Magnetism in MRI
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
From MRIquiz
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
A system operating at 30,000 Gauss has a field strength of:
3 Tesla (10,000 Gauss=1Tesla)
THE MRI system component that produces the magnetization of proton spins (alignment) is known as the
main magnet
Spin-lattice relaxation
The return of the longitudinal magnetization to its equilibrium value along the Z axis (T1 recovery)
Spin-spin relaxation
the return of the transverse magnetization to its equilibrium value, zero (T2 decay)
The MRI system component that provides the ability to perform spatial encoding is the
gradient coil
Hydrogen is used in MR imaging because:
Of its abundance in the body
How many radiofrequency pulses produce a FID?
1
A magnetic vector possesses attributes of both __________ and _____________.
magnitude; direction
What type of magnet is used with most MRI systems currently manufactured?
superconduting
The force that an object can be attracted to the magnetic field is reliant upon:
The field strength (Tesla) of the MR system
The mass of the projectile
The specific ferromagnetic nature/properties of the material
All of the above
All of the above
What element in the body is the principal nucleus utilized in clinical MR imaging?
Hydrogen
The first documented human MR image was obtained on a 15 MHz RF system, what field strength did it operate at?
0.352 Tesla
A Free Induction Decay (FID) is produced from a:
RF pulse
If the RF energy transmitted is __ MHz, the slice through the patient would be in a magnetic field of .995T.
42.36 (42.57*.995—> 42.357)
Hydrogen protons in the anti-parallel state are referred to as:
spin down & high energy spins
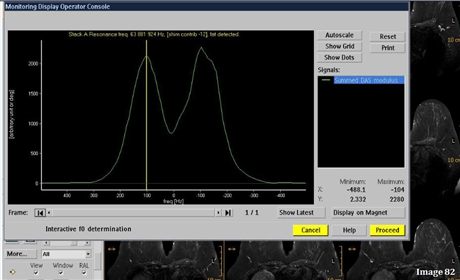
Aside from the center frequency, what other indicator in Image 82 signifies it was acquired at 1.5 Tesla?
The chemical shift between fat and water is 220 Hz
What has a higher precessional frequency?
water
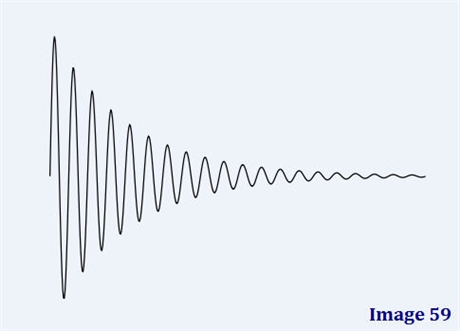
Image 59 is an example of a:
Free induction decay (FID)
The _________ is defined as the resonant frequency, and is equal to the product of the magnetic field and the gyromagnetic ratio
Precessional frequency
Force on an object in an magnetic environment depends on:
Mass of the object
Strength of the magnetic field
Strength of the RF field
Ferromagnetic properties of the object
mass of the object, strength of the magnetic field, and ferromagnetic properites of the object
When thermal equilibrium is reached:
There are more hydrogen protons in the low energy state
___________ substances have strong magnetic properties and can be pulled into the magnetic field
Ferromagnetic
In one T2 relaxation time:
63% of the transverse magnetization has decayed or the time it takes the spins to de-phase to 37% of their original value
Immediately following the application of the 90° RF pulse, the precessing protons:
Begin to precess in phase & Tip into the transverse plane
The fringe magnetic field:
Can cause nearby medical devices to malfunction
All of the following are non-ferrous substances EXCEPT:
Plastic
Titanium
Iron
Copper
iron
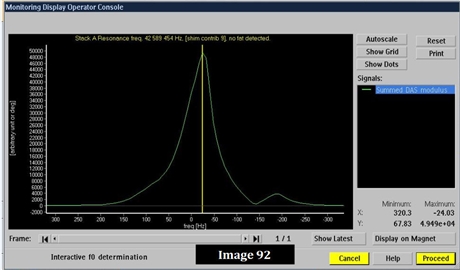
Image 92 was acquired at what field strength?
1.0 Tesla
At 1.5 Tesla, the chemical shift between fat and water is:
220 Hz
____________ states that a changing magnetic field will induce a voltage.
Faraday’s law of induction
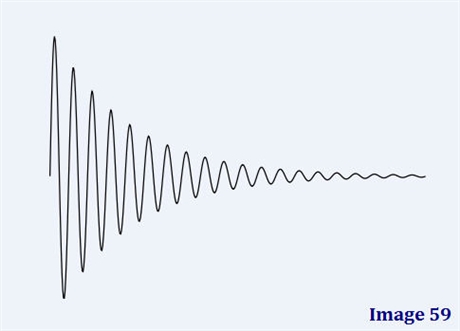
Which of the following most accurately defines what Image 59 is?
