BIS 2C Plant Phylogeny
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
before Coleochaete
plasmodesmata , retention of the egg
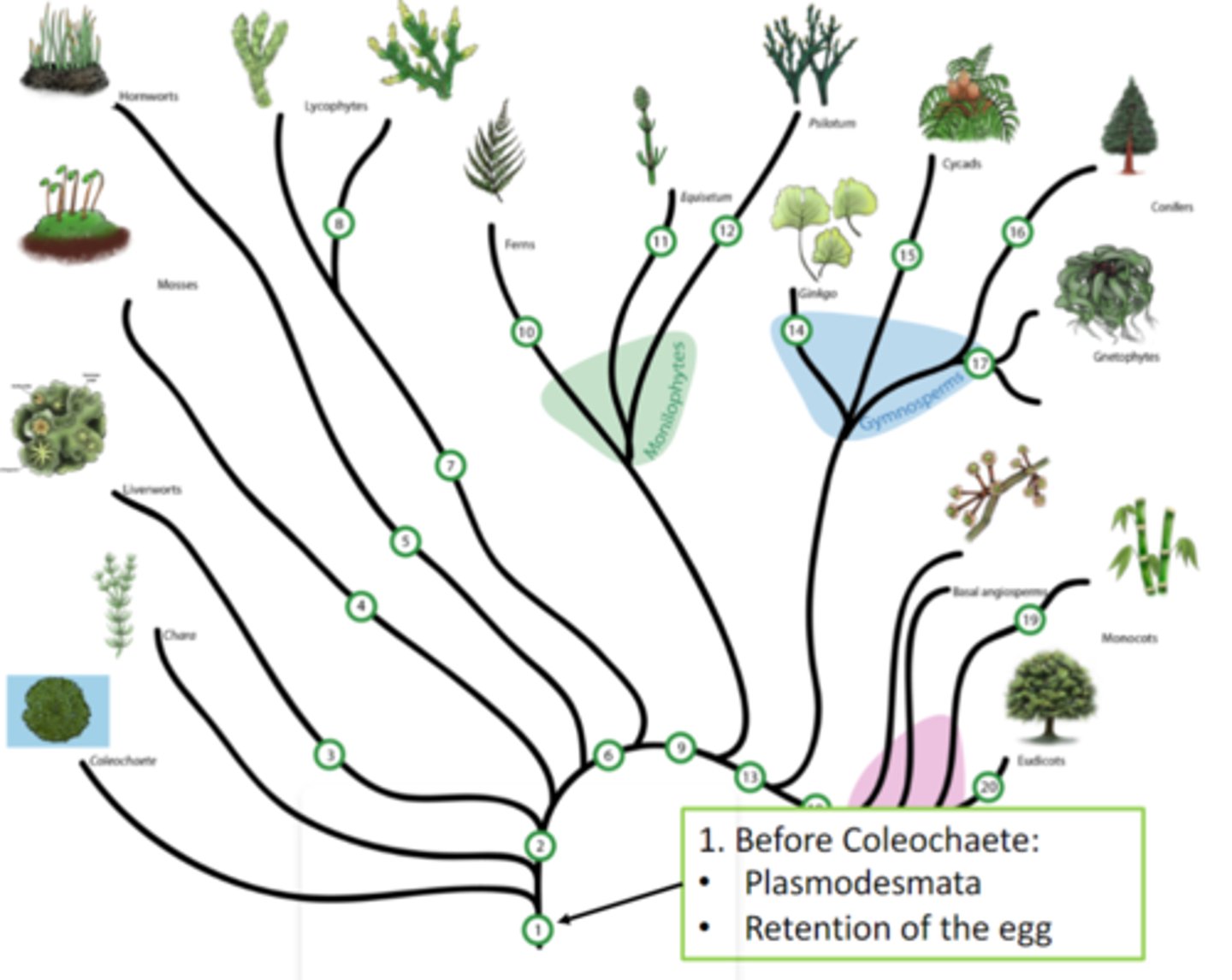
land plants
waxy cuticle, zygote retained, alternation of generations life cycle, airborne spores
includes: every plant past chara
vascular plants
(lycophytes, monilophyte, gymnosperms, angiosperms) vascular tissue, sporophyte dominance
