Nationalism & Imperialism Unit - World History
1/104
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Started 04/01/25 - ...
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
Nationalism
identification with one's own nation and support for its interests, especially to the exclusion or detriment of the interests of other nations.
Unification
the process of being united or made into a whole.
Militarism
derogatory
the belief or desire of a government or people that a country should maintain a strong military capability and be prepared to use it aggressively to defend or promote national interests.
Liberalism
willingness to respect or accept behaviour or opinions different from one's own; openness to new ideas.
a political and social philosophy that promotes individual rights, civil liberties, democracy, and free enterprise.
What happened to the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire, ruled by the Habsburgs, was a major European power that existed from 1804 to 1918, evolving into the Austro-Hungarian Empire in 1867 and ultimately dissolving after World War I.
5 facts about the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire, which evolved into the Austro-Hungarian Empire in 1867, dissolved after World War I in 1918, leading to the creation of new nations and the Republic of German-Austria, later known as the First Austrian Republic.
Fall of Austrian Empire effects on Europe.
The fall of the Austro-Hungarian Empire in 1918 led to the creation of new nations, a redrawing of European borders, and the rise of nationalism, ultimately contributing to the instability that would lead to World War II.
What happened to the Russian Empire?
The Russian Empire, spanning most of northern Eurasia, ended with the Russian Revolution of 1917, leading to the establishment of the Russian Republic and later the Soviet Union. -Knowt Response: The Russian Empire collapsed due to political unrest and social upheaval, resulting in the abdication of Tsar Nicholas II and significant changes in governance, ultimately giving rise to communist rule.
How did the fall of the Russian Empire affect Europe.
The fall of the Russian Empire, culminating in the Russian Revolution and the establishment of the Soviet Union, had profound and lasting effects on Europe, including the end of the Tsarist regime, the rise of communism, the reshaping of Eastern European borders, and the destabilization of the continent, ultimately leading to the Cold War and the Revolutions of 1989.
What happened to the Ottoman empire?
The Ottoman Empire, after a long decline, officially ended in 1922 with the abolition of the sultanate, following its defeat in World War I and the rise of Turkish nationalism, leading to the establishment of the Republic of Turkey in 1923.
How did the fall of the Ottoman Empire affect Europe?
The fall of the Ottoman Empire significantly reshaped Europe, leading to the rise of new nation-states in the Balkans, heightened tensions and wars, and the redrawing of borders, ultimately contributing to the outbreak of World War I.
What happened to the Italian city-states?
The Italian city-states, prominent during the Renaissance, gradually lost their independence and were eventually unified into the Kingdom of Italy in the 19th century, marking the end of their era as independent entities.
5 facts about the Italian city-states.
The Italian city-states, particularly during the Renaissance, were known for their thriving trade, independent governance, and rich cultural and artistic contributions, with some cities like Florence and Venice becoming major centers of power and innovation.
How the Italian City-states affected Europe.
The Italian city-states profoundly impacted Europe by fostering the Renaissance, becoming hubs of trade and finance, and influencing political and diplomatic practices, ultimately shaping the course of European history and culture.
How the Italian City-States affected the rest of the world.
The Italian city-states profoundly impacted the world through their economic innovations, cultural achievements, and political structures, laying the groundwork for modern capitalism, the Renaissance, and international relations.
What happened to the German territory?
After World War I and II, Germany lost significant territory, including its colonies, to neighboring countries and the Soviet Union, with the eastern territories being annexed by Poland and the Soviet Union, and some areas becoming independent states.
5 facts about the German Territory.
Here are 5 facts about the territory of Germany: Germany is the seventh-largest country in Europe, spanning 357,168 square kilometers, with a significant portion covered by forests, and it's known for its diverse landscapes from the Alps to the Baltic Sea.
How the German Territory affected Europe.
German territorial ambitions and actions, particularly during the 20th century, dramatically reshaped Europe, leading to wars, territorial losses, and the rise and fall of empires and nations.
How the German Territory affected the rest of the world.
