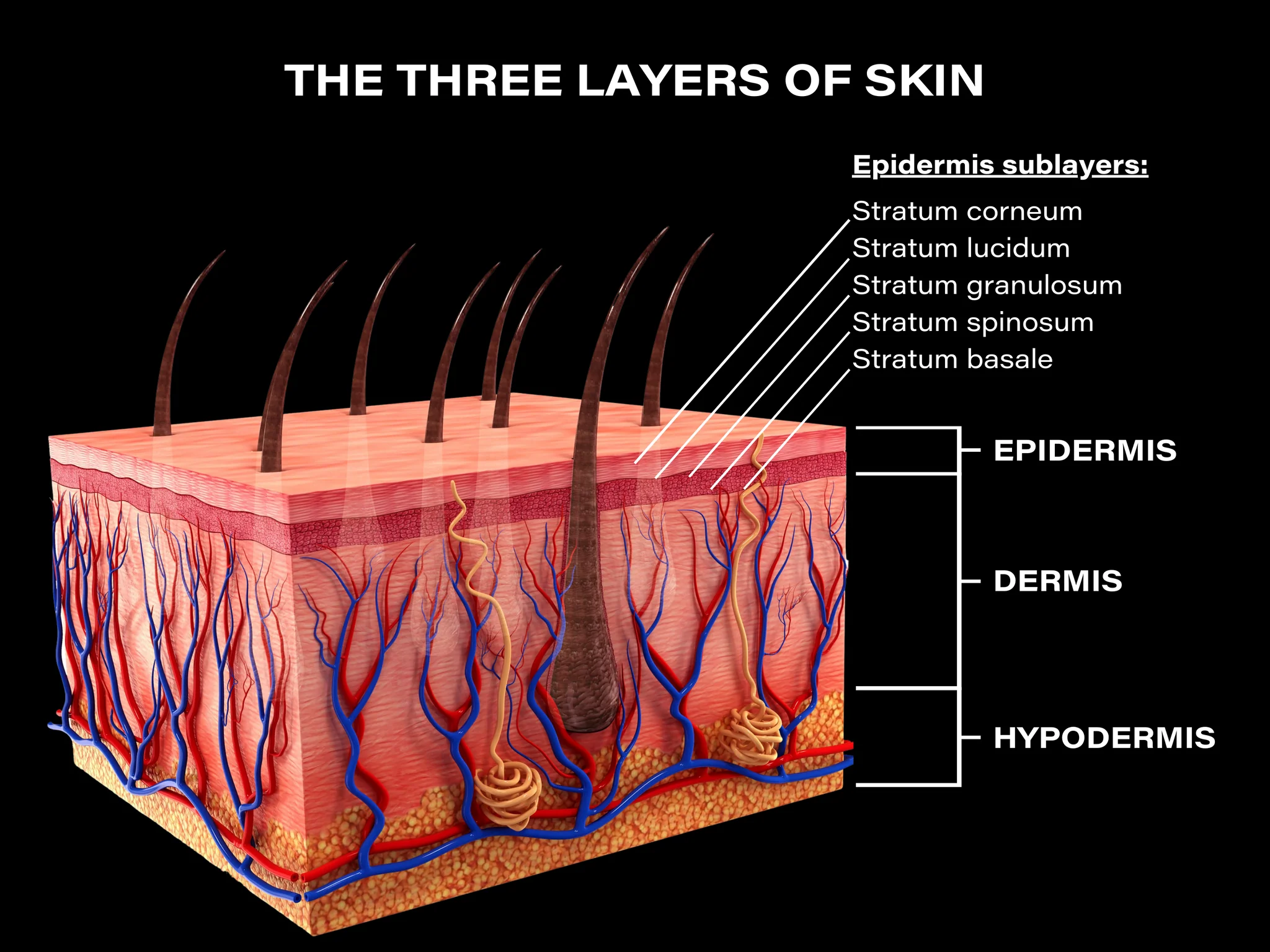
What is the epidermis composed of?
multiple layers of closely packed epithelial cells
the basal layer consists of cuboidal cells
the outer laters consist of squamous, keratinized cells
What are the five layers of the epidermis of thick skin?