includes: everything except bryophytes (liverworts, moss, hornworts)
Euphyllophytes
(monilophytes, gymnosperms, angiosperms) megaphylls, overtopping and lateral branching of stems, chloroplast DNA inversion
seed plants
(gymnosperms, angiosperms) seeds, pollen, BVC, heterospory, ovules
angiosperms
(basal angiosperms, monocots, eudicots) flowers, fruit, double fert and endosperm (3n)
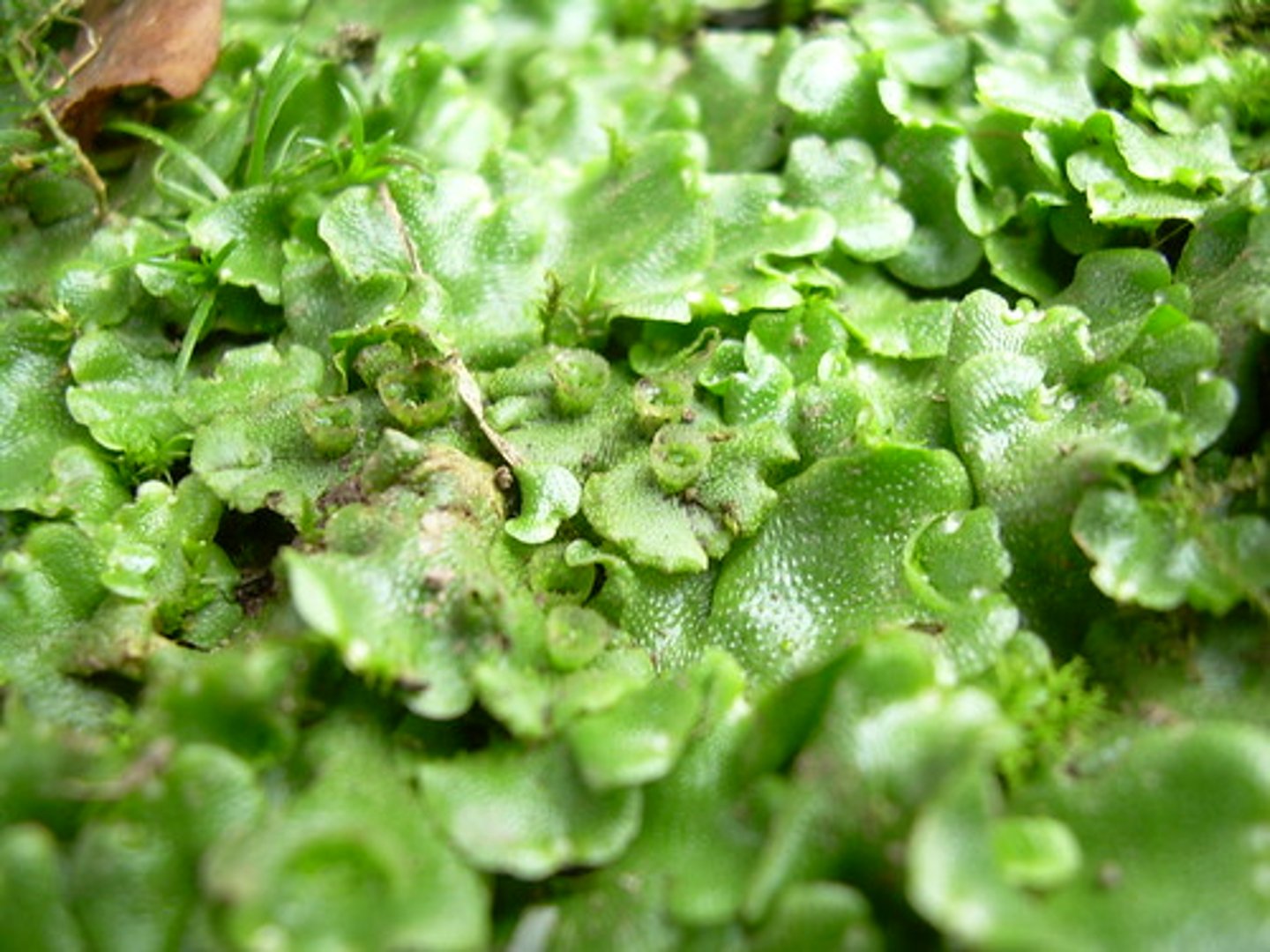
