AP Biology - Topics 6.1 & 6.2
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
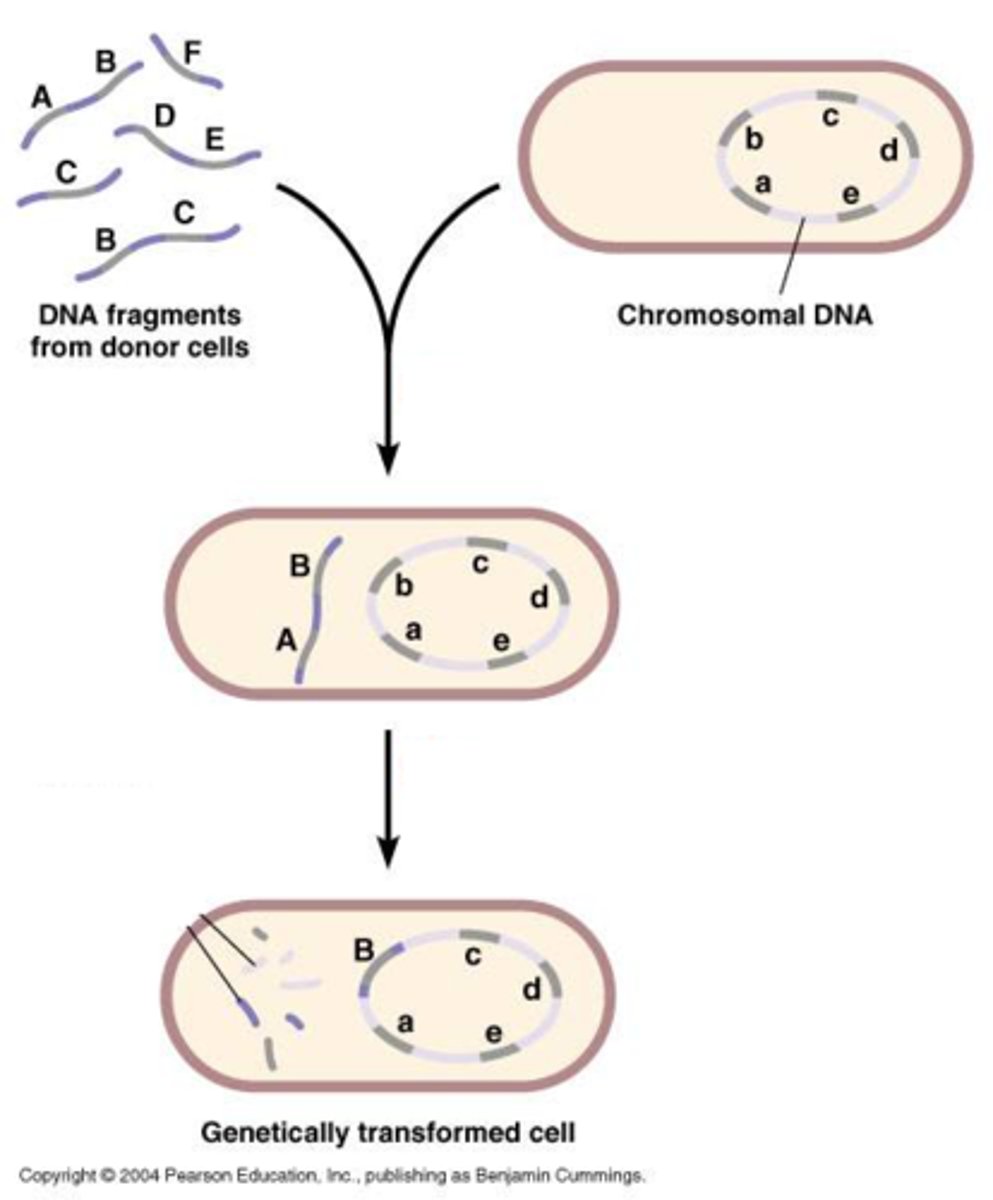
Transformation
a change in genotype and phenotype due to assimilation of foreign DNA
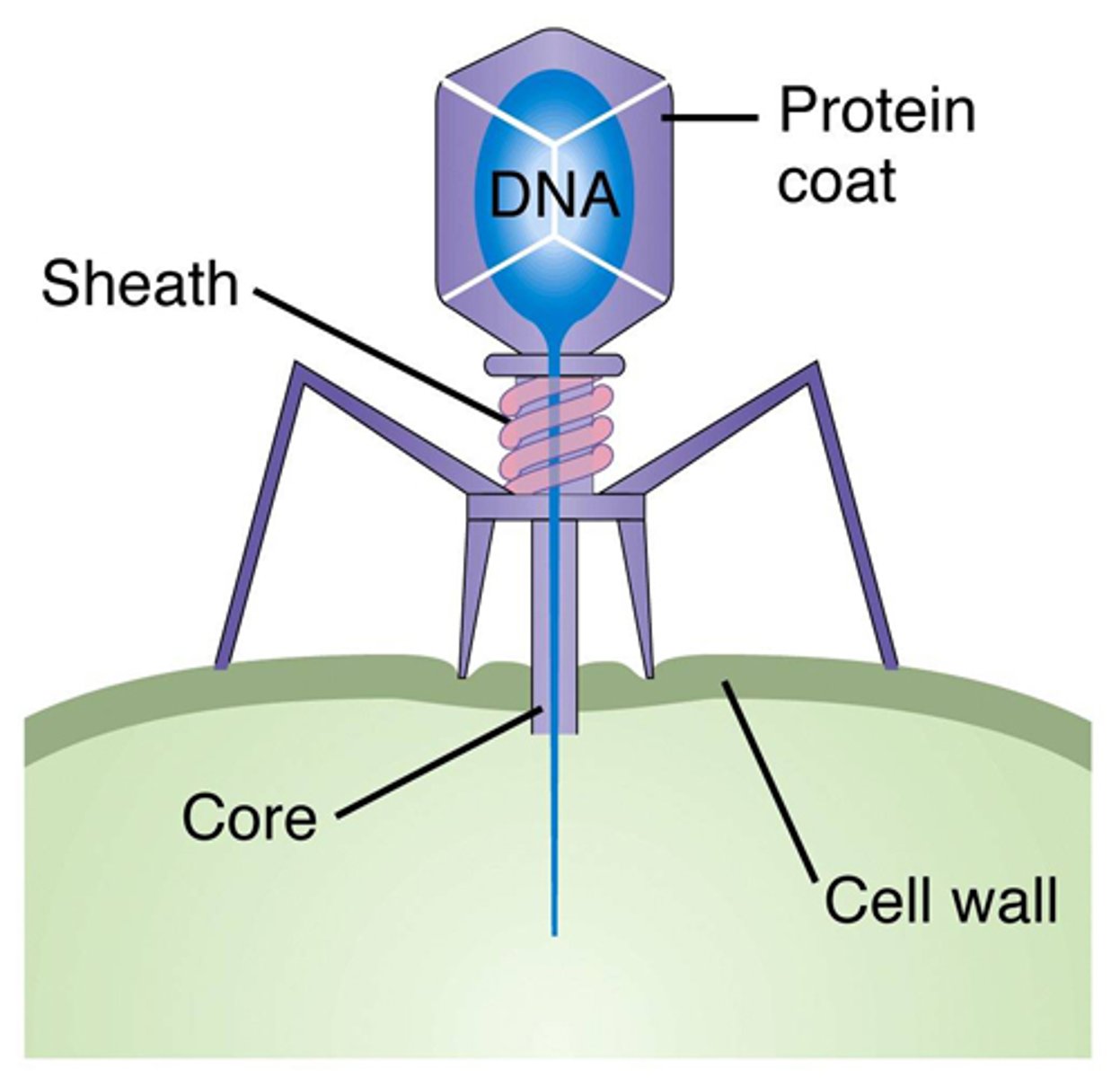
bacteriophages
viruses that infect bacteria. Bacteriophages consist only of proteins and DNA.
