BIOL2311 Practice Exam 1
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
The nose is __________ to the ears.
medial/ventral/anterior
A plane of section that runs parallel to the long axis of the body and divides it into equal right and left halves is called a __________ section.
midsagittal/median
What is the name of the membrane lining the walls of the abdominal cavity?
parietal peritoneum
What is the body cavity in which the stomach and urinary bladder are both located?
abdominopelvic
The term "oral" refers to which region of the body?
mouth
The term "femoral" refers to which region of the body?
wrist
The wrist is __________ to the fingers.
proximal
You are examining a microscope slide under the 10X objective lens and you switch to the 40X objective lens. The total magnification will:
increase
If you are using an objective lens with a power of 40X and ocular lenses with a power of 10X, the total magnification of the specimen will be ____X.
400
What is the body cavity in which the heart and lungs are both located?
thoracic
Identify the indicated part of the microscope.
objective lens
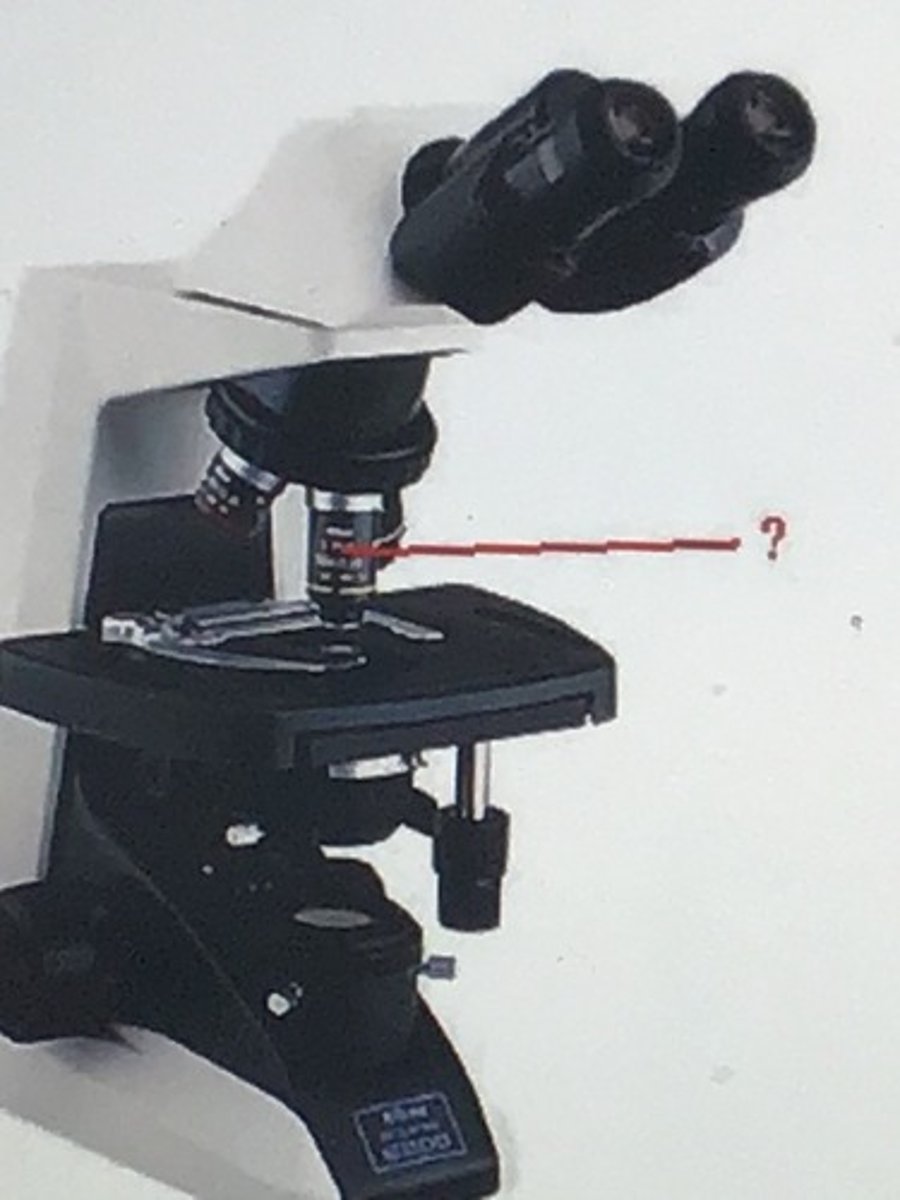

If you focus on a specimen using the 4X objective, then switch to the 10X objective, the specimen will still be in focus. This means that the microscope is __________.
parfocal
Given the following physiological requirements at a particular location within the body, name the specific tissue type that would most likely be found there:
This region must be able to stretch under force, but must also be able to resume its previous shape once the force is removed.
elastic connective tissue
Given the following physiological requirements at a particular location within the body, name the specific tissue type that would most likely be found there:
This material must provide shape to structures that are not intended to deform very much.
hyaline cartilage
What do we call a loose connective tissue containing both collagen and elastin fibers, and in which the primary cell type is the fibroblast?
areolar connective tissue
What do we call a dense connective tissue containing a hard, calcified matrix and populated primarily by osteocytes?
bone/osseous connective tissue
What do we call a loose connective tissue containing both collagen and elastin fibers, and in which the primary cell type is the fat cell?
adipose connective tissue
Name the criteria by which epithelial tissues are classified? (check all that apply)
number of cell layers/cell shape
If an epithelial tissue is more than one cell layer thick, it is classified as a ___________ epithelium.
stratified
What do we call an epithelial tissue that is many cell layers thick and is composed of cells that are as high as they are wide?
stratified cuboidal epithelial tissue
What do we call an epithelial tissue that is many cell layers thick and is composed of cells that are higher than they are wide?
stratified columnar epithelial tissue
What do we call a muscular tissue in which the cells are non-striated, uninucleate, and spindle shaped?
smooth muscle tissue
What primary type of tissue consists of one or more cell types embedded within a non-living matrix?
connective
What are the mucus producing cells in epithelial tissue called?
goblet cells
What are the supporting cells of nervous tissue called?
neuroglia/glial cells
Identify one location in the body where fibrous cartilage can be found.
within the pubic symphysis
Identify one location in the body where adipose connective tissue can be found.
around the kidneys
Identify one location in the body where elastic cartilage can be found.
within the external portion of the ear
Identify one location in the body where simple squamous epithelium can be found.