The decaying, oscillating signal induced after 90º pulse
All of the following are TRUE except:
Excitation is the process of moving the net magnetization away from the Z axis
Magnetic field gradients are static
The RF field oscillates at the Faraday frequency
The resonance frequency in a 1.5 Tesla magnet is 63.86 Mhz
The RF field oscillates at the Faraday frequency (The RF field oscillates at the Larmor Frequency)
_____________ occurs after initial RF application, causing phase differences to appear between precessing spins, resulting in decay of transverse magnetization.
Dephasing
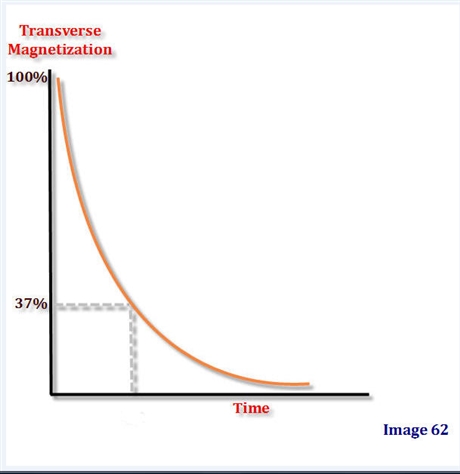
Image 62 represents:
T2 decay
The difference in chemical shift is approximately ______ parts-per-million
3.5
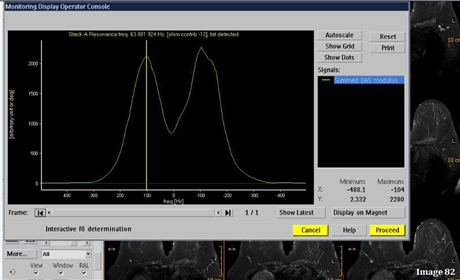
Image 82 was acquired at what field strength?
1.5 Tesla
Immediately following the application of the 90° RF pulse, the transverse magnetization is:
non-zero
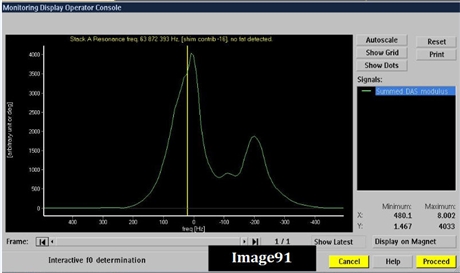
Image 91 was acquired at what field strength?
1.5 Tesla
The extent to which a material or tissue becomes magnetized in an external magnetic field is called:
magnetic susceptibility
Calculate the Larmor frequency for H at 0.5Tesla.
21.28 Mhz (42.58×0.5T)
What is defined as the excess number of hydrogen protons aligned with the static magnetic field direction (B0)?
Longitudinal magnetization
All of the following are true regarding RF EXCEPT:
The RF pulse stimulates the protons into parallel or anti-parallel alignment.
Relaxation begins after the RF is turned off
RF stimulates the protons to be in phase
RF converts FID into an echo
RF converts FID into an echo
______________ is the term used to describe the degree of magnetization of an object.
susceptibility
At 1 Tesla the frequency difference between that of fat and water is approximately:
147 Hz
The precessional frequency of hydrogen, according to the Larmor equation, at 3Tesla is:
127.71 MHz
All of the following are ferromagnetic substances EXCEPT:
Stainless Steel
Gold
Iron
Nickel
gold
In one T1 relaxation time:
63% of the longitudinal magnetization has recovered
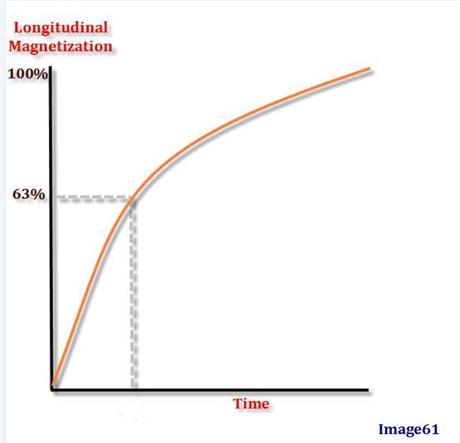
Image 61 represents:
T1 recovery
Superconducting magnet systems -- most commonly used systems due to the high field strength and imaging capabilities. The main magentic field is
parallel to the long axis of B0
can be “shut off” in the quickest case of an emergecy
resistive magnets
Permanent magnets are blocks of _____, and are typically heavy.
ferromagnetic plates used to generate a magnetic field
Are iron and iron-like substances that can generate a relatively strong magnetic field
ferromagentic
have a very weak magnetic field. Gadolinium is used as a contrast material because it is
paramagnetic
has no magnetic field
diamagnetic

Image 60 represents the:
Larmor equation
The protons that align themselves with the direction of the static magnetic field (B0) exist in a ___________energy state than those anti-parallel to the magnetic field.
lower
The net magnetization vector (NMV), when aligned with the magnetic field direction, is aligned __________.
along the longitudinal axis
How well a material attracts the imaginary lines of the magnetic field is defined as:
Magnetic permeability
The energy used to form MRI images is ____________ the patient's tissues.
Emitted from