Stratum Corneum
Stratum Lucidum
Stratum Granulosum
Stratum Spinosum
Stratum Basale
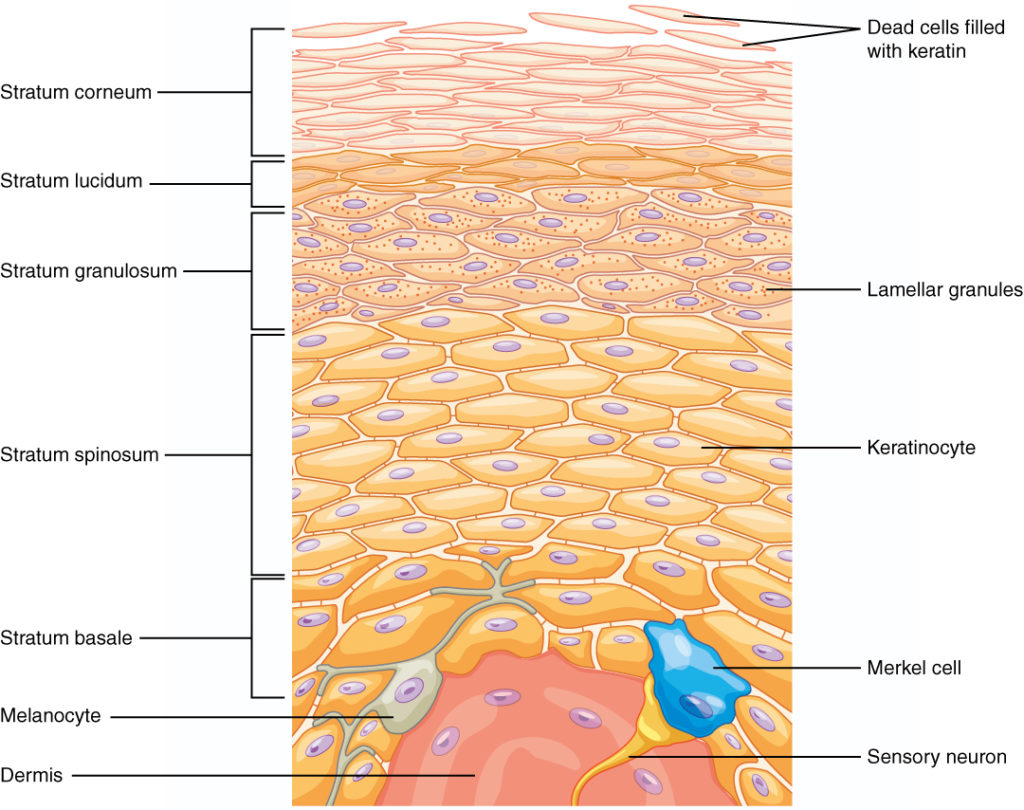
Melanocyte
a skin cell that produces melanin
Merkel Cell
a neuroendocrine cell that plays a role in touch sensation and potentially acting as a touch receptor
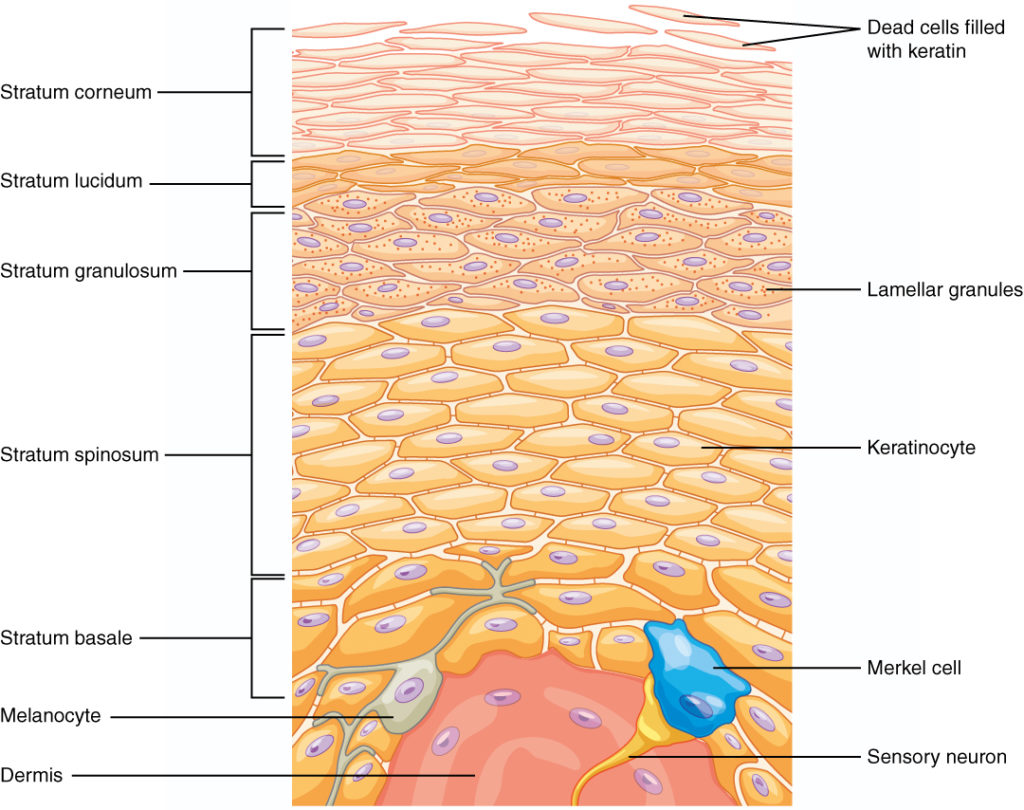
What is the dermis made up of?
dense irregular connective tissue that houses blood vessels, hair follicles, sweat glands, and other structures

What is the hypodermis composed of?
loose connective tissue and fatty tissue
Keratinocyte
the primary cell type found in the epidermis, responsible for producing keratin and forming a protective barrier.
What are calluses?
thick accumulations of dead keratinocytes on the hands or feet
What four important events occur in the stratum granulosum?
Keratohyalin granules release filaggrin—a protein that binds keratin into tough bundles
Cells produce tough envelope proteins beneath their membranes