liverworts
male and female gametes produced on separate stalked structures, gemmae

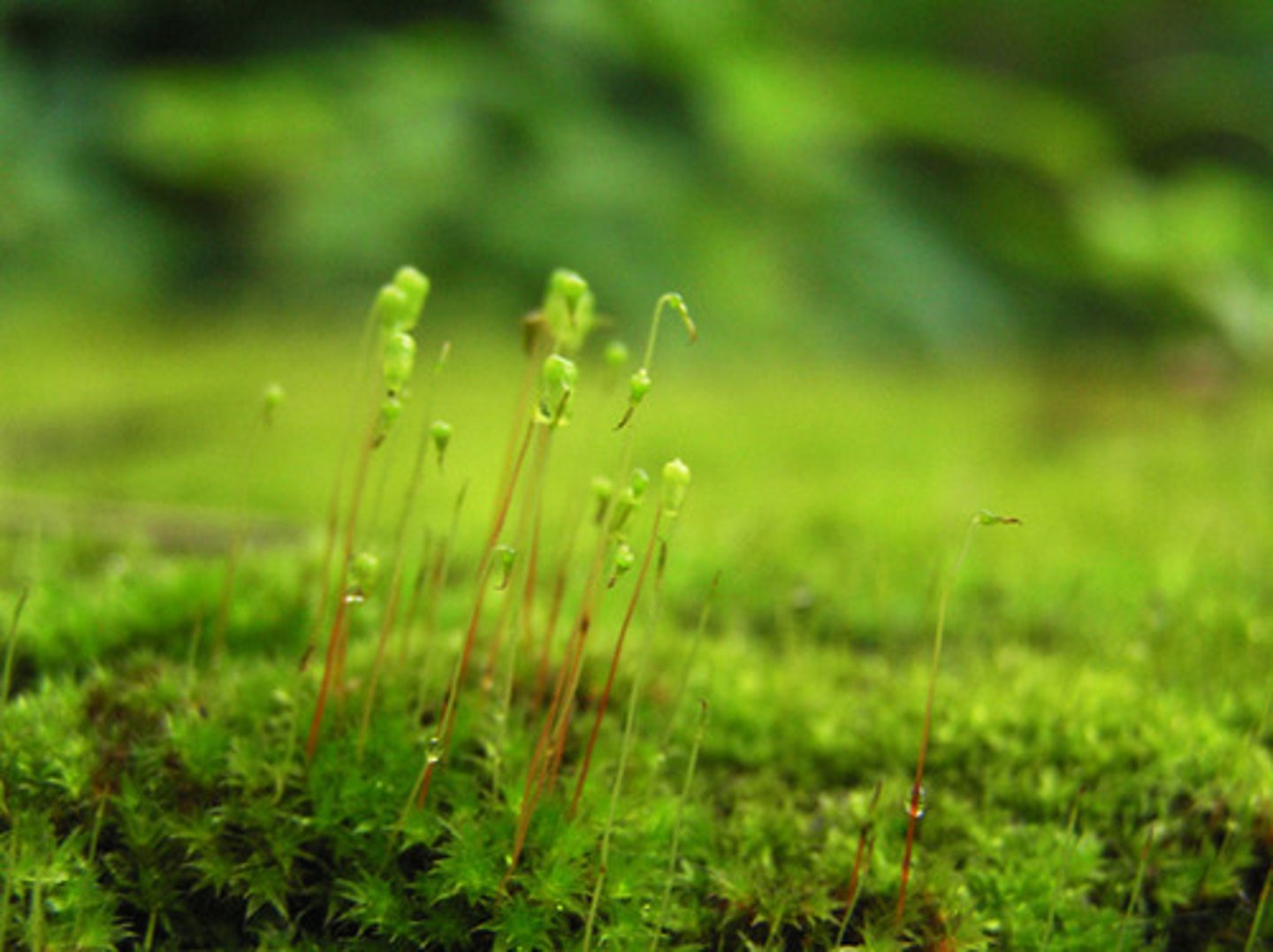
moss
elongate saprophyte with capped like sporangium

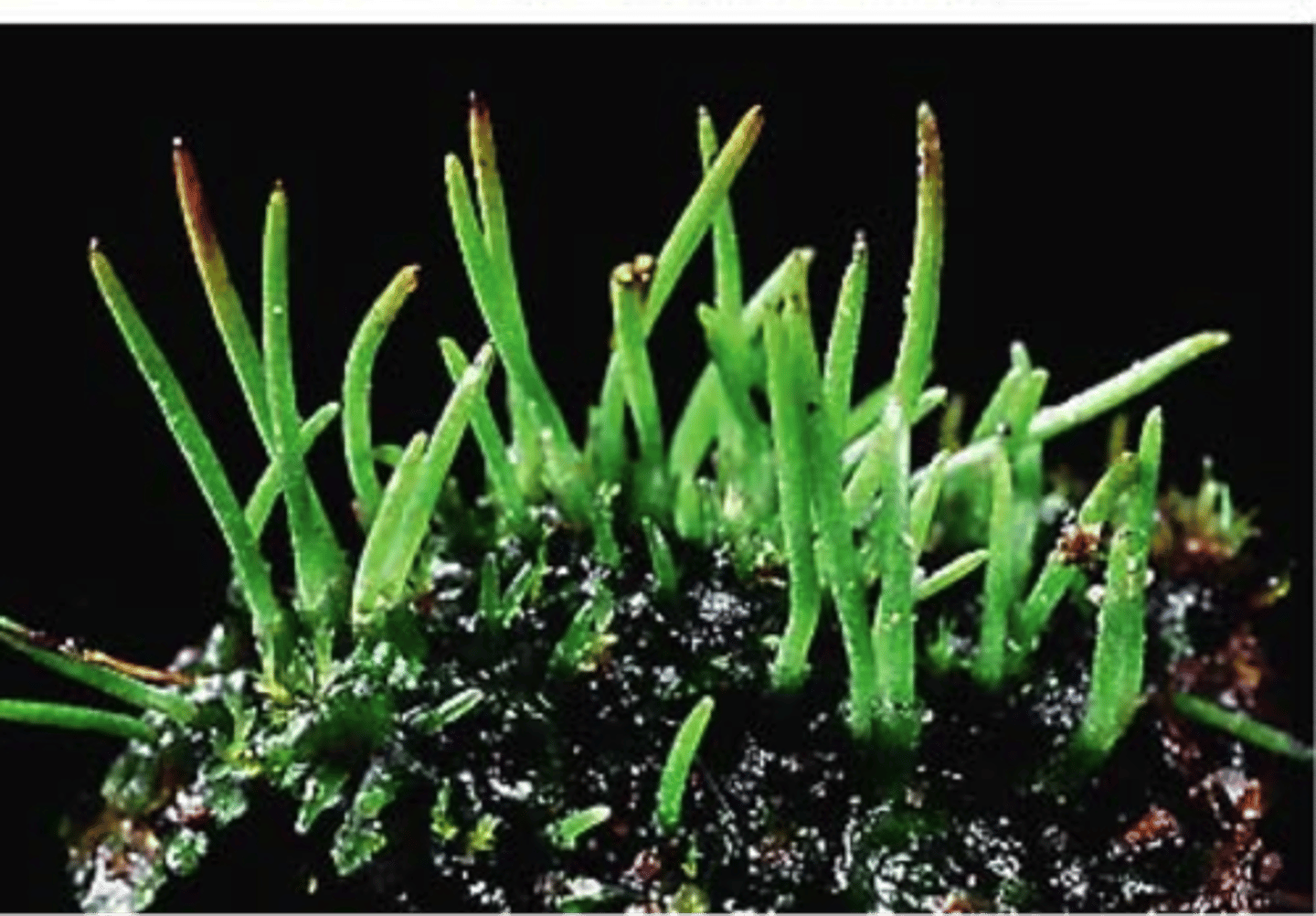
hornworts
elongate, persistently green (photosynthetic) sporophyte, sporophyte with indeterminate growth

non vascular plants
(liverworts, moss, hornwort) no vascular tissue, gametophyte dominant, short in stature