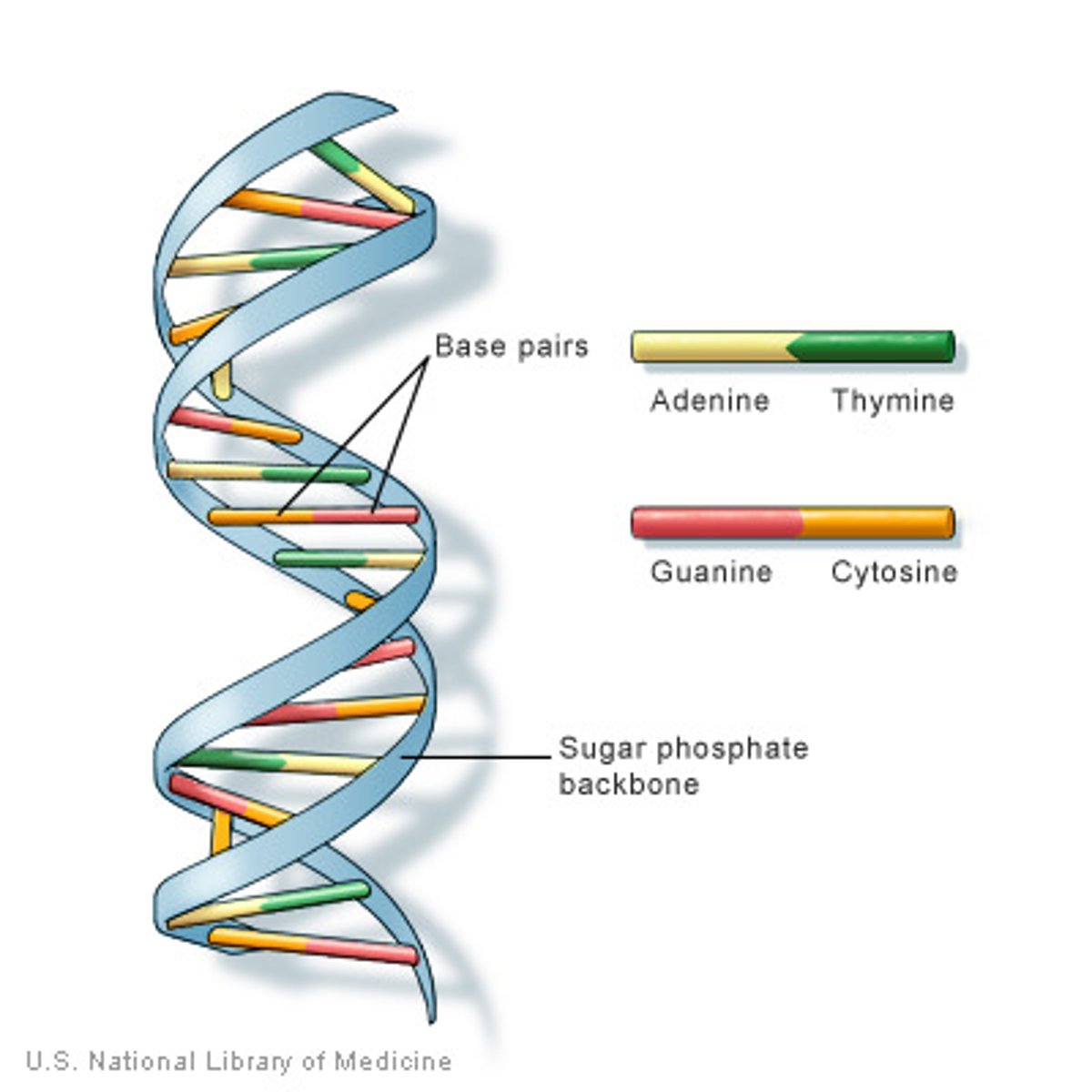
DNA is the genetic material
polymer of nucleotides, DNA composition varies from one species to the next, A and T bases are equal and the number of G and C bases are equal
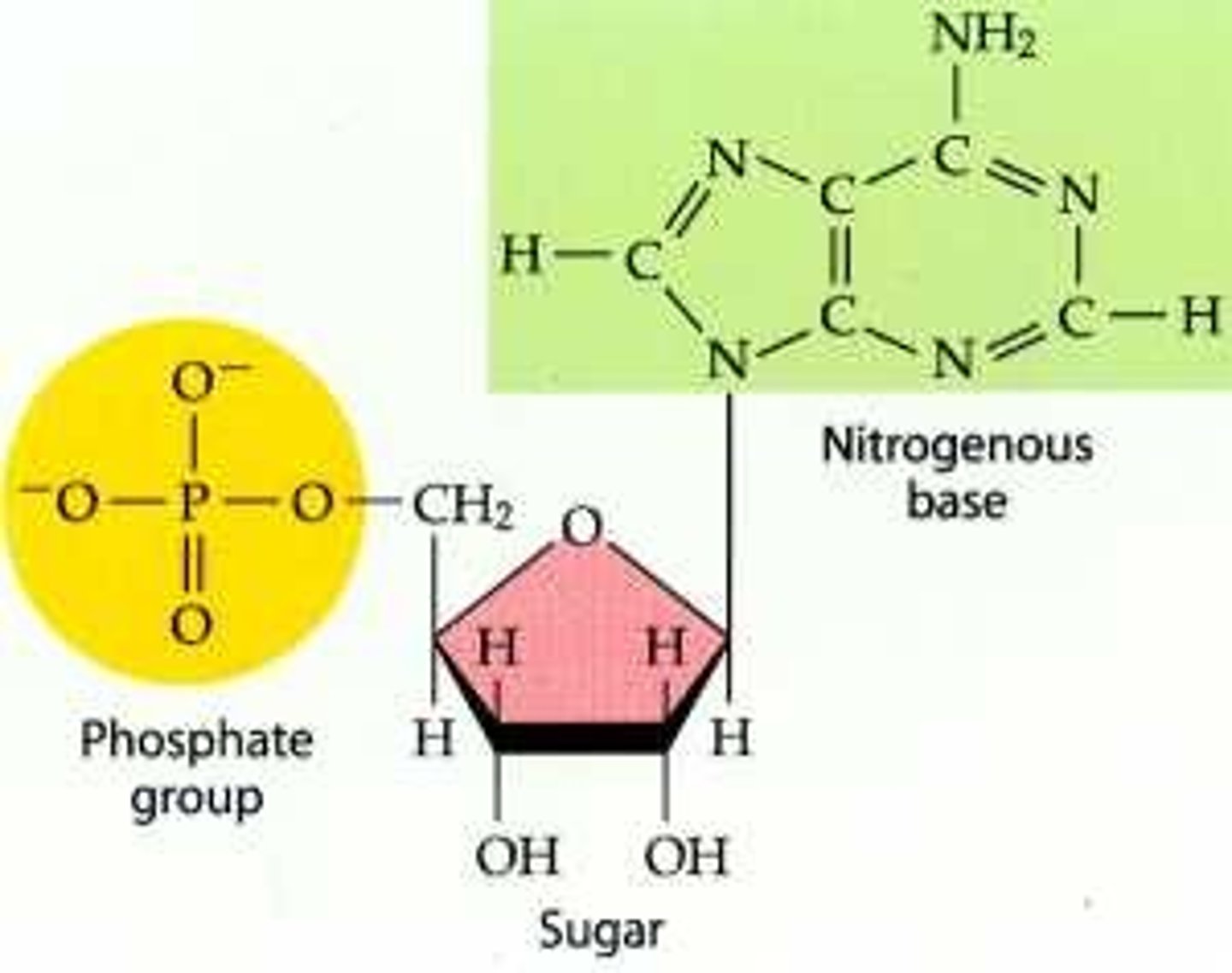
nucleotides
a nitrogenous base, a sugar, and a phosphate group