Membrane-coating vesicles release a lipid mixture that spreads out over cells surface and waterproofs it
Keratinocytes’ organelles degenerate and the cells die
How is the skin waterproofed?
by tight junctions between skin cells and the waterproofing that occurs in the stratum granulosum
What does the epidermal water barrier prevent?
dehydration
Does the epidermal water barrier prevent water absorption from the skin?
No, it only prevents water loss (ex: prune fingers after a bath)
What are the two components of the dermis?
papillary layer
reticular layer
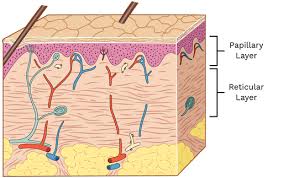
What are the papillary and reticular dermal layers made up of?
connective tissue with fibers of collagen extending from one to the other
What is skin pigmentation determined by?
the amount of melanin produced by melanocytes in the stratum basale and taken up by keratinocytes
What are moles?
anything from benign accumulations of melanocytes to melanomas
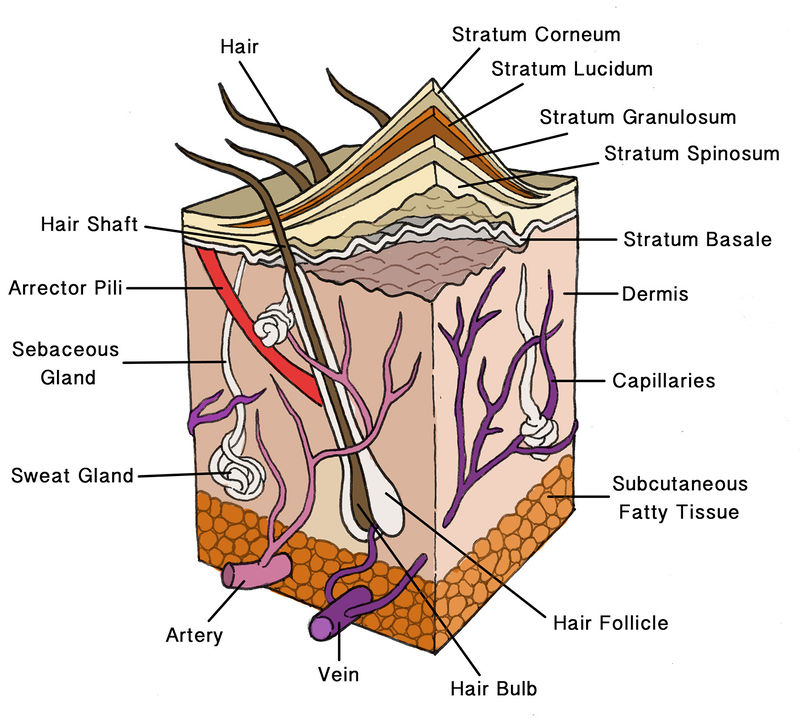
Where do hair follicles originate?