lining the alveoli of the lungs
Identify one location in the body where simple columnar epithelium can be found.
lining the inner surface of the small intestine
Identify one location in the body where stratified cuboidal epithelium can be found.
lining the largest ducts of sweat glands
Identify one location in the body where cardiac muscle tissue can be found.
within the walls of the heart
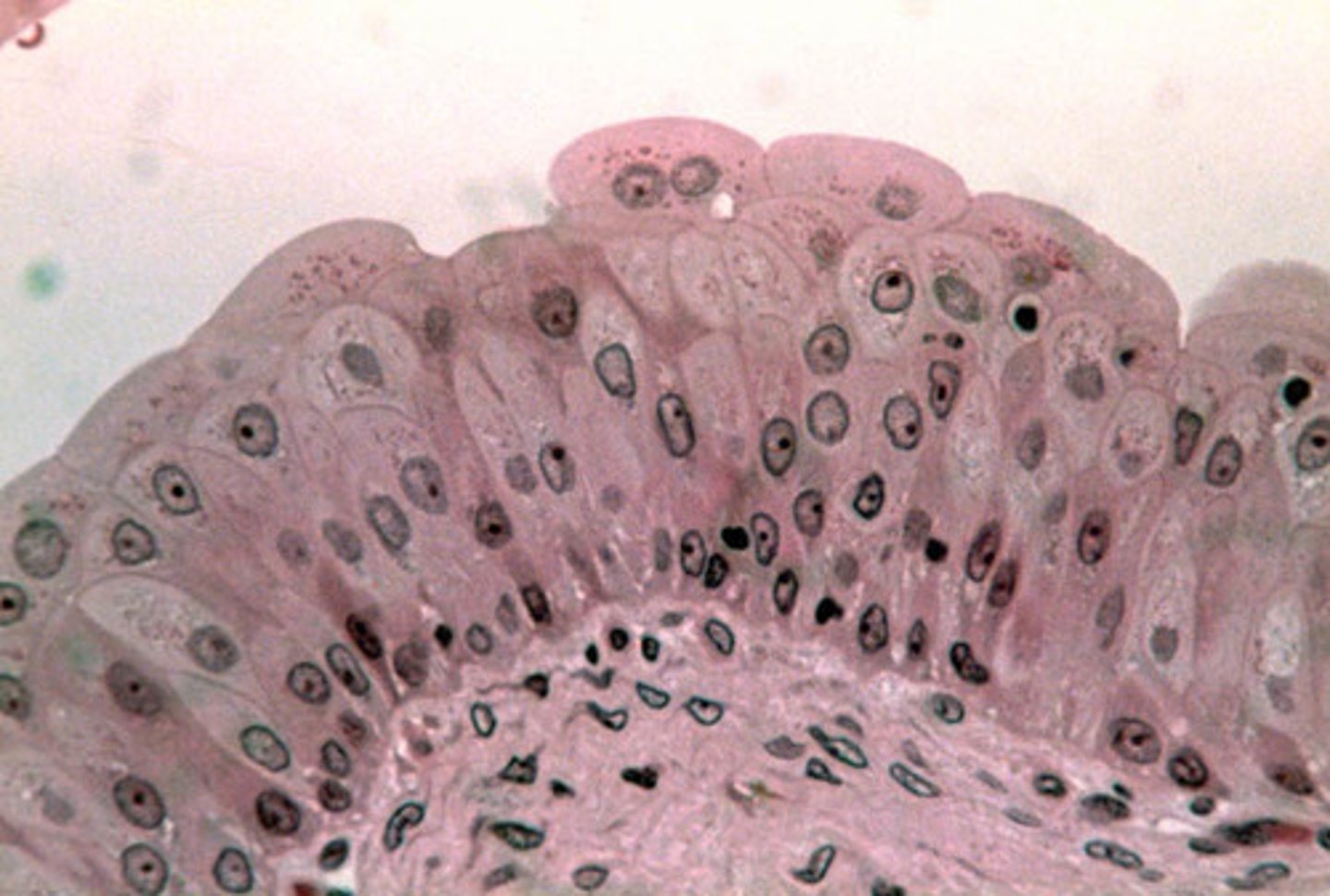
Identify the indicated tissue.
reticular connective tissue
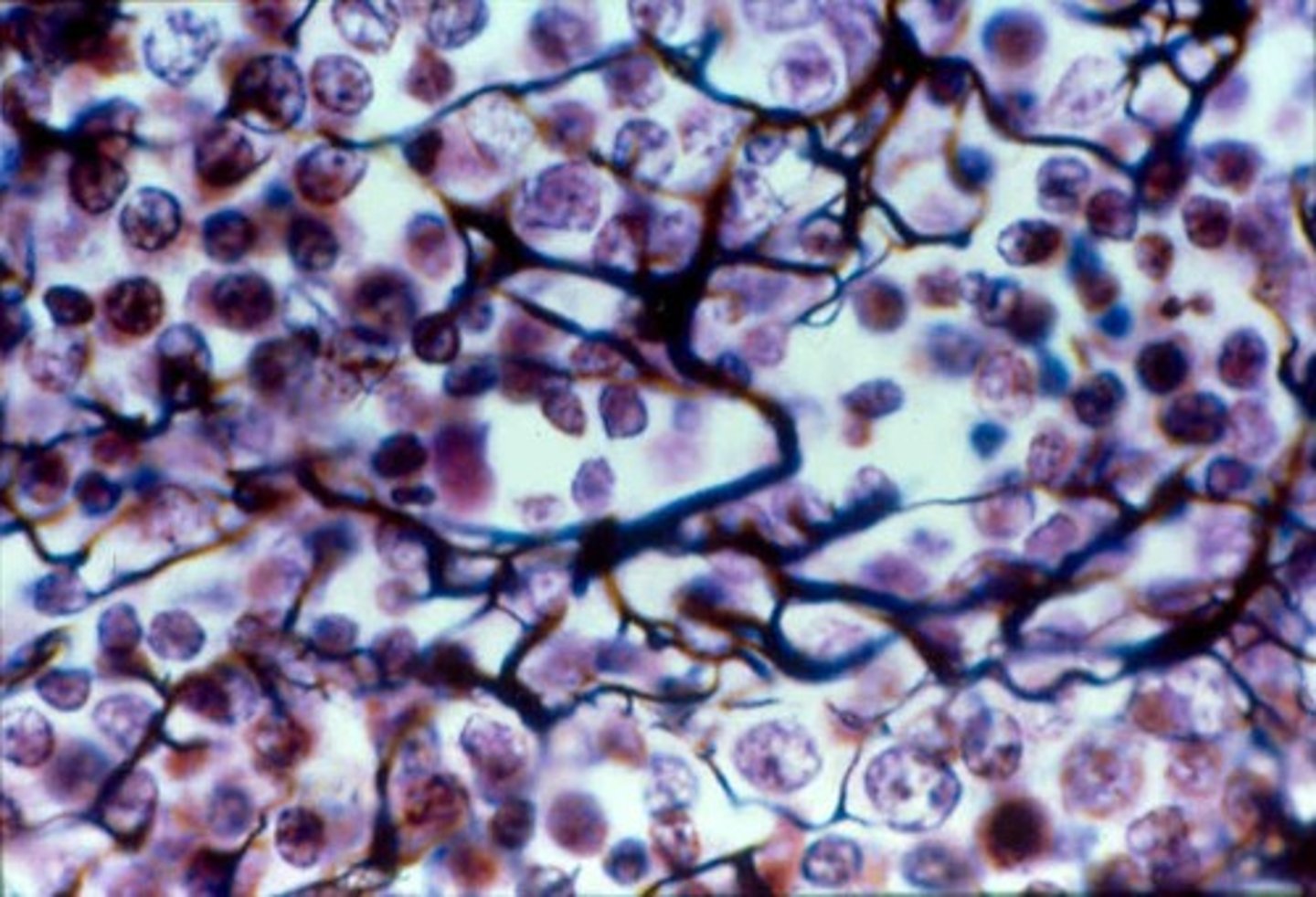
Identify the indicated tissue.