Purine
A/G, 2 organic rings, 2X the size, 2 hydrogen bonds
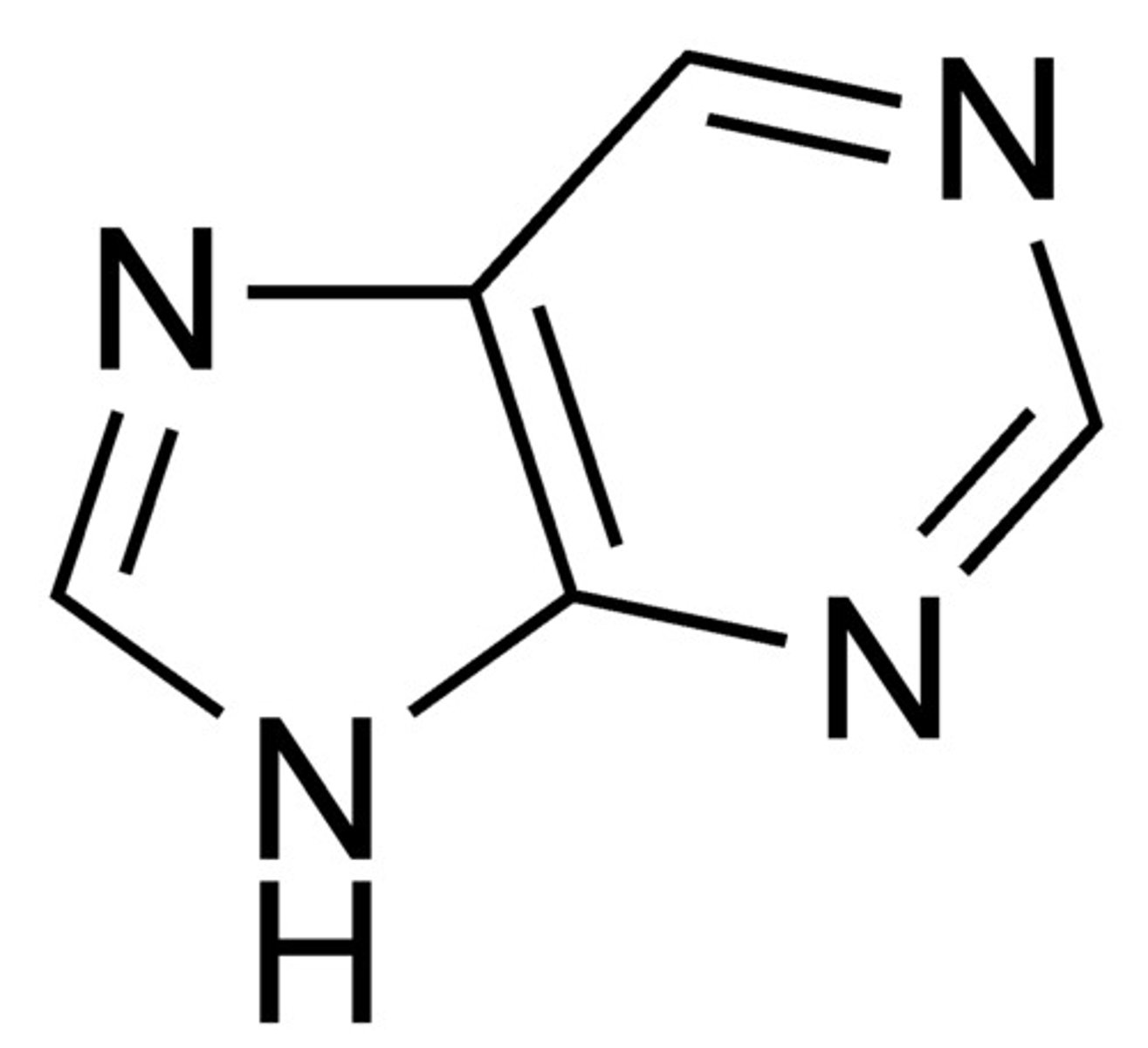
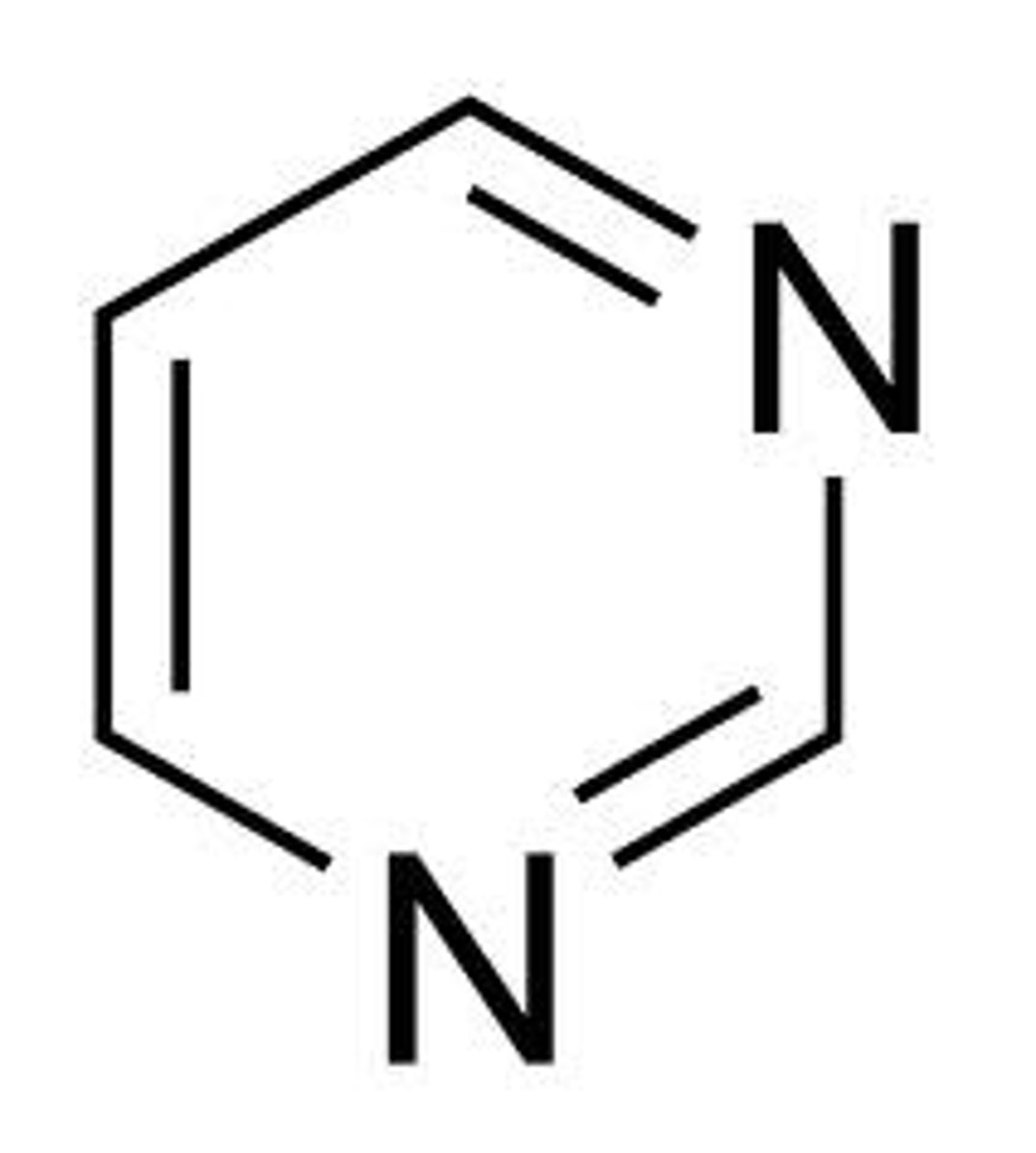
Pyrimidine
C/T, single ring, X size, 3 hydrogen bonds
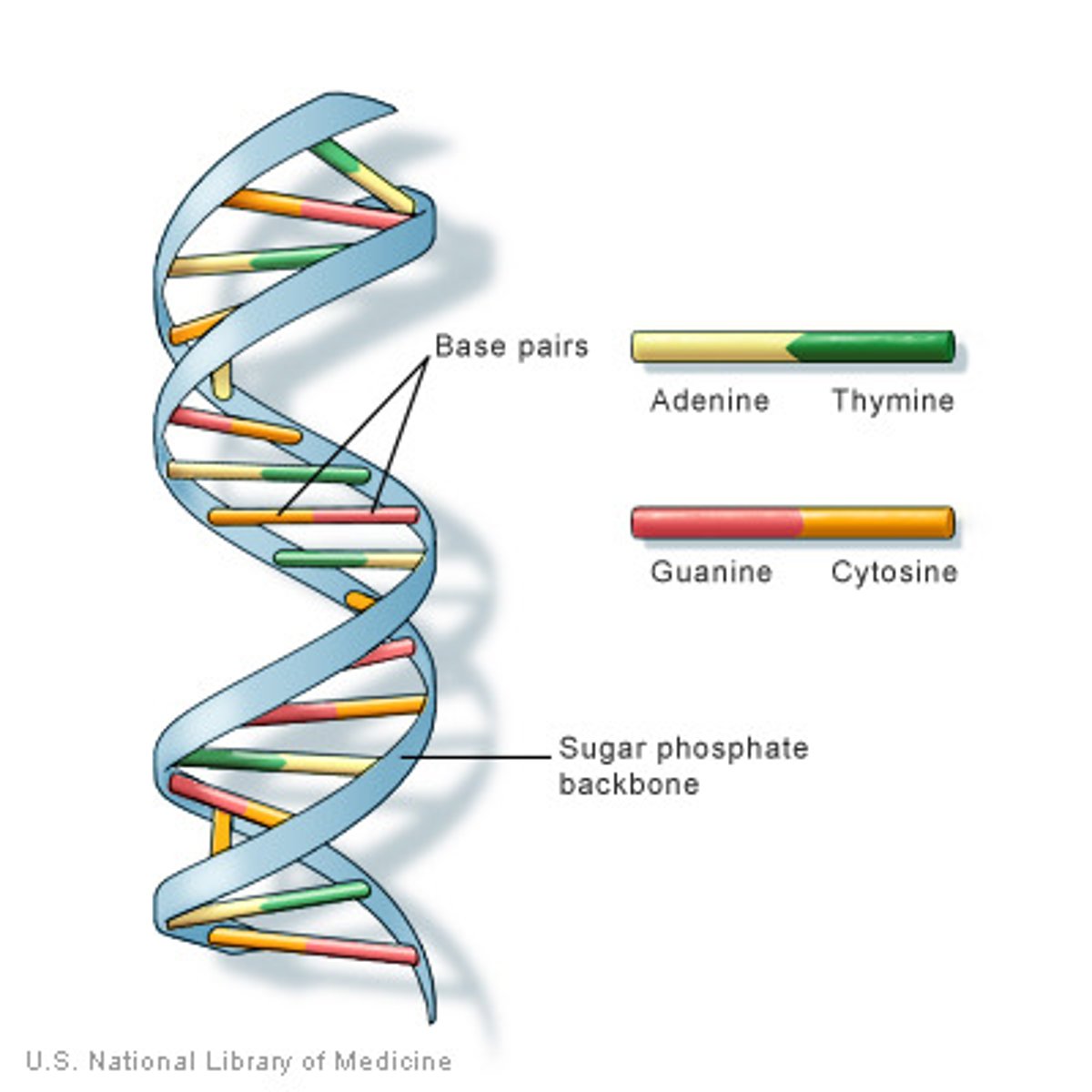
Why do purine and pyrimidines bases always pair together?