Lycopodium
within lycophytes, strobili, dichotomous branching of stem, microphylls
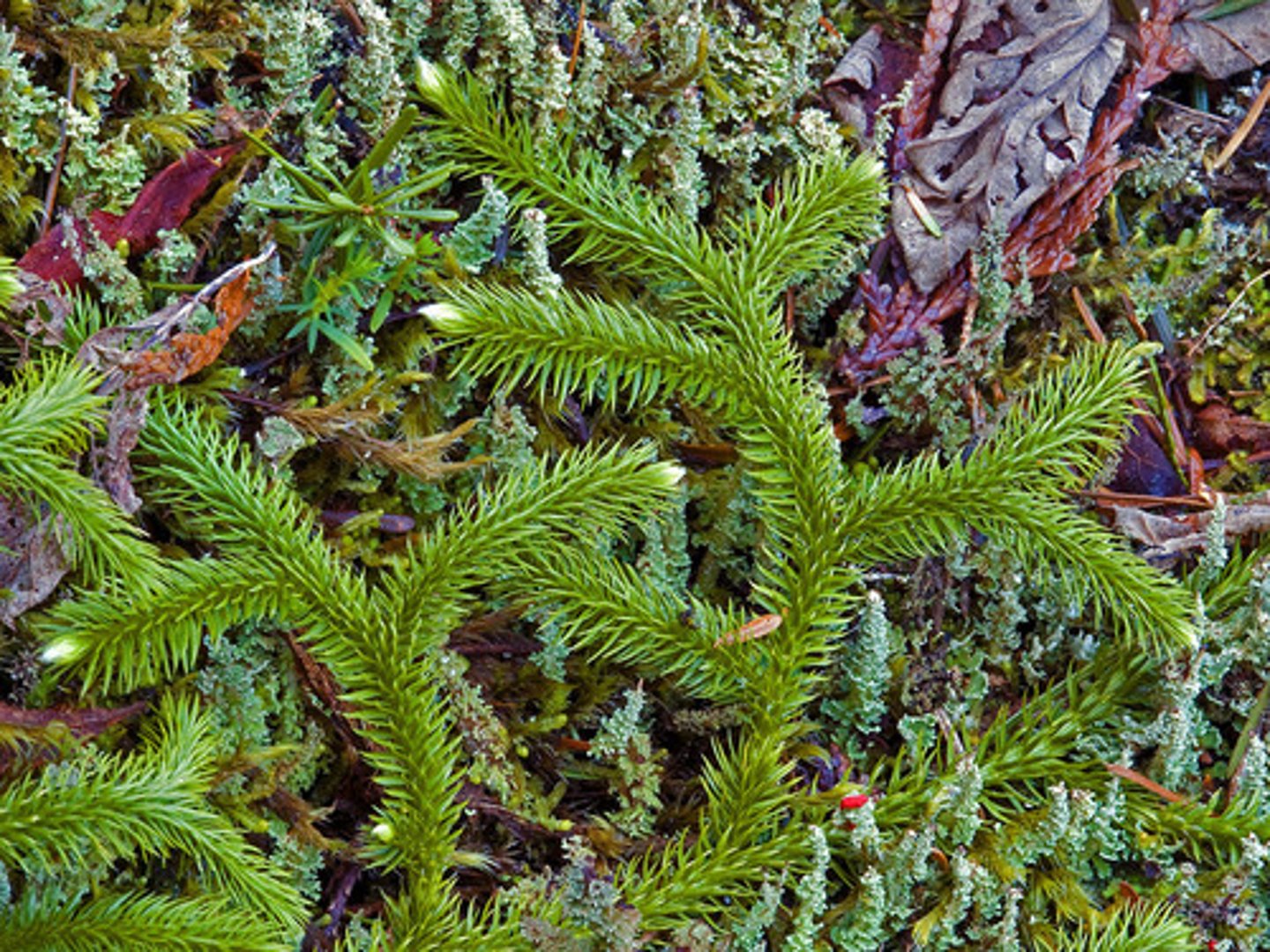

selaginella
within the lycophytes (microphylls, dichotomous branching), heterospory, no sori
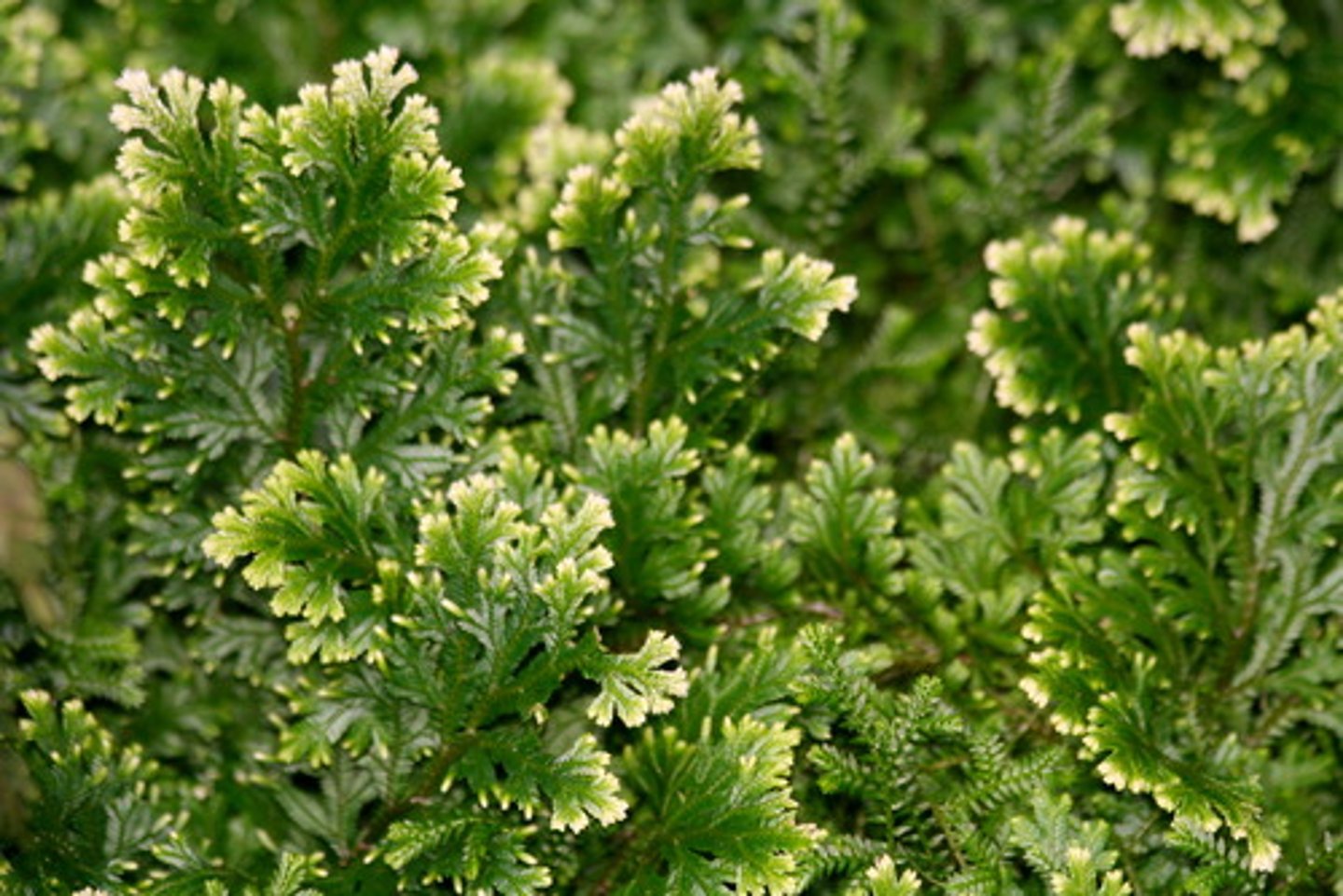

ferns
(monilophyte) sori, megaphylls emerge as fiddleheads
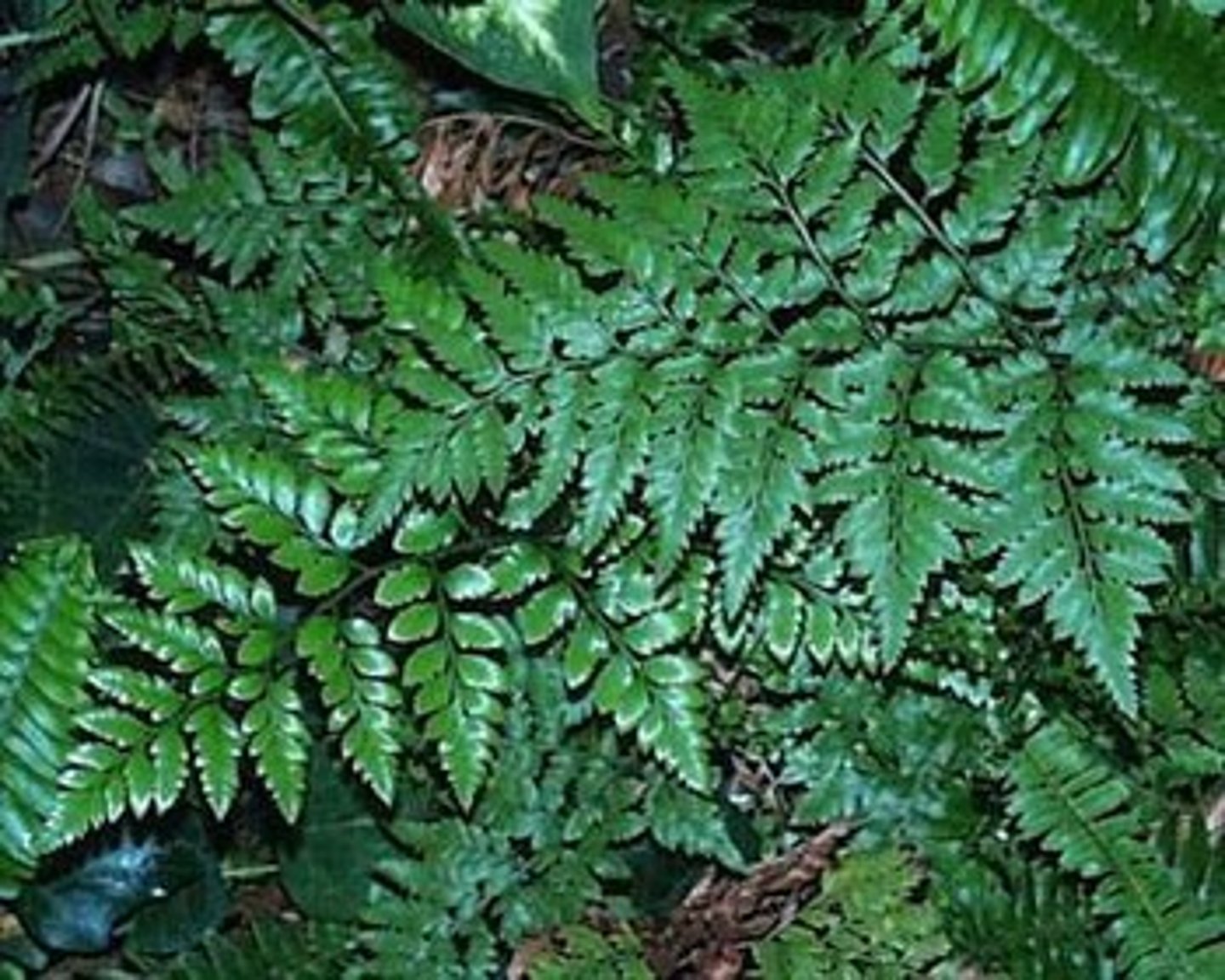

equisetum (horsetail)