elastic cartilage
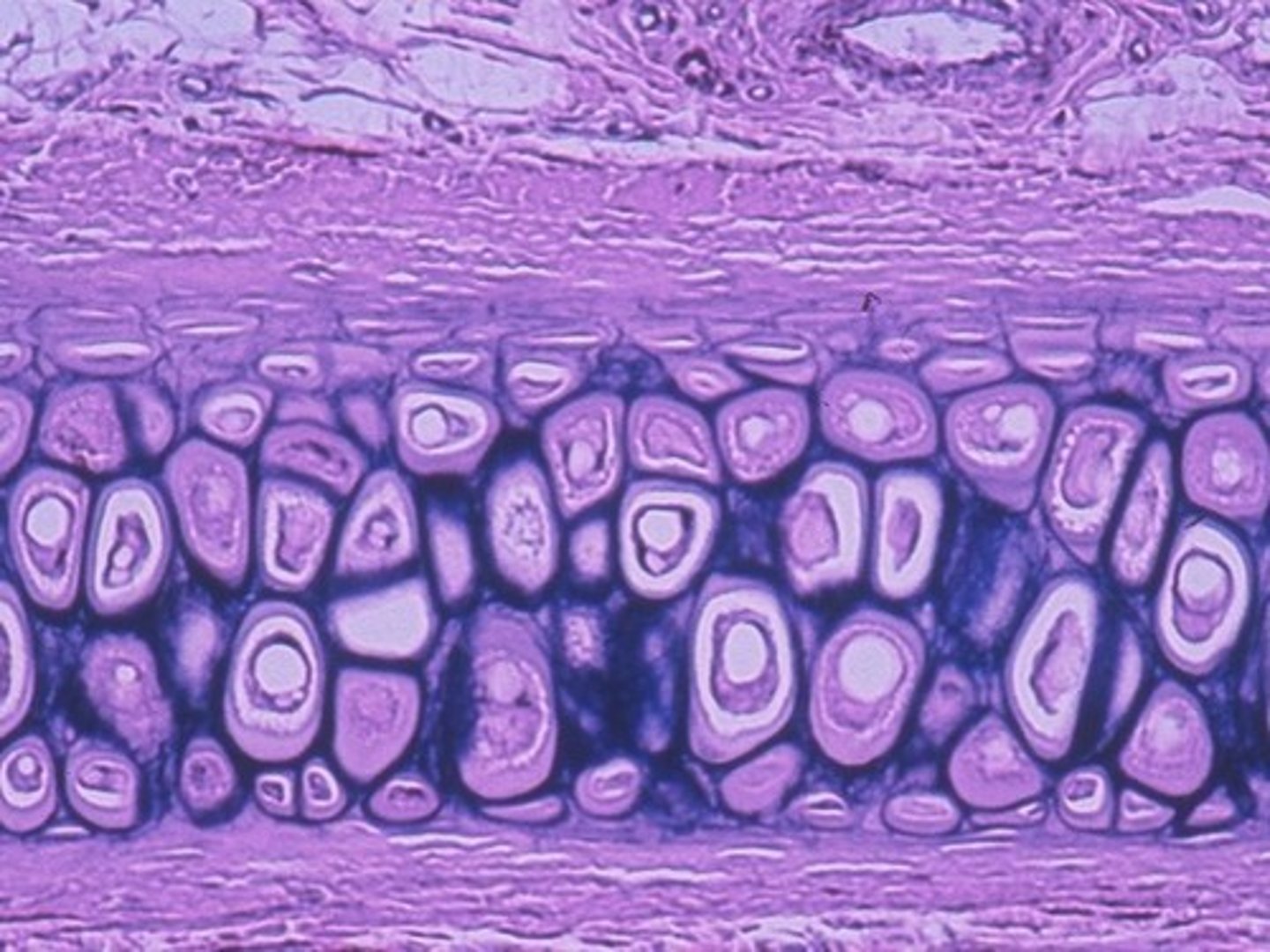
Identify the indicated tissue.