because of the number of hydrogen bonds they are able to form
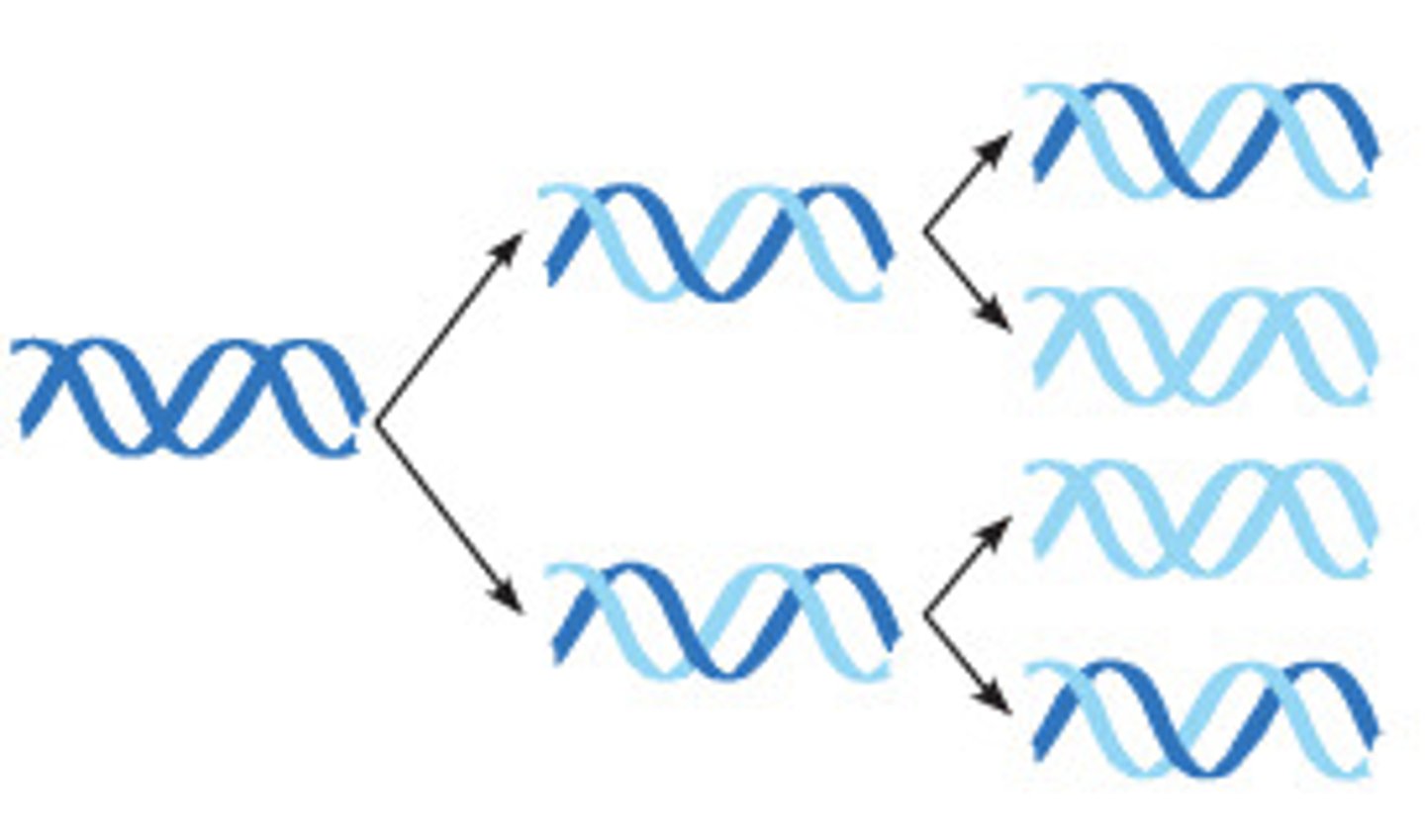
Semiconservative model
the two strands of the parental molecule separate, and each functions as a template for synthesis of a new, complementary strand
origins of replication
The site where replication occurs where the two DNA strands are separated, opening up a replication "bubble".
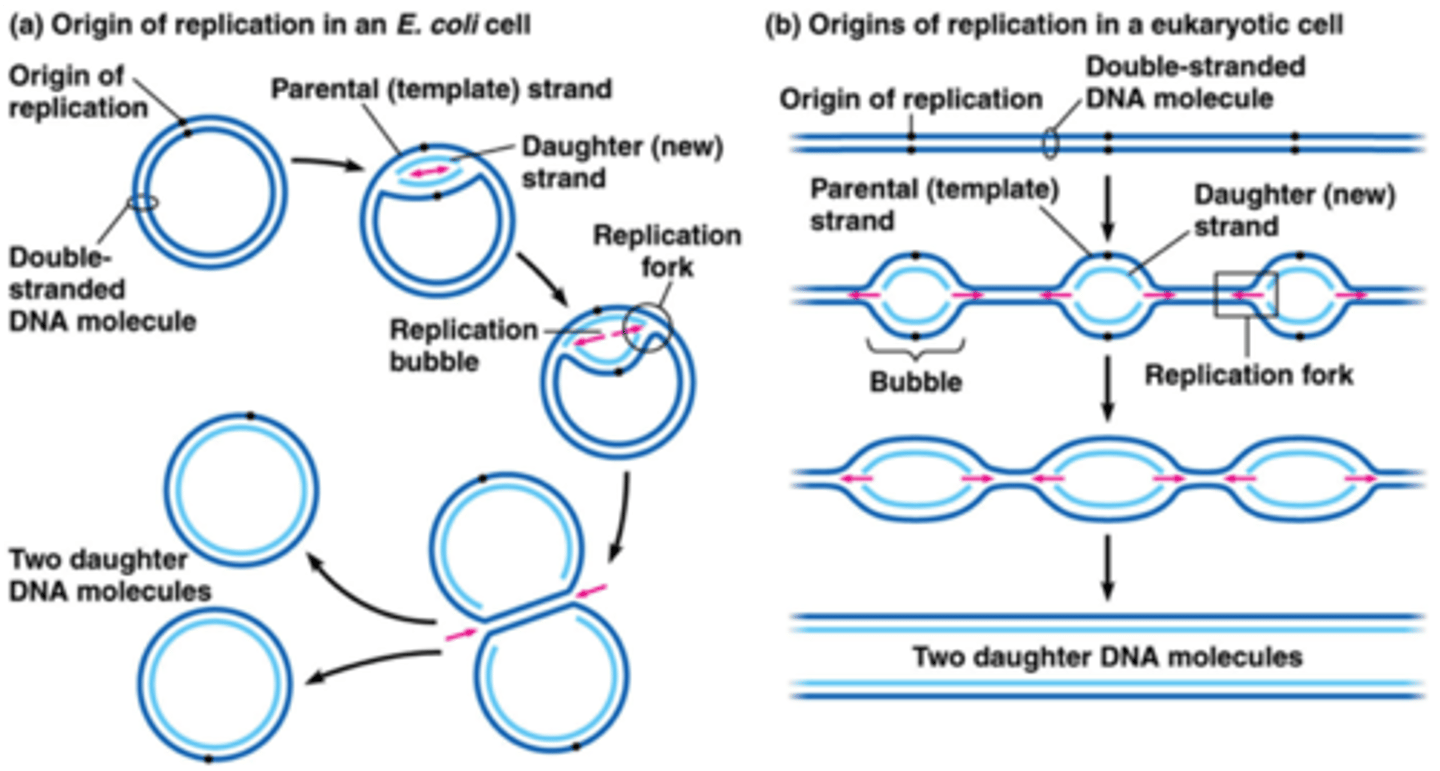
DNA polymerase
Enzyme involved in DNA replication that joins individual nucleotides to produce a DNA molecule
RNA Primase
enzyme that creates an RNA primer for initiation of DNA replication.
