[CYTOGENETICS] Pedigree Analysis
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Sheldon Reed
In 1947, "Genetic counseling" was coined by ________, a geneticist who advises physician on how to explain heredity to patients with single-gene diseases
Thyroid Cancer
Fast to diagnose and manage
Karyotyping Amniocentesis
Genetic Testing technique
15-20th week of pregnancy
Week to do Amniocentesis and Karyotyping
If beyond this, the volume of the fluid may not be enough
Beyond this, the fetus may be at risk of injury; Beyond this, too late to act on the detected fetal problem
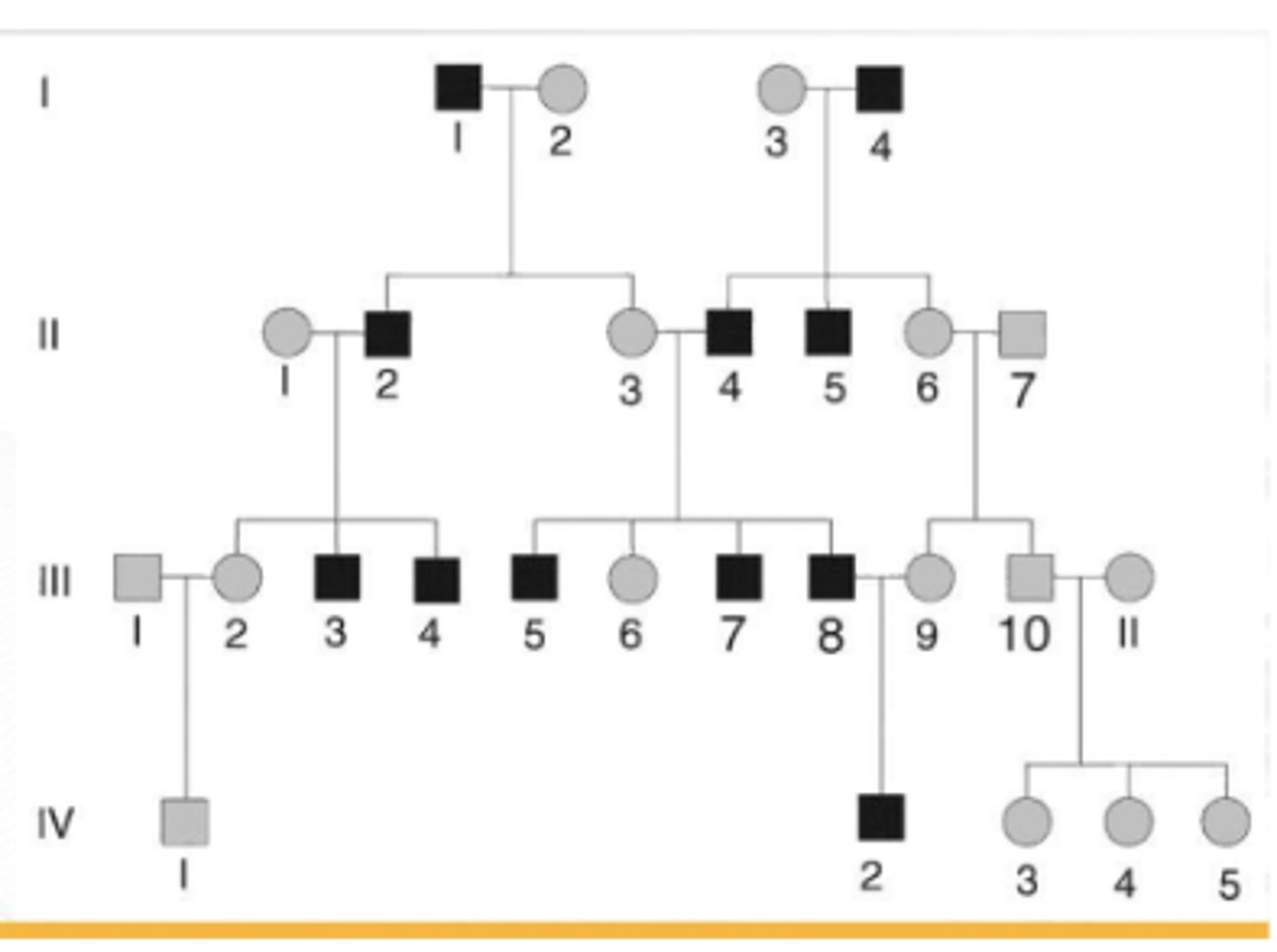
Pedigree Analysis
Genetic analysis method to determine disease family history
Genetic counselor deduce dominance and distinguish autosomal from X-linked inheritance
True
T/F;
The clues in the pedigree have to be interpreted differently depending on whether one of the contrasting phenotypes is a rare disorder or whether both phenotypes of a pair are common morphs of a polymorphism
Pedigree Chart
Family tree, with standard genetic symbols
Shows inheritance patterns
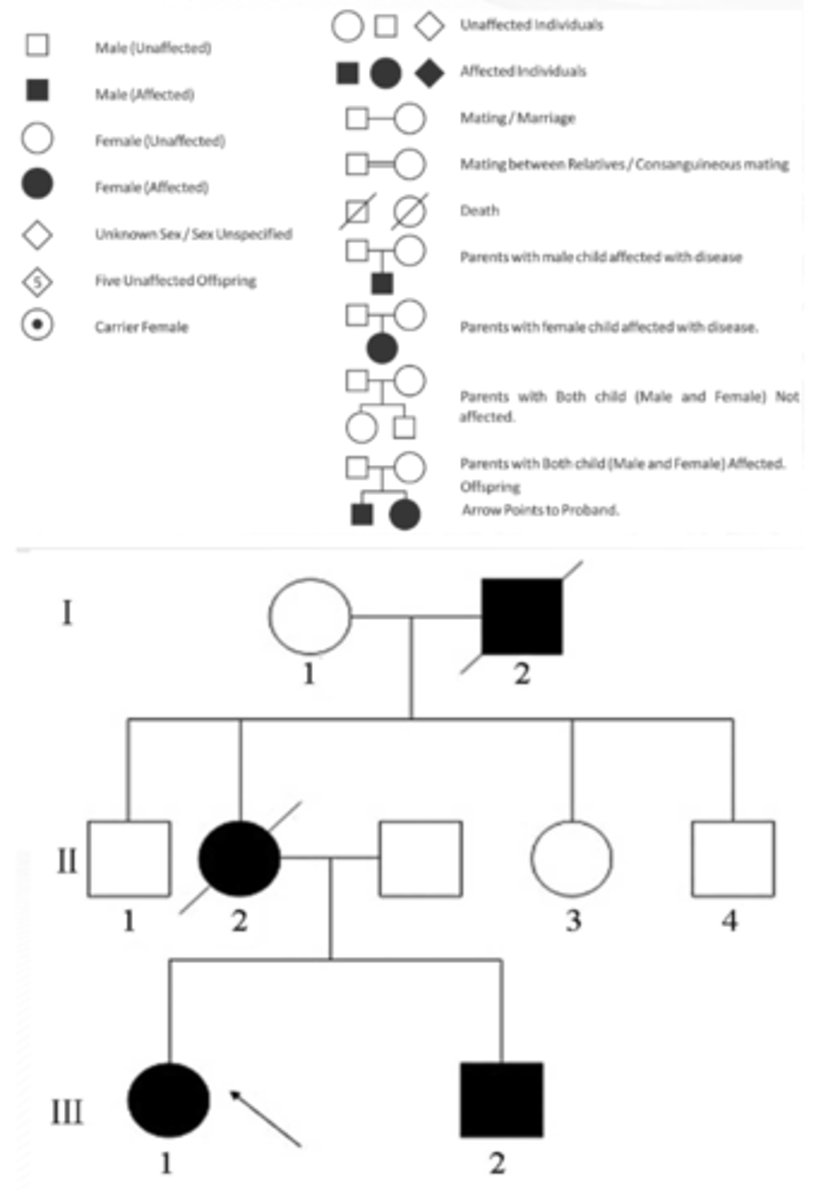
Autosomal Dominant
One mutated allele causes the disease Each affected person usually has one affected parent Appears in every generation of an affected family (Vertical)
Marfan syndrome
Achondroplasia
Huntington disease
Myotonic dystrophy
Autosomal Recessive
Two mutated alleles needed to cause the disease Parents are usually unaffected heterozygotes Not typically seen in every generation (Horizontal).
Beta thalassemia
Cystic fibrosis
Homocystinuria
X-linked Dominant
Females are more frequently affected than males no male-to-male transmission
Rett syndrome
Hypophosphatemia