stratified squamous epithelial tissue
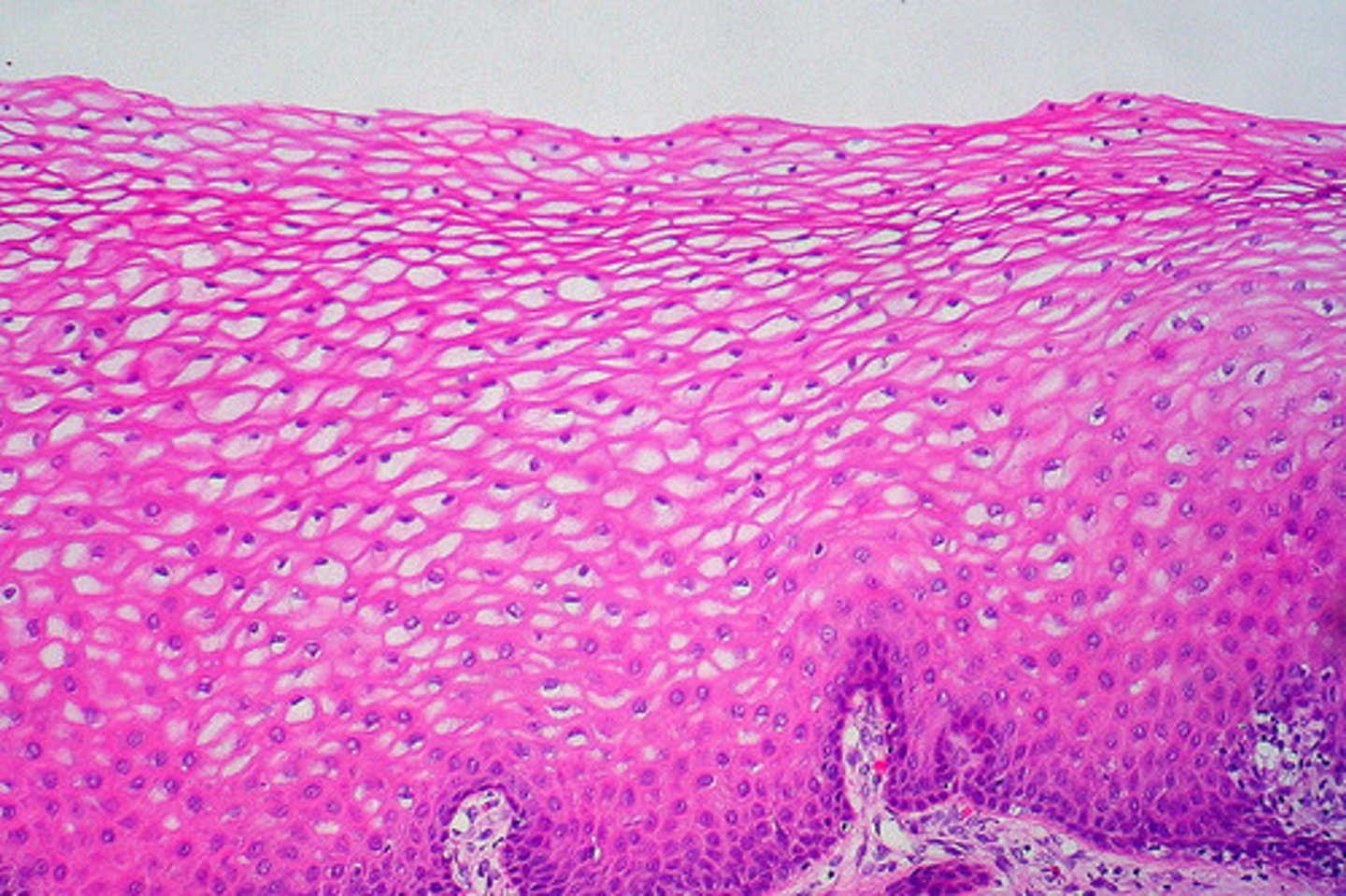
Identify the indicated tissue.
transitional epithelial tissue
This epidermal layer consists of many layers of flattened keratinized dead cells.
stratum corneum
This structure produces a shaft of keratinized cells that extend from the surface of the skin.
hair follice
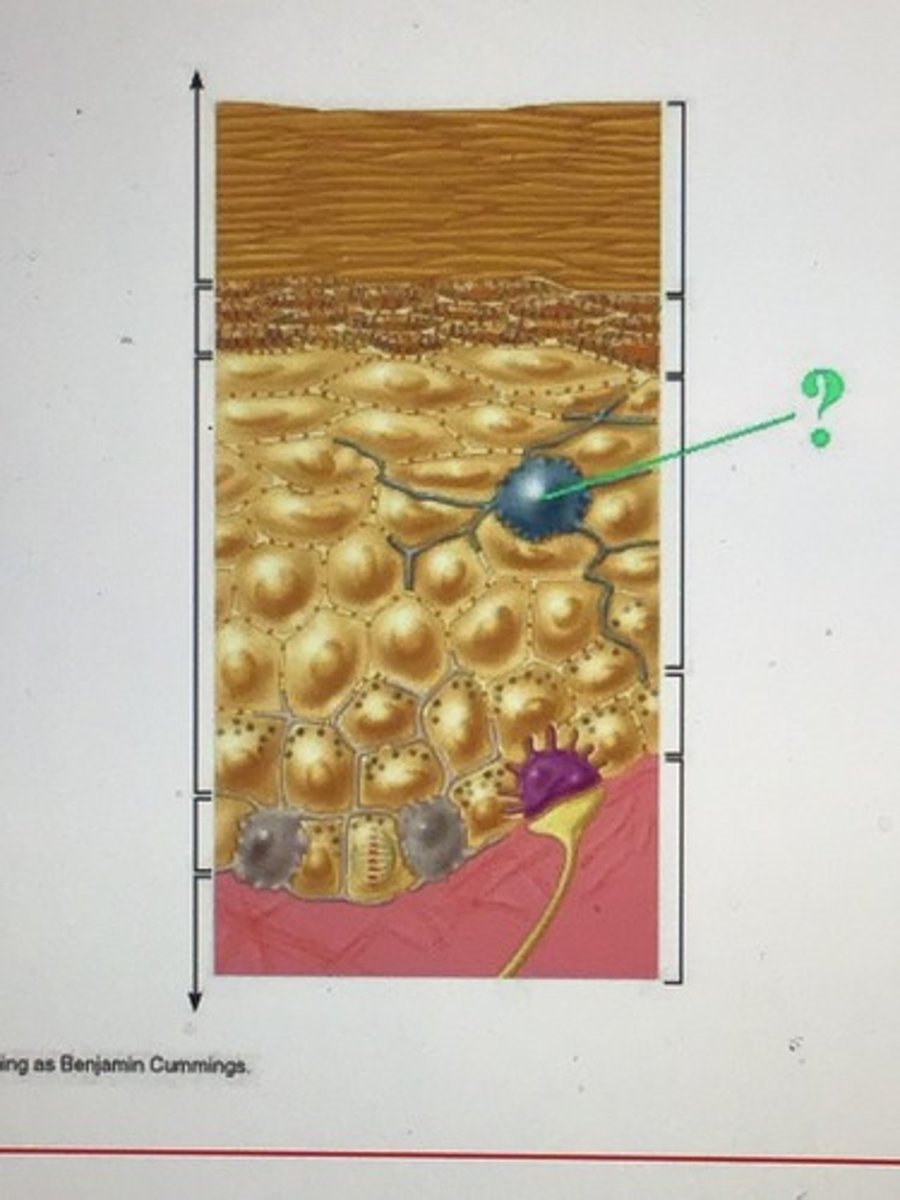
Identify the indicated structure of the epidermis.