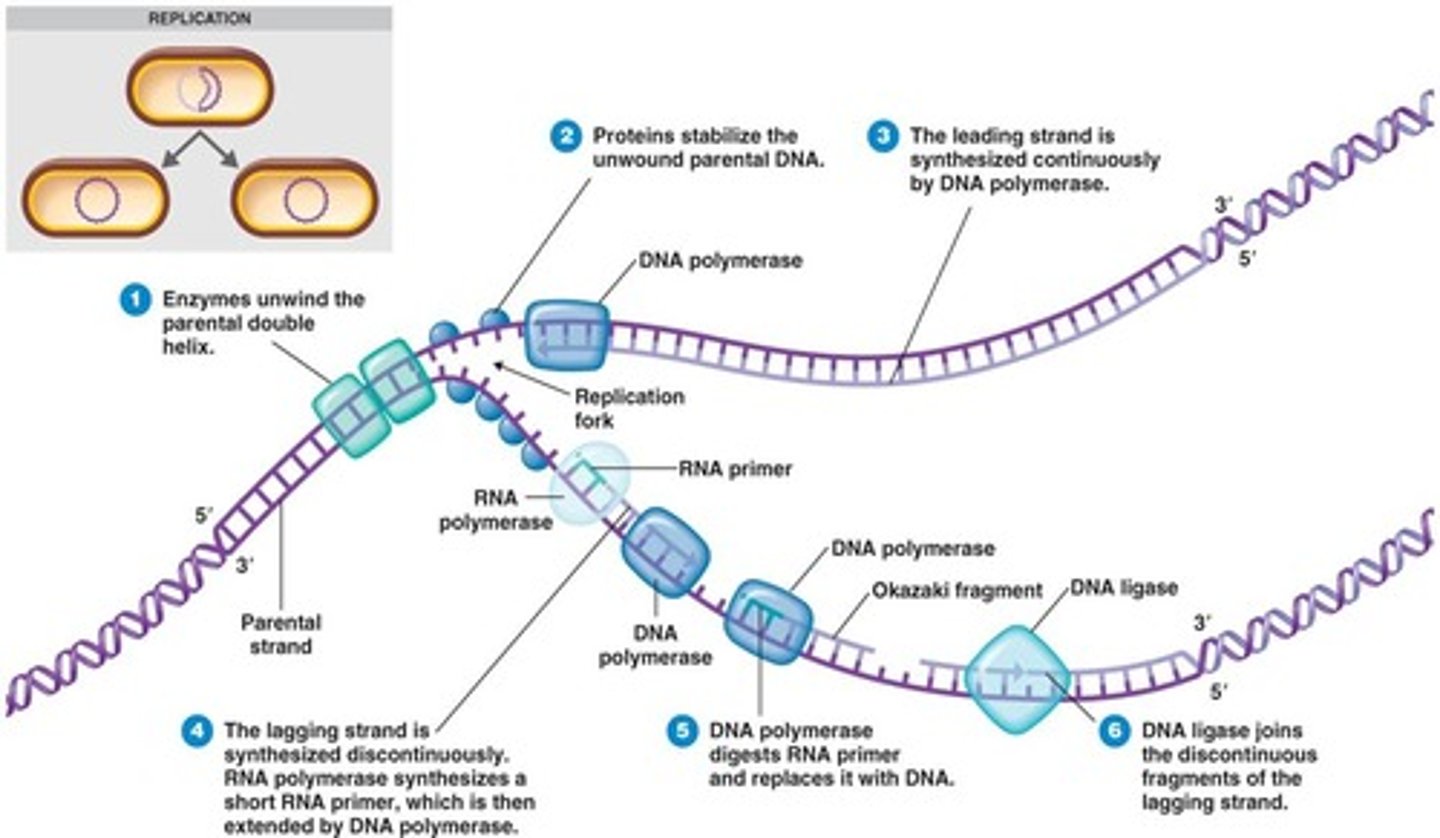
replication fork
a Y-shaped region where new DNA strands are elongating that is located at the end of the replication bubble.

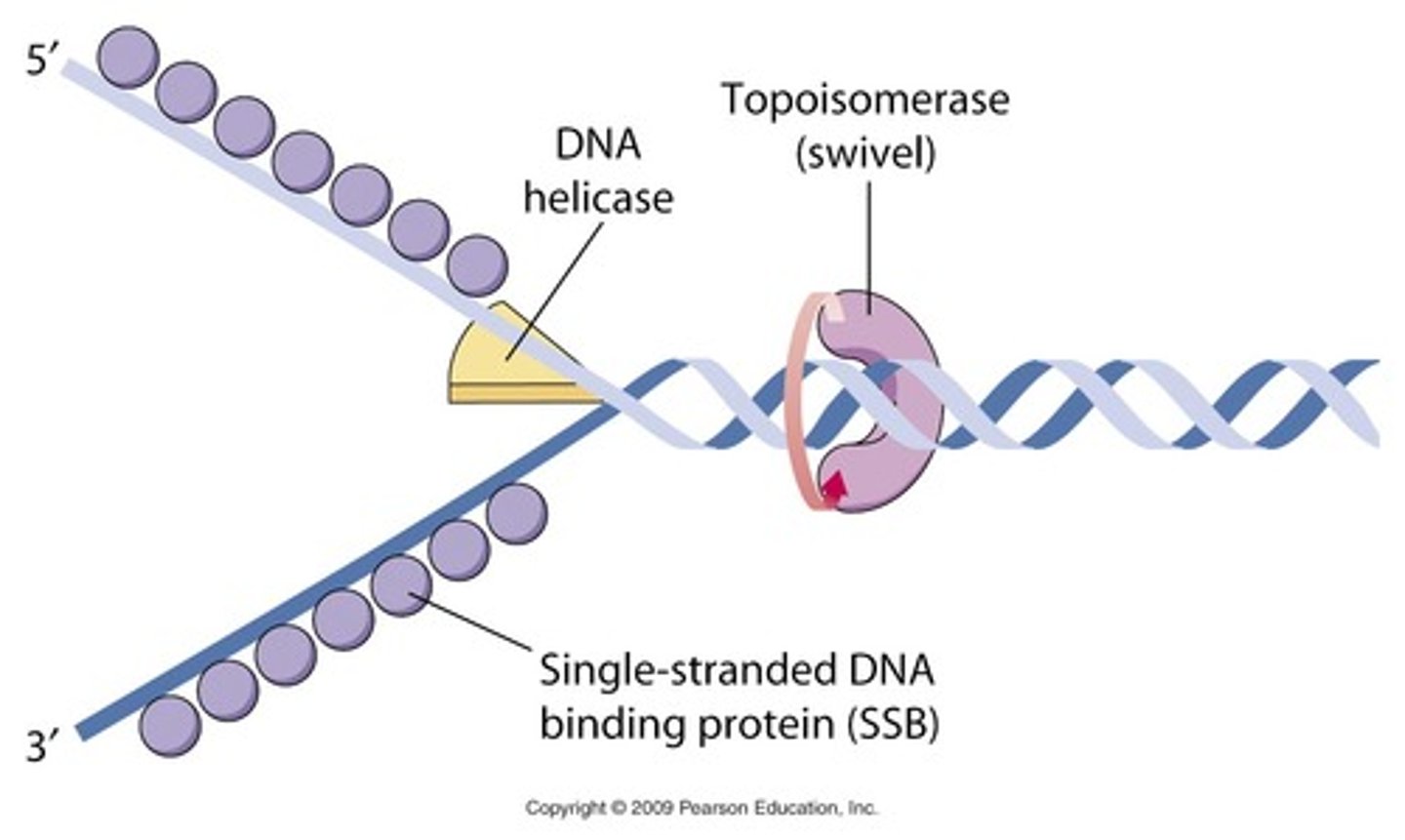
Single-strand binding proteins
bind to and stabilize single-stranded DNA
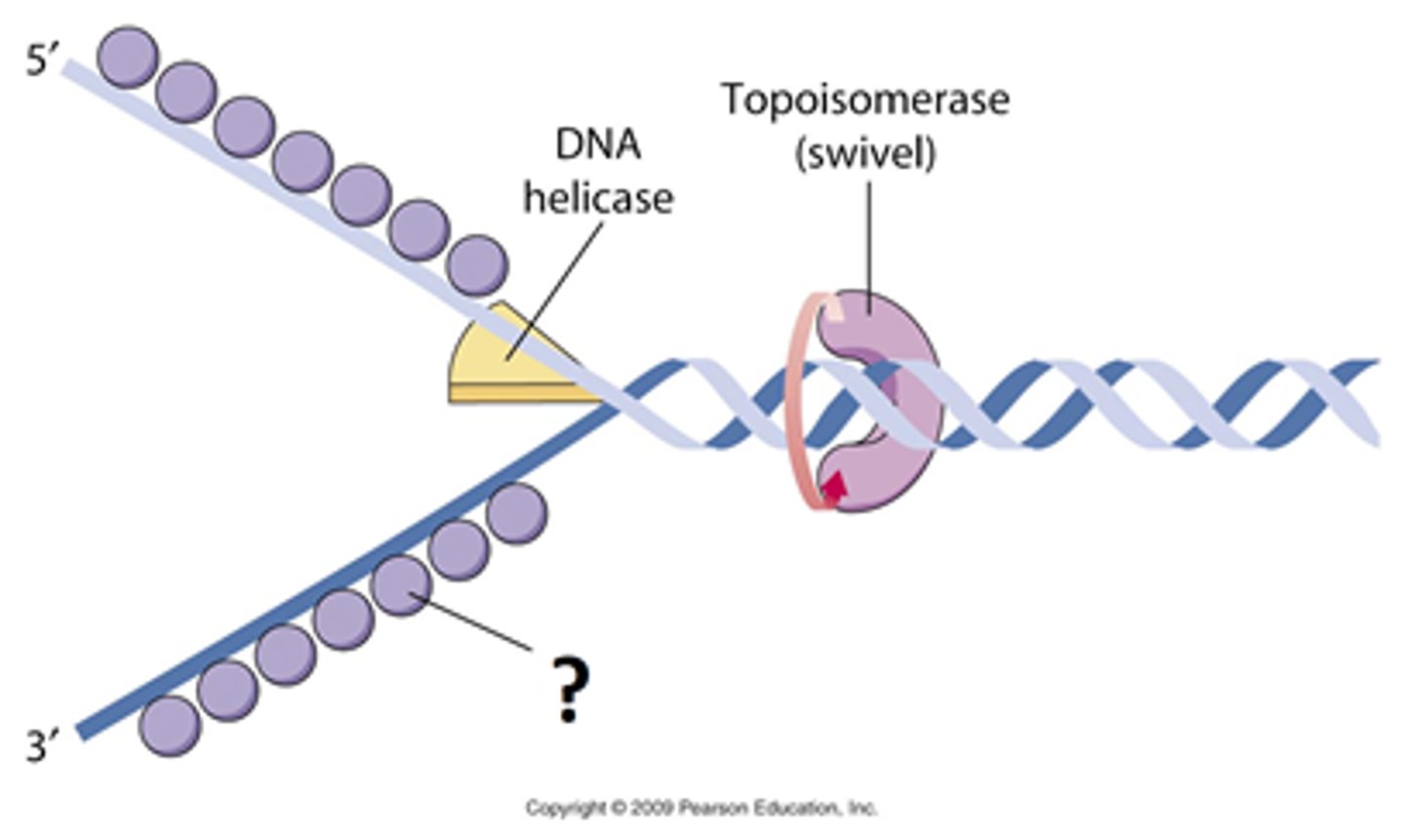
Helicases
enzymes that untwist the double helix at the replication forks.