X-linked Recessive
Males are more frequently affected than females
Both parents of an affected daughter must be carriers. Fathers cannot pass X-linked traits to their sons
Hemophilia
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
Mitochondrial
Only females can pass on mitochondrial conditions to their children (maternal inheritance)
Both males and females can be affected
Can appear in every generation of a family
LHON: Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy
Y-linked inheritance pattern
Trait is always passed from father to son without skipping a generation
Mitochondrial inheritance
The trait is passed from generation to generation
No skipping of generation
Mom → both children (male or female)
Autosomal
The trait is located between Chromosomes 1 to 22
X-linked
A trait found in the X chromosome
Autosomal Dominant
Approximately half of everybody
Males and females affected
All generations
Autosomal Recessive
Rare
Skips generations
Males and females affected
Consanguinity 0=O
X-linked dominant (sex-linked dominant)
Some females can have it
All generations (no skipped generations)
Males get it from affected mothers and give it to their daughters
X-linked recessive (sex-linked recessive)
Rare
Males predominantly have it
Generally skips generations
Males generally get it from unaffected mothers
Y-linked
All males, all the time, all generations (must be direct descendent of the family)
Mitochondrial or Maternal
Every child of affected mother is affected
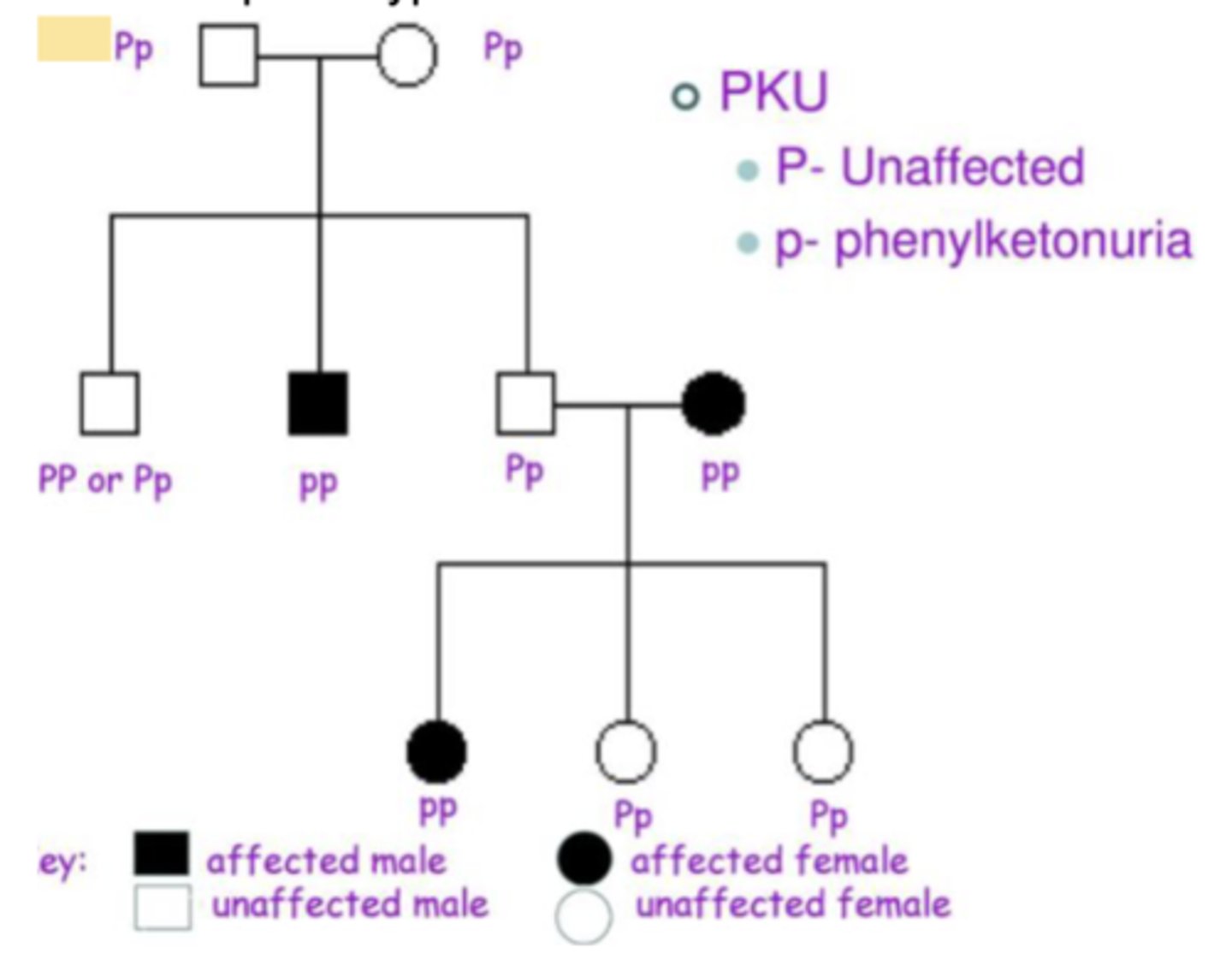
AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE TRAIT
Traits caused by genes on autosomes and requiring two allele copies to influence a phenotype are autosomal recessive.
AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE TRAIT
Several disorders are autosomal recessive, including cystic fibrosis, Tay-Sachs disease, and maple syrup urine disease
AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE TRAIT
Most people with these diseases have heterozygous parents who do not have the condition but carry a causal allele
AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE TRAIT
Most people with these diseases have heterozygous parents who do not have the condition but carry a causal allele.
AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE TRAIT
These carriers can unknowingly impart the disease to their children, which partially explains why autosomal recessive diseases are more common than their dominant counterparts.
AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE TRAIT
Comparing generations on a pedigree can reveal whether an autosomal trait is dominant or recessive. Neither parent has the trait, but one child inherits it. Thus, it must be recessive
PHENYLKETONURIA
A human metabolic disease caused by a mutation in a gene encoding a phenylalanine- processing enzyme, which leads to mental retardation if not treated; inherited as an autosomal recessive phenotype.
AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT TRAIT
These are requiring only one copy of the determining allele to influence phenotype
Freckles and polydactylism (extra fingers or toes) are examples
Such as Huntington's disease, afflict ~50% of offspring with one affected parent.
AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT TRAIT
Many of these diseases do not cause symptoms until later in life and or after reproductive age.
AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT TRAIT
Children can inherit these diseases from unknowingly affected parents, highlighting the importance of analyzing family history
HUNTINGTON'S DISEASE
an autosomal dominant genetic disorder that affects the central nervous system of human beings.
This disease typically shows up when a person reaches their mid 30's or 40's, with no earlier signs or symptoms.
The nerve cells of an affected individual quickly degenerate in certain parts of the brain, which leads to symptoms that include dementia, loss of memory, and severely decreased mental capacity, muscle rigidity, and loss of bodily function and muscle coordination.
Usually shortens an affected persons lifespan, with the average person dying 15-20 years after onset of the disease, making the life expectancy around 50-60 years of age
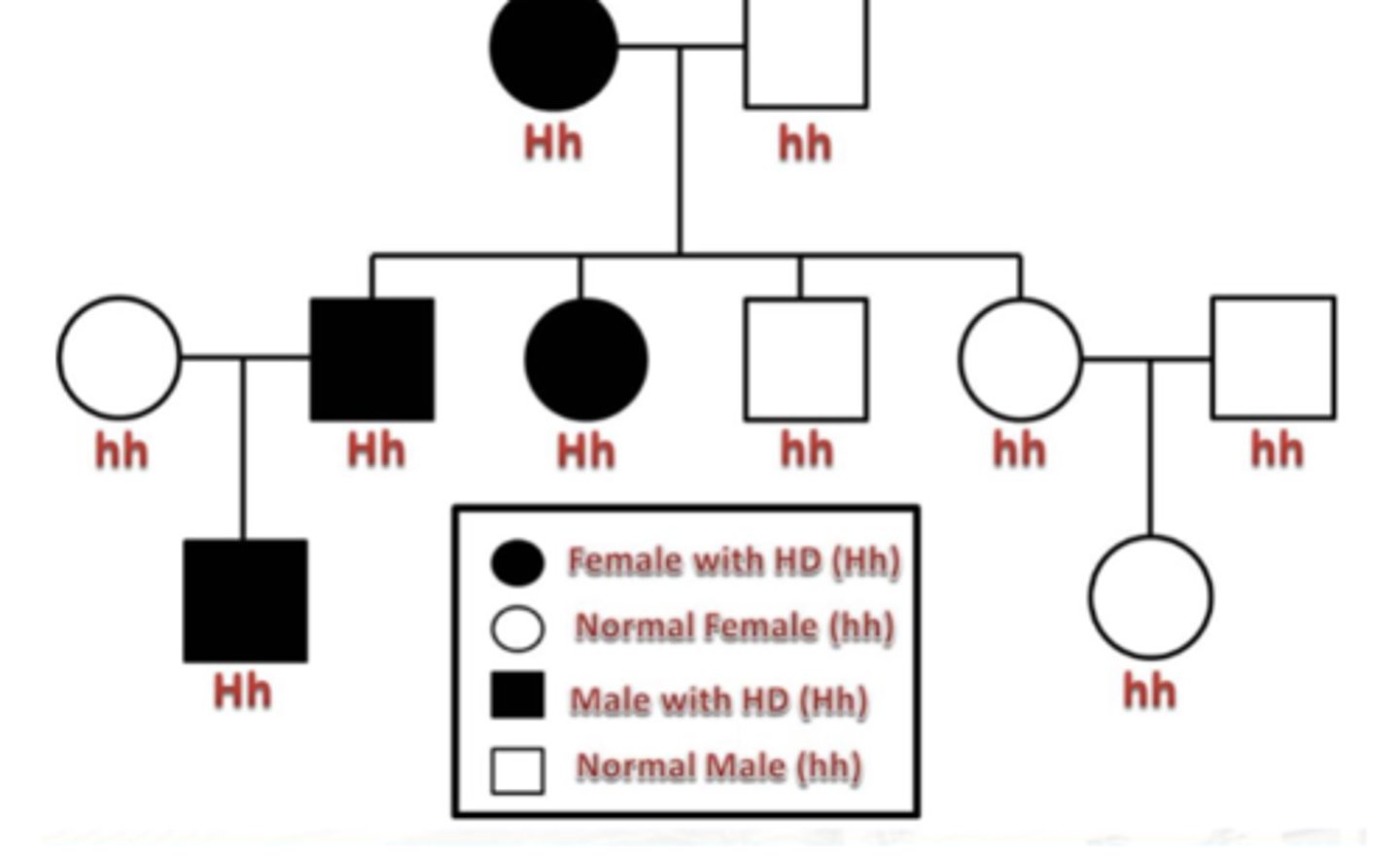
X-LINKED RECESSIVE
The trait is rare in a pedigree.