dendritic cell/langerhans cell
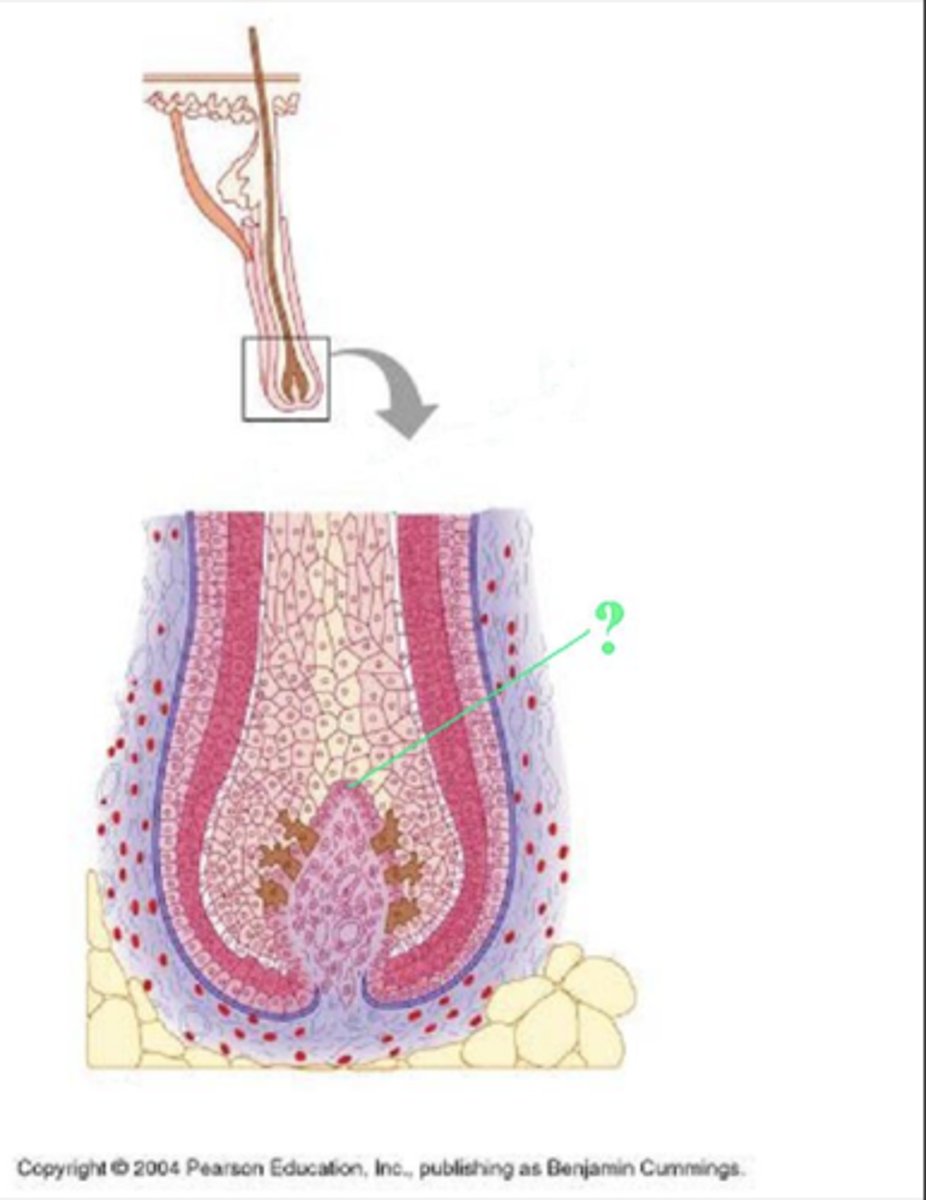
Identify the indicated layer of a hair.
hair matrix
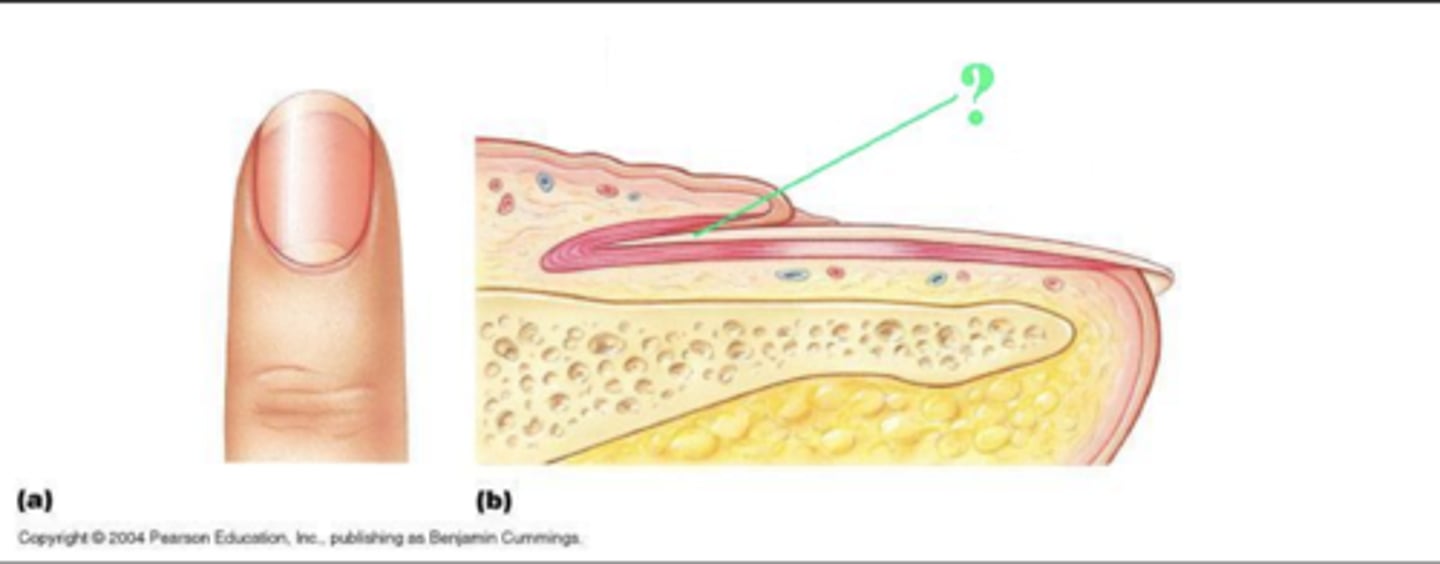
Identify the indicated structure of the nail.