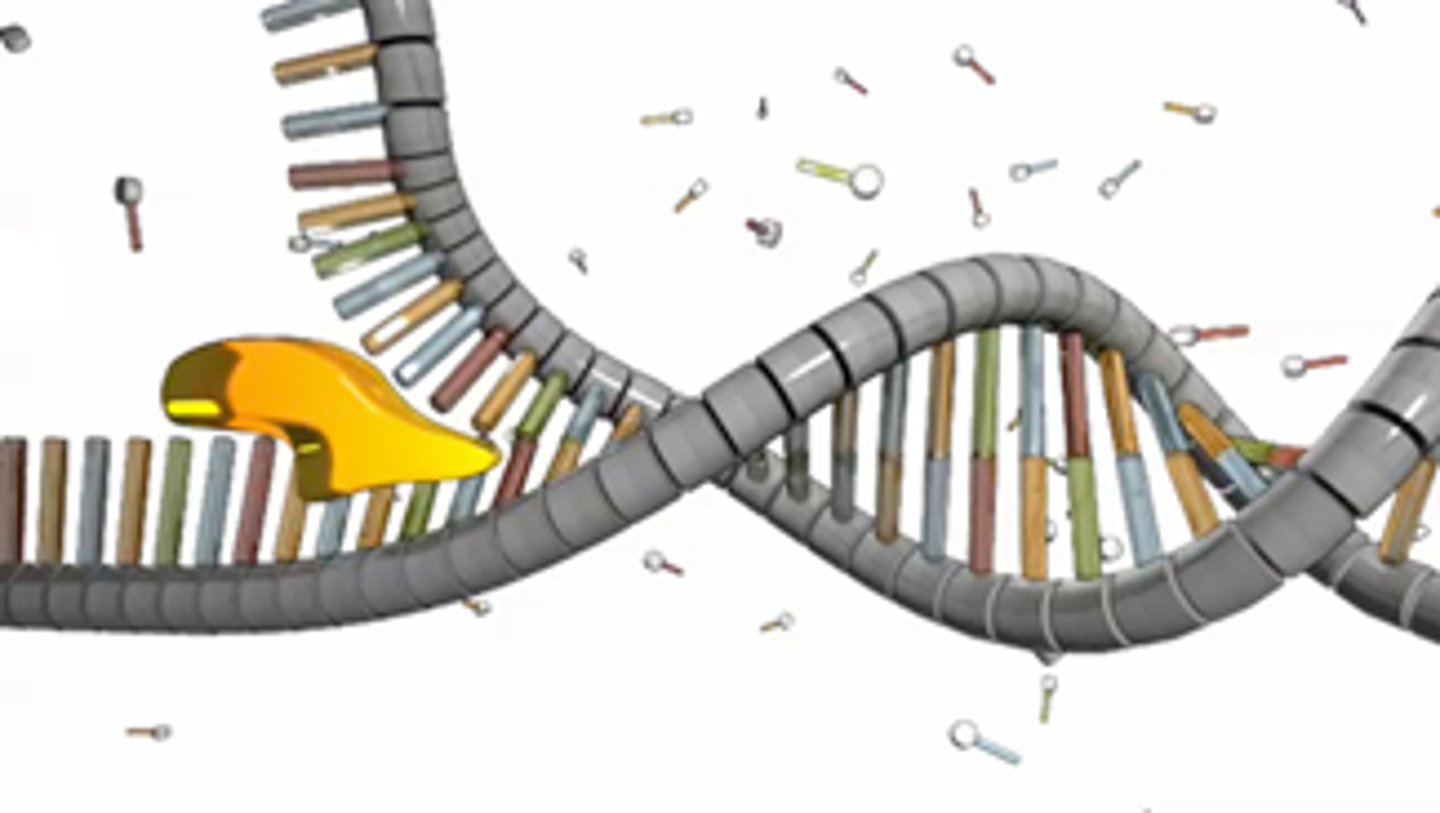
Topoisomerase
Enzyme that functions in DNA replication, helping to relieve strain in the double helix ahead of the replication fork.
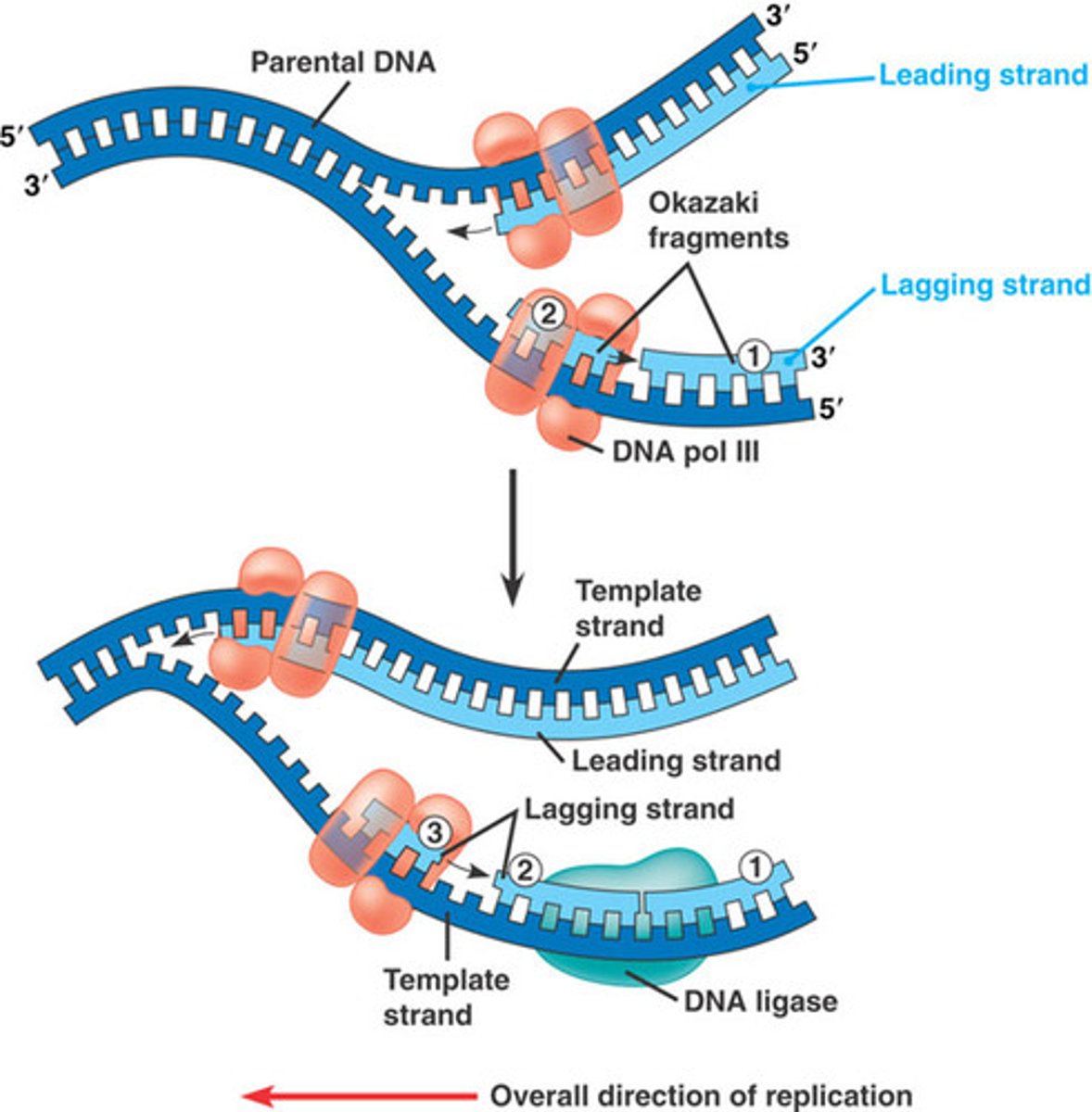
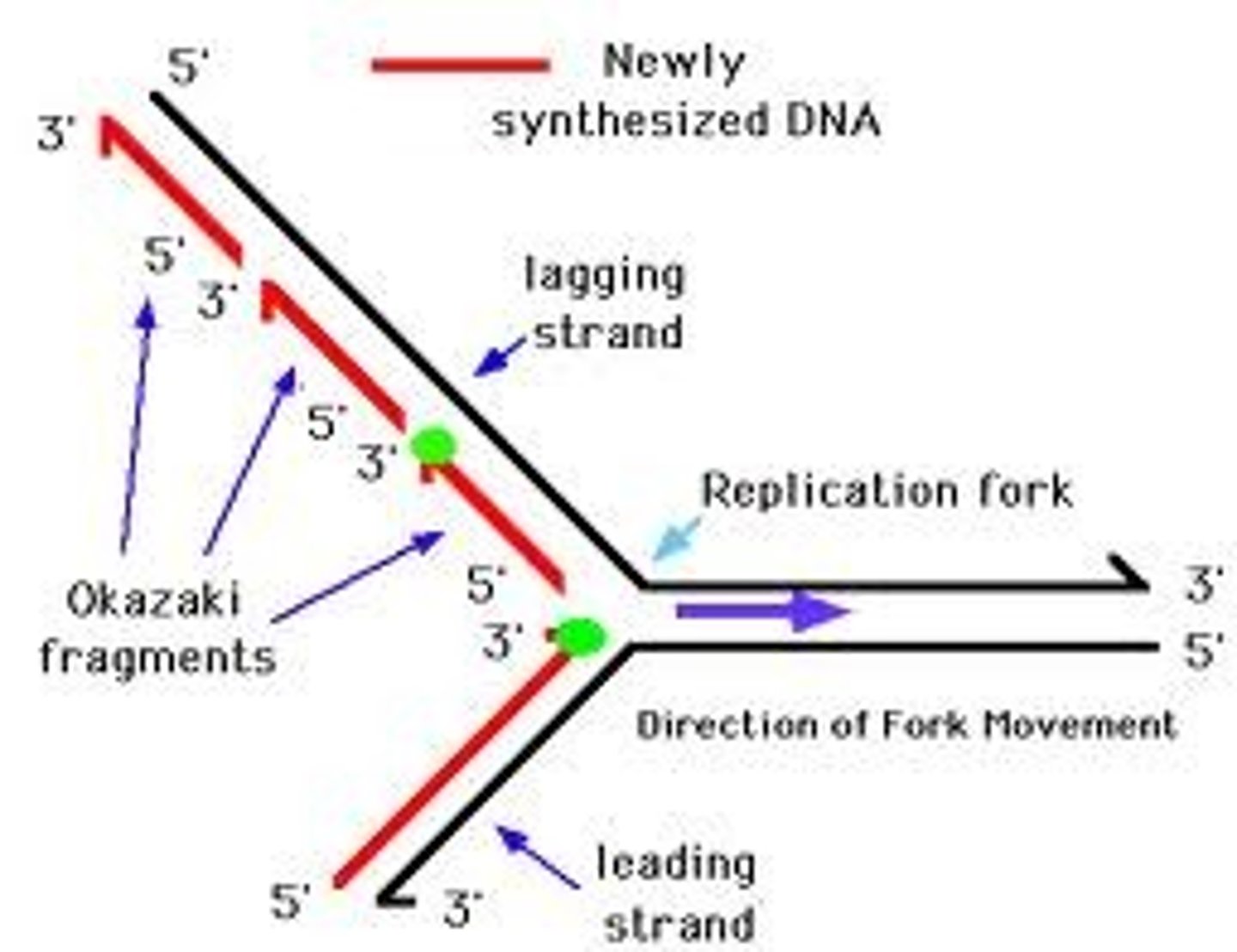
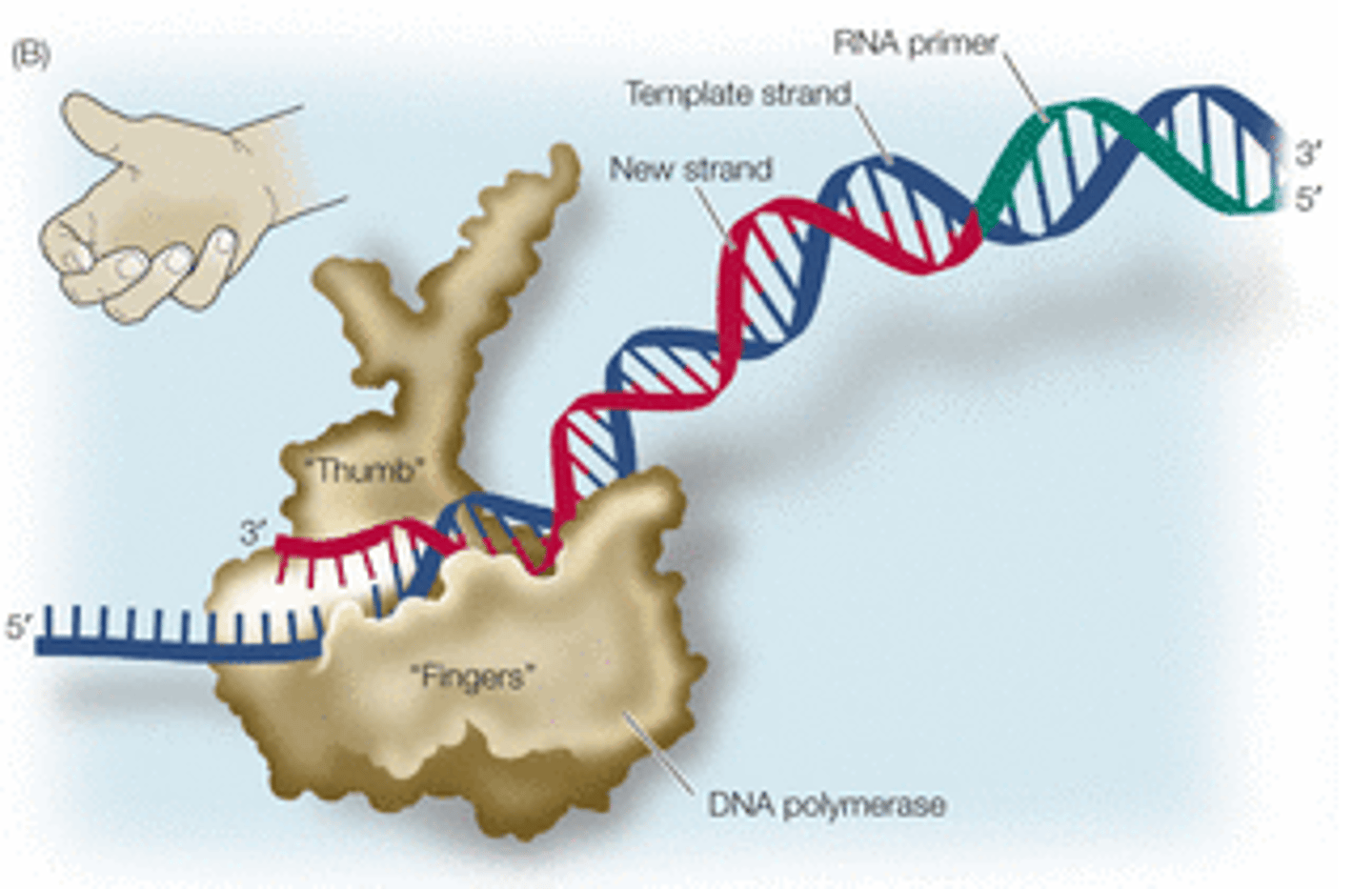
leading strand
The new continuous complementary DNA strand synthesized along the template strand in the mandatory 5' to 3' direction.