German territorial ambitions and actions, particularly during the 20th century, had a profound impact on the world, leading to two devastating World Wars, the Holocaust, and significant geopolitical shifts, including the redrawing of borders and the rise of new ideologies.
What happened to France?
Between 9 May and 22 June 1940, a remarkable German assault on north-west Europe, known as the Battle of France, resulted in the capture and subjugation of not only France but three other countries – Luxembourg, the Netherlands and Belgium.
Five facts about France.
Here are five interesting facts about France: it's the largest country in the European Union by surface area, the French flag is called the Tricolore, the Louvre Museum is the largest museum in the world, France is known as "l'Hexagone" (the hexagon) by French people, and it's the most visited country in the world.
How France affected Europe.
France significantly impacted Europe through its geographic position, economic strength, cultural influence, and revolutionary fervor, particularly during the French Revolution and Napoleonic era, shaping political landscapes, ideas, and societal structures across the continent.
How France affected the rest of the world.
France has profoundly shaped the world through its cultural, political, and economic influence, from the Enlightenment and the French Revolution to its colonial history and contributions to art, cuisine, and fashion, leaving a lasting impact on global culture and political thought.
What happened to Great Britain?
Great Britain, encompassing England, Scotland, and Wales, has a rich history marked by the union of these kingdoms and the rise and subsequent decline of the British Empire, culminating in the formation of the United Kingdom and its eventual withdrawal from the European Union.
Five Facts about Great Britain.
Here are five interesting facts about Great Britain: the UK is a constitutional monarchy, has a long history of tea drinking, is home to the world-famous Stonehenge, the UK invented the first postage stamp, and the UK is a diverse multicultural country.
How did Great Britain affect Europe?
Great Britain's influence on Europe has been profound, marked by periods of both cooperation and conflict, and its legacy continues to shape the continent through its political, economic, and cultural impacts, including the rise of parliamentary systems, imperial rivalries, and the impact of World Wars.
What affect did Great Britain have on the rest of the world?
Great Britain's vast colonial empire and subsequent global influence left a profound and multifaceted legacy, impacting language, law, culture, and politics in numerous countries, while also contributing to both positive and negative developments worldwide.
What happened to Latin America?
In recent events, Latin America has faced issues including environmental concerns like deforestation and pollution, political turmoil, and continued struggles with crime and violence, with some countries also grappling with economic instability and social inequality.
Five facts about Latin America.
Here are 5 interesting facts about Latin America: it's home to the world's longest mountain range (the Andes), the largest salt flats (Salar de Uyuni), the highest navigable lake (Lake Titicaca), and is a major coffee producer with Brazil and Colombia as key players, and the region is highly urbanized.
What affect did Latin America have on Europe?
Latin America profoundly impacted Europe through colonialism, resource extraction, cultural exchange, and the rise of independent nations, leading to both economic and political shifts in Europe.
What affect did Latin America have on the rest of the world?
Latin America has profoundly impacted the world through its rich cultural heritage, economic resources, and political influence, shaping global trends in areas like music, food, and politics, while also facing challenges related to inequality and political instability.
Enclosure Movement
The Enclosure Movement in England (roughly 18th-19th centuries) involved the privatization of land previously held in common, leading to increased agricultural efficiency but also the displacement of many small farmers and rural communities.
Cottage Industry
A business or manufacturing activity carried on in a person's home.
Steam Engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that uses steam as its working fluid to perform mechanical work, typically by expanding steam to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder.
Factory
A building or group of buildings where goods are manufactured or assembled chiefly by machine.
Bessemer Process
A steel-making process, now largely superseded, in which carbon, silicon, and other impurities are removed from molten pig iron by oxidation in a blast of air in a special tilting retort (a Bessemer converter
Mass Production
Mass production is a manufacturing process that utilizes efficient methods, often assembly lines and automation, to produce large quantities of standardized goods quickly and at a lower cost.
Laissez Faire
a policy or attitude of letting things take their own course, without interfering.