Trait skips generations.
Affected fathers DO NOT pass to their sons.
Males are more often affected than females
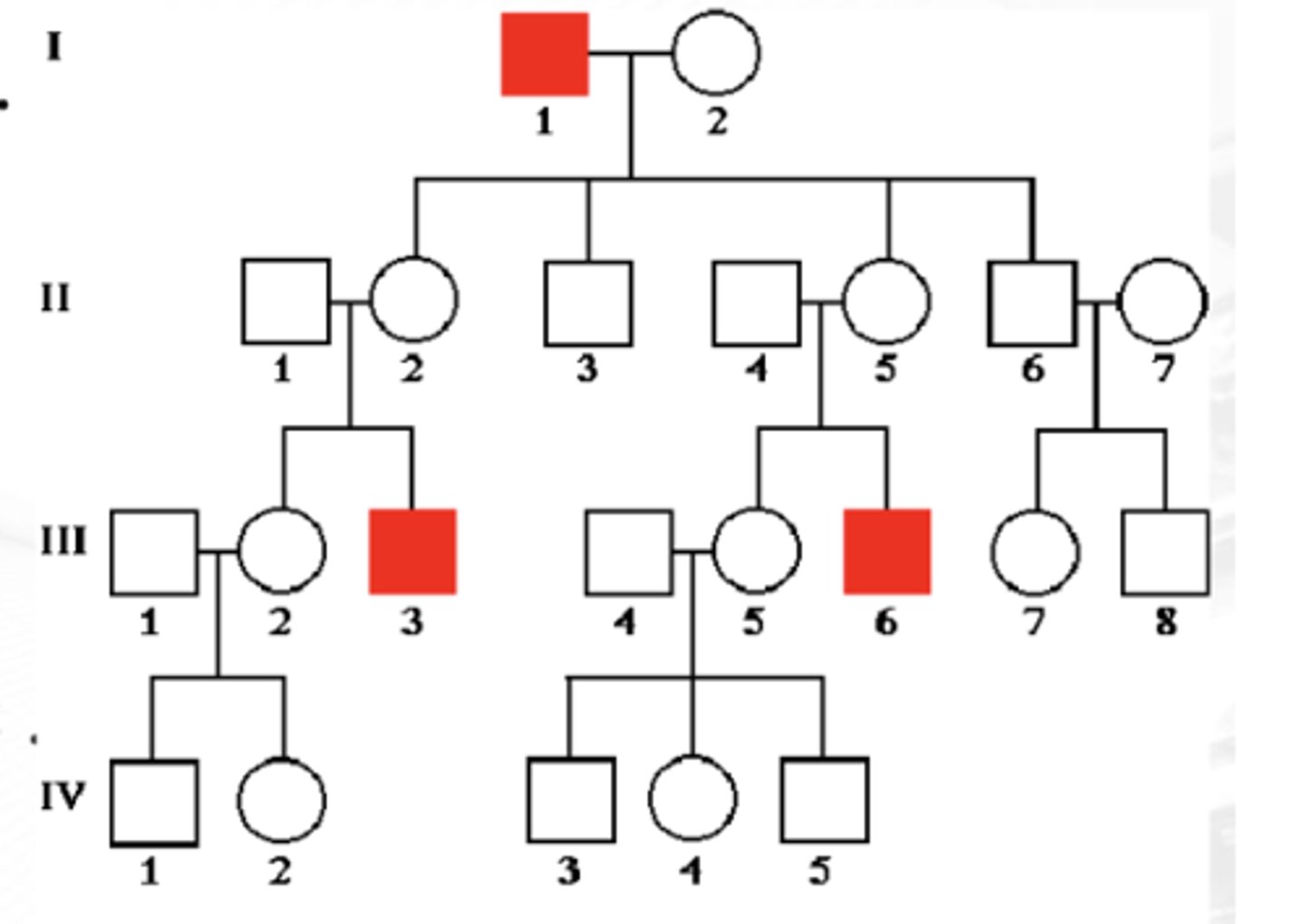
X-LINKED RECESSIVE
Genders affected
males must receive defective gene from carrier mother
carrier mother's sons have 50% of having disease
affected males give copy to all of their daughters
X-LINKED RECESSIVE
Hemophilia
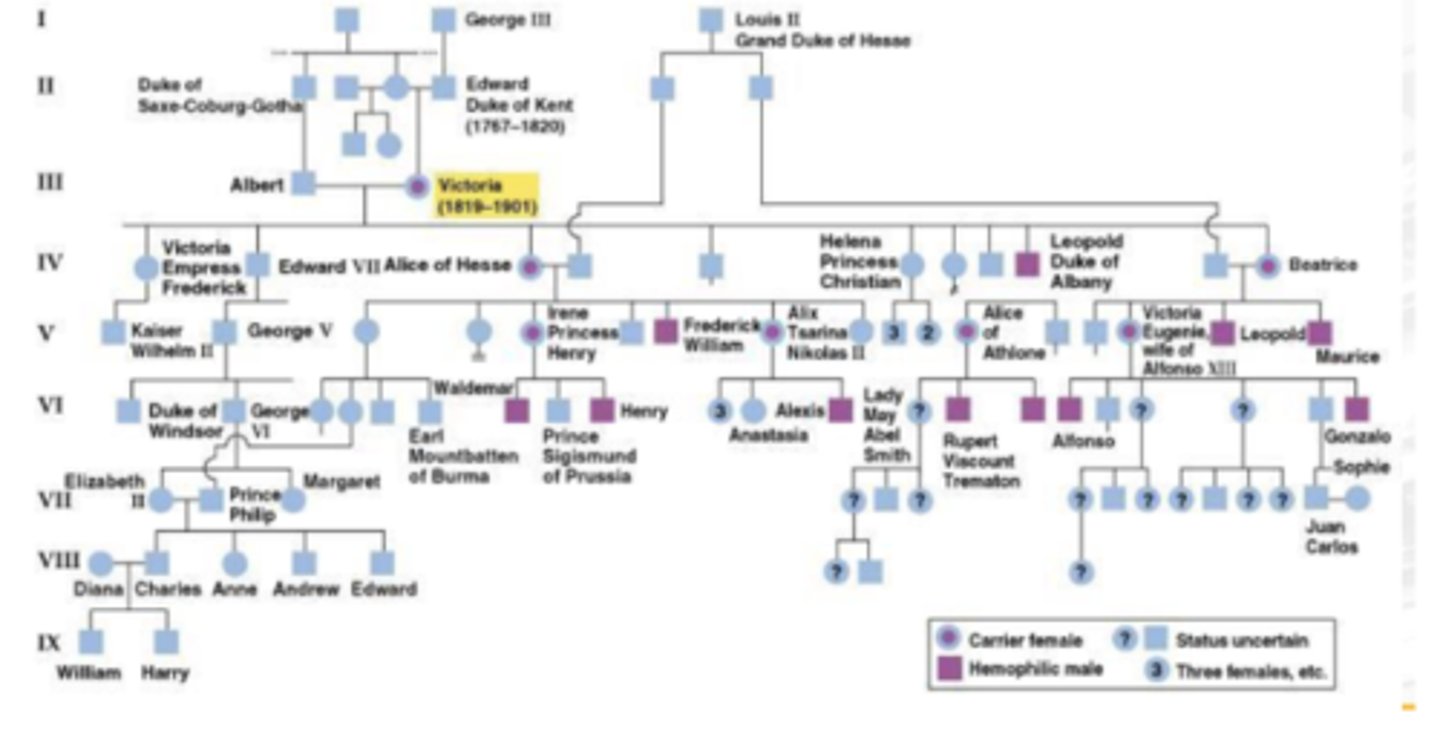
X-LINKED RECESSIVE
Red-green color blindness
Hemophilia
X-linked ichthyosis
X-LINKED DOMINANT
Trait is common in pedigree.