(monilophyte) strobili at stem tips, whorled reduced leaves, hollow stem, highly reduced leaves
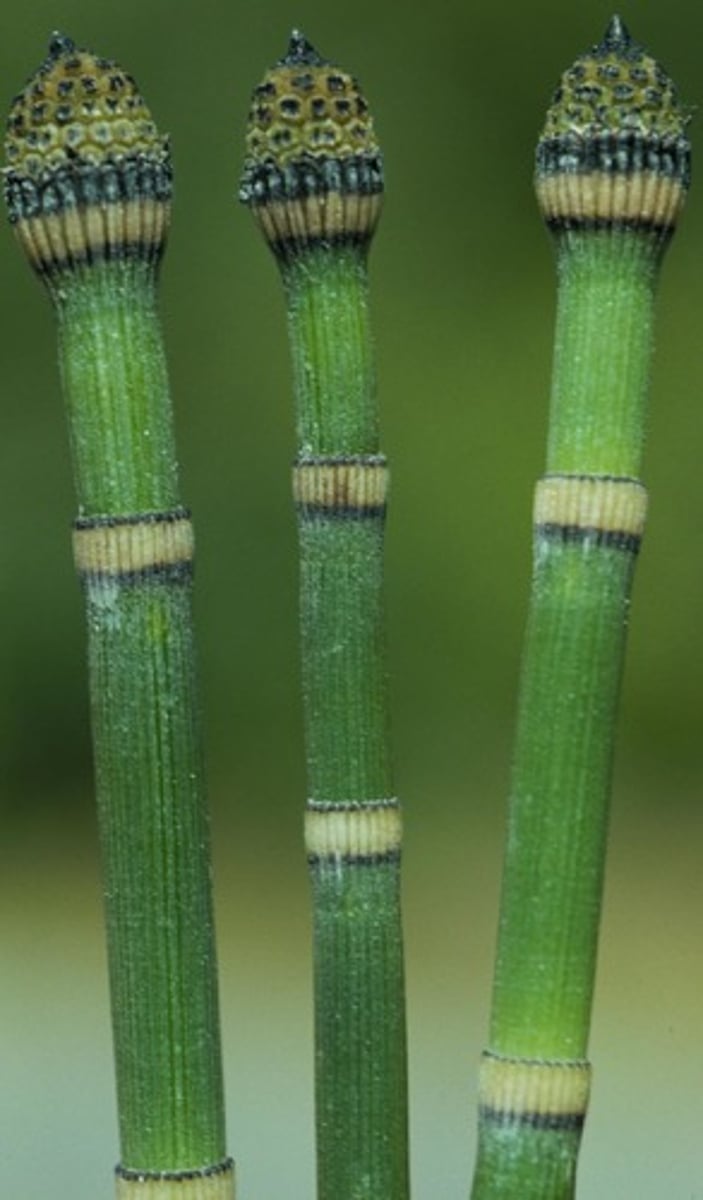

Psilotum
(monilophyte) leaves and roots reduced or lost, yellow + ball like sporangia at stem nodes, dichotomous branching of stem

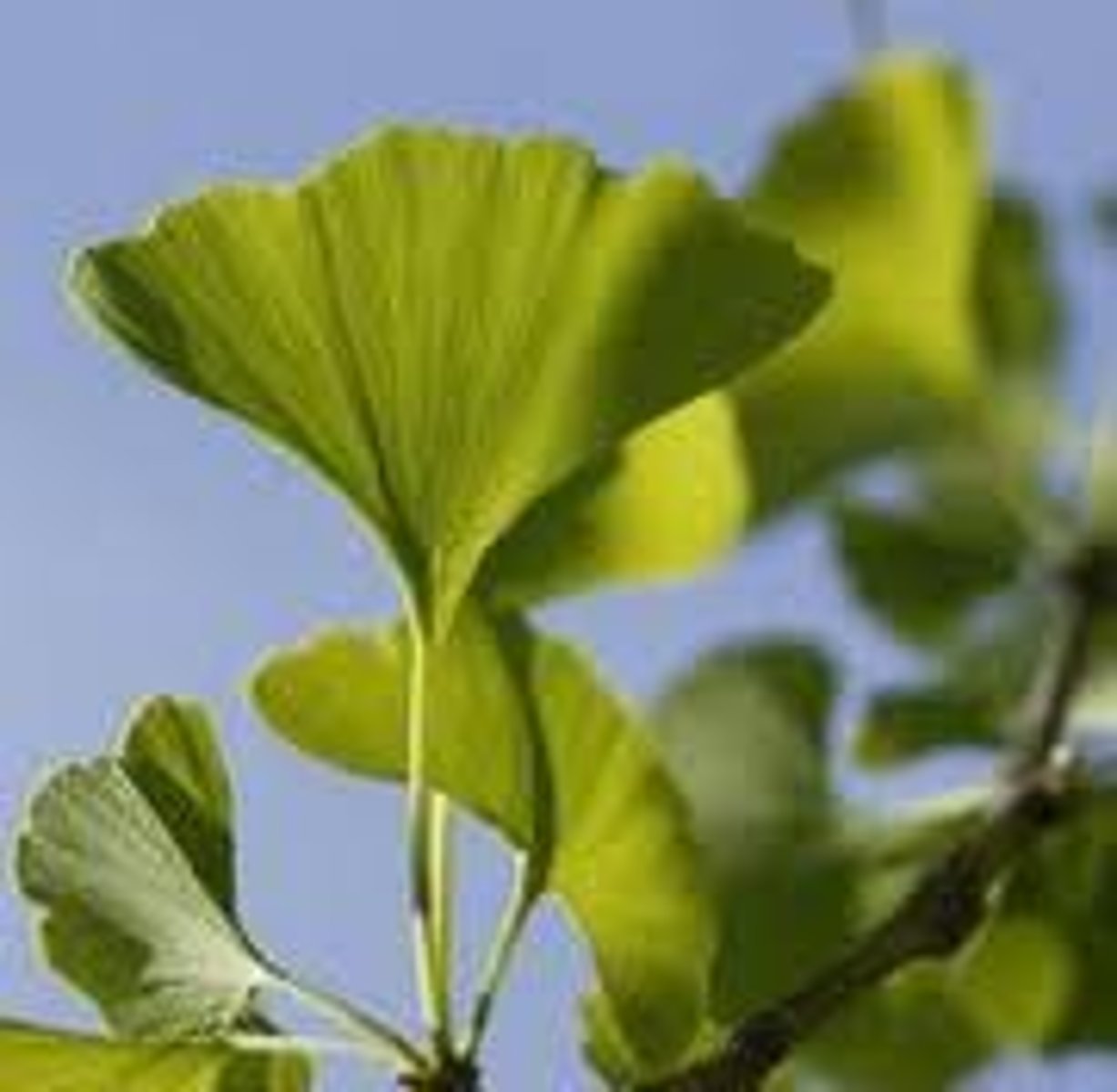
ginko (ginkgo)
(gymnosperm) growth form: tree, male and female strobili on separate plants (dioecious), megaphylls divided into two lobes, foul smelling, fleshy seed coat