"a laissez-faire attitude to life"
Communism
a political theory derived from Karl Marx, advocating class war and leading to a society in which all property is publicly owned and each person works and is paid according to their abilities and needs.
Socialism
A political and economic theory of social organization which advocates that the means of production, distribution, and exchange should be owned or regulated by the community as a whole.
James Hargreaves invents the Spinning Jenny.
1764
James Watt builds the Steam Engine.
1769
Eli Whitney invents the Cotton Gin
1793
Edward Jenner develops small pox vaccine
1796
Samuel Morse’s telegraph sends messages over wire.
1844
Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels published Communist Manifesto.
1848
Darwin Publishes the Theory of Evolution.
1859
1876
Alexander Graham Bell patents the telephone.
1879
Thomas Edison invents incadescent lightbulb.
1883
Brooklyn Bridge opens in New York.
1889
Eiffel Tower opens in France
1903
Wright Brothers make the first flight
Colony
a country or area under the full or partial political control of another country, typically a distant one, and occupied by settlers from that country.
Protectorate
.
a state that is controlled and protected by another.
Sphere of Influence
A country or area in which another country has power to affect developments although it has no formal authority.
Examples of what include the 13 British colonies in North America (like Virginia and Massachusetts)
colonies
Protectorate Examples.
The French protectorate of Tunisia, and the British protectorate of the Maldives.
Sphere of influence examples:
Per Chloe, per internet.
China and North Korea.
Russia's claim to a sphere of influence including Ukraine, and France's "Françafrique" network in sub-Saharan Africa.
1839
First Opium War begins
Commodore Perry forces Japan open to trade
1853-1854
1857
Sepoy Rebellion against British rule in India.
1869
Suez Canal completed
1884-1885
The Berlin Conference
1896
Ethiopia wins the Battle of Adwa
Boxer Rebellion in China
1899-1901

Boxers
Boxers replace

1904-1905
Russo-Japanese War
What was the Boxer Rebellion?
A major anti-foreign, anti-Christian uprising in China between 1899 and 1901.

What was the Boer war? (Type highlighted part, read all).
More information:
The Boer War, also known as the Anglo-Boer War, was a conflict fought between the British Empire and the two Boer republics of the Transvaal (also known as the South African Republic) and the Orange Free State. The war took place in South Africa between 1899 and 1902.
A meeting held in 1884-85 by European powers to regulate European colonization and trade in Africa.
What was the Berlin Conference? (Read photo)
Type: The Berlin Conference (1884-1885) was a meeting of European powers that formalized the Scramble for Africa, regulating colonization and trade in Africa.
The Boers Contributions:
The Sepoys Contributions:

The Boxers Contributions:

Contributions of Empress Dowager Cixi
Empress Dowager Cixi, also known as Cixi, played a significant role in the modernization of China during her long reign, from 1861 to 1908. While some view her as a conservative ruler who hindered progress, others acknowledge her efforts to introduce Western technologies and reforms.
Positive societal reforms in Belgium and the establishment of the Congo free-state.
Contributions of King Leopold II:
King Leopold II of Belgium's contributions were multifaceted, encompassing both positive societal reforms in Belgium and the establishment of the Congo Free State with its subsequent consequences. He enacted significant social changes in Belgium, including labor protections and the abolition of the "livret d'ouvrier". However, his most significant contribution, the Congo Free State, is marked by the severe exploitation and violence inflicted upon the Congolese people.
Commodore Matthew Perry Contributions:
Commodore Matthew Perry is best known for his naval expeditions to Japan in 1853 and 1854, which led to the signing of the Treaty of Kanagawa and the opening of Japan to Western trade. Beyond this, Perry was a key figure in modernizing the U.S. Navy, advocating for steam power and establishing naval academies.
Contributions of Lili’uokalani:
(Read)
Queen Lili'uokalani's most significant contributions include her role as the last monarch of the Hawaiian Kingdom, her efforts to preserve Hawaiian culture and sovereignty, and her lasting legacy through her musical and literary works. She also served as a vocal advocate for Hawaiian rights and protested against the annexation of Hawaii by the United States.