Affected fathers pass to ALL of their daughters, but not their sons
Does not skip generations
Genders affected (male and female at equal frequency)
Y-LINKED INHERITANCE
Inheritance of genes on the Y chromosome
Since only males normally have a Y chromosome, Y-linked genes can
only be transmitted from father to son
Also called holandric inheritance
MITOCHONDRIAL
Genders affected - male and females at equal frequency
Generations affected - does not skip generations
Pathology
> defects in electron transport/oxidative phosphorylation process
> presents as neuropathies/myopathies
> neurons and muscle cells require high amounts of energy and depend on mitochondria
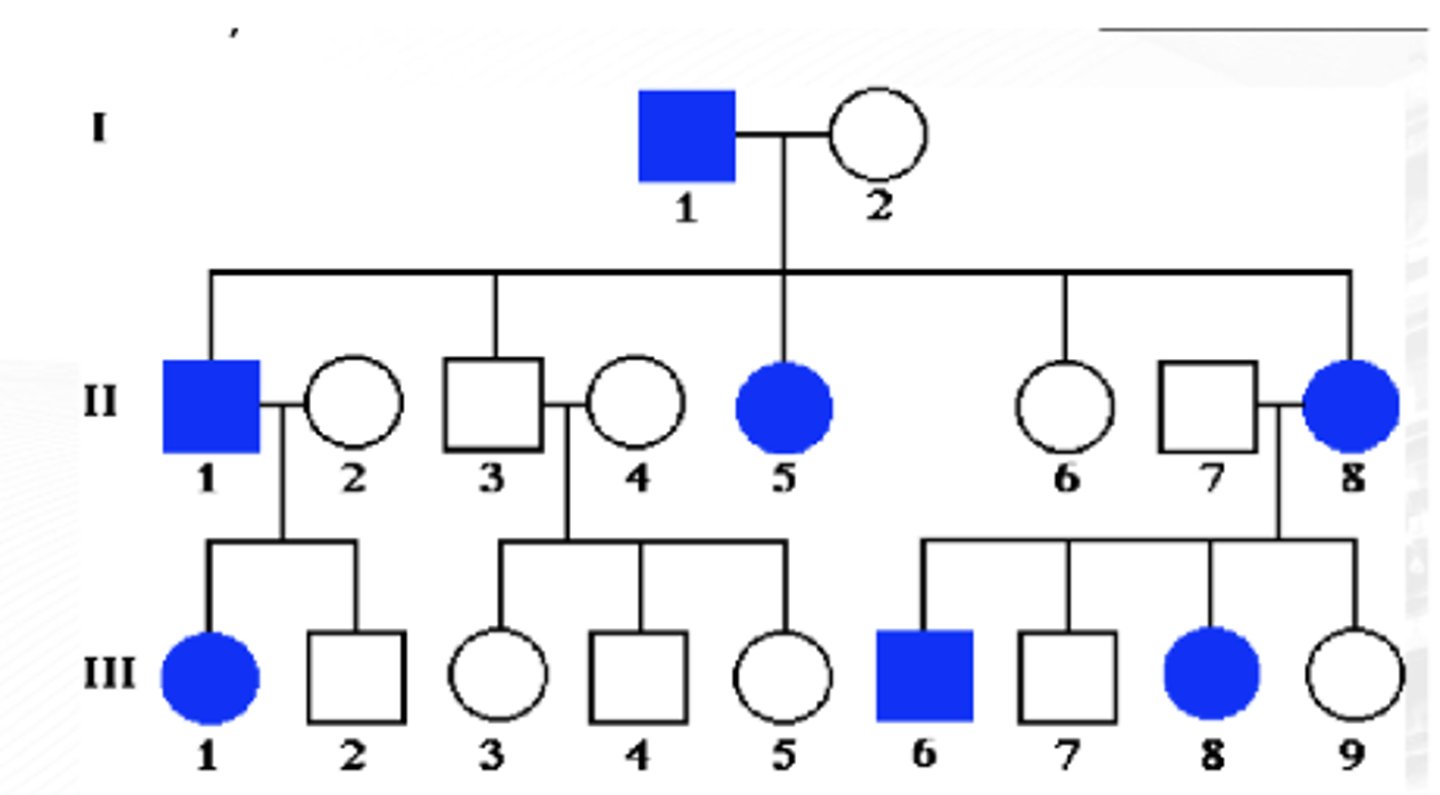
Autosomal recessive inheritance
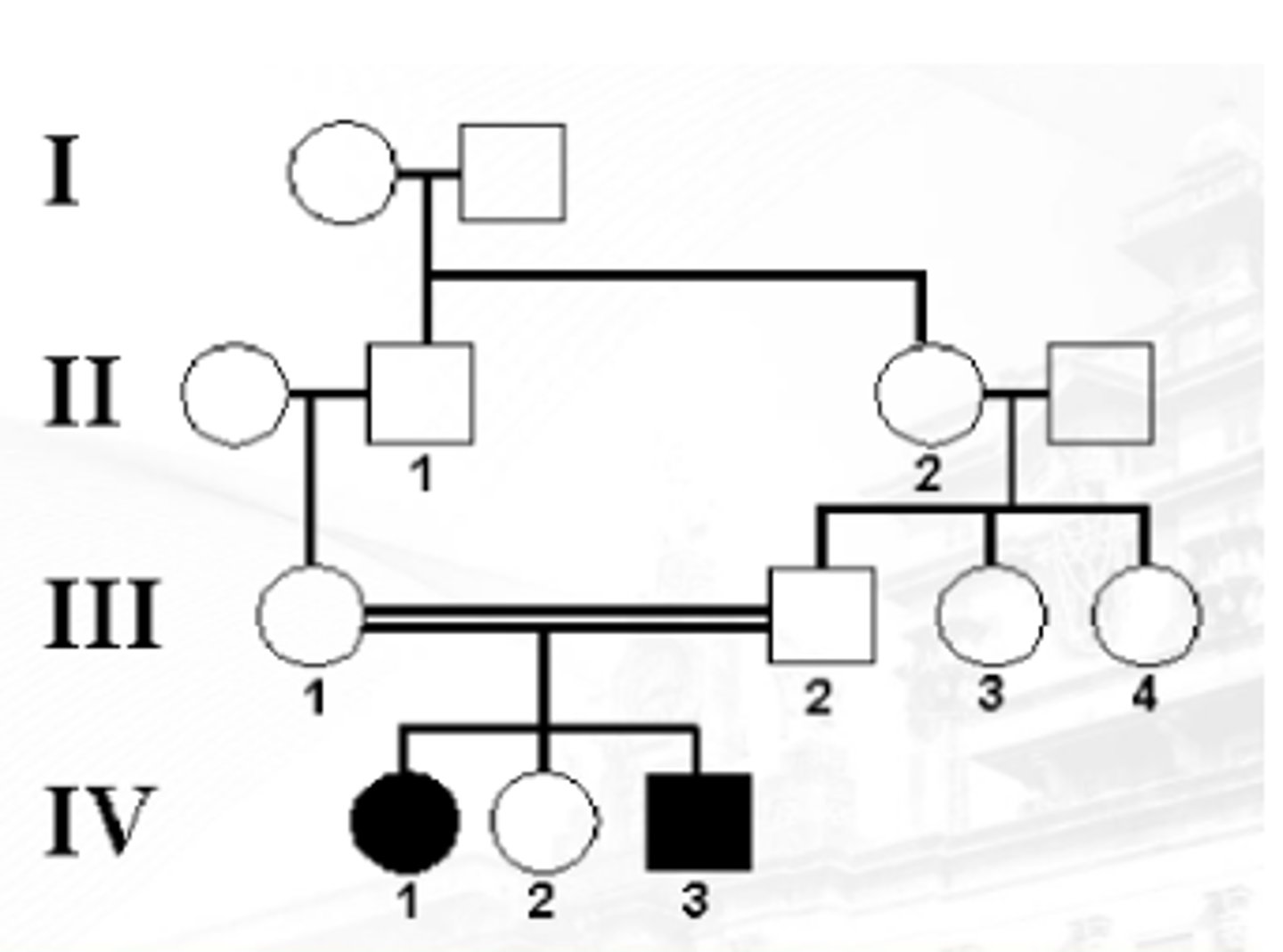
X-linked recessive