nail root/root/root of nail
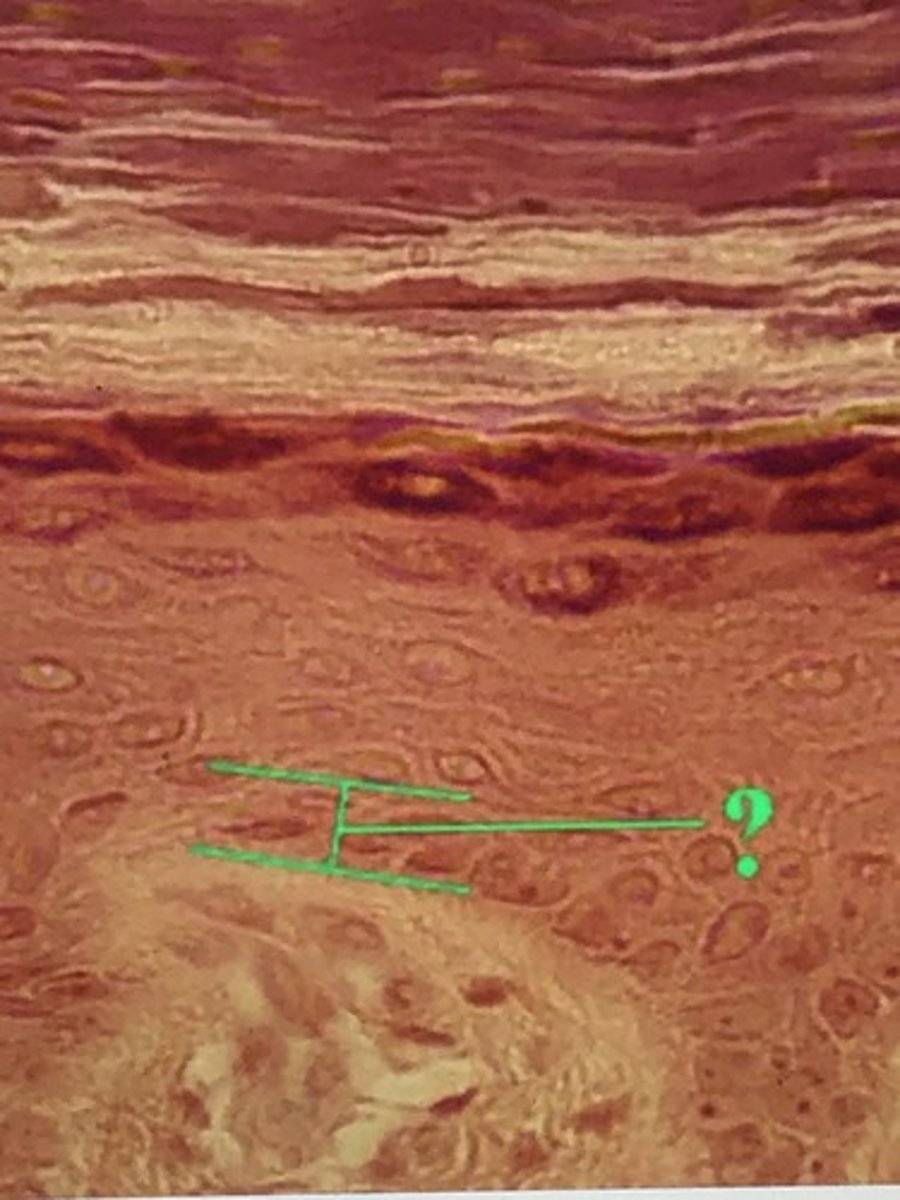
Identify the indicated layer of thick skin.
stratum basale/stratum germinativum
Identify the indicated structure of the integument.
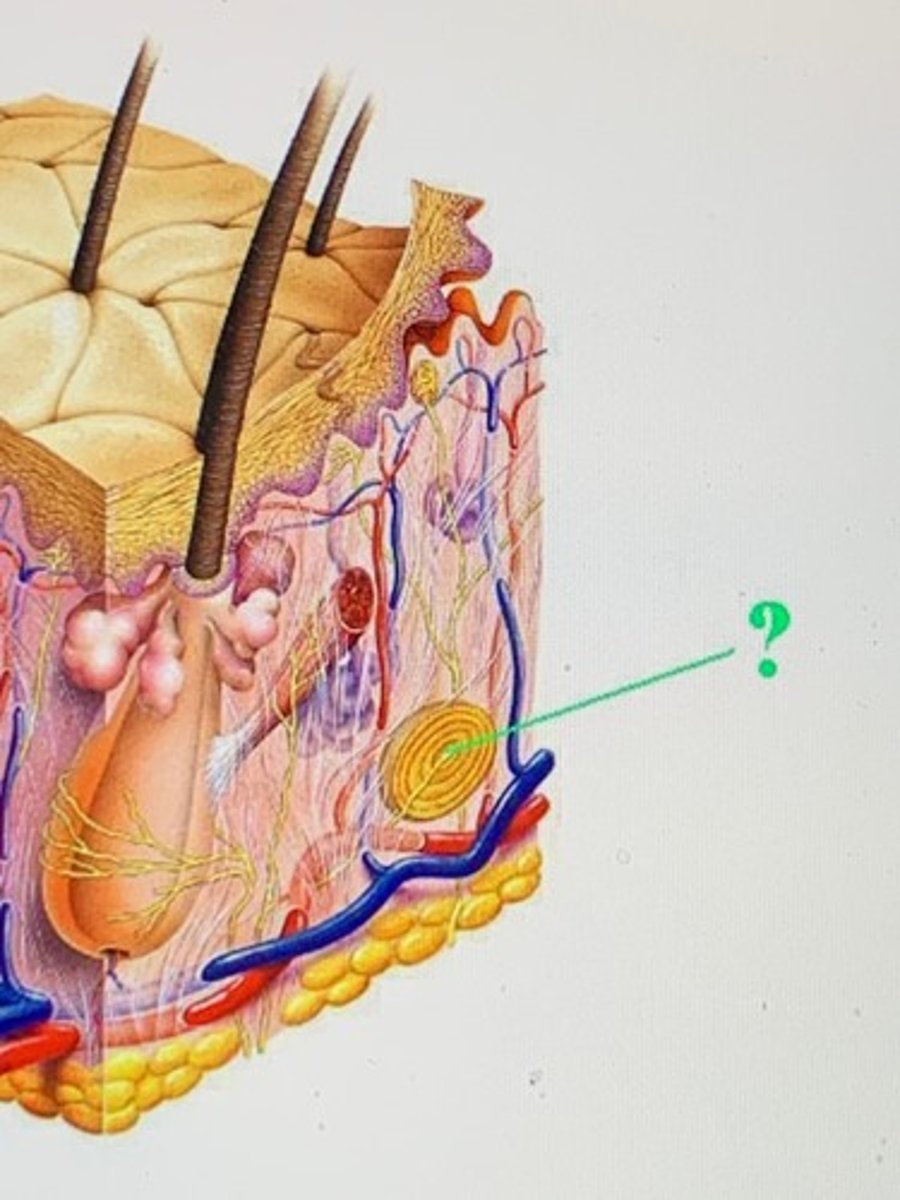
pacinian corpuscle
What cytoskeletal element is primarily composed of tubulins and helps determine the shape of the cell?