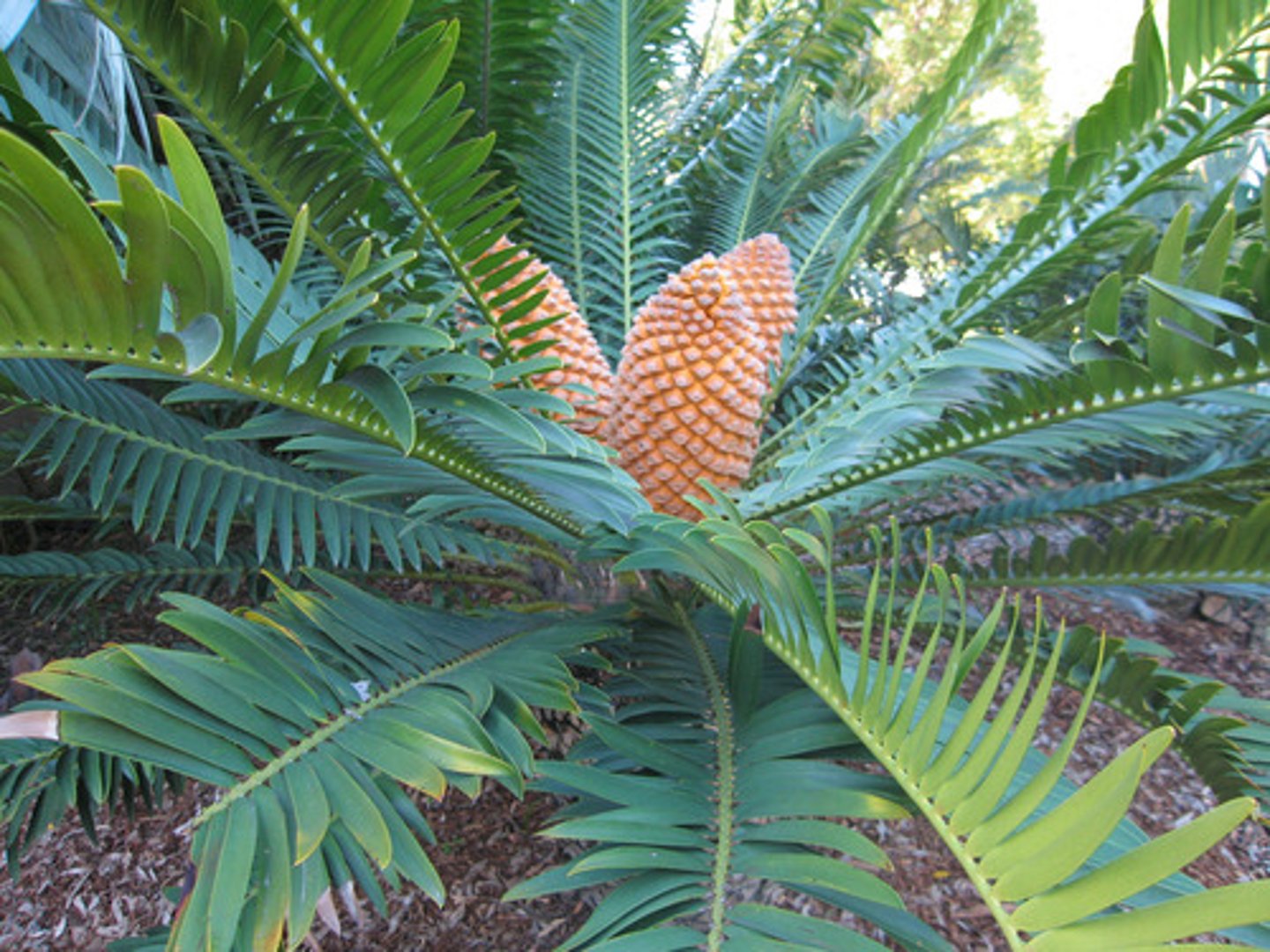
cycad
(gymnosperm) male and female strobili on separate plants (dioecious), large + compound megaphylls, no sori under leaves

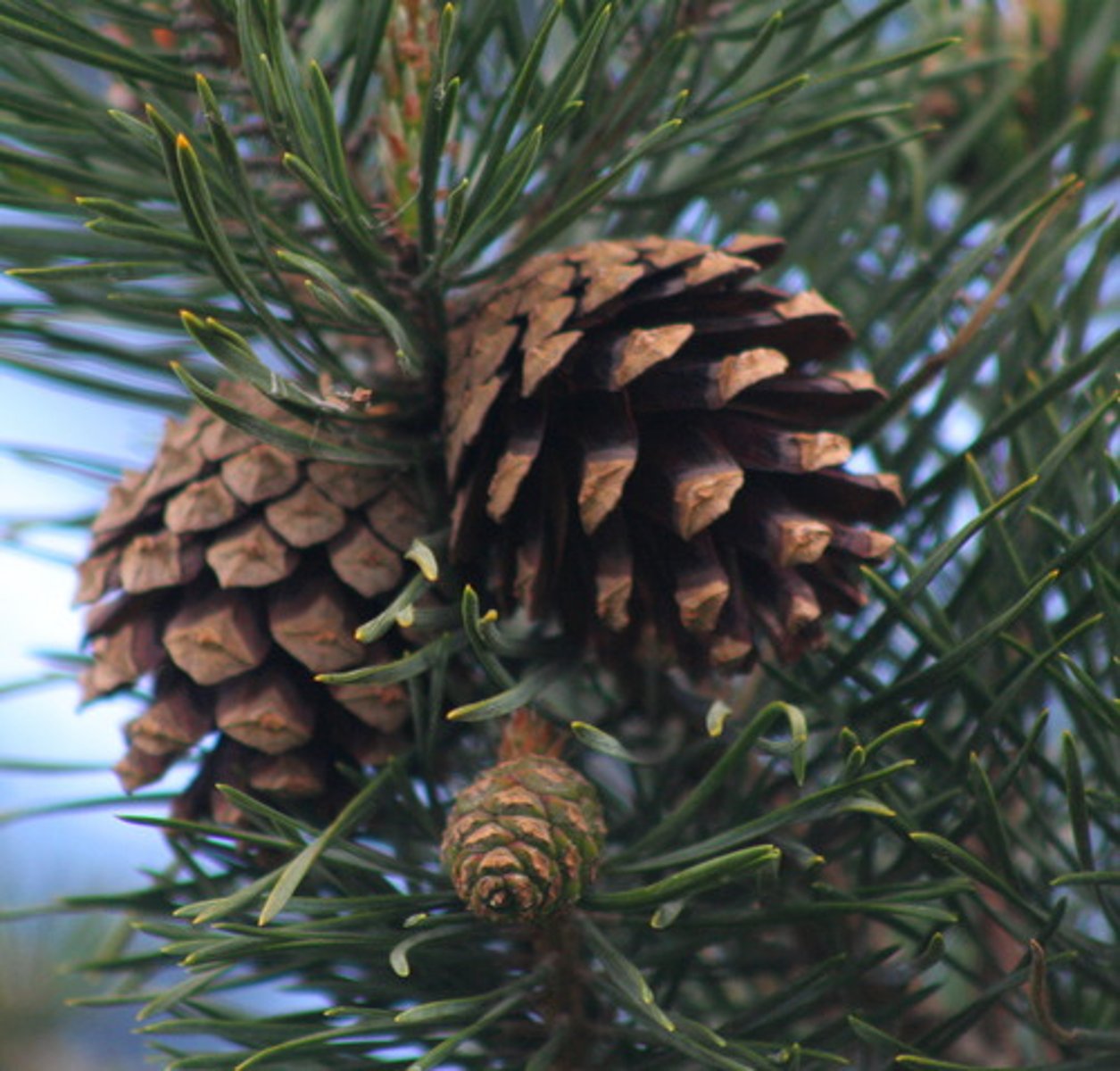
conifers
(gymnosperm) growth forms: tree, male and female strobili on same plant (monoecious), large + woody ovulate cones, smaller + soft pollen cones, modified + narrow megaphylls with resin ducts