Read
Define Annexation: Annexation is…
the illegal acquisition of another state's territory by force, usually after military occupation.
Read
Contributions of Menelik II:
(Read)
Menelik II, Emperor of Ethiopia, is celebrated for his modernization efforts, expansion of Ethiopian territory, and preservation of Ethiopian independence during the Scramble for Africa. His contributions include founding the Bank of Abyssinia, introducing a modern postal system, initiating the Addis Ababa-Djibouti railway, and establishing modern educational institutions. He also played a key role in maintaining Ethiopia's independence through strategic alliances and military victories, particularly at the Battle of Adwa.
Read
Rudyard Kipling contributions:
(Read)
Rudyard Kipling's contributions to literature are significant and multifaceted. He is best known for his stories and poems about British soldiers in India and for his children's tales, including The Jungle Book. His ability to capture the essence of social settings and create vivid character portraits earned him the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1907.
Define: Colony:
A country or area under the full or partial political control of another country, typically a distant one, and occupied by settlers from that country.
South and Southeast Asia
Define: British East India Company:
The East India Company (EIC) was a British joint-stock company founded in 1600 to trade with the East Indies (what region). It evolved into a powerful political and military entity, ultimately leading to British rule in India. The company was dissolved in 1874.
1839-1842, 1856-1860, China, Western, Britain, France, opium trade, suppress.
Define: Opium War:
The Opium Wars were two conflicts, the First (dates) and Second (dates), fought between (who) and - powers (primarily -, and later - and others) over the issue of - - and China's attempts to - it.
Define: Berlin Conference:
Define: Jewel in the Crown:
The most valuable or successful part of something.
Define: Boxer Rebellion:
a violent anti-foreign, anti-Christian, and anti-imperialist uprising in China that took place from 1899 to 1901.
Define: Crimes Against Humanity:
AI Overview
Crimes against humanity, as defined by international law, are ..(fill in).. These crimes include acts like murder, extermination, enslavement, deportation, torture, rape, and other inhumane acts causing great suffering or serious injury. The key is that these acts must be part of a larger, intentional plan or policy targeting a civilian population.
widespread or systematic attacks directed against any civilian population.
a major rebellion against the rule of the British East India Company (EIC) in India in 1857-1858.
Define: Sepoy Rebellion:
The Sepoy Rebellion, also known as the Indian Mutiny or the First Indian War of Independence, was ...(fill in)… It began as a mutiny among the Indian soldiers, or sepoys, in the EIC army, but quickly expanded to include a broad range of Indian people in various regions.
Define: Suez Canal:
The Suez Canal is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez and dividing Africa and Asia (and by extension, the Sinai Peninsula from the rest of Egypt). The 193.30-kilometre-long (120.11 mi) canal is a key trade route between Europe and Asia.
?
Ethiopia: Battle of Adwa
The Battle of Adwa, fought on March 1, 1896, was a decisive military victory for Ethiopia against invading Italian forces, resulting in the preservation of Ethiopia's independence.
The Maji Maji Rebellion was
A significant armed uprising in German East Africa (modern-day Tanzania) that took place from 1905 to 1907.
1883-1898, French, Mandingo people, Samori Ture, West Africa.
Mandigo Rebellion: The Mandingo Wars were a series of military conflicts (dates) fought between the - and the - - , led by (who) in (what region).
Definition of Mutiny
An open rebellion against the proper authorities, especially by soldiers or sailors against their officers.
The Zulu War, also known as the Anglo-Zulu War, was
A conflict between the British Empire and the Zulu Kingdom in 1879, primarily fought in South Africa
Crimean War:
(Read + Date + Summary)
The Crimean War (1853-1856) was a major European conflict primarily fought in the Crimean Peninsula, involving the Russian Empire against an alliance of France, Britain, the Ottoman Empire, and Sardinia. It was driven by disputes over religious and territorial claims in the Ottoman Empire, particularly in the Holy Land, and broader geopolitical tensions.