microtubule
What membranous vesicles contain oxidase enzymes that detoxify alcohol, hydrogen peroxide, and other harmful chemicals?
peroxisomes
Identify the indicated cellular organelle.
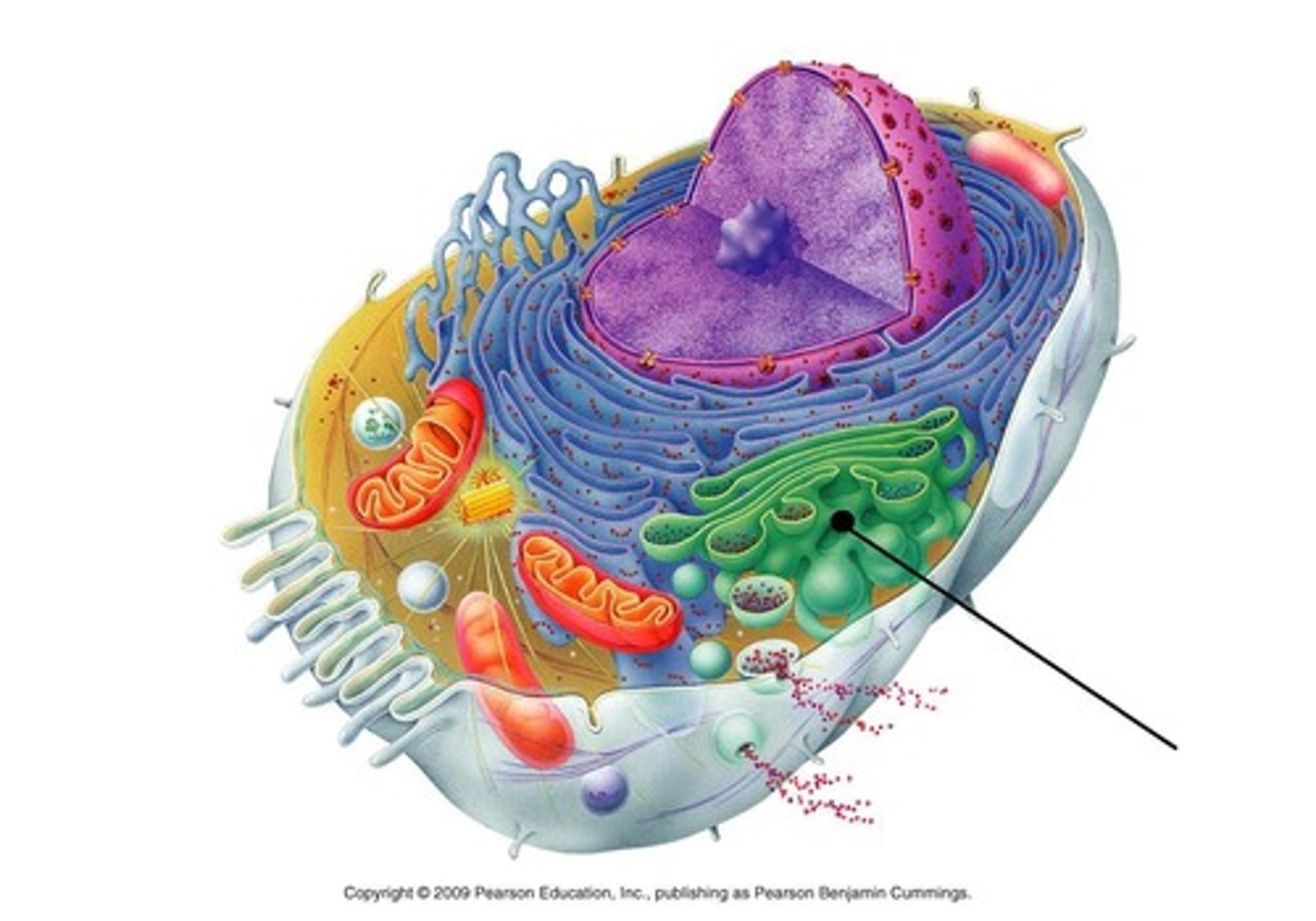
golgi apparatus
Identify the indicated cellular organelles.