lagging strand
The strand in replication that is copied 3' to 5' as Okazaki fragments and then joined up.
Other functions of DNA polymerases
proof reading by replacing any incorrect nucleotides
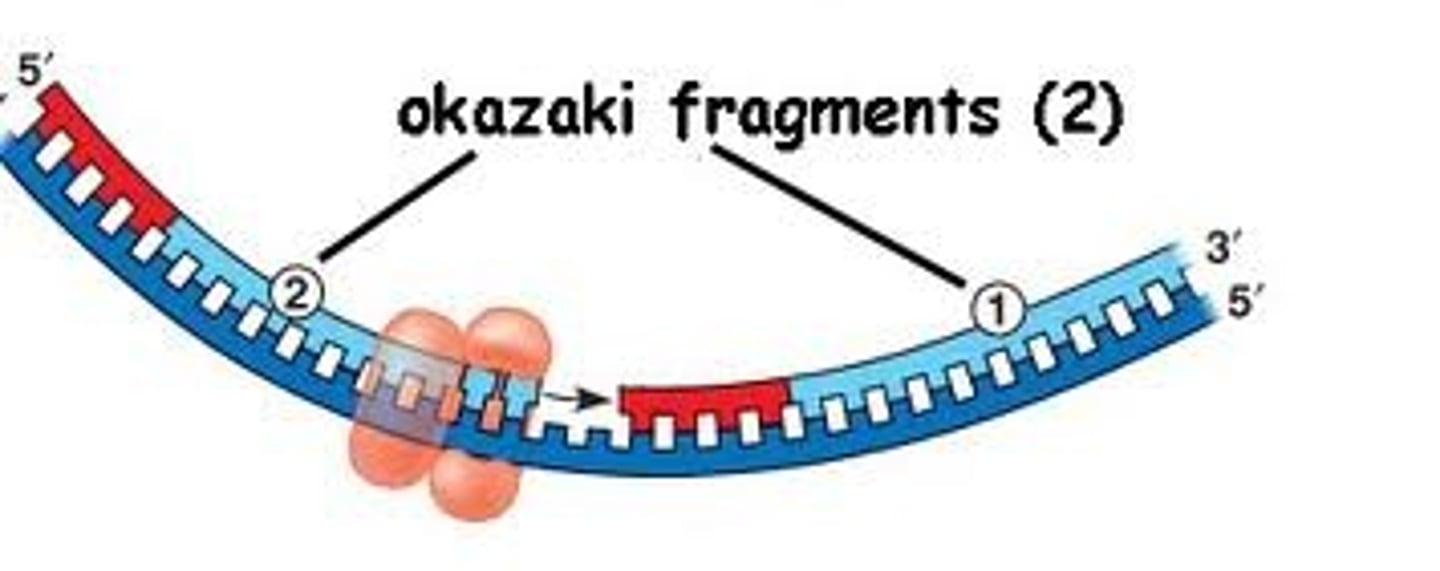
Okazaki fragments
Small fragments of DNA produced on the lagging strand during DNA replication, joined later by DNA ligase to form a complete strand.