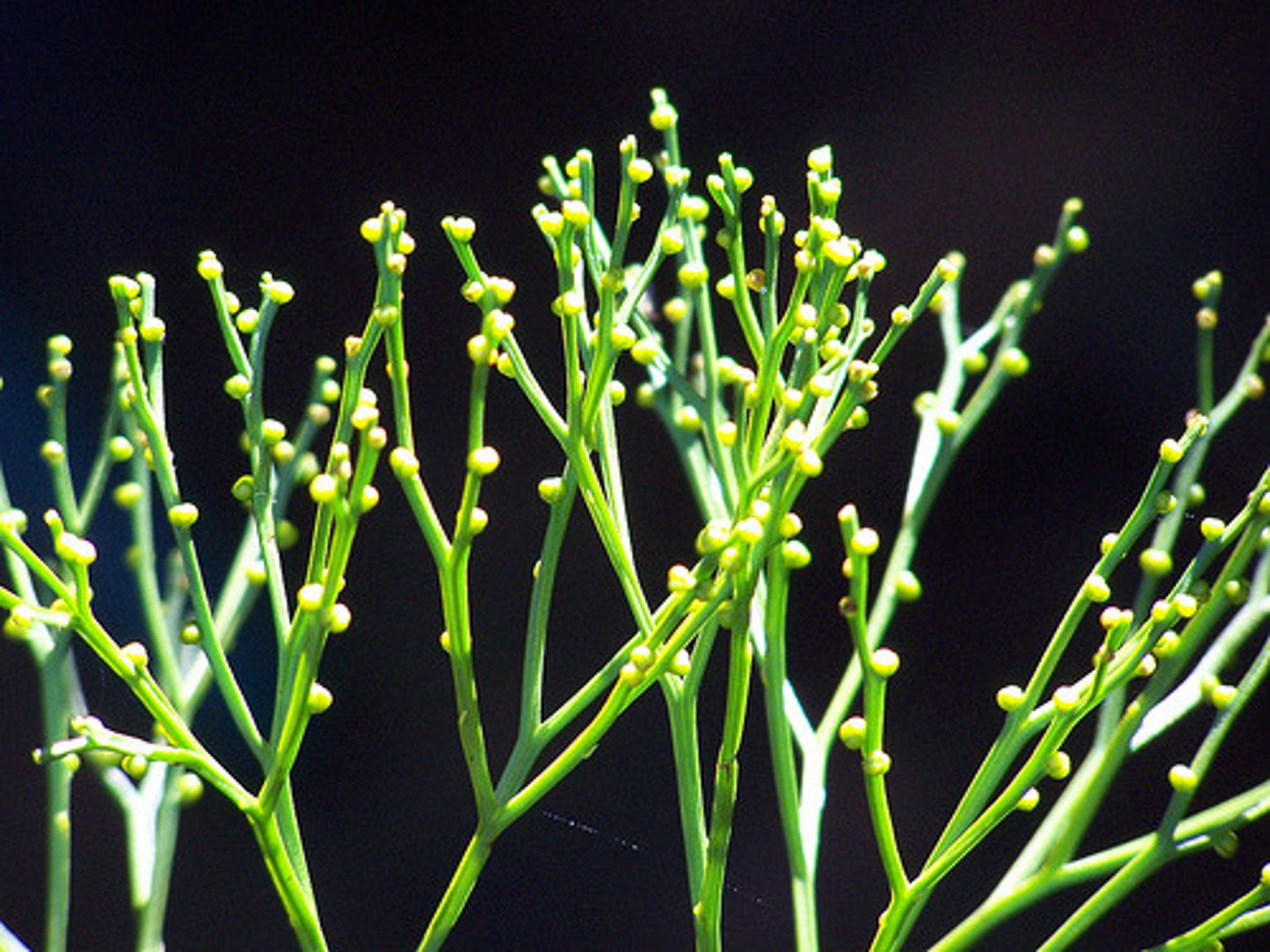
gnetophytes
(gymnosperm) male and female strobili on separate plants (dioecious), paired + opposite megaphylls, double fertilization and vessel elements (in some species)
indeterminate leaf growth (welwitschia), distinctive cones (gnetum)

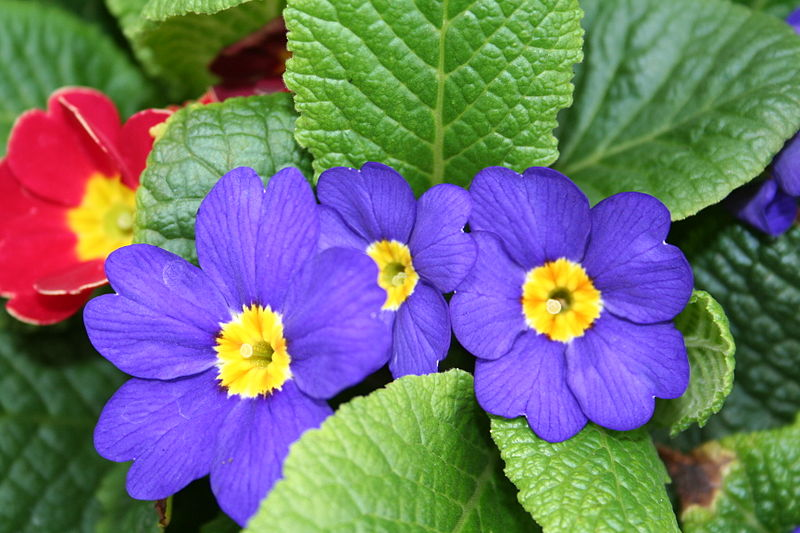
monocots