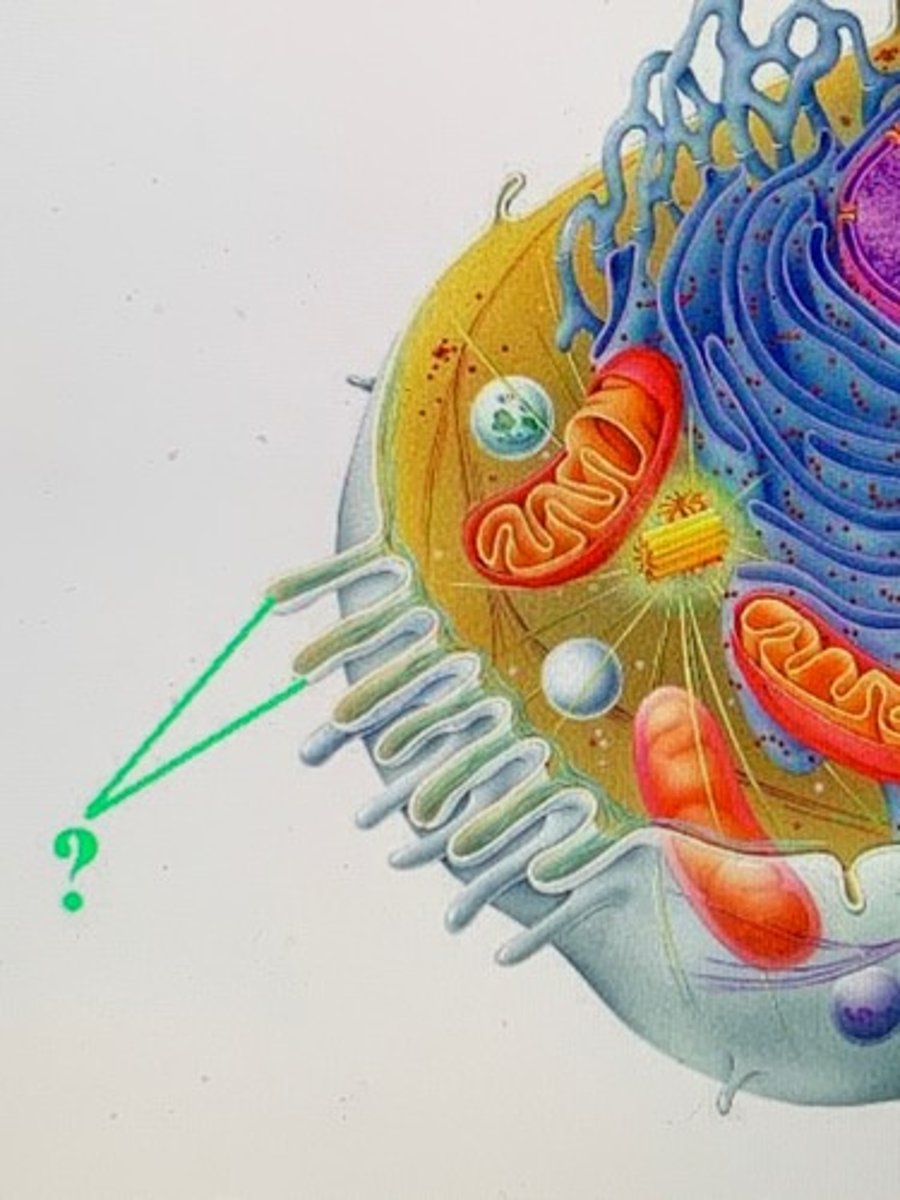
microvilli
Identify the indicated phase of mitosis.
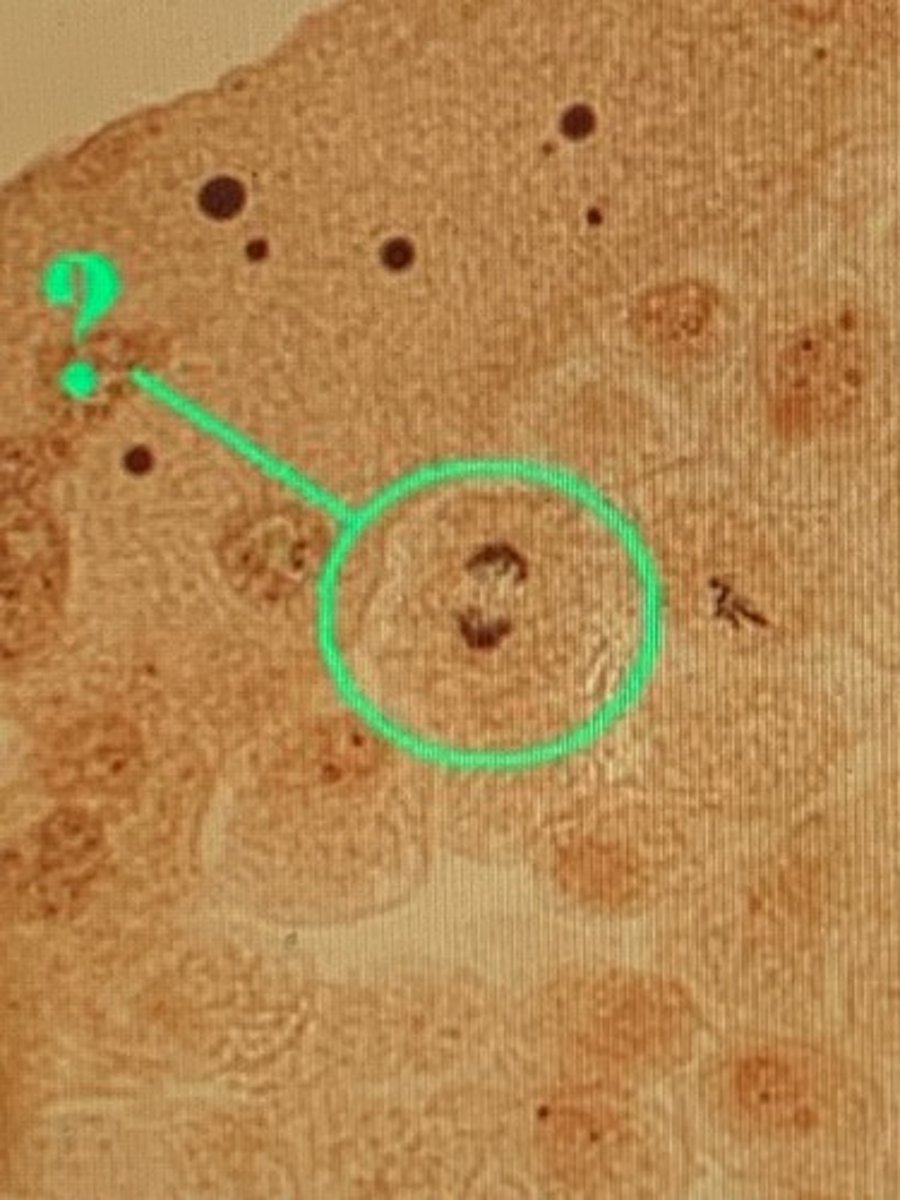
anaphase
The cell completes its division into two daughter cells during which portion of the cell cycle?
The cell completes its division into two daughter cells during which portion of the cell cycle?