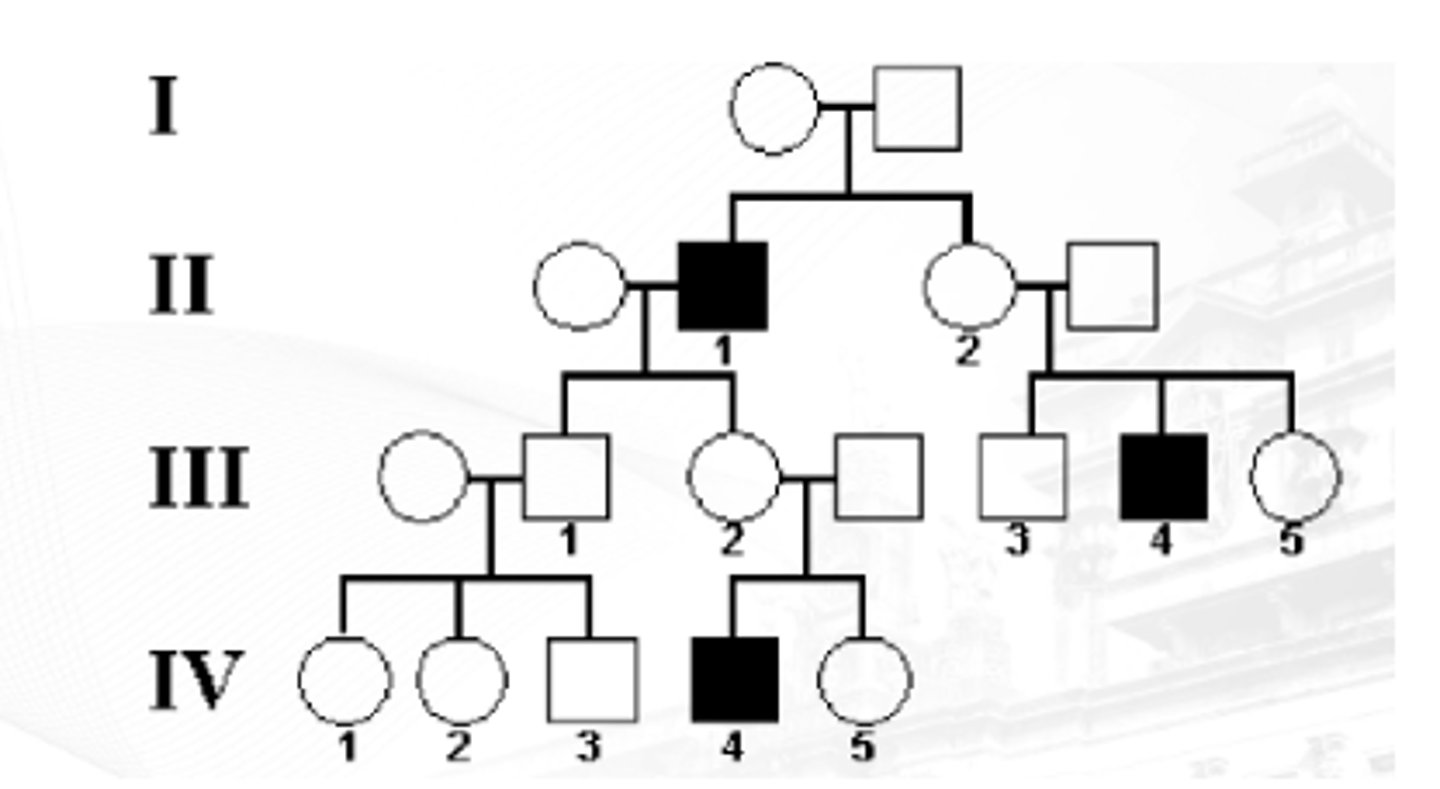
Autosomal Dominant
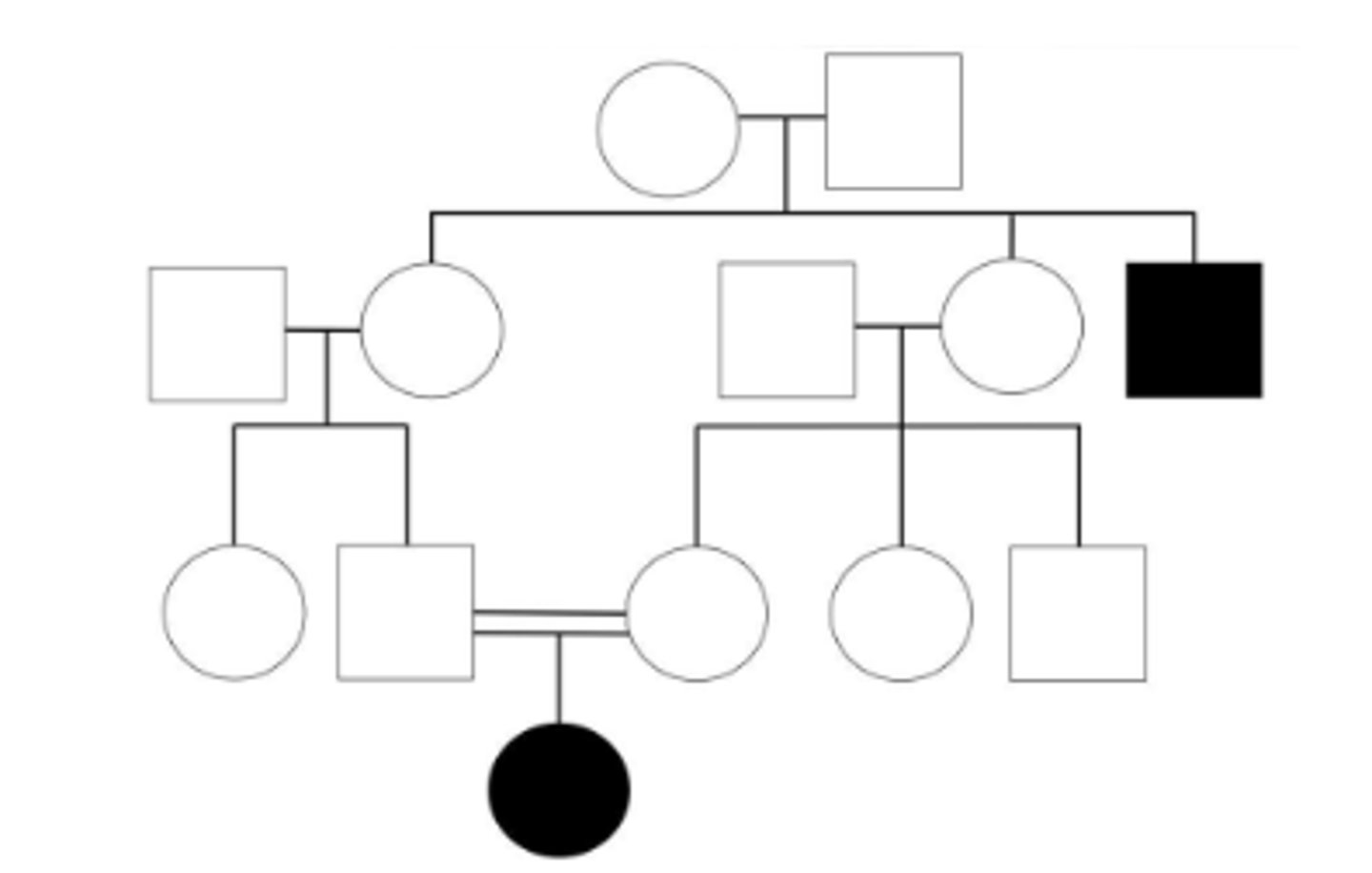
Autosomal Recessive
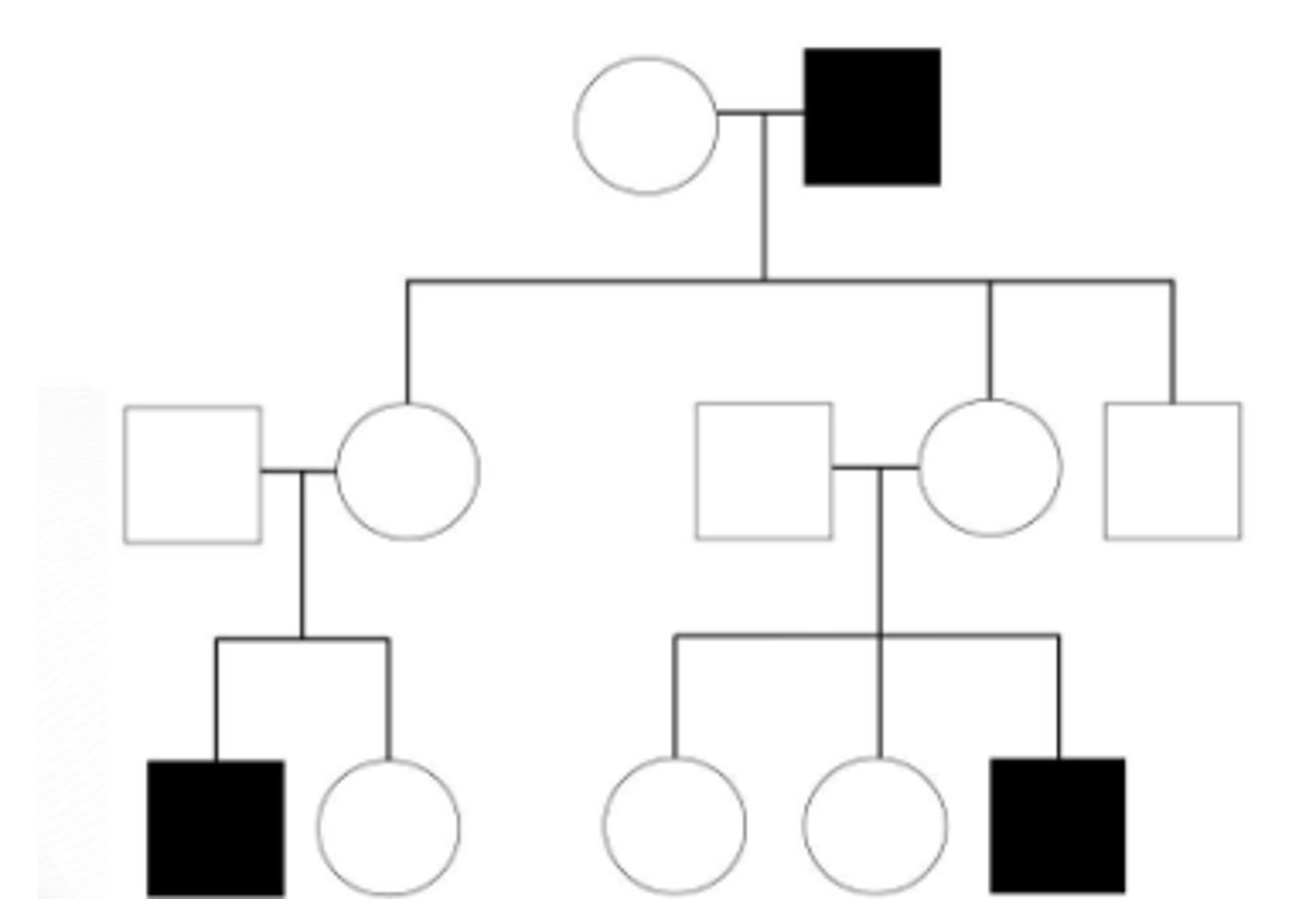
X-linked recessive
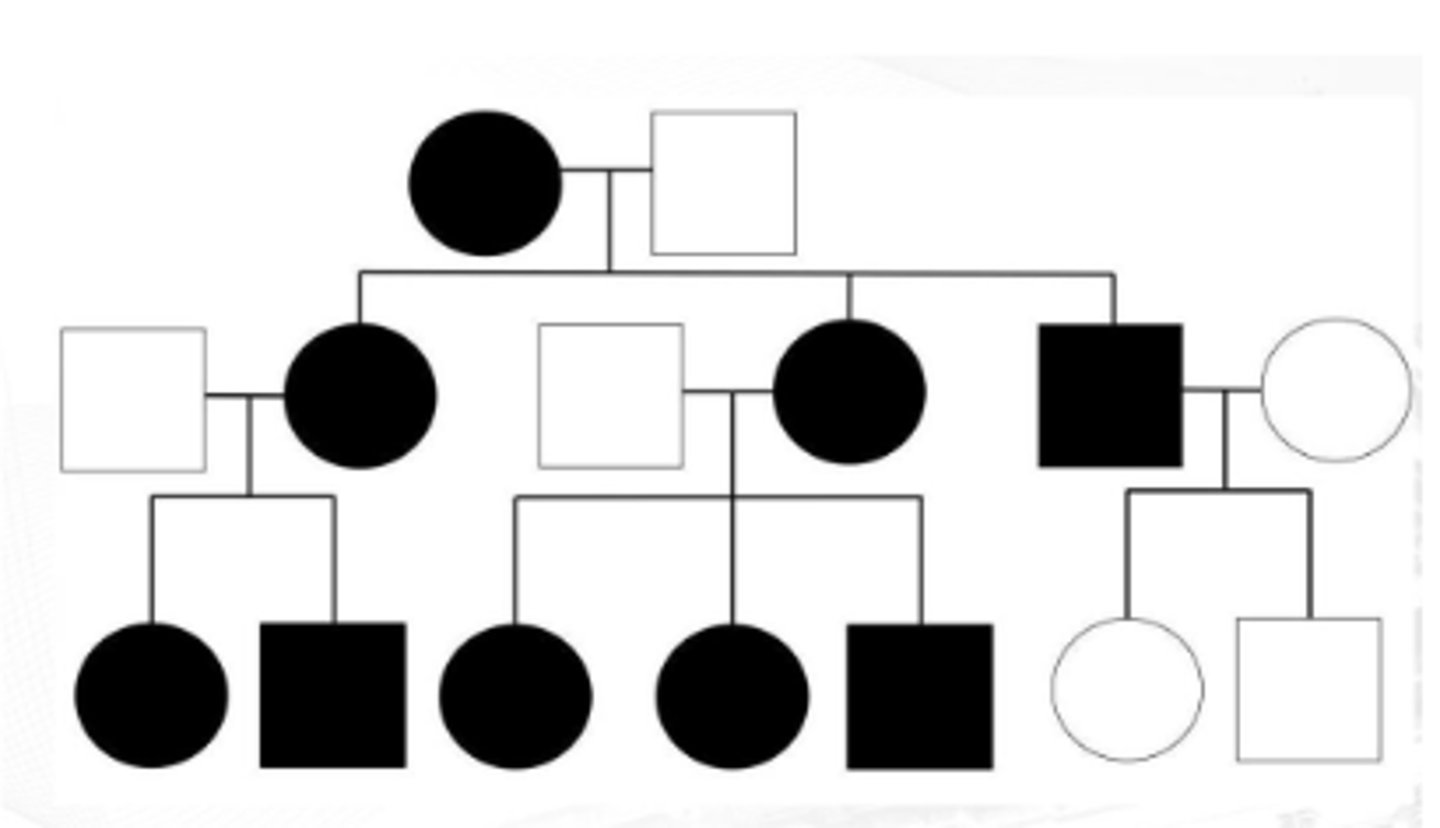
Mitochondrial Dominant
Y-Linked Dominant