in the epidermis
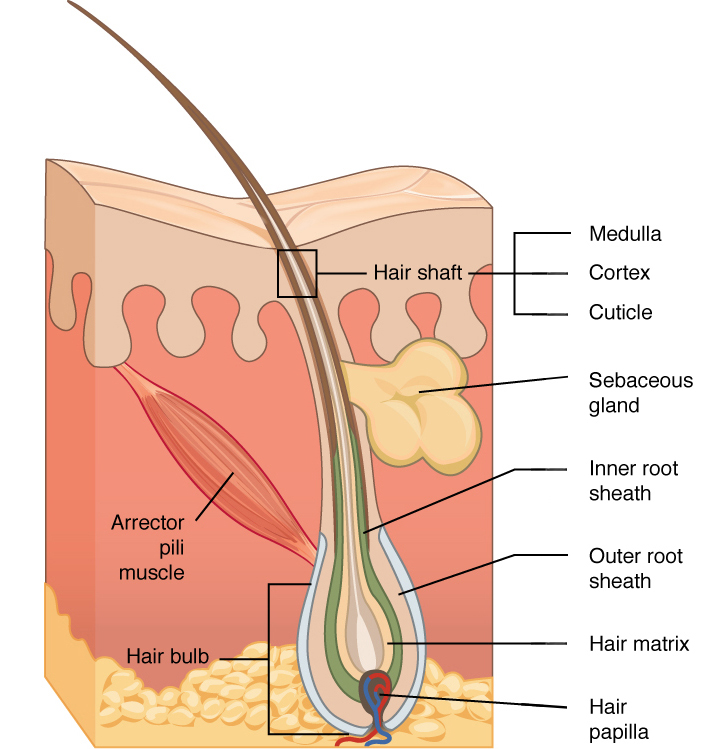
What are the different parts of a hair follice?
the hair bulb, hair shaft, inner root sheath, outer root sheath, and sebaceous gland
Nails are an accessory structure of the _______ system.
integumentary
Sudoriferous glands
sweat glands
What are the two types of sudoiferous glands (sweat glands)?
Merocrine glands
Apocrine glands
Merocrine glands
Sweat glands that are widely distributed over the body surface
Function as evaporative cooling
Apocrine glands
Sweat glands that are found in regions covered by the pubic, axillary, and male facial hair
Function as scent glands
Sebaceous Glands
oil glands associated with hair follicles
Ceruminous Glands
glands of the ear canal that contribute to earwax
Mammary Glands
milk producing glands located in the breasts
How is the body able to achieve thermoregulation (maintain body temperature)?
When the body is hot dermal blood vessels dilate and sweat secretion increases
When the body is cold dermal blood vessels constrict to minimize heat loss
First Degree Burn
involves only the epidermis and heals within days
symptoms: redness and pain
Second Degree Burn
this is a partial thickness burn and involves parts of the dermis
symptoms: skin may appear red, tan, or white; blistered and painful
takes two weeks or several months to heal
Third Degree Burn
this is a full thickness burn and involves the epidermis, all of the dermis, and often some deeper tissue
often requires skin grafts
needs fluid replacement, infection control, and supplemental nutrition
What are the graft options for someone with a third degree burn?
Autograft
Split-Skin-graft
Isograft
Autograft
tissue taken from another location on the same person’s body
Split-skin-graft
taking epidermis and part of the dermis from an undamaged area such as the thigh or buttocks and grafting it into the burned area
Isograft
skin from an identical twin
Tanning rays and burning rays are thought to cause ______.
cancer
Sunscreens protect you from _____, but not necessarily against cancer.
sunburn
Chemicals in sunscreen damage ____ and generate harmful free radicals
DNA
Those who use tanning beds before the age of 35 increase their chance of skin cancer by ____%
75