Kin 483-Ch.3: Percentiles
1/5
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
Percentile (definition)
point or position on a continuous scale of 100 theoretical divisions
or
percentage of observations that fall at a given point and below that point
Percentile (example)
Percentiles are obtained from raw scores
Sheena did 200lbs (raw score) on a 1 RM squat test
Is this good or poor?
We need to evaluate her based on the performance of other competitors
Sheena is in the 85th percentile
A percentile score of 85% means Sheena performed equal to or better than 85% of her competitors
Common Percentile Divisions
Quartiles: Q1 = 0- 25th percentile, Q2 = 25-50th, Q3 = 50-75th, Q4 = 75-100th
Deciles: same premise as quartiles but divided into 10 parts
Quintiles: same premise as quartiles but divided into 5 parts
Calculating Percentiles (Rank Order Distributions example)
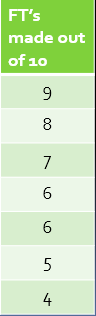
7 basketball players are asked to shoot 10 Free throws
How many scores fall at or below 8 FT’s made?
1) Count the number of scores from 8 down
2) Divide the number of scores you counted by the total players
6/7 = .86
3) Multiply 100
4) 86th percentile
Calculating Percentiles (Simple Frequency Distributions)
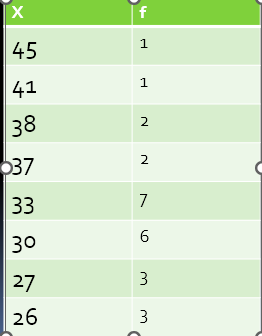
What is the percentile for the athletes with a vertical leap of 33 inches?
1) Add the frequency numbers for raw scores 33 and below
2) Divide the number by the total number of athletes
19/25 = .76
3) Multiply by 100 = 76th percentile
Calculating Percentiles (Grouped Frequency Distributions)
What is the percentile of an athlete who is in the 23 inch vertical leap range?
1) We must assume a normal distribution because we don’t know individual scores within a range
2) P =[(X - L)/ i )] * f + C / N
P = percentile
X = raw score
L = lower limit of interval
i = size of interval
f = frequency of interval
C = cumulative frequency of interval below the
interval in question
N = total number of cases
![<p>What is the percentile of an athlete who is in the 23 inch vertical leap range?</p><p>1) We must assume a normal distribution because we don’t know individual scores within a range</p><p>2) <mark data-color="blue">P =[(X - L)/ i )] * f + C / N</mark></p><p> P = percentile</p><p> X = raw score</p><p> L = lower limit of interval</p><p> i = size of interval</p><p> f = frequency of interval</p><p> C = cumulative frequency of interval below the </p><p> interval in question</p><p> N = total number of cases</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/6b68c953-c2d0-4289-befb-20c890035a03.jpeg)