(angiosperm) flower parts in multiples of 3, megaphylls with parallel veins, loss of BVC, single cotyledon in the seed
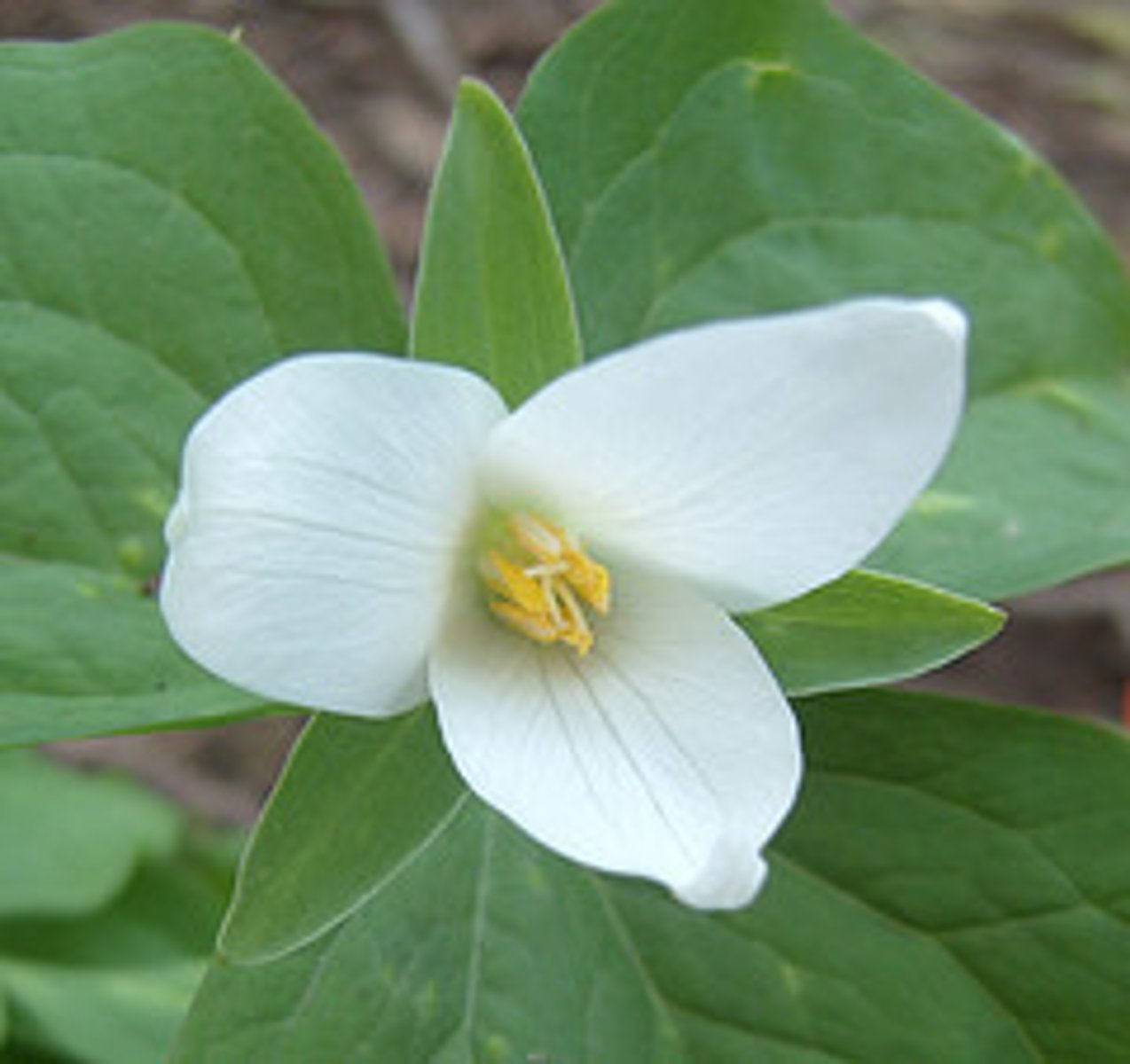

eudicots
(angiosperm) flower parts in multiples of 4 or 5, megaphylls with netted veins, two cotyledons in the seed

Monilophytes
Equisetum, Psilotum, and Ferns
Lycophytes
Lycopodium and Selaginella
Microphylls, dichotomous branching, strobili
Gymnosperms
Cycads, ginkgos, gnetophytes, conifers