(Read + Date + Summary)
Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867, World War I
Fill in the blanks:
The Austrian Empire transitioned into the Austro-Hungarian Empire primarily due to the - - - -.
The Austro-Hungarian empire fell due to - - -, the 1918 crop failure, general starvation and the economic crisis.
democratic, capitalist.
What characterizes a western nation?
Western nations are generally characterized by - governance, - economies, and a strong emphasis on individualism, rationalism, and human rights. They also often exhibit a Christian cultural heritage and a history of colonization and industrialization, influencing their social and political structures.
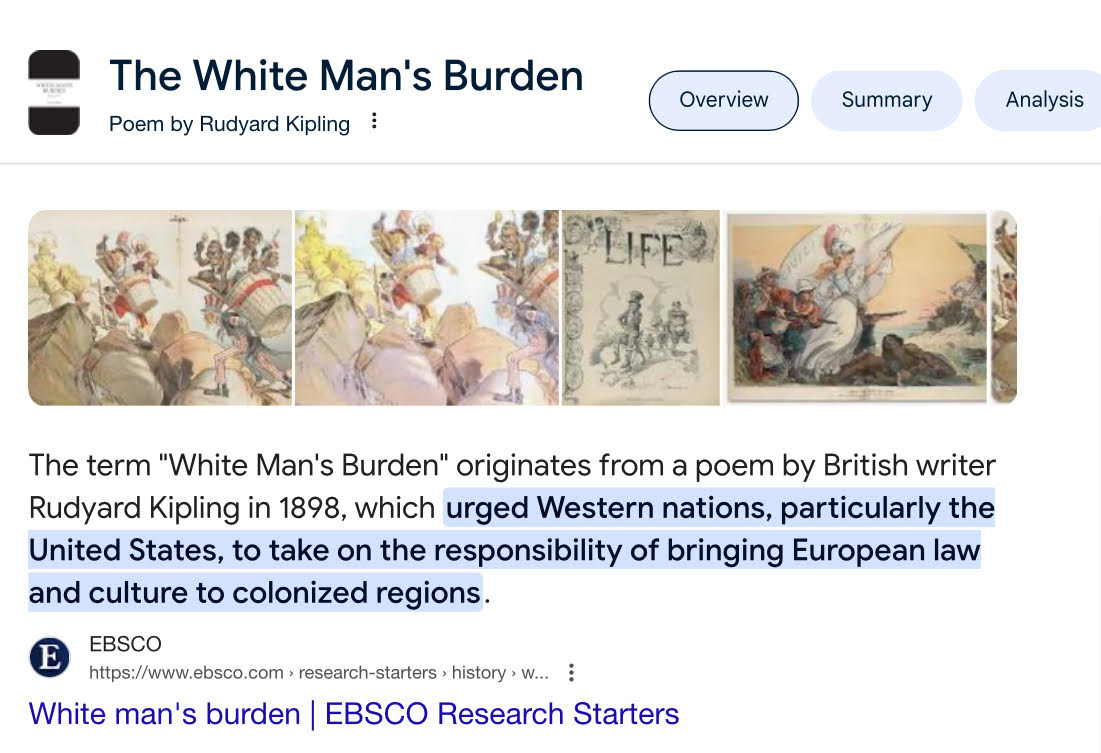
What was The White Man’s Burden:
The term “White Man’s Burden” originates from a - by - writer - -, in (date), which urged - -, particularly the - , to take on the responsibility of bringing - - and - to - -.
poem, British, Rudyard Kipling, 1898, Western nations, United States, European law, culture, colonized regions.
economics, 1776, labor, consumption, trade, good government, wealthier.
The Wealth of Nations Summary. Often considered the foundational text of modern -, Adam Smith's massive (date) treatise The Wealth of Nations addresses a wide range of interconnected questions about how -, -, -, and - -, can help societies grow - over time.
From Lit Charts .com