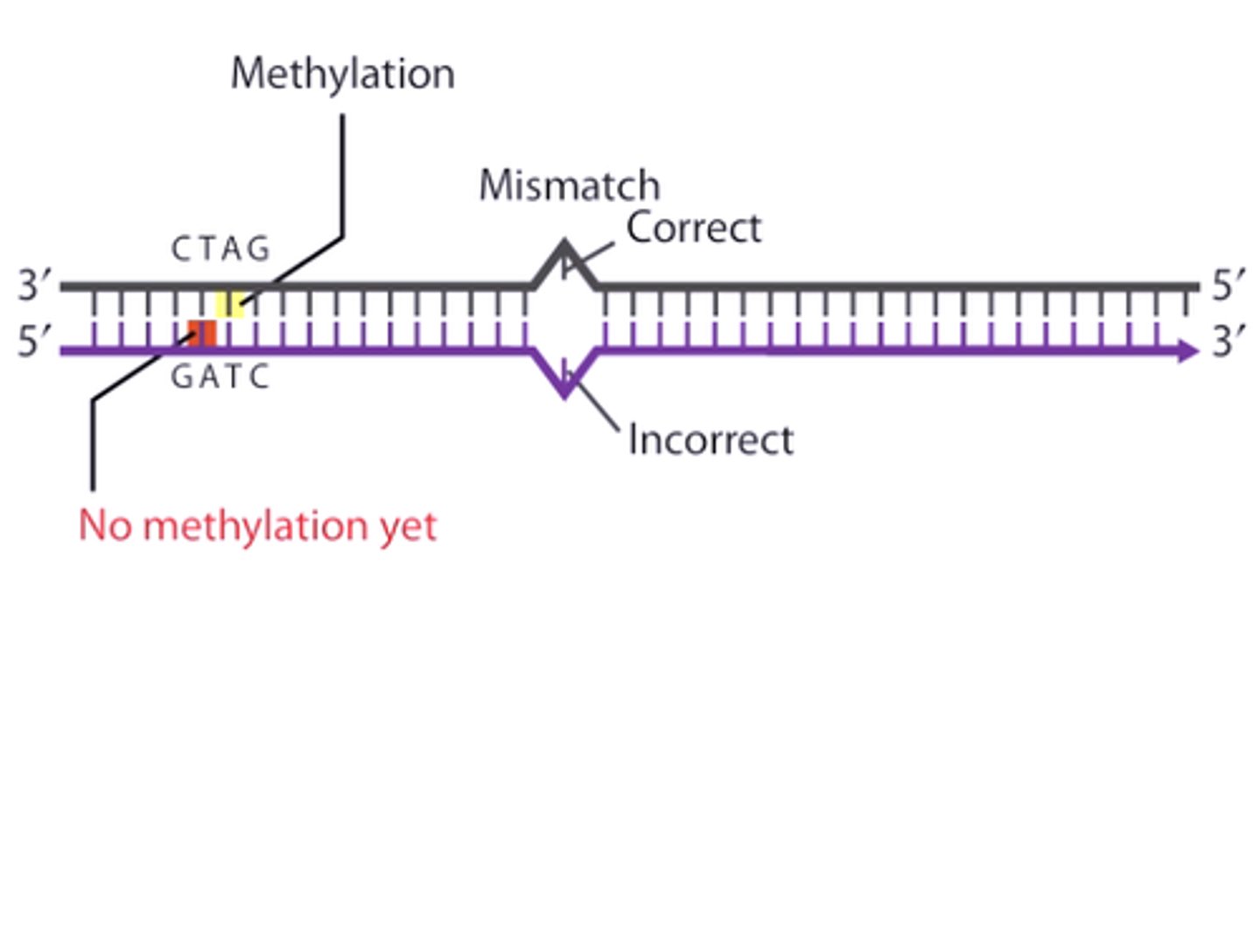
mismatch repair
repair enzymes correct errors in base pairing
nucleotide excision repair
a nuclease cuts out and replaces damaged stretches of DNA
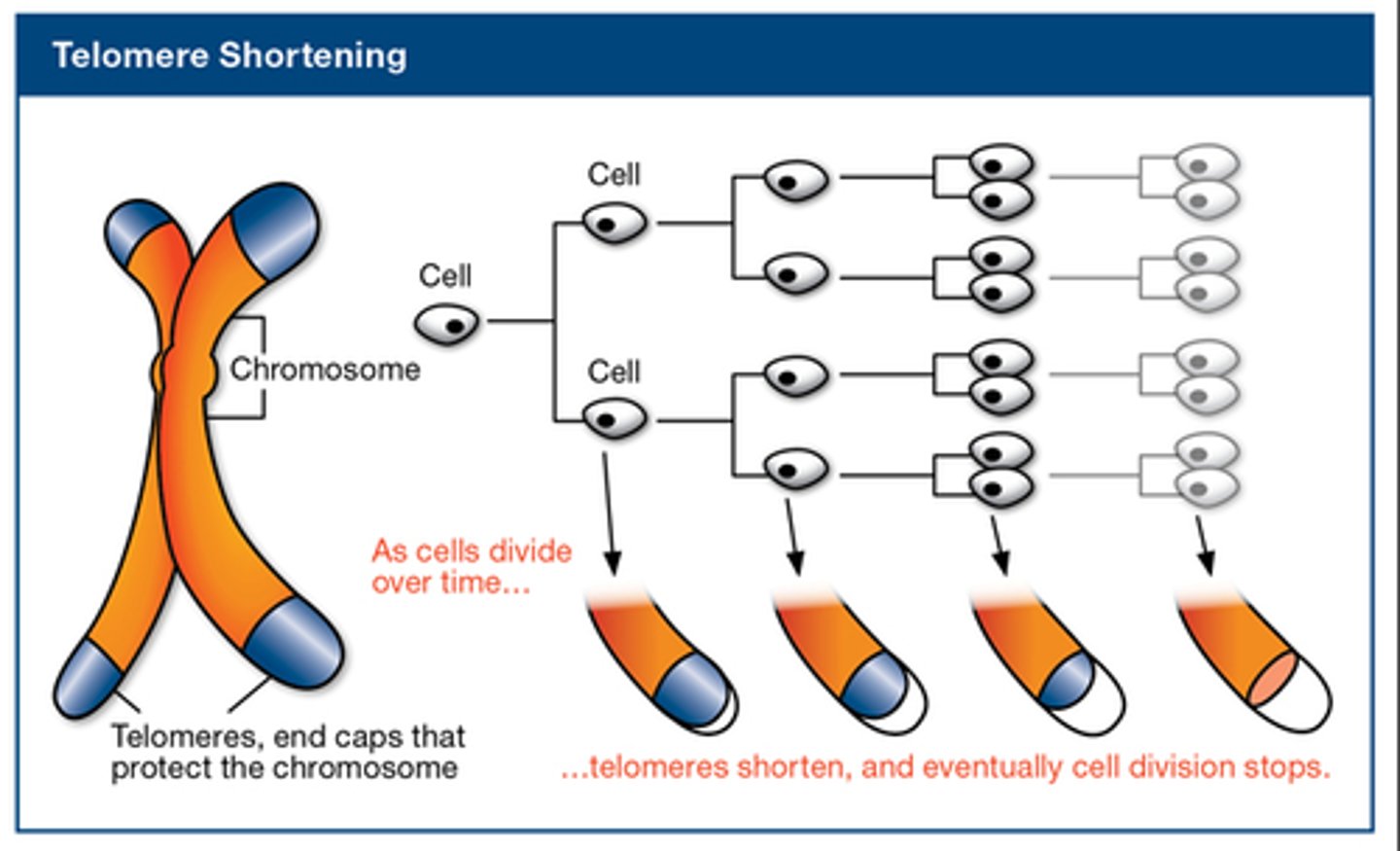
Telomeres
Repeated DNA sequences at the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes.
bacterial chromosome
circular and single thread of DNA that contains the cell's genetic information
eukaryotic chromosome
linear, large amount of protein
chromatin
a complex of DNA and protein, is found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells
euchromatin
Loosely packed chromatin
heterochromatin
densely pack chromatin
What is a gene?
region of DNA that can be expressed to produce a final functional product, either a polypeptide or an RNA molecule